字段类型的约束条件
一、约束条件
1、unsigned
unsigned 无符号 id int unsigned
2、zerofill
zerofill 0填充 id int zerofill
3、not null
not null 非空(不能为空)案例: create table t1(id int,name varchar(16) not null); insert into t1(name) values("Yie"); #成功 insert into t1(id) values(1); #报错
4、default
default 默认值(用户给了就使用用户的,不给就使用默认的)案例: create table t2(id int,name varchar(16) default "匿名用户"); insert into t2(id) values(1); #name字段显示 '匿名用户' insert into t2 values(2,"Yie"),(3,"zpx");
5、unique
unique 唯一(保证字段(一个、多个)在整个表中没有重复的数据)# 单列唯一 create table t3(id int,name varchar(16) unique); insert into t3 values(1,"Yie"),(2,"Yie"); #name字段不唯一报错 insert into t3 values(1,"Yie"),(2,"zpx"); #成功# 联合唯一 create table server( id int, host varchar(32), port varchar(32), unique(host,port) ); 这时,插入的记录两两组合唯一才行。 insert into server(host,port) values(127.0.0.1,3306),(127.0.0.1,8080); #成功 insert into server(host,port) values(127.0.0.1,3306); #重复,失败
6、primary key
primary key 主键 1.但从约束条件上而言主键相当于not null + unique(非空且唯一) 2.主键的功能目前简单的理解为能够加快数据的查询速度相当于书的目录 3.InnoDB存储引擎规定每张表都必须有且只有一个主键 2.1.表中没有任何的主键和其他约束条件 InnoDB默认会采用一个隐藏字段作为表的主键 2.2.表中没有主键但是有非空且唯一的字段 InnoDB会自动将该字段升级为主键 结论:每张表都必须要有一个id(sid nid uid gid等等任一id)字段并且该字段就是主键和unique一样,也分单列和联合主键# 单列主键 案例一:# 使用primary key,将id字段设置为主键 mysql> create table t4 ( id int primary key, name char(8) ); 案例二:# 不使用primary key,但是有费控且唯一的字段,InnoDB自动将该字段升级为主键 mysql> mysql> create table t5( id int, name char(8), phone_num int not null unique, age int not null unique, birth int not null unique ); mysql> desc t5; +-----------+---------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +-----------+---------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | id | int(11) | YES | | NULL | | | name | char(8) | YES | | NULL | | | phone_num | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | | | age | int(11) | NO | UNI | NULL | | | birth | int(11) | NO | UNI | NULL | | +-----------+---------+------+-----+---------+-------+ 5 rows in set (0.05 sec) #将age,phone_num,birth字段设置为not null和unique,InnoDB自动将最靠前的字段升级为primary。# 联合主键 案例三:# 将手机号和QQ号设置为联合主键 create table t6( id int, name char(8), phone_num bigint, QQ bigint, primary key(phone_num,QQ) ); mysql> desc t6; +-----------+------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +-----------+------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | id | int(11) | YES | | NULL | | | name | char(8) | YES | | NULL | | | phone_num | bigint(20) | NO | PRI | 0 | | | QQ | bigint(20) | NO | PRI | 0 | | +-----------+------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ 4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
7、auto_increment
auto_increment 自增(专门配合主键一起使用的 让主键能够自增)案例:#创建一个自增的整数主键id create table t7( id int primary key auto_increment, name varchar(32) );主键的自增特性#主键的自增是不会收到delete from删除操作的影响 也就是使用delete删除某条记录,下一次再插入记录的时候,不会依据跟现有表的id增加#truncate既可以清空表数据也会重置主键值 使用truncat清空表的时候,再插入记录,id会从1开始。
8、外键foreign key # 很重要
8.1使用外键的原因:
当一张表,出现'重复'数据,造成存取数据'速度缓慢',并且'浪费磁盘空间'的时候,可以引入一个概念,两张表建立关系。例如,有这么一张员工表 id name age dep_name dep_desc 1 yly 18 外交部 搞外交 2 zpx 28 教学部 教书育人 3 aaa 38 教学部 教书育人 4 bbb 48 安保部 保家卫国 5 ccc 58 财务部 发工资显示了每个员工的信息,以及所处部门的信息。"""上述表不合理之处 1.表内部数据混乱(可忽略) 2.反复的录入重复数据(可忽略) 3.修改数据太过繁琐 浪费磁盘空间(可忽略) 4.极大地影响了操作数据的效率"""可以拆分为两张基本表,员工表,部门表id name age 1 yly 182 zpx 283 aaa 384 bbb 485 ccc 58id dep_name dep_desc1 外交部 搞外交2 教学部 教书育人3 安保部 保家卫国4 财务部 发工资"""拆分完之后解决了上述四个缺陷"""外键 用来记录表与表之间的关系
8.2如何判断两张表的关系
1.多对一:'多条记录对一条记录' 多的一方设置外键2.多对多:'多条记录对多条记录' 创建第三张表,在第三张表上创建外键3.一对一:'一条记录对一条记录' 一对一就没有必要使用外键4.'没有关系'"""查找表关系:换位思考"""书籍表与出版社表 1.先站在书籍表 问:一本书能够对应多个出版社 答:不可以 2.再站在出版社表 问:一个出版社能否对应多本书 答:可以 结论:一个可以一个不可以 表关系为"多对一" 那么外键字段建在"多"的一方
8.3外键格式
格式: [外键字段名] [字段类型] [约束条件], foreign key(外键字段名) references 外表名(id) on update cascade on delete cascade,容易出错的地方: 1、foreign key是需要逗号分隔; 2、references是复数形式,有s; 3、连接外表的id必须是主键。外键约束: 1.在创建表的时候需要先创建被关联表(没有外键的表) 2.在写入数据的时候也需要先写入被关联表(没有外键的表) 3.被关联表里面的数据无法直接删除和修改关联字段的操作# 级联更新 级联删除create table emp( id int primary key auto_increment, name varchar(32), age int, dep_id int, foreign key(dep_id) references dep(id) on update cascade on delete cascade);create table dep( id int primary key auto_increment, name varchar(32));
8.4多对一
# 针对具有表关系的SQL建议先写普通字段 最后再考虑外键字段create table publish( id int primary key auto_increment, name varchar(32));create table book( id int primary key auto_increment, title varchar(32), price int, pub_id int, foreign key(pub_id) references publish(id));"注意:得先建立没有外键依赖的表"
8.5多对多
以书籍表与作者表为例 1.先站在书籍表的基础之上 问:一本书能否对应多个作者 答:可以 2.在站在作者表的基础之上 问:一个作者能否对应多本书 答:可以 结论:两个都可以那么表关系就是"多对多" 外键字段建在第三张关系表中# 先写普通字段之后在考虑外键字段'''错误的创建方式'''create table book1( id int primary key auto_increment, title varchar(32), author_id int, foreign key(author_id) references author1(id) on update cascade on delete cascade);create table author1( id int primary key auto_increment, name varchar(32), book_id int, foreign key(book_id) references book1(id) on update cascade on delete cascade);'''正确的创建方式'''create table book1( id int primary key auto_increment, title varchar(32));create table author1( id int primary key auto_increment, name varchar(32));create table book2author( id int primary key auto_increment, author_id int, foreign key(author_id) references author1(id) on update cascade on delete cascade, book_id int, foreign key(book_id) references book1(id) on update cascade on delete cascade);分析: 此时有三个表 1、book表:负责存储有哪些书及id号 2、作者表:负责存储有哪些作者及id号 3、关系表:可以清楚看到,哪些作者出了哪些书,哪些书对应着哪些作者
8.6 一对一
# 简介 当一个表储存了很多数据,但有些数据是经常查询的,另外一部分数据是偶尔才查询, 可以拆分开为一对一的对应关系以加快存取效率。# 场景 QQ用户表 id name gender age | phone_num hobby 1 yly male 18 | 152xxxx6666 swim、play 2 zpx female 15 | 153xxxx6666 watch、dance 3 aaa male 12 | 154xxxx6666 play此时的QQ用户表,常用的是name,gender,age,想查看某个人的'详细信息'phone_num、hobby,需要另外再点击,这个时候就可以分为用户表和用户详细表,并且关系为一一对应。外键字段建在哪里? 理论上建在任何一方都可以但是推荐建在查询频率较高的表中,并且外键需要设置为unique。create table user( id int primary key auto_increment, name varchar(32), detail_id int unique, foreign key(detail_id) references user_detail(id) on update cascade on delete cascade);create table user_detail( id int primary key auto_increment, addr varchar(32), phone bigint);
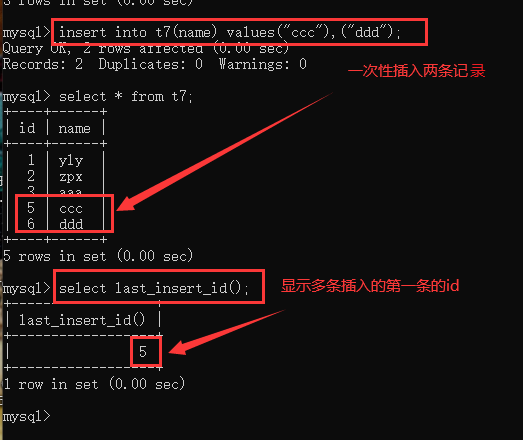
二、查看最后一次插入的ID号:select last_insert_id();
查看最后一次插入的id号select last_insert_id(); #查看最后一次插入的主键id,当一次性查入多条时,只会显示第一个。