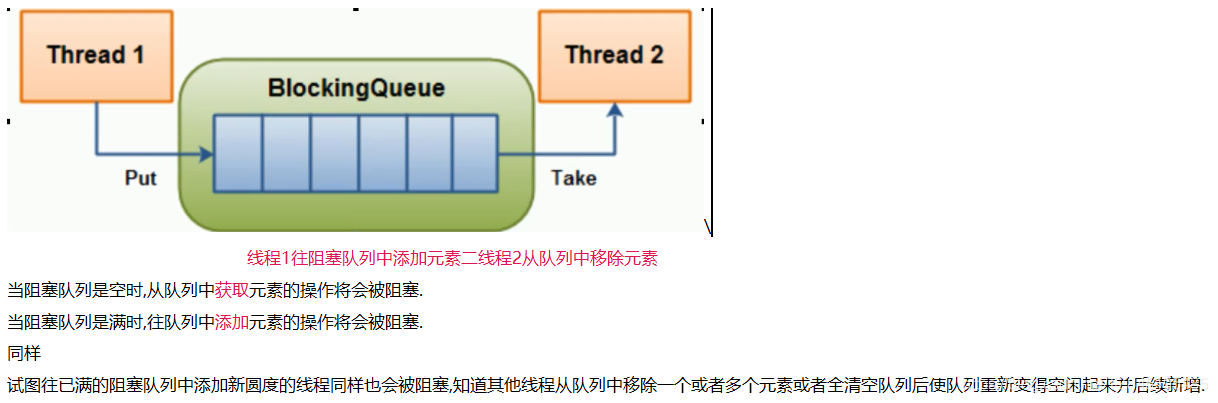
1. 阻塞队列
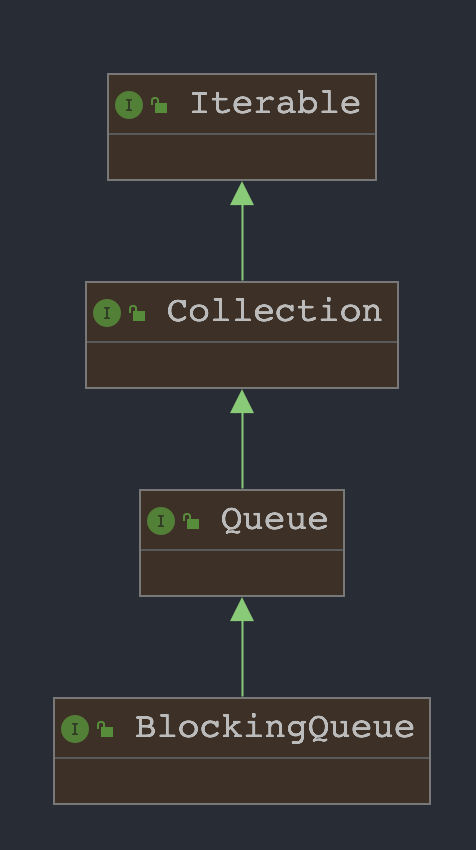
1.1 类图
1.2 7个实现类
- ArrayBlockQueue:由数组结构组成的有界阻塞队列
- LinkedBlockingQueue:由链表结构组成的有界(但是默认大小 Integer.MAX_VALUE)的阻塞队列
- 有界,但是界限非常大,相当于无界,可以当成无界
- PriorityBlockQueue:支持优先级排序的无界阻塞队列
- DelayQueue:使用优先级队列实现的延迟无界阻塞队列
- SynchronousQueue:不存储元素的阻塞队列,也即单个元素的队列
- 生产一个,消费一个,不存储元素,不消费不生产
- LinkedTransferQueue:由链表结构组成的无界阻塞队列
LinkedBlockingDeque:由链表结构组成的双向阻塞队列
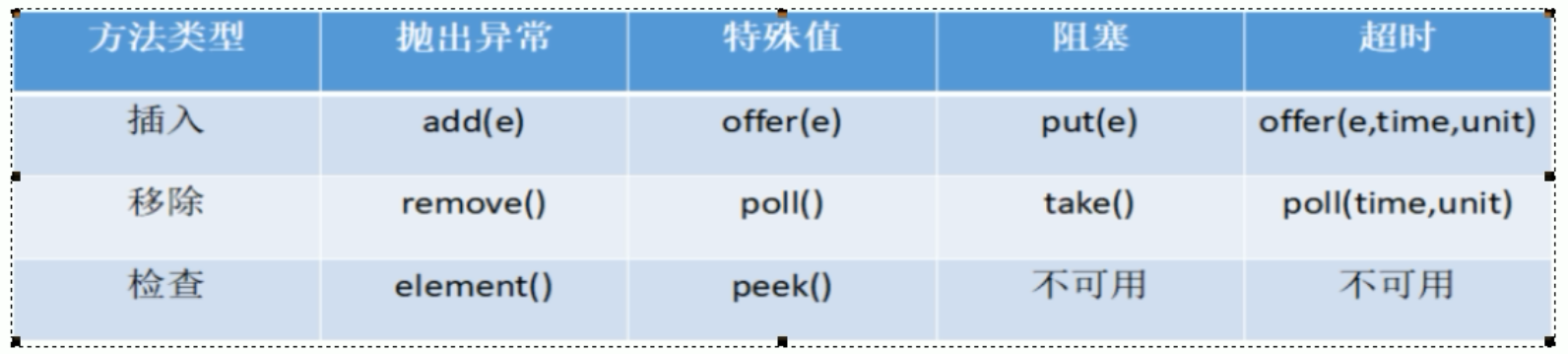
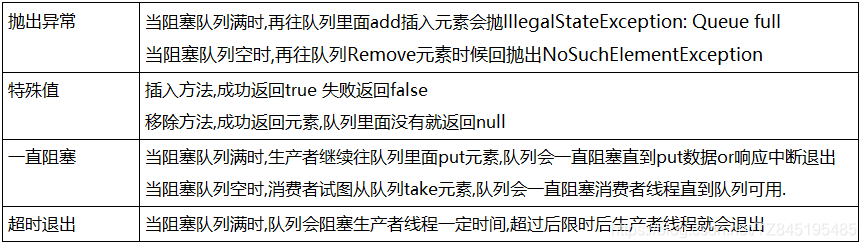
1.3 阻塞队列的方法
1.4 ArrayBlockQueue
1.5 应用-消费者生产问题
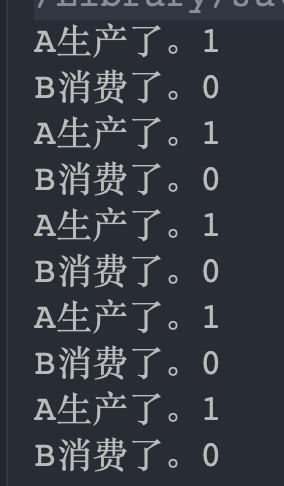
传统版本的生产者和消费者问题(不使用阻塞队列)
生产一个,消费一个。
public class ProductConsumerTradition {public static void main(String[] args) {ShareData shareData = new ShareData();new Thread(()->{for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {try {shareData.increment();} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}, "A").start();new Thread(()->{for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {try {shareData.decrement();} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}, "B").start();}}// 资源类class ShareData{private int number = 0;private final Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();private Condition condition = lock.newCondition();public void increment() throws Exception{lock.lock();try {// 判断,防止虚假唤醒,用whilewhile (number > 0){// 等待,不能生产condition.await();}// 生产者生产number ++;System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "生产了。" + number);// 唤醒消费者condition.signalAll();}finally {lock.unlock();}}public void decrement() throws Exception{lock.lock();try {// 判断,防止虚假唤醒,用whilewhile (number == 0){// 等待,不能消费condition.await();}// 消费者消费number --;System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "消费了。" + number);// 唤醒生产者condition.signalAll();}finally {lock.unlock();}}
2. 线程池
2.1 线程池概念
池化技术相比大家已经屡见不鲜了,线程池、数据库连接池、Http 连接池等等都是对这个思想的应用。池化技术的思想主要是为了减少每次获取资源的消耗,提高对资源的利用率。线程池提供了一种限制和管理资源(包括执行一个任务)。 每个线程池还维护一些基本统计信息,例如已完成任务的数量。特点:线程复用、控制最大并发数、管理线程
这里借用《Java 并发编程的艺术》提到的来说一下使用线程池的好处:
- 降低资源消耗。通过重复利用已创建的线程降低线程创建和销毁造成的消耗。
- 提高响应速度。当任务到达时,任务可以不需要的等到线程创建就能立即执行。
提高线程的可管理性。线程是稀缺资源,如果无限制的创建,不仅会消耗系统资源,还会降低系统的稳定性,使用线程池可以进行统一的分配,调优和监控。
2.2 自定义线程池
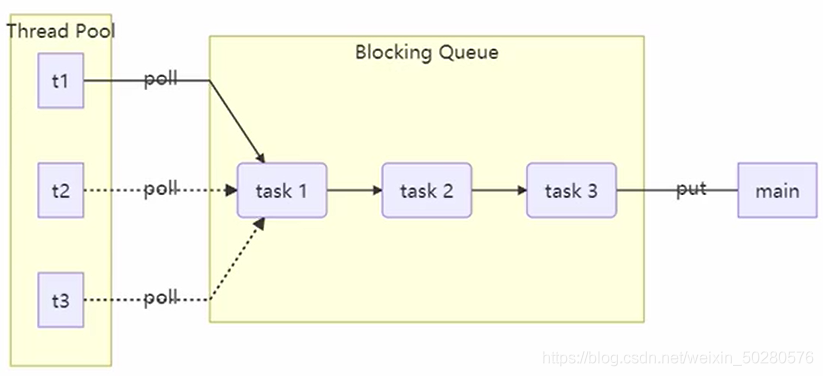
上图就是一个线程池的实现,先初始化线程池、阻塞队列大小,然后开几个线程通过线程池对象调用方法执行任务,线程池中的线程会执行任务,如果任务过多,会添加到阻塞队列中,执行完任务再从阻塞队列中取值继续执行。当执行的线程数大于线程池和阻塞队列的大小,我们可以定义拒绝策略,类似 jdk 线程池那样。 ```java @Slf4j(topic = “c.TestPool”) public class TestPool {public static void main(String[] args) { ThreadPool pool=new ThreadPool(2, 1000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, 10); for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
int j = i;pool.execute(()->{log.debug("{}", j);});
} } }
@Slf4j(topic = “ThreadPool”)
class ThreadPool {
// 任务队列
private BlockingQueue
// 线程集合private HashSet<Worker> workers = new HashSet<>();// 核心线程数private int coreSize;// 任务超时时间private long timeOut;private TimeUnit timeUnit;public ThreadPool(int coreSize, long timeOut, TimeUnit timeUnit, int queueCapacity) {this.coreSize = coreSize;this.timeOut = timeOut;this.timeUnit = timeUnit;this.taskQueue = new BlockingQueue<>(queueCapacity);}// 执行任务public void execute(Runnable task){// 当任务数没有超过coreSize时,直接交给worker对象执行// 如果任务数超过coreSize,加入任务队列暂存synchronized (workers){if (workers.size()< coreSize){Worker worker = new Worker(task);log.debug("新增worker{},{}", worker,task);workers.add(worker);worker.start();} else {log.debug("加入任务队列{}", task);taskQueue.put(task);}}}class Worker extends Thread{private Runnable task;public Worker(Runnable task) {this.task = task;}@Overridepublic void run() {// 执行任务// 1 当task不为空,执行任务// 2 task执行完毕 任务队列中获取任务并执行// 无超时//while (task != null || (task = taskQueue.take()) != null){// 有超时while (task != null || (task = taskQueue.poll(timeOut, timeUnit))!= null){try {log.debug("正在执行{}", task);task.run();}catch (Exception e){e.printStackTrace();}finally {task = null;}}synchronized (workers){log.debug("worker被移除{}", this);workers.remove(this);}}}
}
class BlockingQueue
// 任务队列private Deque<T> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();// 锁private ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();// 生产者条件变量private Condition fullWaitSet = lock.newCondition();// 消费者条件变量private Condition emptyWaitSet = lock.newCondition();// 容量private int capacity;public BlockingQueue(int capacity) {this.capacity = capacity;}// 带超时的阻塞获取public T poll(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) {lock.lock();try {// 将超时时间同意转换为 纳秒long nanos = unit.toNanos(timeout);while (queue.isEmpty()) {try {if (nanos <= 0) {return null;}//awaitNanos方法返回的就是剩余时间nanos = emptyWaitSet.awaitNanos(nanos);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}T t = queue.removeFirst();fullWaitSet.signal();return t;} finally {lock.unlock();}}// 阻塞获取public T take() {lock.lock();try {while (queue.isEmpty()) {try {emptyWaitSet.await();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}T t = queue.removeFirst();fullWaitSet.signal();return t;} finally {lock.unlock();}}// 阻塞添加public void put(T e) {lock.lock();try {while (queue.size() == capacity) {try {fullWaitSet.await();} catch (InterruptedException interruptedException) {interruptedException.printStackTrace();}}queue.addLast(e);emptyWaitSet.signal();} finally {lock.unlock();}}// 获取大小public int getSize() {lock.lock();try {return queue.size();} finally {lock.unlock();}}
无超时等待:(可以一直等下去)```java14:52:01.161 [main] DEBUG ThreadPool - 新增workerThread[Thread-0,5,main],com.ll.ch7.TestPool$$Lambda$1/431687835@2ff4f00f14:52:01.167 [main] DEBUG ThreadPool - 新增workerThread[Thread-1,5,main],com.ll.ch7.TestPool$$Lambda$1/431687835@1b0375b314:52:01.167 [Thread-0] DEBUG ThreadPool - 正在执行com.ll.ch7.TestPool$$Lambda$1/431687835@2ff4f00f14:52:01.168 [Thread-0] DEBUG c.TestPool - 014:52:01.168 [main] DEBUG ThreadPool - 加入任务队列com.ll.ch7.TestPool$$Lambda$1/431687835@2d20907914:52:01.168 [Thread-1] DEBUG ThreadPool - 正在执行com.ll.ch7.TestPool$$Lambda$1/431687835@1b0375b314:52:01.168 [Thread-1] DEBUG c.TestPool - 114:52:01.168 [Thread-1] DEBUG ThreadPool - 正在执行com.ll.ch7.TestPool$$Lambda$1/431687835@2d20907914:52:01.168 [Thread-1] DEBUG c.TestPool - 214:52:01.168 [main] DEBUG ThreadPool - 加入任务队列com.ll.ch7.TestPool$$Lambda$1/431687835@6bdf28bb14:52:01.168 [main] DEBUG ThreadPool - 加入任务队列com.ll.ch7.TestPool$$Lambda$1/431687835@6b71769e14:52:01.169 [Thread-0] DEBUG ThreadPool - 正在执行com.ll.ch7.TestPool$$Lambda$1/431687835@6bdf28bb14:52:01.169 [Thread-1] DEBUG ThreadPool - 正在执行com.ll.ch7.TestPool$$Lambda$1/431687835@6b71769e14:52:01.169 [Thread-0] DEBUG c.TestPool - 314:52:01.169 [Thread-1] DEBUG c.TestPool - 4
有超时等待:
14:56:28.720 [main] DEBUG ThreadPool - 新增workerThread[Thread-0,5,main],com.ll.ch7.TestPool$$Lambda$1/431687835@2ff4f00f14:56:28.725 [main] DEBUG ThreadPool - 新增workerThread[Thread-1,5,main],com.ll.ch7.TestPool$$Lambda$1/431687835@1b0375b314:56:28.725 [Thread-0] DEBUG ThreadPool - 正在执行com.ll.ch7.TestPool$$Lambda$1/431687835@2ff4f00f14:56:28.725 [main] DEBUG ThreadPool - 加入任务队列com.ll.ch7.TestPool$$Lambda$1/431687835@2d20907914:56:28.725 [Thread-0] DEBUG c.TestPool - 014:56:28.725 [Thread-1] DEBUG ThreadPool - 正在执行com.ll.ch7.TestPool$$Lambda$1/431687835@1b0375b314:56:28.725 [main] DEBUG ThreadPool - 加入任务队列com.ll.ch7.TestPool$$Lambda$1/431687835@6bdf28bb14:56:28.725 [Thread-0] DEBUG ThreadPool - 正在执行com.ll.ch7.TestPool$$Lambda$1/431687835@2d20907914:56:28.725 [Thread-1] DEBUG c.TestPool - 114:56:28.726 [main] DEBUG ThreadPool - 加入任务队列com.ll.ch7.TestPool$$Lambda$1/431687835@6b71769e14:56:28.726 [Thread-1] DEBUG ThreadPool - 正在执行com.ll.ch7.TestPool$$Lambda$1/431687835@6bdf28bb14:56:28.726 [Thread-1] DEBUG c.TestPool - 314:56:28.726 [Thread-0] DEBUG c.TestPool - 214:56:28.726 [Thread-1] DEBUG ThreadPool - 正在执行com.ll.ch7.TestPool$$Lambda$1/431687835@6b71769e14:56:28.726 [Thread-1] DEBUG c.TestPool - 414:56:29.731 [Thread-0] DEBUG ThreadPool - worker被移除Thread[Thread-0,5,main]14:56:29.731 [Thread-1] DEBUG ThreadPool - worker被移除Thread[Thread-1,5,main]
当任务队列满时 ```java @Slf4j(topic = “c.TestPool”) public class TestPool {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadPool pool=new ThreadPool(2, 1000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, 10);for (int i = 0; i < 15; i++) {int j = i;pool.execute(()->{try {Thread.sleep(100000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}log.debug("{}", j);});}
} }
@Slf4j(topic = “ThreadPool”)
class ThreadPool {
// 任务队列
private BlockingQueue
// 线程集合private HashSet<Worker> workers = new HashSet<>();// 核心线程数private int coreSize;// 任务超时时间private long timeOut;private TimeUnit timeUnit;public ThreadPool(int coreSize, long timeOut, TimeUnit timeUnit, int queueCapacity) {this.coreSize = coreSize;this.timeOut = timeOut;this.timeUnit = timeUnit;this.taskQueue = new BlockingQueue<>(queueCapacity);}// 执行任务public void execute(Runnable task){// 当任务数没有超过coreSize时,直接交给worker对象执行// 如果任务数超过coreSize,加入任务队列暂存synchronized (workers){if (workers.size()< coreSize){Worker worker = new Worker(task);log.debug("新增worker{},{}", worker,task);workers.add(worker);worker.start();} else {taskQueue.put(task);}}}class Worker extends Thread{private Runnable task;public Worker(Runnable task) {this.task = task;}@Overridepublic void run() {// 执行任务// 1 当task不为空,执行任务// 2 task执行完毕 任务队列中获取任务并执行// 无超时//while (task != null || (task = taskQueue.take()) != null){// 有超时while (task != null || (task = taskQueue.poll(timeOut, timeUnit))!= null){try {log.debug("正在执行{}", task);task.run();}catch (Exception e){e.printStackTrace();}finally {task = null;}}synchronized (workers){log.debug("worker被移除{}", this);workers.remove(this);}}}
}
@Slf4j(topic = “c.BlockingQueue”)
class BlockingQueue
// 任务队列private Deque<T> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();// 锁private ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();// 生产者条件变量private Condition fullWaitSet = lock.newCondition();// 消费者条件变量private Condition emptyWaitSet = lock.newCondition();// 容量private int capacity;public BlockingQueue(int capacity) {this.capacity = capacity;}// 带超时的阻塞获取public T poll(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) {lock.lock();try {// 将超时时间同意转换为 纳秒long nanos = unit.toNanos(timeout);while (queue.isEmpty()) {try {if (nanos <= 0) {return null;}//awaitNanos方法返回的就是剩余时间nanos = emptyWaitSet.awaitNanos(nanos);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}T t = queue.removeFirst();fullWaitSet.signal();return t;} finally {lock.unlock();}}// 阻塞获取public T take() {lock.lock();try {while (queue.isEmpty()) {try {emptyWaitSet.await();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}T t = queue.removeFirst();fullWaitSet.signal();return t;} finally {lock.unlock();}}// 阻塞添加public void put(T e) {lock.lock();try {while (queue.size() == capacity) {try {log.debug("等待加入任务队列:{}", e);fullWaitSet.await();} catch (InterruptedException interruptedException) {interruptedException.printStackTrace();}}log.debug("加入任务队列{}", e);queue.addLast(e);emptyWaitSet.signal();} finally {lock.unlock();}}// 获取大小public int getSize() {lock.lock();try {return queue.size();} finally {lock.unlock();}}
}
```java14:59:24.108 [main] DEBUG ThreadPool - 新增workerThread[Thread-0,5,main],com.ll.ch7.TestPool$$Lambda$1/431687835@2ff4f00f14:59:24.113 [main] DEBUG ThreadPool - 新增workerThread[Thread-1,5,main],com.ll.ch7.TestPool$$Lambda$1/431687835@1b0375b314:59:24.113 [Thread-0] DEBUG ThreadPool - 正在执行com.ll.ch7.TestPool$$Lambda$1/431687835@2ff4f00f14:59:24.113 [main] DEBUG c.BlockingQueue - 加入任务队列com.ll.ch7.TestPool$$Lambda$1/431687835@2d20907914:59:24.113 [Thread-1] DEBUG ThreadPool - 正在执行com.ll.ch7.TestPool$$Lambda$1/431687835@1b0375b314:59:24.113 [main] DEBUG c.BlockingQueue - 加入任务队列com.ll.ch7.TestPool$$Lambda$1/431687835@6bdf28bb14:59:24.113 [main] DEBUG c.BlockingQueue - 加入任务队列com.ll.ch7.TestPool$$Lambda$1/431687835@6b71769e14:59:24.113 [main] DEBUG c.BlockingQueue - 加入任务队列com.ll.ch7.TestPool$$Lambda$1/431687835@2752f6e214:59:24.114 [main] DEBUG c.BlockingQueue - 加入任务队列com.ll.ch7.TestPool$$Lambda$1/431687835@e58092914:59:24.114 [main] DEBUG c.BlockingQueue - 加入任务队列com.ll.ch7.TestPool$$Lambda$1/431687835@1cd072a914:59:24.114 [main] DEBUG c.BlockingQueue - 加入任务队列com.ll.ch7.TestPool$$Lambda$1/431687835@7c75222b14:59:24.114 [main] DEBUG c.BlockingQueue - 加入任务队列com.ll.ch7.TestPool$$Lambda$1/431687835@4c203ea114:59:24.114 [main] DEBUG c.BlockingQueue - 加入任务队列com.ll.ch7.TestPool$$Lambda$1/431687835@27f674d14:59:24.114 [main] DEBUG c.BlockingQueue - 加入任务队列com.ll.ch7.TestPool$$Lambda$1/431687835@1d25189114:59:24.114 [main] DEBUG c.BlockingQueue - 等待加入任务队列:com.ll.ch7.TestPool$$Lambda$1/431687835@48140564
给主线程加入各种拒绝机制 ```java @Slf4j(topic = “c.TestPool”) public class TestPool {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadPool pool=new ThreadPool(1, 1000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, 1, (queue, task)->{// 1.死等// queue.put(task);// 2 带超时等待// queue.offer(task, 500, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);// 3 放弃任务执行// log.debug("放弃任务{}", task);// 4 让调用者抛出异常// throw new RuntimeException("任务执行失败" + task);// 5 让调用者自己执行任务task.run();});for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {int j = i;pool.execute(()->{try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}log.debug("{}", j);});}
} }
// 策略模式
// 拒绝策略
@FunctionalInterface
interface RejectPolicy
@Slf4j(topic = “ThreadPool”)
class ThreadPool {
// 任务队列
private BlockingQueue
// 线程集合private HashSet<Worker> workers = new HashSet<>();// 核心线程数private int coreSize;// 任务超时时间private long timeOut;private TimeUnit timeUnit;// 拒绝策略private RejectPolicy<Runnable> rejectPolicy;public ThreadPool(int coreSize, long timeOut, TimeUnit timeUnit, int queueCapacity, RejectPolicy<Runnable> rejectPolicy) {this.coreSize = coreSize;this.timeOut = timeOut;this.timeUnit = timeUnit;this.rejectPolicy = rejectPolicy;this.taskQueue = new BlockingQueue<>(queueCapacity);}// 执行任务public void execute(Runnable task){// 当任务数没有超过coreSize时,直接交给worker对象执行// 如果任务数超过coreSize,加入任务队列暂存synchronized (workers){if (workers.size()< coreSize){Worker worker = new Worker(task);log.debug("新增worker{},{}", worker,task);workers.add(worker);worker.start();} else {//taskQueue.put(task);// 1 死等// 2 带超时等待// 3 放弃任务执行// 4 让调用者抛出异常// 5 让调用者自己执行任务taskQueue.trtPut(rejectPolicy, task);}}}class Worker extends Thread{private Runnable task;public Worker(Runnable task) {this.task = task;}@Overridepublic void run() {// 执行任务// 1 当task不为空,执行任务// 2 task执行完毕 任务队列中获取任务并执行// 无超时//while (task != null || (task = taskQueue.take()) != null){// 有超时while (task != null || (task = taskQueue.poll(timeOut, timeUnit))!= null){try {log.debug("正在执行{}", task);task.run();}catch (Exception e){e.printStackTrace();}finally {task = null;}}synchronized (workers){log.debug("worker被移除{}", this);workers.remove(this);}}}
}
@Slf4j(topic = “c.BlockingQueue”)
class BlockingQueue
// 任务队列private Deque<T> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();// 锁private ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();// 生产者条件变量private Condition fullWaitSet = lock.newCondition();// 消费者条件变量private Condition emptyWaitSet = lock.newCondition();// 容量private int capacity;public BlockingQueue(int capacity) {this.capacity = capacity;}// 带超时的阻塞获取public T poll(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) {lock.lock();try {// 将超时时间同意转换为 纳秒long nanos = unit.toNanos(timeout);while (queue.isEmpty()) {try {if (nanos <= 0) {return null;}//awaitNanos方法返回的就是剩余时间nanos = emptyWaitSet.awaitNanos(nanos);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}T t = queue.removeFirst();fullWaitSet.signal();return t;} finally {lock.unlock();}}// 阻塞获取public T take() {lock.lock();try {while (queue.isEmpty()) {try {emptyWaitSet.await();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}T t = queue.removeFirst();fullWaitSet.signal();return t;} finally {lock.unlock();}}// 阻塞添加public void put(T e) {lock.lock();try {while (queue.size() == capacity) {try {log.debug("等待加入任务队列:{}", e);fullWaitSet.await();} catch (InterruptedException interruptedException) {interruptedException.printStackTrace();}}log.debug("加入任务队列{}", e);queue.addLast(e);emptyWaitSet.signal();} finally {lock.unlock();}}// 带超时时间阻塞添加public boolean offer(T task, long timeOut, TimeUnit timeUnit){lock.lock();try {long nanos = timeUnit.toNanos(timeOut);while (queue.size() == capacity) {try {log.debug("等待加入任务队列:{}", task);if (nanos <=0){return false;}fullWaitSet.awaitNanos(nanos);} catch (InterruptedException interruptedException) {interruptedException.printStackTrace();}}log.debug("加入任务队列{}", task);queue.addLast(task);emptyWaitSet.signal();return true;} finally {lock.unlock();}}// 获取大小public int getSize() {lock.lock();try {return queue.size();} finally {lock.unlock();}}public void trtPut(RejectPolicy<T> rejectPolicy, T task) {lock.lock();try {// 判断队列是否已满if (queue.size() == capacity){rejectPolicy.reject(this, task);}else {// 有空闲log.debug("加入任务队列{}", task);queue.addLast(task);emptyWaitSet.signal();}}finally {lock.unlock();}}
<a name="I2g66"></a>## 2.3 ThreadPoolExecutor<a name="dFYUr"></a>### 2.3.1 线程池状态ThreadPoolExecutor 使用 int 的高 3 位来表示线程池状态,低 29 位表示线程数量,<br />ThreadPoolExecutor 类中的线程状态变量如下:```java// Integer.SIZE 值为 32private static final int COUNT_BITS = Integer.SIZE - 3;// runState is stored in the high-order bitsprivate static final int RUNNING = -1 << COUNT_BITS;private static final int SHUTDOWN = 0 << COUNT_BITS;private static final int STOP = 1 << COUNT_BITS;private static final int TIDYING = 2 << COUNT_BITS;private static final int TERMINATED = 3 << COUNT_BITS;
| 状态名称 | 高3位的值 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| RUNNING | 111 | 接收新任务,同时处理任务队列中的任务 |
| SHUTDOWN | 000 | 不接受新任务,但是处理任务队列中的任务 |
| STOP | 001 | 中断正在执行的任务,同时抛弃阻塞队列中的任务 |
| TIDYING | 010 | 任务执行完毕,活动线程为0时,即将进入终结阶段 |
| TERMINATED | 011 | 终结状态 |
线程池状态和线程池中线程的数量由一个原子整型ctl来共同表示,使用一个数来表示两个值的主要原因是:可以通过一次CAS同时更改两个属性的值
// 原子整数,前 3 位保存了线程池的状态,剩余位保存的是线程数量private final AtomicInteger ctl = new AtomicInteger(ctlOf(RUNNING, 0));// 并不是所有平台的 int 都是 32 位。// 去掉前三位保存线程状态的位数,剩下的用于保存线程数量// 高3位为0,剩余位数全为1private static final int COUNT_BITS = Integer.SIZE - 3;// 2^COUNT_BITS次方,表示可以保存的最大线程数// CAPACITY 的高3位为 0private static final int CAPACITY = (1 << COUNT_BITS) - 1;
获取线程池状态、线程数量以及合并两个值的操作
// Packing and unpacking ctl// 获取运行状态// 该操作会让除高3位以外的数全部变为0private static int runStateOf(int c) { return c & ~CAPACITY; }// 获取运行线程数// 该操作会让高3位为0private static int workerCountOf(int c) { return c & CAPACITY; }// 计算ctl新值private static int ctlOf(int rs, int wc) { return rs | wc; }
线程池属性:
// 工作线程,内部封装了Threadprivate final class Workerextends AbstractQueuedSynchronizerimplements Runnable {...}// 阻塞队列,用于存放来不及被核心线程执行的任务private final BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue;// 锁private final ReentrantLock mainLock = new ReentrantLock();// 用于存放核心线程的容器,只有当持有锁时才能够获取其中的元素(核心线程)private final HashSet<Worker> workers = new HashSet<Worker>();
2.3.2 构造方法
ThreadPoolExecutor 类参数最多、最全的有参构造方法。
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,int maximumPoolSize,long keepAliveTime,TimeUnit unit,BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,ThreadFactory threadFactory,RejectedExecutionHandler handler)
2.3.3 七大参数
- corePoolSize:核心线程数
- maximumPoolSize:最大线程数(≥1)
- maximumPoolSize - corePoolSize = 救急(空闲)线程数
- keepAliveTime:救急线程空闲时的最大生存时间
- unit:时间单位
- workQueue:阻塞队列(存放任务)
- 有界阻塞队列 ArrayBlockingQueue
- 无界阻塞队列 LinkedBlockingQueue
- 最多只有一个同步元素的队列 SynchronousQueue
- 优先队列 PriorityBlockingQueue
- threadFactory:线程工厂(给线程取名字)
- handler:拒绝策略。表示当队列满了并且工作线程大于线程池的最大线程数(maximumPoolSize)时,如何来拒绝请求执行的Runnable的策略。以下所有拒绝策略都实现了RejectedExecutionHandler接口
- AbortPolicy:默认,直接抛出RejectedExcutionException异常,阻止系统正常运行
- DiscardPolicy:直接丢弃任务,不予任何处理也不抛出异常,如果运行任务丢失,这是一种好方案
- CallerRunsPolicy:该策略既不会抛弃任务,也不会抛出异常,而是将某些任务回退到调用者
- DiscardOldestPolicy:抛弃队列中等待最久的任务,然后把当前任务加入队列中尝试再次提交当前任务
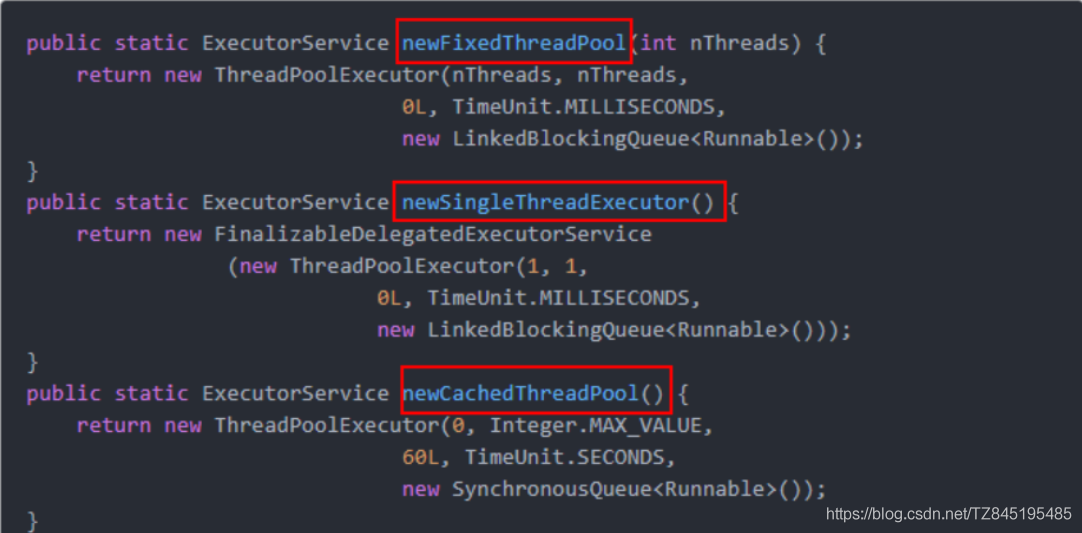
2.3.4 三种线程池
- newFixedThreadPool:执行长期任务,性能好
- newCachedThreadPool:执行很多短期异步的小程序或者负载较轻的服务器
- newSingleThreadExecutor:一个任务一个任务执行的场景
2.3.5 底层原理
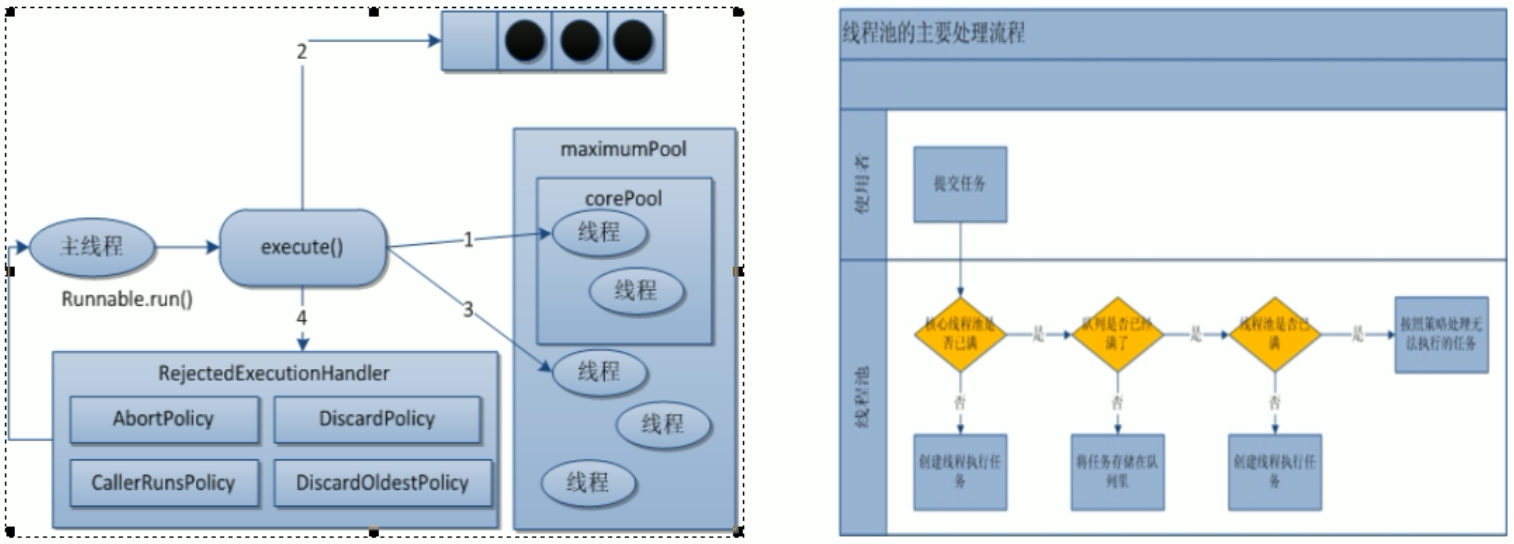
- 在创建了线程池后,等待提交过来的任务请求
- 当调用execute()方法添加一个请求任务时,线程池会做出如下判断
- 如果正在运行的线程池数量小于corePoolSize,那么马上创建线程运行这个任务
- 如果正在运行的线程数量大于或等于corePoolSize,那么将这个任务放入队列
- 如果这时候队列满了,并且正在运行的线程数量还小于maximumPoolSize,那么还是创建非核心线程来运行这个任务;
- 如果队列满了并且正在运行的线程数量大于或等于maximumPoolSize,那么线程池会启动饱和拒绝策略来执行
- 当一个线程完成任务时,它会从队列中取下一个任务来执行
- 当一个线程无事可做操作一定的时间(keepAliveTime)时,线程池会判断:
- 线程资源必须通过线程池提供,不允许在应用中自行显式创建线程
- 使用线程池的好处是减少在创建和销毁线程上所消耗的时间以及系统资源的开销,解决资源不足的问题,如果不使用线程池,有可能造成系统创建大量同类线程而导致消耗完内存或者“过度切换”的问题
线程池不允许使用Executors去创建,而是通过 ThreadPoolExecutor 的方式,这样的处理方式让写的同学更加明确线程池的运行规则,规避资源耗尽的风险
- Executors返回的线程池对象弊端如下:
- FixedThreadPool和SingleThreadPool:
- 运行的请求队列长度为:Integer.MAX_VALUE,可能会堆积大量的请求,从而导致OOM
- CacheThreadPool和ScheduledThreadPool
- 允许创建的线程数量为:Integer.MAX_VALUE,可能会创建大量的线程,从而大导致oom
参数如何配置
- 允许创建的线程数量为:Integer.MAX_VALUE,可能会创建大量的线程,从而大导致oom
- FixedThreadPool和SingleThreadPool:
- Executors返回的线程池对象弊端如下:
CPU密集型(需要大量运算,没有阻塞)一般公式:CPU核数 + 1个线程数
- IO密集型
- 由于IO密集型任务线程并不是一直在执行任务,则可能多的线程,如 CPU核数 * 2
- 在单线程上运行IO密集型的任务会导致浪费大量的CPU运算能力花费在等待上。所以IO密集型任务中使用多线程可以大大的加速程序的运行,即使在单核CPU上,这种加速主要就是利用了被浪费掉的阻塞时间。IO密集时,大部分线程都被阻塞,故需要多配置线程数:CPU核数 / (1 - 阻塞系数) 阻塞系数在0.8 ~ 0.9左右