运行时类型信息使得可以在程序运行时发现和实用类型信息
运行时识别对象和类的信息有两种方式
1 RTTI:假设我们在编译时就已经知道了所有的类型
2 反射:允许我们在运行时发现和使用类的信息
为什么需要RTTI
让代码只操纵对基类的使用
abstract class Shape {void draw(){System.out.println(this + ".draw()");}//只对基类进行编程//shape对象实际执行什么样的代码都是由子类决定的@Overrideabstract public String toString();}class Circle extends Shape{@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Circle";}}class Square extends Shape{@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Square";}}class Triangle extends Shape{@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Triangle";}}public class Shapes {public static void main(String[] args) {List<Shape> shapes = Arrays.asList(new Circle(), new Square(), new Triangle());for (Shape shape : shapes) {shape.draw();}}}
在java中所有的类型转换都是在运行时进行正确检查的,在运行时识别一个对象的类型
Class对象
Class对象:包含了与类的相关信息
Class对象就是用来创建类的所有常规对象的,java使用Class对象来执行它的RTTI
类是程序的一部分,每个类都有一个Class对象,所有的类都是对其第一次使用时动态的加载到虚拟机中的。
一旦某个类的Class对象被载入内存,他就被用来创建这个类的所有对象
class Candy{static {System.out.println("Loading Candy");}}class Gum{static {System.out.println("Loading Gum");}}class Cookie{static {System.out.println("Loading Cookie");}}public class SweetShop {public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println("Inside main");new Candy();//执行静态代码块System.out.println("After creating Candy");try {Class.forName("stu.chapter14.Gum");//获取Class对象的引用//如果类Gum类在还没有加载的时候就加载他,它的static语句就会之心} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {System.out.println("Couldn't find Gum");}System.out.println("After Class.forName(Gum)");new Cookie();System.out.println("After creating Cookie");}}
只要想在运行时获得类型信息,就需要首先获得对恰当的Class对象的引用
可以通过getClass对象获取Class引用
interface HasBatteries{}interface Waterproof{}interface Shoots{}class Toy{Toy(){}Toy(int i){}}class FancyToy extends Toy implements HasBatteries,Waterproof,Shoots{FancyToy(){ super(1);}}public class ToyTest {static void printInfo(Class cc){System.out.println("Class name = " + cc.getName() + "is interface ? [" + cc.isInterface() + "]");System.out.println("Simple name = " + cc.getSimpleName());System.out.println("Canonical name = " + cc.getCanonicalName());}public static void main(String[] args) {Class c = null;try {c = Class.forName("stu.chapter14.FancyToy");} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {System.out.println("Can't find Fancy");System.exit(1);//退出}printInfo(c);for (Class anInterface : c.getInterfaces()) {//循环遍历它的所有接口printInfo(anInterface);}Class up = c.getSuperclass();//获取父类引用Object obj = null;try {obj = up.newInstance();//创建实例,并且使用这个方法的类必须由默认构造器(无参)} catch (InstantiationException e) {System.out.println("Can't instantiate");System.exit(1);} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {System.out.println("Can't Access");System.exit(1);}System.out.println(obj.getClass());}}
类字面常量
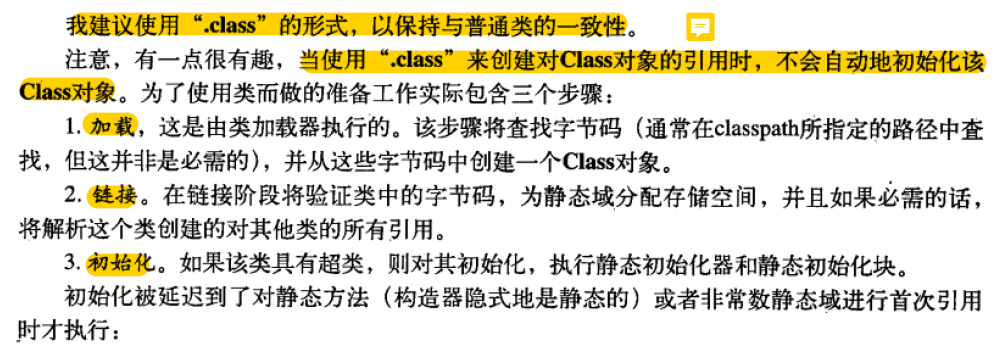
引用.class
类字面常量不仅仅可以应用于普通的类,也可以应用于接口,数组,以及基本数据类型
当使用“.class”来创建对Class对象的引用的时候不会自动的初始化该Class对象
泛化的Class引用
Class引用表示的就是他所指向的对象的确切类型,而该对象就是Class类的一个对象
通过泛型语法,可以让编译器强制的进行额外的类型检查
public class GenericClassReferences {public static void main(String[] args) {Class intClass = int.class;Class<Integer> genericIntClass = int.class;genericIntClass = Integer.class;intClass = double.class;//genericIntClass = double.class;//已经是同泛型指定了,所以不能再转换成为其他的类型}}
使用newInstance创建实例
class CountedInteger{private static long counter;private final long id = counter++;@Overridepublic String toString() {return Long.toString(id);}}public class FilledList<T> {private Class<T> type;public FilledList(Class<T> type){this.type = type;}public List<T> create(int nElements) {List<T> res = new ArrayList<>();//返回值是一个集合try {for (int i = 0; i < nElements; i++) {res.add(type.newInstance());//创建实例} }catch (Exception e) {throw new RuntimeException();}return res;}public static void main(String[] args) {FilledList<CountedInteger> countedIntegerFilledList = new FilledList<>(CountedInteger.class);System.out.println(countedIntegerFilledList.create(15));}}
类型转换之前先做检查
instanceof:返回一个布尔值,告诉我们前者是否时后者的一个实例
public class PetCount {static class PetCounter extends HashMap<String,Integer>{public void count(String type){Integer quantity = get(type);if (quantity == null){put(type, 1);}else {put(type, quantity + 1);}}}public static void countPets(PetCreator creator){PetCounter counter = new PetCounter();for (Pet pet : creator.creatArray(20)) {System.out.print(pet.getClass().getSimpleName() + " " );if (pet instanceof Pet){counter.count("Pet");}if (pet instanceof Dog){counter.count("Dog");}if (pet instanceof Mutt){counter.count("Mutt");}if (pet instanceof Pug){counter.count("Pug");}if (pet instanceof Cat){counter.count("Cat");}if (pet instanceof Manx){counter.count("EgyptianMau");}if (pet instanceof Manx){counter.count("Manx");}if (pet instanceof Manx){counter.count("Cymric");}if (pet instanceof Rodent){counter.count("Rodent");}if (pet instanceof Rat){counter.count("Rat");}if (pet instanceof Mouse){counter.count("Mouse");}if (pet instanceof Hamster){counter.count("Hamster");}}System.out.println();System.out.println(counter);}public static void main(String[] args) {countPets(new ForNameCreator());}}
使用类字面常量
class Initable {static final int staticFinal = 47;static final int staticFinal2 = ClassInitialization.rand.nextInt(1000);static{System.out.println("Initializing Initable");}}class Initable2 {static int staticNonFinal = 147;static {System.out.println("Initializing Initable2");}}class Initable3 {static int staticNonFinal = 74;static {System.out.println("Initializing Initable3");}}public class ClassInitialization {public static Random rand = new Random(47);public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException {final Class initableClass = Initable.class;System.out.println("After creating Initable ref");//staticFinal是static final的,是一个编译期常量,它不需要对类进行初始化就可以被读取System.out.println(Initable.staticFinal);//staticFinal虽然也是static final的,但是他却需要进行运算才可以获取它的值,所以此时的类需要加载到虚拟机中System.out.println(Initable.staticFinal2);//下面的常量都是static但是不是的static final的,所以他们在读取之前都要进行初始化System.out.println(Initable2.staticNonFinal);final Class initable3 = Class.forName("thinkinginjava.Initable3");System.out.println("After creating Initable3 ref");System.out.println(Initable3.staticNonFinal);}}
public class LiteralPetCreator extends PetCreator {public static final List<Class<? extends Pet>> allType =Collections.unmodifiableList(Arrays.asList(Pet.class, Dog.class, Cat.class, Rodent.class, Mutt.class, Pug.class, EgyptianMau.class,Manx.class, Cymric.class, Mouse.class, Hamster.class));private static final List<Class<? extends Pet>> types = allType.subList(allType.indexOf(Mutt.class), allType.size());public List<Class <? extends Pet>> types(){return types;}public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println(types);}}
动态的instanceof
public class PetCount3 {static class PetCount extends LinkedHashMap<Class<? extends Pet>,Integer>{public PetCount(){super(MapData.map(LiteralPetCreator.allType,0));}public void count(Pet pet){for (Map.Entry<Class<? extends Pet>, Integer> pair : entrySet()) {if (pair.getKey().isInstance(pet)){put(pair.getKey(), pair.getValue() + 1);}}}public String toString(){final StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder("{");for (Map.Entry<Class<? extends Pet>, Integer> pair : entrySet()) {result.append(pair.getKey().getSimpleName());result.append("=");result.append(pair.getValue());result.append(", ");}result.delete(result.length() - 2, result.length());result.append("}");return result.toString();}}public static void main(String[] args) {final PetCount petCount = new PetCount();for (Pet pet : Pets.creatArray(20)) {System.out.print(pet.getClass().getSimpleName() + " ");petCount.count(pet);}System.out.println();System.out.println(petCount);}}
注册工厂
将对象的创建工作交给自己去完成,工厂方法可以多态的被调用
public interface Factory<T> {T creat();}class Part{@Overridepublic String toString() {return getClass().getSimpleName();}static List<Factory<? extends Part>> partFactories = new ArrayList<>();static {partFactories.add(new FanBelt.Factory());partFactories.add(new FuelFilter.Factory());}private static Random rand = new Random(47);static Part createRandom(){int n = rand.nextInt(partFactories.size());//随机的创建实例return partFactories.get(n).creat();}}class Filter extends Part{} //分类标识,创建的是他们的子类class FuelFilter extends Filter{public static class Factory implements stu.chapter14.Factory<FuelFilter>{@Overridepublic FuelFilter creat() {return new FuelFilter();}}}class Belt extends Part{}class FanBelt extends Belt{public static class Factory implements stu.chapter14.Factory<FanBelt>{@Overridepublic FanBelt creat() {return new FanBelt();}}}public class RegisteredFactories {public static void main(String[] args) {final Part part = new Part();for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {System.out.println(Part.createRandom());}}}
instanceof和Class的等价性
在查询类型信息的时候,instanceof或者isInstance()和直接比较Class对象由一个很重要的差别
class Base{}class Derived extends Base{}public class FamilyVsExactType {static void test(Object x){System.out.println("Testing x of type: " + x.getClass());System.out.println("x instanceof Base: " + (x instanceof Base));System.out.println("x instanceof Derived: " + (x instanceof Derived));System.out.println("Base.class.isInstance(x): " + Base.class.isInstance(x));System.out.println("Derived.class.isInstance(x): " + Derived.class.isInstance(x));System.out.println("x.getClass() == Base.class: " + (x.getClass() == Base.class));System.out.println("x.getClass() == Derived.class: " + (x.getClass() == Derived.class));System.out.println("x.getClass().equals(Base.class): " + (x.getClass().equals(Base.class)));System.out.println("x.getClass().equals(Derived.class): " + (x.getClass().equals(Derived.class)));}public static void main(String[] args) {test(new Base());test(new Derived());}}
instanceof或者isInstance()表示的是你是这个类吗?或者说是它的子类吗
==和equals表示的是实际的对象,没有继承关系
反射:运行时的类型信息
对于反射机制而言.class文件在编译时时不可取的,所以时在运行时打开和检查.class文件
类方法提取器
可以动态的提取某个类的信息
静态代理:
interface Interface{void doSomething();void somethingElse(String arg);}class RealObject implements Interface{@Overridepublic void doSomething() {System.out.println("doSomething");}@Overridepublic void somethingElse(String arg) {System.out.println("doSomethingElse" + arg);}}class SimpleProxy implements Interface{private Interface proxied;public SimpleProxy(Interface proxied){this.proxied = proxied; //调用父类的方法}@Overridepublic void doSomething() {System.out.println("SimpleProxy doSomething");proxied.doSomething();//调用父类的方法}@Overridepublic void somethingElse(String arg) {System.out.println("SimpleProxy somethingElse" + arg);proxied.somethingElse(arg);}}public class SimpleProxyDemo {public static void consumer(Interface iFace){iFace.doSomething();iFace.somethingElse("bonobo");}public static void main(String[] args) {consumer(new RealObject());consumer(new SimpleProxy(new RealObject()));//SimpleProxy中的构造器要传入Interface类型}}
动态代理:动态的创建代理,并且动态的处理对代理方法的调用。在动态代理上所作的所有调用都会被重定向到单一的调用处理器上(InvacationHandler)上。
class DynamicProxyHandler implements InvocationHandler{ //实现InvocationHandlerprivate Object proxied;public DynamicProxyHandler(Object proxied){this.proxied = proxied;}@Overridepublic Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {System.out.println("proxy: " + proxy.getClass() + ", method: " + method + ", args: " + args);/*if (args != null){for (Object arg : args) {System.out.println(" " + arg);}}*/return method.invoke(proxied, args);//通过这个方法来调用外部的方法}}public class SimpleDynamicProxy {public static void consumer(Interface iFace){//iFace.doSomething();iFace.somethingElse("bonobo");}public static void main(String[] args) {RealObject real = new RealObject();//consumer(real);//类加载器final Object o = Proxy.newProxyInstance(Interface.class.getClassLoader(),new Class[]{Interface.class}, new DynamicProxyHandler(real));//最后一个就是调用处理器//必须实现InvocationHandler//通过它传递一个实际对象的引用//final Object o = Proxy.newProxyInstance(Interface.class.getClassLoader(),//RealObject.class.getInterfaces(),//需要干活的类的所有接口//new DynamicProxyHandler(real));consumer((Interface) o);}}
还可以筛选某些方法
interface SomeMethods{void boring1();void boring2();void interesting(String arg);void boring3();}class Implementation implements SomeMethods{@Overridepublic void boring1() {System.out.println("boring1()");}@Overridepublic void boring2() {System.out.println("boring2()");}@Overridepublic void interesting(String arg) {System.out.println("interesting " + arg);}@Overridepublic void boring3() {System.out.println("boring3");}}class MethodSelector implements InvocationHandler{private Object proxied;public MethodSelector(Object proxied){this.proxied = proxied;}@Overridepublic Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {if (method.getName().equals("interesting"))System.out.println("Proxy detected the interesting");return method.invoke(proxied,args);}}public class SelectingMethods {public static void main(String[] args) {SomeMethods proxy = (SomeMethods) Proxy.newProxyInstance(SomeMethods.class.getClassLoader(),Implementation.class.getInterfaces(), new MethodSelector(new Implementation()));//proxy.boring1();//proxy.boring2();proxy.interesting("ahah");//proxy.boring3();}}
接口和类型信息
public interface A {void f();}class B implements A{@Overridepublic void f(){}public void g(){}}public class InterfaceViolation {public static void main(String[] args) {A a = new B();a.f();System.out.println(a.getClass().getName());// a这个实例中看不到g方法B b = (B) a;b.f();b.g();//通过转型可以调用A中不存在的方法}}
可以借助访问权限对其进行限制
class C implements A{@Overridepublic void f() {System.out.println("public.C.f()");}public void g(){System.out.println("public.C.g()");}void u(){System.out.println("Package.C.u()");}protected void v(){System.out.println("protect.C.v()");}private void w(){System.out.println("private.C.w()");}}public class HiddenC {public static A makeA(){return new C();}public static void main(String[] args) {C c = (C) HiddenC.makeA();c.v();}}
但是通过反射可以拿到任何的域或者方法,甚至时私有的
public class HiddenImplementation {static void callHiddenMethods(Object a ,String methodName) throws Exception {Method g = a.getClass().getDeclaredMethod(methodName);g.setAccessible(true);g.invoke(a);}public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {A a = HiddenC.makeA();System.out.println(a.getClass().getName());a.f();/*if (a instanceof C){C c = (C)a;c.g();}*/callHiddenMethods(a, "g");callHiddenMethods(a, "u");callHiddenMethods(a, "v");callHiddenMethods(a, "w");}}
此时只能通过final修饰,使其只读但是不可以更改
class WithPrivateFinalField{private int i = 1;private final String s = "I'm totally safe";private String s2 = "Am I safe?";@Overridepublic String toString() {return "WithPrivateFinalField{" +"i=" + i +", s='" + s + '\'' +", s2='" + s2 + '\'' +'}';}}public class ModifyingPrivateFields {public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException {WithPrivateFinalField pf = new WithPrivateFinalField();System.out.println(pf);Field f = pf.getClass().getDeclaredField("i");f.setAccessible(true);System.out.println("f.getInt(pf) : " + f.getInt(pf));f.setInt(pf,47);System.out.println(pf);f = pf.getClass().getDeclaredField("s");f.setAccessible(true);System.out.println("f.get(pf) : " + f.get(pf));f.set(pf,"haha");System.out.println(pf);f = pf.getClass().getDeclaredField("s2");f.setAccessible(true);System.out.println("f.get(pf) : " + f.get(pf));f.set(pf,"heihei");System.out.println(pf);}}

