title: 【学习之路】IO流学习
draft: true
tags:
- 学习之路
- Java
- IO流
categories: - JavaSE
- IO流
description: IO流学习
cover: ‘https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/gh/CodeZixuan/Blog_Images/IO/2021-04-05_19-06-18.png‘
abbrlink: ‘19222411’
date: 2021-04-05 14:16:50
Java IO原理
IO是Input/Output的缩写,用于处理设备之间的数据传输。如读写文件等。
输入Input:读取外部数据到内存中
输出Output:将程序内存数据输出到磁盘等储存设备
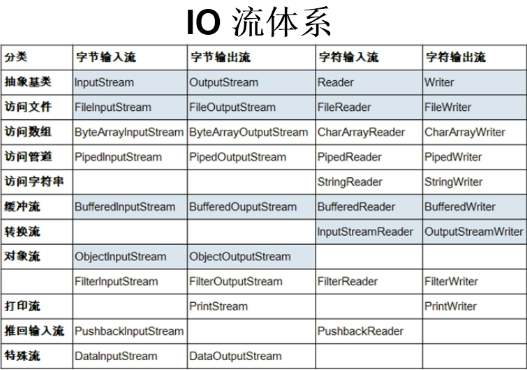
IO流的分类
- 按照操作数据单位不同分为:字节流(8 bit),字符流(16 bit)
- 按数据流的流向不同分为:输入流,输出流
- 按流的角色的不同分为:节点流,处理流
FileReader
read()方法的使用
- 空参方法
// 实列化File类对象,指明要操作的文件File file = new File("hello.txt");// 提供具体的流FileReader fr = new FileReader(file);// 数据的读入// read():返回读入的一个字符,如果达到文件末尾,返回-1int data = fr.read();while(data != -1){System.out.println((char)data);data = fr.read();}// 流的关闭操作fr.close();
// 读入操作语法上的修改int data;while ((data = fr.read()) != -1){System.out.println((char) data);}
FileReader fr = null;try{// 实列化File对象File file = new File("D:\\java-code\\JavaSETest\\src\\hello.txt");// 实列化FileReader对象将File对象传入fr = new FileReader(file);// 数据的读入// read():返回读入的一个字符如果达到末尾,返回-1int data;while ((data = fr.read()) != -1){System.out.println((char) data);}}catch (IOException e){e.printStackTrace();}finally {// 流的关闭操作try {if (fr != null) {fr.close();}} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}
- char[]重载方法
FileReader fr = null;try{File file = new File("D:\\java-code\\JavaSETest\\src\\hello.txt");fr = new FileReader(file);// 读入操作char[] cbuf = new char[5];int len;while ((len = fr.read(cbuf)) != -1){// 错误的写法for (int i = 0; i < cbuf.length; i++) {System.out.print(cbuf[i]);}}}catch (Exception e){e.printStackTrace();}finally{// 关闭流的操作try {if (fr != null) {fr.close();}} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}
这样写输出有问题,每次写入都是覆盖数组的操作,如果读到最后一次没有5个字符那么上次读取剩下来的字符就会保留

正确的写法
FileReader fr = null;try{File file = new File("D:\\java-code\\JavaSETest\\src\\hello.txt");fr = new FileReader(file);// 读入操作char[] cbuf = new char[5];int len;while ((len = fr.read(cbuf)) != -1){// 错误的写法// for (int i = 0; i < cbuf.length; i++) {// System.out.print(cbuf[i]);// }// 正确的写法for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {System.out.print(cbuf[i]);}}}catch (Exception e){e.printStackTrace();}finally{// 关闭流的操作try {if (fr != null) {fr.close();}} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}

或者使用String的构造器来获取
// 读入操作char[] cbuf = new char[5];int len;while ((len = fr.read(cbuf)) != -1){// 错误写法// String str = new String(cbuf);// System.out.print(str);// 正确写法 获取数组,从第0位置到len的位置String str = new String(cbuf, 0, len);System.out.print(str);}
FileWriter
输出操作,对应的File可以不存在
如果不存在,那么就会自动创建此文件
如果存在:如果流使用的构造器是:FileWriter(file, true):再原有文件追加内容 / FileWriter(File):对原有文件的覆盖
writer()方法的使用
FileWriter fw = null;try{File file = new File("D:\\java-code\\JavaSETest\\src\\hello1.txt");// 覆盖原有文件fw = new FileWriter(file);// 追加原有文件// fw = new FileWriter(file, true);fw.write("CodeXuan");}catch (Exception e){e.printStackTrace();}finally{try {if (fw != null) {fw.close();}} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}
File Input/Output Stream
如果使用字节流读取文件可能会出现乱码问题
File file = new File("D:\\java-code\\JavaSETest\\src\\hello.txt");FileInputStream fis = null;try{// 创建流fis = new FileInputStream(file);// 读取数据byte[] buffer = new byte[5];int len;while ((len = fis.read(buffer)) != -1){String str = new String(buffer, 0, len);System.out.print(str);}}catch (Exception e){e.printStackTrace();}finally{try {if (fis != null) {fis.close();}} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}
使用字节流复制文件,也可以使用字节流复制文本文件,但是最好不要再内存层面读取否则有可能出现乱码的情况
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();File srcFile = new File("background.png");File destFile = new File("background-副本.png");FileInputStream fis = null;FileOutputStream fos = null;try{fis = new FileInputStream(srcFile);fos = new FileOutputStream(destFile);// 复制操作byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];int len;while ((len = fis.read(bytes)) != -1) {fos.write(bytes, 0, len);}System.out.println("复制成功");}catch (Exception e){e.printStackTrace();}finally{try {if (fis != null) {fis.close();}} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}try {if (fos != null) {fos.close();}} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}long end = System.currentTimeMillis();System.out.println("复制花费的时间" + (end - start));
Buffered Input/Output Stream
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();File srcFile = new File("background.png");File destFile = new File("background-副本.png");FileInputStream fis = null;FileOutputStream fos = null;BufferedInputStream bis = null;BufferedOutputStream bos = null;try{// 创建节点流fis = new FileInputStream(srcFile);fos = new FileOutputStream(destFile);// 创建缓冲流bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis);bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos);// 复制细节byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];int len;while ((len = bis.read(bytes)) != -1){bos.write(bytes, 0, len);}System.out.println("复制成功");}catch (Exception e){e.printStackTrace();}finally{// 资源关闭// 要求:先关闭外层流,再关闭内层流// 关闭外层流后,内层流会自动关闭,内层流的关闭可以省略try {if (bis != null) {bis.close();}} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}try {if (bos != null) {bos.close();}} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}long end = System.currentTimeMillis();System.out.println("复制花费的时间" + (end - start));
BufferedReader/Writer
- 方式一
BufferedReader br = null;BufferedWriter bw = null;try {br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("hello.txt"));bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("hello-副本.txt"));char[] chars = new char[1024];int len;while ((len = br.read(chars)) != -1){bw.write(chars, 0, len);}} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {try {if (br != null) {br.close();}} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}try {if (bw != null) {bw.close();}} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}
- 方式二
BufferedReader br = null;BufferedWriter bw = null;try {br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("hello.txt"));bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("hello-副本.txt"));String data;// readLine()一次读一行,使用这种方法不包含换行符while ((data = br.readLine()) != null){// 方式一:增加换行符// bw.write(data + "\n");// 方式二:增加换行符bw.write(data);bw.newLine();}} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {try {if (br != null) {br.close();}} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}try {if (bw != null) {bw.close();}} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}
InputStreamReader
- 将一个字节的输入流转换为字符的输入流
InputStreamReader isr = null;try {FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("hello.txt");// 参数二指明字符集,具体使用的字符集,取决于文件保存时使用的字符集isr = new InputStreamReader(fis, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);char[] chars = new char[20];int len;while ((len = isr.read(chars)) != -1){String str = new String(chars, 0, len);System.out.println(str);}} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {try {if (isr != null) {isr.close();}} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}
OutputStreamWriter
- 将一个字符的输出流转换为字节的输出流
InputStreamReader isr = null;OutputStreamWriter osw = null;try {// 获取文件File file1 = new File("hello.txt");File file2 = new File("hello-gbk.txt");FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file1);FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file2);isr = new InputStreamReader(fis, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);osw = new OutputStreamWriter(fos, "GBK");// 读写过程char[] cbuf = new char[20];int len;while ((len = isr.read(cbuf)) != -1){osw.write(cbuf, 0, len);}} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {// 关闭流try {if (isr != null) {isr.close();}} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}try {if (osw != null) {osw.close();}} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}

