数组是一种简单的线性序列,可以快速地访问数组元素,效率高。如果从效率和类型检查的角度讲,数组是最好的。但不灵活。容量需要事先定义好,不能随着需求的变化而扩容
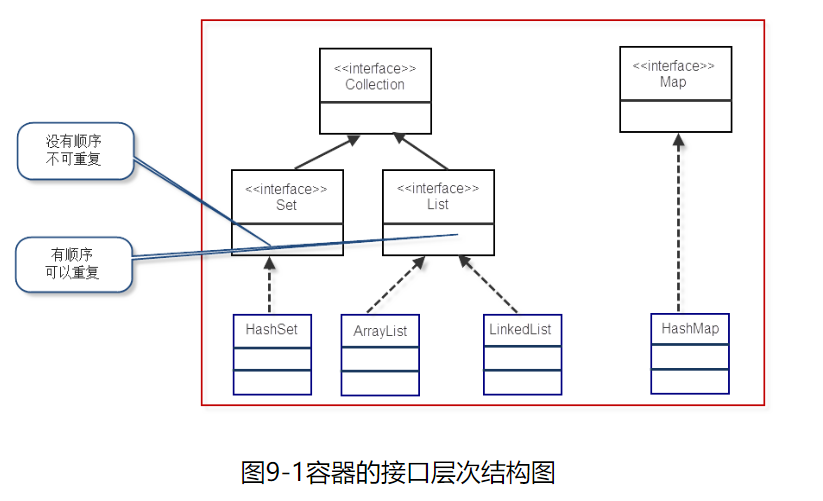
Collection接口
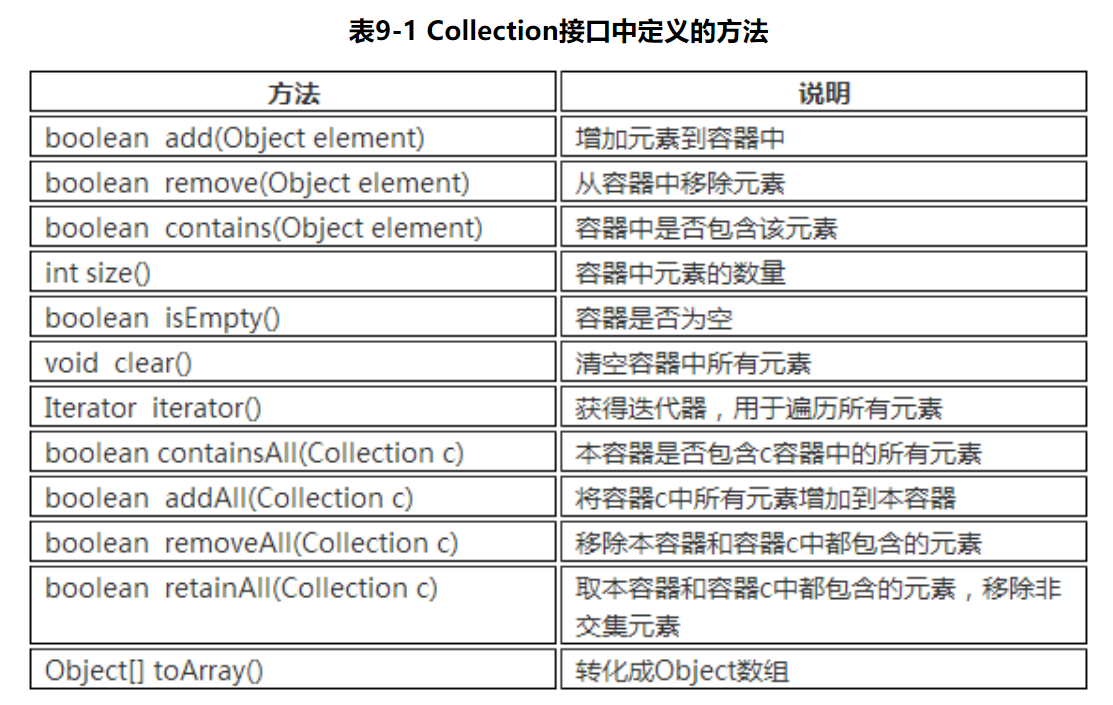
//容器常用方法public class CollectionInterface {public static void main(String[] args) {Collection<String> c = new ArrayList<>();System.out.println(c.size()); //容器元素数量System.out.println(c.isEmpty()); //判断容器是否为空c.add("张三"); //添加某个元素c.add("李四");System.out.println(c);System.out.println(c.size());Object[] objs = c.toArray();System.out.println(objs); //转换成object数组c.remove("李四"); //移除某个元素 并不是删除了 存储的只是对象的地址System.out.println(c);c.clear(); //清除容器内所有元素System.out.println(c);}}
list
List是有序、可重复的容器,允许多个null元素
- 有序:List中每个元素都有索引标记。可以根据元素的索引标记(在List中的位置)访问元素,从而精确控制这些元素。
可重复:List允许加入重复的元素。更确切地讲,List通常允许满足 e1.equals(e2) 的元素重复加入容器。
除了Collection接口中的方法,**List多了一些跟顺序(索引)有关的方法**:
List接口常用的实现类有3个:ArrayList(数组)、LinkedList(链表)和Vector(向量)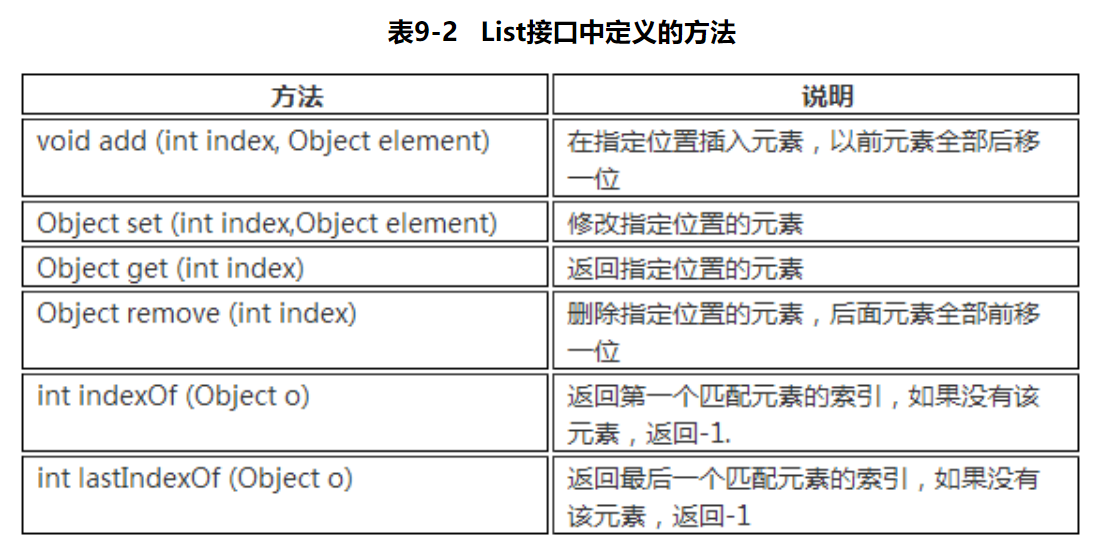
ArrayList
public static void text03() {List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();list.add("a");list.add("b");list.add("c");list.add("d");System.out.println(list);list.add(2,"e"); //添加指定位置的数据System.out.println(list);list.remove(2); //删除指定位置的数据System.out.println(list);list.set(2,"e"); //修改指定位置的元素System.out.println(list);System.out.println(list.get(2));//返回指定索引位置的数据list.add("e");list.add("f");list.add("g");System.out.println(list);System.out.println(list.indexOf("e")); // 返回第一个索引匹配的位置System.out.println(list.lastIndexOf("e")); //返回最后个索引匹配的位置}
ArrayList底层是用数组实现的存储。 特点:查询效率高,增删效率低,线程不安全。一般使用它
注:List集合中的toString继承自AbstractCollection,它重写了Object里定义的toString方法;所以直接输出集合可以遍历
arraylist重写
//arraylist重写public class RwArrayList2<E>{ //增加范型//类的属性全部私有private Object elementDate[]; //核心数组存储内容private int size; //数组元素长度private static final int DEFALT_CAPACITY=10; //静态变量public RwArrayList2() { //构造器方法elementDate = new Object[DEFALT_CAPACITY];//默认数组长度}public RwArrayList2(int capacity) { //构造器方法elementDate = new Object[capacity]; //定义数组长度}//添加方法public void add(E obj) {//扩容操作if (size == elementDate.length) {//扩大数组长度的一半Object[] newarray = new Object[elementDate.length+(elementDate.length>>1)];//拷贝原数组System.arraycopy(elementDate, 0, newarray, 0, elementDate.length);elementDate = newarray; //把老数组指向新数组地址}elementDate[size++] = obj;}public E get(int index) {check(index); //检查索引return (E)elementDate[index];}public void set(int index,E s2) {check(index);elementDate[index] = s2;}public void check(int index) {//判断索引合法性if(index < 0 || index > elementDate.length) {throw new RuntimeException("索引不合法: "+index);}}public void remove(E element) {//将element与所有元素比较 获得第一个返回true的 返回for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {if(element.equals(get(i))){remove(i);}}}//删除操作public void remove(int index) {//核心是数组拷贝int num = elementDate.length-index-1;if(num >0) {System.arraycopy(elementDate, index+1, elementDate, index, num);}elementDate[size-1] = null;size--;}//重写tostring方法 打印数组内数据@Overridepublic String toString() {StringBuilder b1 = new StringBuilder();b1.append("[");for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {b1.append(elementDate[i]+" ");}b1.setCharAt(b1.length()-1, ']'); //改变最后一个字符return b1.toString();}public static void main(String[] args) {RwArrayList2 s1 = new RwArrayList2(); //数组对象for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {s1.add("h"+i);}s1.add("a");s1.add("b");s1.set(10, "aa");System.out.println(s1);System.out.println(s1.get(10));s1.remove("aa");System.out.println(s1);}}
LinkedList
LinkedList底层用双向链表实现的存储。特点:查询效率低,增删效率高,线程不安全。它的每个数据节点中都有两个指针,分别指向前一个节点和后一个节点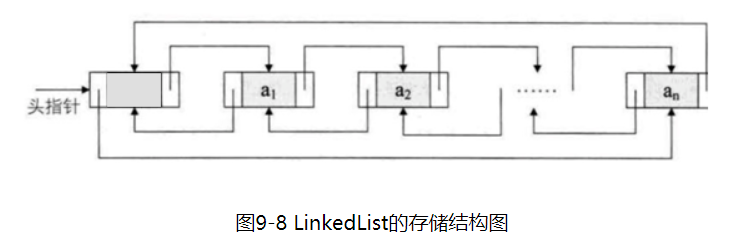
重写Linkedlist
//重写Linkedlistpublic class RwLinkedList <E>{private Node first;private Node last;private int size;public void add(E element) {Node node =new Node(element);if (first == null) {first = node;last = node;}else {node.previous = last;node.next = null;last.next = node;last = node;}size++;}public E get(int index) {if (index<0 || index>size-1) {throw new RuntimeException("索引不合法:"+index);}Node temp = getNode(index);return temp != null?(E)temp.element:null;}//封装获取节点public Node getNode(int index) {Node temp = null;if (index<=(size>>1)) { //size右移一位相当于除以2temp = first;for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {temp = temp.next;}}else {temp = last;for (int i = size-1; i > index; i--) {temp = temp.previous;}}return temp;}public void remove(int index) {if (index<0 || index>size-1) {throw new RuntimeException("索引不合法:"+index);}Node temp = getNode(index);if(temp!=null) {Node upNode = temp.previous;Node dowNode = temp.next;if(upNode!=null) {upNode.next = dowNode;}if(dowNode != null) {dowNode.previous = upNode;}//删除第一个元素时if(index == 0) {first = dowNode;}//删除最后一个元素时if(index == size-1) {last = upNode;}size--;}}public void insert(int index,E element) {Node newnNode = new Node(element);Node tempNode = getNode(index);if (tempNode!=null) {Node upNode = tempNode.previous;if (index == 0) { //插入首元素first = newnNode;newnNode.next = tempNode;tempNode.previous = newnNode;}else if (index == size-1) { //插入尾元素last = newnNode;tempNode.next = newnNode;newnNode.previous = tempNode;}else {upNode.next = newnNode;newnNode.previous = upNode;newnNode.next = tempNode;tempNode.previous = newnNode;}}}//规范输出格式@Overridepublic String toString() {StringBuilder s1 = new StringBuilder();s1.append("[");Node temp = first;while (temp != null) {s1.append(temp.element+" ");temp = temp.next;}s1.setCharAt(s1.length()-1, ']');return s1.toString();}public static void main(String[] args) {RwLinkedList<String> list = new RwLinkedList<>();list.add("a");list.add("b");list.add("c");list.add("e");list.add("f");list.add("g");list.remove(5);list.insert(1, "aa");System.out.println(list);System.out.println(list.get(3));}}
Vector
Vector与ArrayList一样,也是通过数组实现的,但它支持线程的同步,即某一时刻只有一个线程能够写Vector.但实现同步需要很高的花费。因此,访问它比访问ArrayList慢
set
Set容器特点:无序、不可重复,只允许一个null元素。无序指Set中的元素没有索引(没有get方法),只能遍历查找;不允许加入重复的元素
//基本用法public class TestHashSet {public static void main(String[] args) {Set<String> s1 = new HashSet<String>();s1.add("a");s1.add("b");s1.add("a");System.out.println(s1);s1.remove("a");System.out.println(s1);Set<String> s2 = new HashSet<String>();s2.add("A");s2.addAll(s1);System.out.println(s2);}}
TreeSet
TreeSet底层实际是用TreeMap实现的,通过key来存储Set的元素。TreeSet内部需要对存储的元素进行排序,因此,我们对应的类需要实现Comparable接口。
public class TreeSet {public static void main(String[] args) {Set<Integer> s1 = new java.util.TreeSet<Integer>();s1.add(3);s1.add(2);s1.add(1);//按元素递增模式输出for(Integer i:s1) {System.out.println(i);Set<employee2> s2 = new java.util.TreeSet<>();s2.add(new employee2(1001, "A", 10000));s2.add(new employee2(1003, "B", 20000));s2.add(new employee2(1004, "C", 30000));for(employee2 i:s2) {System.out.println(i);}}}
Map接口
Map就是用来存储“键(key)-值(value) 对”的。 Map类中存储的 “键值对” 通过键来标识,所以“键对象”不能重复。这就是一种成对存储的关系。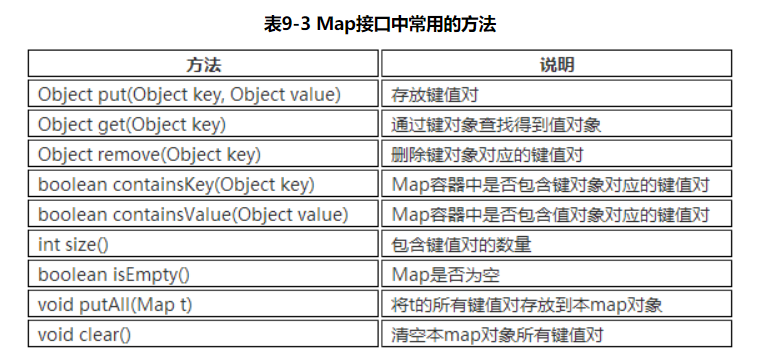
Map 接口的实现类有HashMap、TreeMap、HashTable、Properties等。
常用方法
//常用方法public static void main(String[] args) {Map<Integer, String> m1 = new HashMap<>();m1.put(1, "a");m1.put(2, "b");m1.put(3, "c");System.out.println(m1.get(1));System.out.println(m1.size());System.out.println(m1.containsValue("a"));Map<Integer, String> m2 = new HashMap<>();m2.put(4, "A"); //注意键不能重复m2.put(5, "B");m2.put(6, "C");m1.putAll(m2);System.out.println(m1);}
HashMap采用哈希算法实现,是Map接口最常用的实现类。 由于底层采用了哈希表存储数据,要求键不能重复,如果发生重复,新的键值对会替换旧的键值对。 HashMap在查找、删除、修改方面都有非常高的效率。
HashTable类和HashMap用法几乎一样,底层实现几乎一样,只不过HashTable的方法添加了synchronized关键字确保线程同步检查,效率较低
HashMap与HashTable的区别
- HashMap
- 线程不安全,效率高
- 允许key或value为null
- 初始容量是16,扩容是2n
- 在首次调用put方法时放入元素时才会初始化数组
- HashTable
- 线程安全,效率低
- 不允许key或value为null
- 初始容量是11,扩容2n+1
- 构造函数里面就初始化数组
TreeMap
TreeMap和HashMap实现了同样的接口Map,因此,用法对于调用者来说没有区别。HashMap效率高于TreeMap;在需要排序的Map时才选用TreeMap。
public class TestTreeMap {public static void main(String[] args) {Map<Integer, String> map1 = new TreeMap<>();map1.put(10, "a");map1.put(20, "b");map1.put(30, "c");//按照key递增的方式排序for(Integer key:map1.keySet()) {System.out.println(key+"--"+map1.get(key));}Map<employee2, String> treeMap = new TreeMap<>();treeMap.put(new employee2(1001, "张三",6000),"。。。");treeMap.put(new employee2(1002, "张",3000),"。。");treeMap.put(new employee2(1003, "张4",5000),"。");for(employee2 key:treeMap.keySet()) {System.out.println(key+"--"+treeMap.get(key));}}}//Comparable接口可按照自定义变量进行递增class employee2 implements Comparable<employee2>{int id;String name;int salary;public employee2(int id, String name, int salary) {super();this.id = id;this.name = name;this.salary = salary;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "id:"+id+" name:"+name+" salary:"+salary;}//按照工资排序@Overridepublic int compareTo(employee2 o) {//负数:小于 0:等于 正数:大于if(this.salary > o.salary) {return 1;}else if (this.salary < o.salary) {return -1;}else { //工资相等if(this.id > o.id) {return 1;}else if (this.id <o.id) {return -1;}else {return 0;}}}}
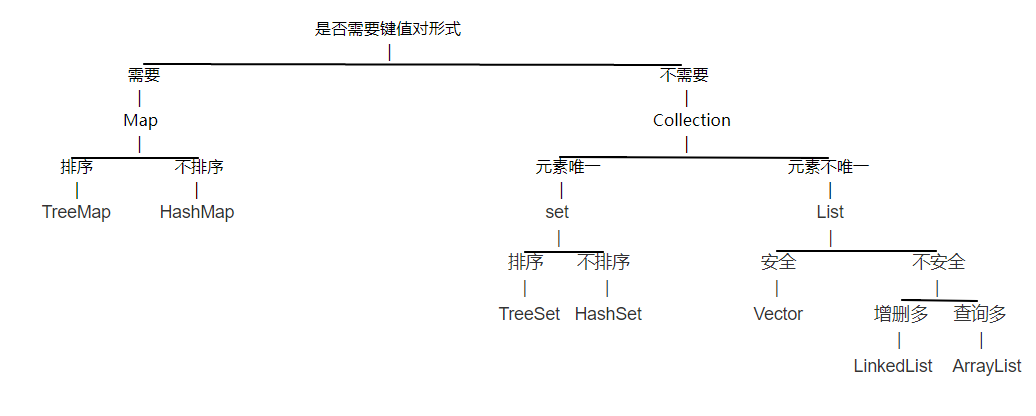
接口使用的选择
Iterator迭代器遍历容器
遍历容器元素(List/Set/Map)
hashnext():如果任有元素可以迭代,则返回true
public class TestIterator {public static void main(String[] args) {TestIterator();TestIterator2();TestIterator3();TestIterator4();}public static void TestIterator() {List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();list.add("a");list.add("b");list.add("c");//用迭代器遍历listfor(Iterator<String> iterator= list.iterator(); iterator.hasNext();) {String temp = iterator.next();System.out.println(temp);}System.out.println("******");}public static void TestIterator2() {Set<String> set1 = new HashSet<>();set1.add("a");set1.add("b");set1.add("c");//用迭代器遍历setfor(Iterator<String> iterator= set1.iterator(); iterator.hasNext();) {String temp = iterator.next();System.out.println(temp);}System.out.println("******");}public static void TestIterator3() {Map<Integer, String> map1 = new HashMap<>();map1.put(1, "a");map1.put(2, "b");map1.put(3, "c");//获取hashmap的位桶数组Set<Entry<Integer, String>> se = map1.entrySet();//用迭代器遍历map//法一:取出map内的每一个结点,再遍历每一个节点的keyfor(Iterator<Entry<Integer, String>> iterator= se.iterator(); iterator.hasNext();) {Entry<Integer, String> temp = iterator.next();System.out.println(temp.getKey()+"--"+temp.getValue());}System.out.println("******");}public static void TestIterator4() {Map<Integer, String> map1 = new HashMap<>();map1.put(1, "a");map1.put(2, "b");map1.put(3, "c");//通过map1获取key和value的集合 再去遍历它们Set<Integer > keySet = map1.keySet();//用迭代器遍历map 法2:直接遍历map节点的集合for(Iterator<Integer> iter = keySet.iterator(); iter.hasNext();) {Integer key = iter.next();System.out.println(key+"--"+map1.get(key));}System.out.println("******");//jdk8新特性 函数式编程map.forEach((key,value)-> System.out.println(key+"="+value));}}
Collections工具类
类 java.util.Collections 提供了对Set、List、Map进行排序、填充、查找元素的辅助方法。
public class TestCollections {public static void main(String[] args) {List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();for(int i=0; i<10; i++) {list.add("a"+i);}System.out.println(list);//逆序排序Collections.reverse(list);System.out.println(list);//随机排列数组中的元素Collections.shuffle(list);System.out.println(list);//正常排序Collections.sort(list);System.out.println(list);//二分查找System.out.println(Collections.binarySearch(list, "a1"));//用一个特定的对象覆盖重写整个容器Collections.fill(list, "b");System.out.println(list);}}

