API文档 => java.lang => Throwable
异常简介
在程序运行中,意外发生的情况,背离程序本身意图的表现,都可以理解为异常。
Java中的异常,根类是Throwable,子类可以分为Error类和Exception类。
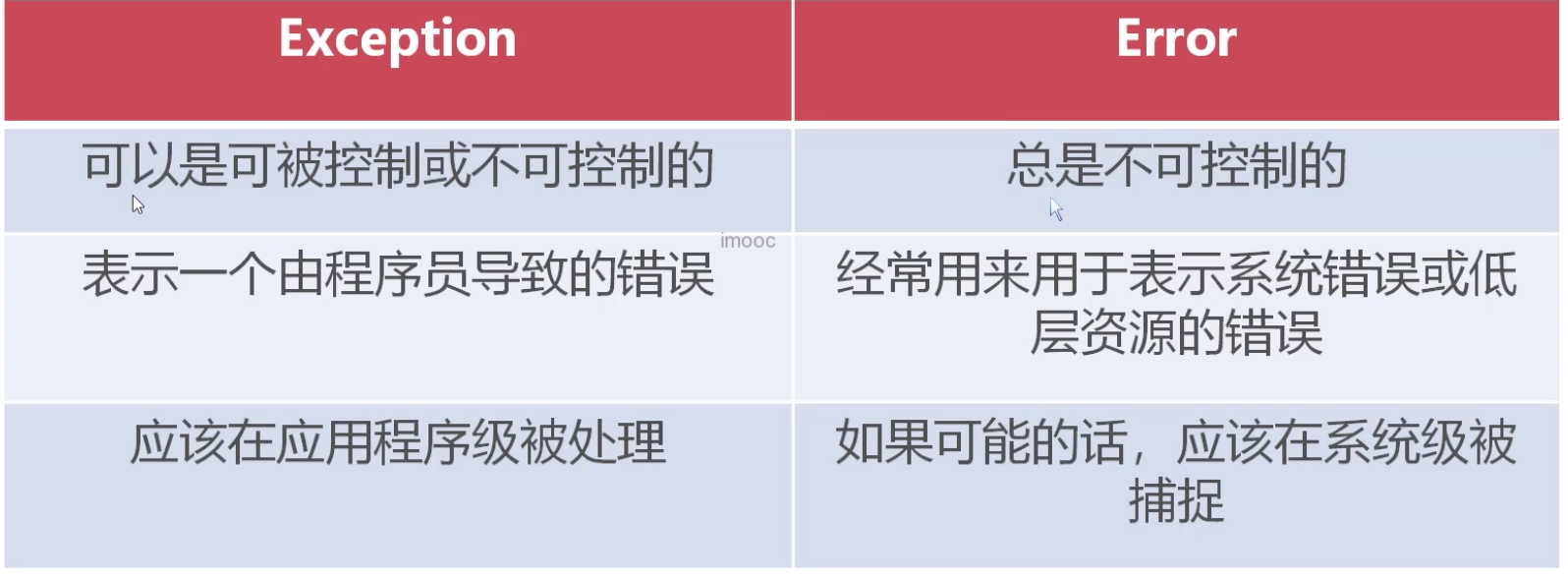
Error
Error是程序无法处理的错误,表示运行应用程序中较严重的问题。大多数错误与代码编写者执行的操作是没有关系的,而表示代码执行的时候,Java虚拟机出现了一系列的问题。这些错误在应用程序的控制和处理能力之外,而且绝大多数是程序运行是不允许出现的状况。
对于设计合理的应用程序来说,即使确实发生了错误,本质上也不应该试图去处理它所引起的异常状况。所以,对于Error及其子类所产生的异常,我们通常是不需要关心的。当然我们也不希望在程序运行中出现此类型错误。
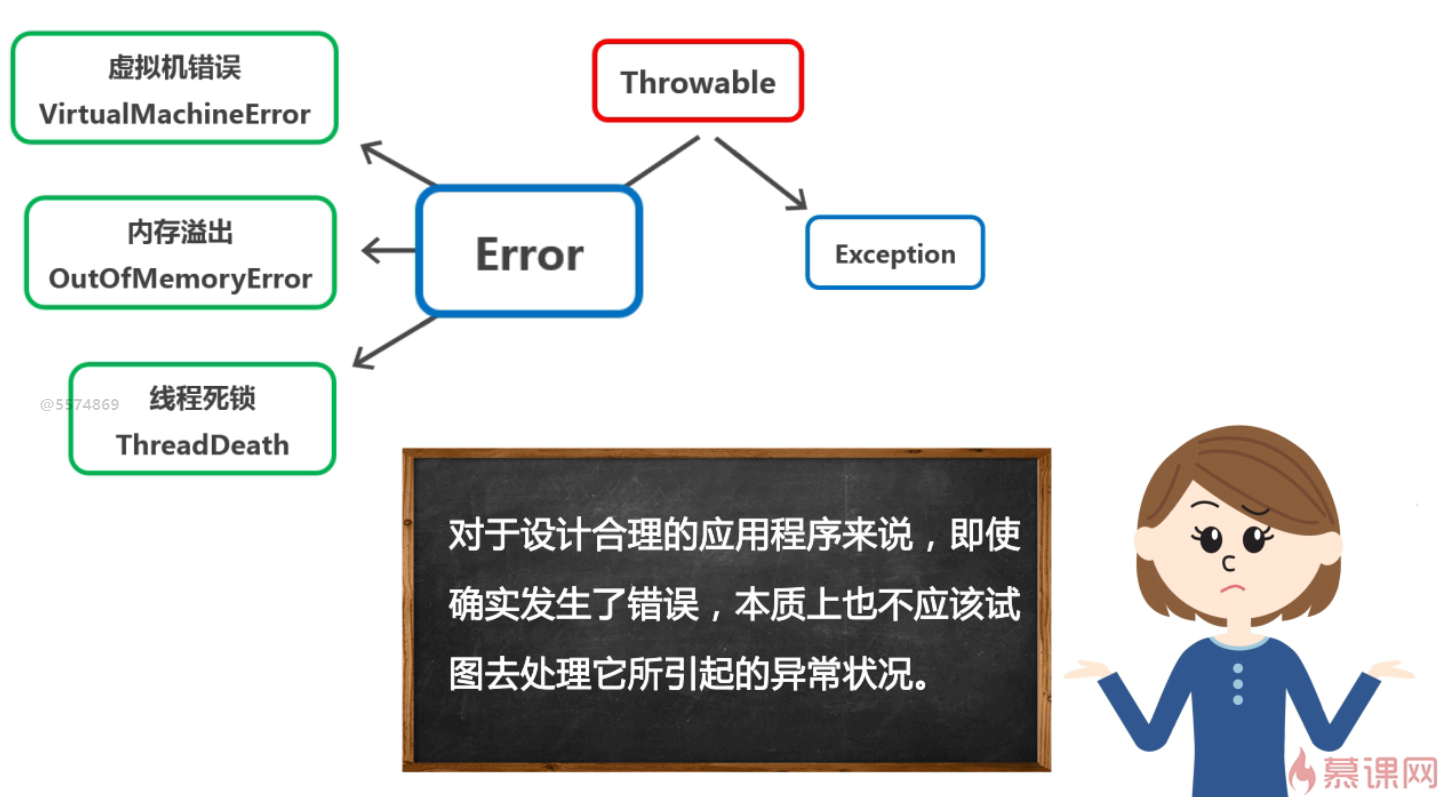
Exception
Exception是程序本身可以处理的异常。异常处理通常指针对这种类型异常的处理。
Exception可分为非检查异常(UncheckedException)和检查异常(CheckedException)两个方向。
非检查异常(UncheckedException):
编译器不要求强制处理的异常,包含RuntimeExceptio及其子类,比如空指针异常。。。等等
检查异常(CheckedException):
编译器要求强制处理的异常,除了RuntimeExceptio及其子类,其他都属于检查异常,比如IO异常。。。等等
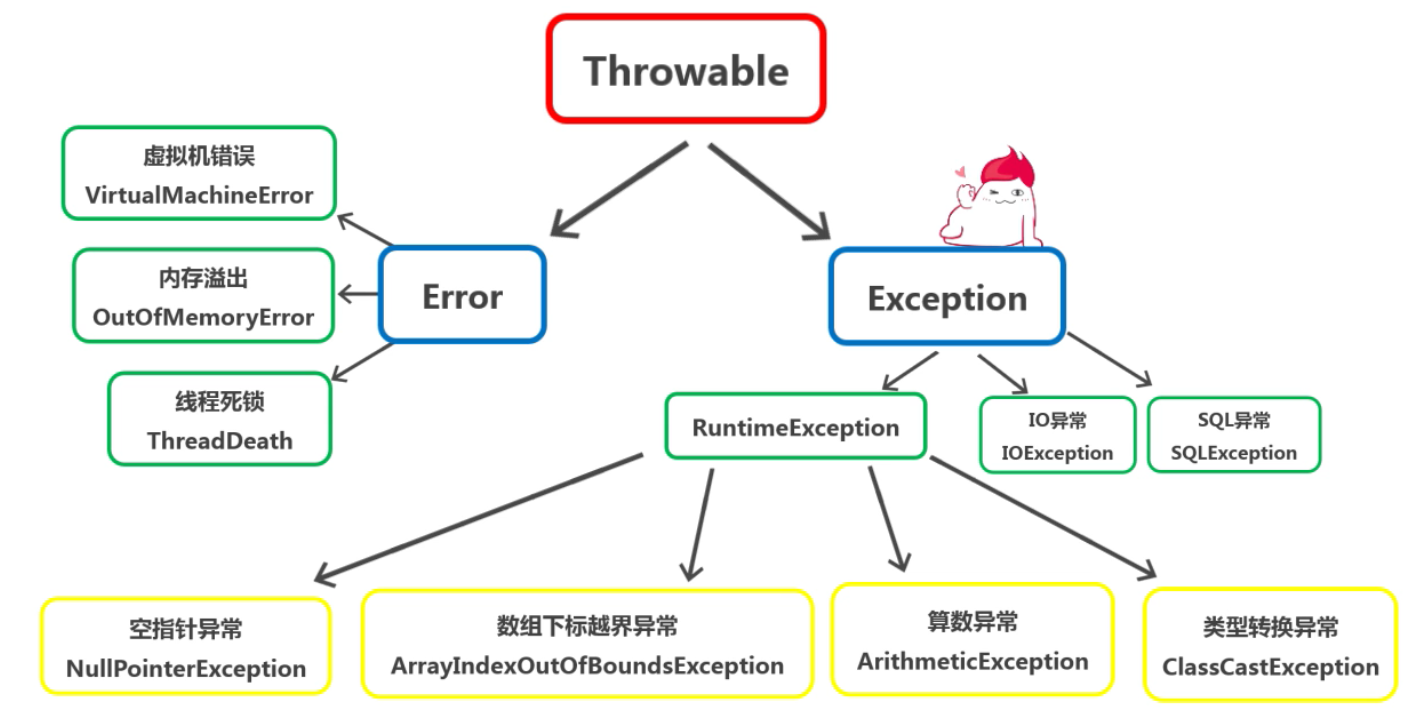
异常处理简介
Java中的异常处理机制为:先抛出异常,然后捕获异常
这里的抛出异常是指,当一个方法中出现了错误引发异常的时候,方法会创建异常对象,并且交付给运行时系统来处理。异常对象中,通常包含异常类型,异常出现时的程序状态等信息。
而当运行时系统捕获到异常之后,就会进入捕获异常环节,在这个阶段中,运行时系统会去寻找合适的处理器,如果找到与抛出异常匹配的处理器,就会执行相关的处理逻辑,如果没有找到,那么运行时系统将会终止,这也就意味着Java程序停止了。
抛出异常和捕获异常,是通过五个关键字实现的:try,catch,finally,throw,throws
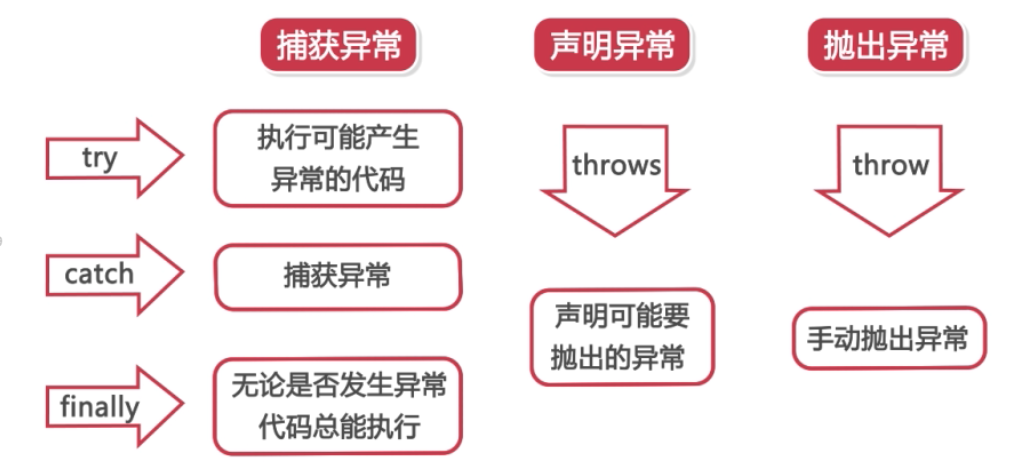
使用try…catch…finally处理异常
try块后可接零个或多个catch块,如果没有catch块,则必须跟一个finally块

1,简单处理异常
package com.song.test;import java.util.Scanner;public class TryDemoOne {public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);System.out.println("=====运算开始=====");try {System.out.print("请输入第一个整数:");int one = input.nextInt();System.out.print("请输入第二个整数:");int two = input.nextInt();System.out.println("one和two的商是:" + (one / two));} catch (Exception e) {System.out.println("程序出错啦。。");e.printStackTrace(); // 显示错误信息} finally {System.out.println("=====运算结束=====");}}}
2,多重catch结构处理异常
package com.song.test;import java.util.InputMismatchException;import java.util.Scanner;public class TryDemoOne {public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);System.out.println("=====运算开始=====");try {System.out.print("请输入第一个整数:");int one = input.nextInt();System.out.print("请输入第二个整数:");int two = input.nextInt();System.out.println("one和two的商是:" + (one / two));} catch (ArithmeticException e) { // 运算错误System.out.println("除数不能为0");} catch (InputMismatchException e) { // 输入错误System.out.println("请输入整数");} catch (Exception e) { // 所有错误System.out.println("程序出错啦。。");e.printStackTrace();} finally {System.out.println("=====运算结束=====");}}}
3,终止finally执行的方法
System.exit(1)
package com.song.test;import java.util.InputMismatchException;import java.util.Scanner;public class TryDemoOne {public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);System.out.println("=====运算开始=====");try {System.out.print("请输入第一个整数:");int one = input.nextInt();System.out.print("请输入第二个整数:");int two = input.nextInt();System.out.println("one和two的商是:" + (one / two));} catch (ArithmeticException e) { // 运算错误System.exit(1); // 终止程序运行System.out.println("除数不能为0");} catch (InputMismatchException e) { // 输入错误System.out.println("请输入整数");} catch (Exception e) { // 所有错误System.out.println("程序出错啦。。");e.printStackTrace();} finally {System.out.println("=====运算结束=====");}}}
4, return关键字
finally中的处理执行完之后,才会执行return语句
【错误示范】:在finally中有return
如果finally中有return,那么一定try,catch中的return就无效了,一定是返回finally中的return的
package com.song.test;import java.util.Scanner;public class TryDemoOne {public static void main(String[] args) {int result = test();System.out.println("one和two的商是:" + result);}public static int test() {Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);System.out.println("=====运算开始=====");try {System.out.print("请输入第一个整数:");int one = input.nextInt();System.out.print("请输入第二个整数:");int two = input.nextInt();return one/two;} catch (Exception e) {System.out.println("程序出错啦。。");return 0;} finally {System.out.println("=====运算结束=====");return -100000;}}}
=====运算开始=====
请输入第一个整数:12
请输入第二个整数:2
=====运算结束=====
one和two的商是:-100000
=====运算开始=====
请输入第一个整数:12
请输入第二个整数:0
程序出错啦。。
=====运算结束=====
one和two的商是:-100000
【正确示范】:在try,catch中return ,finally中没有return
package com.song.test;import java.util.Scanner;public class TryDemoOne {public static void main(String[] args) {int result = test();System.out.println("one和two的商是:" + result);}public static int test() {Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);System.out.println("=====运算开始=====");try {System.out.print("请输入第一个整数:");int one = input.nextInt();System.out.print("请输入第二个整数:");int two = input.nextInt();return one/two;} catch (Exception e) {System.out.println("程序出错啦。。");return 0;} finally {System.out.println("=====运算结束=====");}}}
=====运算开始=====
请输入第一个整数:12
请输入第二个整数:2
=====运算结束=====
one和two的商是:6
=====运算开始=====
请输入第一个整数:12
请输入第二个整数:0
程序出错啦。。
=====运算结束=====
one和two的商是:0
使用throw和throws抛出异常
可以通过throws声明将要抛出何种类型的异常,通过throw将产生的异常抛出
1,使用throws声明异常类型
- throws语句用在方法定义时声明该方法要抛出的异常类型
- 当方法抛出异常列表中的异常时,方法将不对这些类型及其子类类型的异常作处理,而抛向调用该方法的方法,由他去处理
- 处理异常的类必须范围大于抛出异常的类
- 抛出检查异常必须处理

抛出ArithmeticException,处理ArithmeticException => OK
package com.song.test;import java.util.Scanner;public class TryDemoOne {public static void main(String[] args) {try {int result = test();System.out.println("one和two的商是:" + result);} catch (ArithmeticException e) {System.out.println("除数不能为0");e.printStackTrace();}}public static int test() throws ArithmeticException {Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);System.out.println("=====运算开始=====");System.out.print("请输入第一个整数:");int one = input.nextInt();System.out.print("请输入第二个整数:");int two = input.nextInt();return one / two;}}
抛出ArithmeticException,处理Exception=> OK
#Exception可以接受所有异常
package com.song.test;import java.util.Scanner;public class TryDemoOne {public static void main(String[] args) {try {int result = test();System.out.println("one和two的商是:" + result);} catch (Exception e) {System.out.println("除数不能为0");e.printStackTrace();}}public static int test() throws ArithmeticException {Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);System.out.println("=====运算开始=====");System.out.print("请输入第一个整数:");int one = input.nextInt();System.out.print("请输入第二个整数:");int two = input.nextInt();return one / two;}}
抛出Exception,处理Exception=> OK
package com.song.test;import java.util.Scanner;public class TryDemoOne {public static void main(String[] args) {try {int result = test();System.out.println("one和two的商是:" + result);} catch (Exception e) {System.out.println("除数不能为0");e.printStackTrace();}}public static int test() throws Exception {Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);System.out.println("=====运算开始=====");System.out.print("请输入第一个整数:");int one = input.nextInt();System.out.print("请输入第二个整数:");int two = input.nextInt();return one / two;}}
抛出Exception,处理ArithmeticException=> NG
#处理异常的类必须范围大于抛出异常的类,否则会报错
package com.song.test;import java.util.Scanner;public class TryDemoOne {public static void main(String[] args) {try {int result = test();System.out.println("one和two的商是:" + result);} catch (ArithmeticException e) {System.out.println("除数不能为0");e.printStackTrace();}}public static int test() throws Exception {Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);System.out.println("=====运算开始=====");System.out.print("请输入第一个整数:");int one = input.nextInt();System.out.print("请输入第二个整数:");int two = input.nextInt();return one / two;}}
抛出ArithmeticException, InputMismatchException,不处理 => OK
#ArithmeticException, InputMismatchException属于非检查异常类,不处理没关系
#函数注释可以提示我们在调用的test()的时候,处理非检查异常
package com.song.test;import java.util.Scanner;public class TryDemoOne {public static void main(String[] args) {int result = test();System.out.println("one和two的商是:" + result);}/*** 测试接受数据相除结果的方法* @return 两个接受数据的商* @throws ArithmeticException* @throws InputMismatchException*/public static int test() throws ArithmeticException, InputMismatchException {Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);System.out.println("=====运算开始=====");System.out.print("请输入第一个整数:");int one = input.nextInt();System.out.print("请输入第二个整数:");int two = input.nextInt();return one / two;}}
抛出Exception,不处理 => NG
#编译阶段就会提示报错,因为Exception包含检查异常类,而检查异常是必须处理的
package com.song.test;import java.util.Scanner;public class TryDemoOne {public static void main(String[] args) {int result = test();System.out.println("one和two的商是:" + result);}public static int test() throws Exception {Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);System.out.println("=====运算开始=====");System.out.print("请输入第一个整数:");int one = input.nextInt();System.out.print("请输入第二个整数:");int two = input.nextInt();return one / two;}}
2,使用throw抛出异常对象
- throw用来抛出一个异常,例如 throw new IOException();
- throw抛出的只能够是可抛出类Throwable或者其子类的实例对象
- 例如throw new String(“出错啦”); 是错误的
处理throw抛出异常的两种方式:自己处理和交给调用函数处理
自己处理
#当输入数字88的时候,执行throw new Exception语句,抛出异常
#当输入字母a的时候,抛出的是输入异常,所以是不会执行throw new Exception语句的
package com.song.test;import java.util.Scanner;public class TryDemoOne {public static void main(String[] args) {test();}/*** 通过try...catch包含throw语句--自己抛自己处理*/public static void test() {try {System.out.print("请输入年龄:");Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);int age = input.nextInt();if (age < 18 || age > 80) {throw new Exception("18岁以下,80岁以上的住客必须由亲友陪同");}} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}
请输入年龄:56
欢迎入住本酒店
请输入年龄:88
java.lang.Exception: 18岁以下,80岁以上的住客必须由亲友陪同
at com.song.test.TryDemoOne.test(TryDemoOne.java:20)
at com.song.test.TryDemoOne.main(TryDemoOne.java:8)
请输入年龄:a
java.util.InputMismatchException
at java.util.Scanner.throwFor(Unknown Source)
at java.util.Scanner.next(Unknown Source)
at java.util.Scanner.nextInt(Unknown Source)
at java.util.Scanner.nextInt(Unknown Source)
at com.song.test.TryDemoOne.test(TryDemoOne.java:18)
at com.song.test.TryDemoOne.main(TryDemoOne.java:8)
交给调用函数处理
package com.song.test;import java.util.Scanner;public class TryDemoOne {public static void main(String[] args) {try {test();} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}/*** 通过throws在方法声明处抛出异常类型--谁调用谁处理--调用者可以自己处理,也可以继续上抛** @throws Exception*/public static void test() throws Exception {System.out.print("请输入年龄:");Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);int age = input.nextInt();if (age < 18 || age > 80) {throw new Exception("18岁以下,80岁以上的住客必须由亲友陪同");} else {System.out.println("欢迎入住本酒店");}}}
请输入年龄:56
欢迎入住本酒店
请输入年龄:88
java.lang.Exception: 18岁以下,80岁以上的住客必须由亲友陪同
at com.song.test.TryDemoOne.test(TryDemoOne.java:25)
at com.song.test.TryDemoOne.main(TryDemoOne.java:9)
请输入年龄:q
java.util.InputMismatchException
at java.util.Scanner.throwFor(Unknown Source)
at java.util.Scanner.next(Unknown Source)
at java.util.Scanner.nextInt(Unknown Source)
at java.util.Scanner.nextInt(Unknown Source)
at com.song.test.TryDemoOne.test(TryDemoOne.java:23)
at com.song.test.TryDemoOne.main(TryDemoOne.java:9)
注意1:可以声明异常类型Throwable,这个异常类与Exception类是匹配的
package com.song.test;import java.util.Scanner;public class TryDemoOne {public static void main(String[] args) {try {test();} catch (Throwable e) {e.printStackTrace();}}/*** 通过throws在方法声明处抛出异常类型--谁调用谁处理--调用者可以自己处理,也可以继续上抛** @throws Exception*/public static void test() throws Throwable {System.out.print("请输入年龄:");Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);int age = input.nextInt();if (age < 18 || age > 80) {throw new Exception("18岁以下,80岁以上的住客必须由亲友陪同");} else {System.out.println("欢迎入住本酒店");}}}
注意2:throws 声明的异常类型必须是抛出异常类的父类,或其本身
#以下是会出错的
package com.song.test;import java.util.Scanner;public class TryDemoOne {public static void main(String[] args) {try {test();} catch (Throwable e) {e.printStackTrace();}}/*** 通过throws在方法声明处抛出异常类型--谁调用谁处理--调用者可以自己处理,也可以继续上抛** @throws Exception*/public static void test() throws ArithmeticException {System.out.print("请输入年龄:");Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);int age = input.nextInt();if (age < 18 || age > 80) {throw new Exception("18岁以下,80岁以上的住客必须由亲友陪同");} else {System.out.println("欢迎入住本酒店");}}}
自定义异常
所谓自定义异常,就是定义一个类,去继承Throwable类或者它的子类
HotelAgeException.java
package com.song.test;public class HotelAgeException extends Exception {public HotelAgeException() {super("18岁以下,80岁以上的住客必须由亲友陪同");}}
HotelAgeException.java
package com.song.test;import java.util.Scanner;public class TryDemoOne {public static void main(String[] args) {try {test();} catch (HotelAgeException e) {System.out.println(e.getMessage());System.out.println("酒店前台工作人员不允许办理入住登记");} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}public static void test() throws HotelAgeException {System.out.print("请输入年龄:");Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);int age = input.nextInt();if (age < 18 || age > 80) {throw new HotelAgeException();} else {System.out.println("欢迎入住本酒店");}}}
请输入年龄:88
18岁以下,80岁以上的住客必须由亲友陪同
酒店前台工作人员不允许办理入住登记
请输入年龄:34
欢迎入住本酒店
请输入年龄:w
java.util.InputMismatchException
at java.util.Scanner.throwFor(Unknown Source)
at java.util.Scanner.next(Unknown Source)
at java.util.Scanner.nextInt(Unknown Source)
at java.util.Scanner.nextInt(Unknown Source)
at com.song.test.TryDemoOne.test(TryDemoOne.java:28)
at com.song.test.TryDemoOne.main(TryDemoOne.java:9)
异常链
- 有时候我们会捕获一个异常后再抛出另一个异常
- 将异常发生的原因一个传一个串起来,即把底层的异常信息传给上层,这样逐层抛出
package com.song.test;public class TryDemoOne {public static void main(String[] args) {try {testThree();} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}public static void testOne() throws HotelAgeException {throw new HotelAgeException();}public static void testTwo() throws Exception {try {testOne();} catch (HotelAgeException e) {throw new Exception("我是新产生的异常1");}}public static void testThree() throws Exception {try {testTwo();} catch (Exception e) {throw new Exception("我是新产生的异常2");}}}
java.lang.Exception: 我是新产生的异常2
at com.song.test.TryDemoOne.testThree(TryDemoOne.java:31)
at com.song.test.TryDemoOne.main(TryDemoOne.java:9)
可以看到,只有最后一个异常输出了,前两个异常被无视了。
怎么样才能把异常都输出呢?请继续往下看。
package com.song.test;public class TryDemoOne {public static void main(String[] args) {try {testThree();} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}public static void testOne() throws HotelAgeException {throw new HotelAgeException();}public static void testTwo() throws Exception {try {testOne();} catch (HotelAgeException e) {throw new Exception("我是新产生的异常1", e);}}public static void testThree() throws Exception {try {testTwo();} catch (Exception e) {Exception e1 = new Exception("我是新产生的异常2");e1.initCause(e);throw e1;}}}
java.lang.Exception: 我是新产生的异常2
at com.song.test.TryDemoOne.testThree(TryDemoOne.java:29)
at com.song.test.TryDemoOne.main(TryDemoOne.java:7)
Caused by: java.lang.Exception: 我是新产生的异常1
at com.song.test.TryDemoOne.testTwo(TryDemoOne.java:21)
at com.song.test.TryDemoOne.testThree(TryDemoOne.java:27)
… 1 more
Caused by: com.song.test.HotelAgeException: 18岁以下,80岁以上的住客必须由亲友陪同
at com.song.test.TryDemoOne.testOne(TryDemoOne.java:14)
at com.song.test.TryDemoOne.testTwo(TryDemoOne.java:19)
… 2 more

