API文档 => java.util => List,Map,Set
概念:
Java中的集合是工具类,可以存储任意数量的具有共同属性的对象
场景:
- 无法预测存储数据的数量
- 同时存储具有一对一关系的数据
- 需要进行数据的增删
- 数据重复问题
集合框架的体系结构:
Collection:类的对象,Map:键值对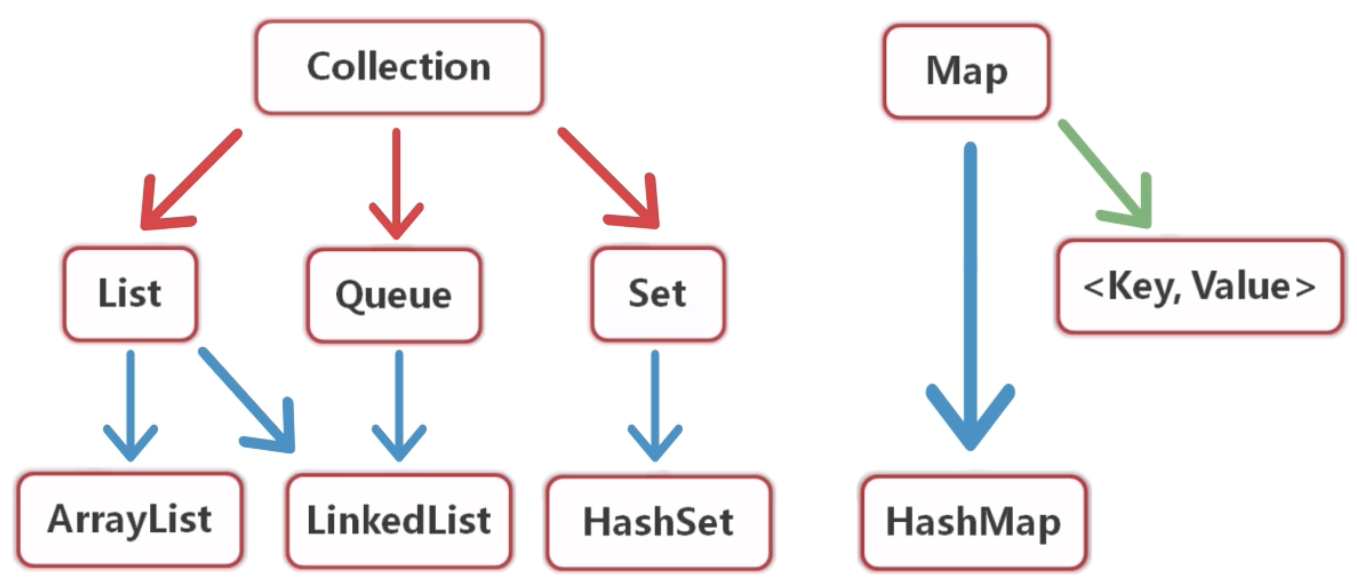
List(列表)
- List是接口
- List是元素有序并且可以重复的集合,称为序列
- List可以精确的控制每个元素的插入位置,或删除某个元素的位置
- List的两个主要实现类是ArrayList和LinkedList
ArrayList
由于ArrayList用的比较多,所以接下来主要说明ArrayLsit
- ArrayList底层由数组实现
- 动态增长,以满足应用程序的需求
- 在列表尾部插入或删除数据非常有效
- 更适合查找和更新元素
- ArrayList中的元素可以为null
在List中操作字符串
```java package com.song.test;
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List;
public class TryDemoOne {
public static void main(String[] args) {// 用ArrayList存储编程语言的名称,并输出List list = new ArrayList();list.add("Java");list.add("C");list.add("C++");list.add("Go");list.add("swift");// 输出列表中元素的个数System.out.println("列表中元素的个数为:" + list.size());// 遍历输出所有的编程语言for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {System.out.print(list.get(i) + ",");}System.out.println();// 移除列表中的C++list.remove(2);for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {System.out.print(list.get(i) + ",");}System.out.println();// 移除列表中的Golist.remove("Go");for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {System.out.print(list.get(i) + ",");}System.out.println();// 判断list中是否包含"Java"字符串System.out.println(list.contains("Java"));}
}
<a name="glXsn"></a>#### 在List中操作自定义对象Notice.java```javapackage com.song.test;import java.util.Date;public class Notice {private int id;private String title;private String creator;private Date createTime;public Notice(int id, String title, String creator, Date createTime) {super();this.id = id;this.title = title;this.creator = creator;this.createTime = createTime;}...get,set方法...}
NoticeTest.java
package com.song.test;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.Date;public class NoticeTest {public static void main(String[] args) {// 创建Notice类的对象,生成三条公告Notice notice1 = new Notice(1, "欢迎来到我的教室", "管理员", new Date());Notice notice2 = new Notice(2, "请同学们按时提交作业", "老师", new Date());Notice notice3 = new Notice(3, "考勤通知", "老师", new Date());// 添加公告ArrayList noticeList = new ArrayList();noticeList.add(notice1);noticeList.add(notice2);noticeList.add(notice3);// 显示公告for (int i = 0; i < noticeList.size(); i++) {System.out.println(i + 1 + ":" + ((Notice) noticeList.get(i)).getTitle());}// 在第一条公告后面添加一条新公告Notice notice4 = new Notice(4, "在线编辑器可以使用啦!", "管理员", new Date());noticeList.add(1, notice4);System.out.println("*********************************");for (int i = 0; i < noticeList.size(); i++) {// 注意这里需要强制类型转换为Notice类,否则无法调用getTitle()System.out.println(i + 1 + ":" + ((Notice) noticeList.get(i)).getTitle());}// 删除按时完成作业的公告noticeList.remove(2);System.out.println("*********************************");for (int i = 0; i < noticeList.size(); i++) {System.out.println(i + 1 + ":" + ((Notice) noticeList.get(i)).getTitle());}// 修改第二条公告的titlenotice4.setTitle("Java在线编辑器可以使用了");System.out.println("*********************************");for (int i = 0; i < noticeList.size(); i++) {System.out.println(i + 1 + ":" + ((Notice) noticeList.get(i)).getTitle());}}}
Set
Set是元素无序并且不可以重复的集合,称为集,Set是接口
HashSet
- HashSet是Set的一个重要实现类,称为哈希集
- HashSet的元素无序并且不可重复
- HashSet中只允许一个null元素
- 具有良好的存取和查找功能
- HashSet是在HashMap的基础上实现的
Iterator(迭代器)
- Iterator接口可以以统一的方式对各种几何元素进行遍历
- hasNext()方法检测集合中是否还有下一个元素
- next()方法返回集合中的下一个元素
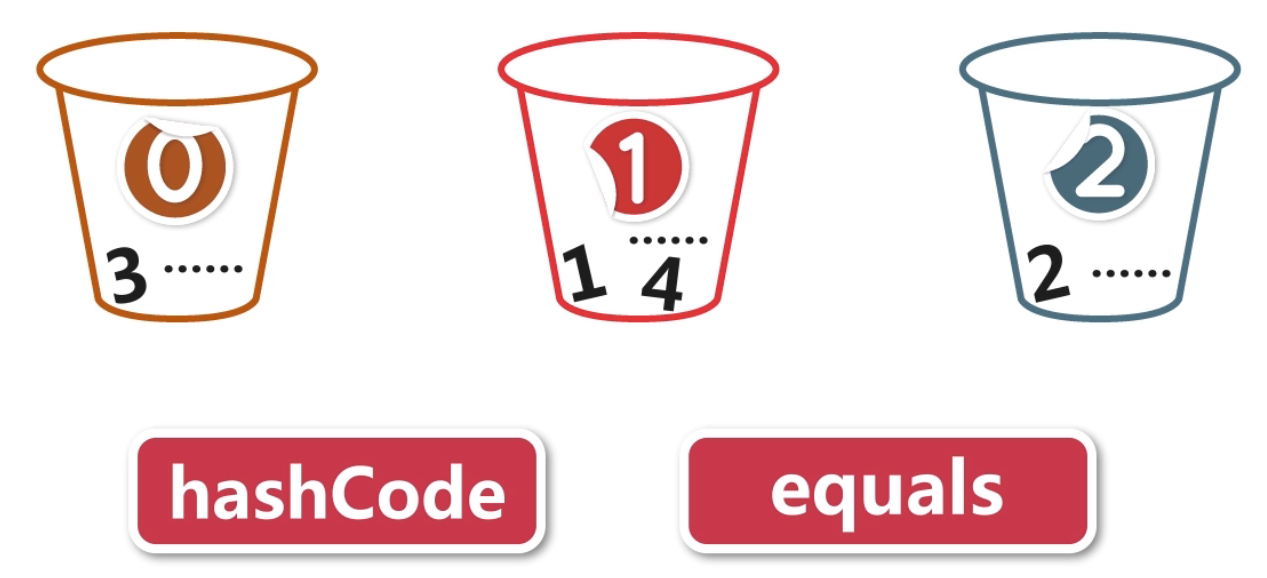
哈希表
想象一下,有一个数组,其中有100个整数。要查找其中一个元素的话,需要全部遍历一遍,这个效率是很低的。
哈希表可以解决这个问题。
具体做法:
- 在内存中开辟三个区域来存放正整数,什么数据放到哪个区域,是需要规则的,而这个规则就是HashCode
具体的HashCode如何得到,需要严格的算法,而对于简单需求,Eclipse中自动生成的HashCode就够用了
- 比如设置HashCode = n % 3,也就是说1放到第二个区域,2放到第三个区域,0放到第一个区域,依次类推
- 要查找一个整数,先判断在哪个区域,然后再在这个区域里查找,效率就会提高很多了
判断在哪个区域用的就是hashCode()方法,在这个区域里查找用的就是equals()方法
在HashSet中操作字符串
package com.song.test;import java.util.HashSet;import java.util.Iterator;import java.util.Set;public class NoticeTest {public static void main(String[] args) {Set set = new HashSet();// 向集合中添加元素set.add("blue");set.add("red");set.add("black");set.add("yellow");set.add("white");// 显示元素Iterator it = set.iterator();while (it.hasNext()) {System.out.print(it.next() + " ");}System.out.println();// 在集合中插入重复元素// 结果:不会报错,但是也不会出错set.add("red");it = set.iterator();while (it.hasNext()) {System.out.print(it.next() + " ");}}}
在HashSet中操作自定义对象
Cat.java
package com.set;public class Cat {private String name;private int month;private String species;// 构造方法public Cat(String name, int month, String species) {super();this.name = name;this.month = month;this.species = species;}// getter与setter方法...省略...// 方便显示输出自定义对象的内容@Overridepublic String toString() {return "[姓名:" + name + ", 年龄:" + month + ", 品种:" + species + "]";}// 添加自定义对象需要重写hashCode()方法和equals()方法@Overridepublic int hashCode() {final int prime = 31;int result = 1;result = prime * result + month;result = prime * result + ((name == null) ? 0 : name.hashCode());result = prime * result + ((species == null) ? 0 : species.hashCode());return result;}@Overridepublic boolean equals(Object obj) {// 判断对象是否相等,相等则返回true,不用继续比较属性了if (this == obj) {return true;}// 判断比较对象obj是否是Cat类对象if (obj.getClass() == Cat.class) {// 保存并强制类型装换比较对象Cat cat = (Cat) obj;// 只有比较对象和当前对象的所有属性都一致,才认为是相同的// 所以需要比较name,month,speciesreturn cat.getName().equals(name) && (cat.getMonth() == month) && cat.getSpecies().equals(species);}return false;}}
CatTest.java - 1
#添加,查找宠物猫信息
package com.set;import java.util.HashSet;import java.util.Iterator;import java.util.Set;public class CatTest {public static void main(String[] args) {// 定义宠物猫对象Cat huahua = new Cat("花花", 12, "英国短毛猫");Cat fanfan = new Cat("凡凡", 3, "中华田园猫");// 将宠物猫对象放入HashSet中Set set = new HashSet();set.add(huahua);set.add(fanfan);// 显示宠物猫信息Iterator it = set.iterator();while (it.hasNext()) {System.out.println(it.next()); // 自动调用toString()方法}System.out.println();// 再添加一个与花花属性一样的猫Cat huahua01 = new Cat("花花", 12, "英国短毛猫");set.add(huahua01);System.out.println("********* 添加重复数据后的宠物猫信息: **********");it = set.iterator();while (it.hasNext()) {System.out.println(it.next()); // 自动调用toString()方法}System.out.println();// 重新插入一个新宠物猫Cat huahua02 = new Cat("花花二代", 2, "英国短毛猫");set.add(huahua02);System.out.println("********* 添加花花二代后的宠物猫信息: **********");it = set.iterator();while (it.hasNext()) {System.out.println(it.next()); // 自动调用toString()方法}System.out.println();// 在集合中查找花花的信息并输出System.out.println("********* 查找花花的宠物猫信息: **********");if (set.contains(huahua)) {System.out.println("花花找到了");System.out.println(huahua);} else {System.out.println("花花没找到!");}System.out.println();// 在集合中使用名字查找花花的信息System.out.println("********* 查找名字查找花花的信息: **********");boolean flag = false;Cat c = null;it = set.iterator();while (it.hasNext()) {// next()方法返回的值是object类型的,所以需要强制类型转换// 但是这里你必须知道next()方法取出的对象类型是Cat类型// 否则,如果转换成其他类型的话,编译不会出错,但是运行的时候就会出错// 所以存在安全隐患,最好是编译的时候就提示我们出错// 解决方案请参照CatTest.java -1,使用泛型c = (Cat) it.next();if (c.getName().equals("花花")) {flag = true;break;}}if (flag) {System.out.println("花花找到了");System.out.println(c);} else {System.out.println("花花没找到");}}}
[姓名:花花, 年龄:12, 品种:英国短毛猫]
[姓名:凡凡, 年龄:3, 品种:中华田园猫]
* 添加重复数据后的宠物猫信息: **
[姓名:花花, 年龄:12, 品种:英国短毛猫]
[姓名:凡凡, 年龄:3, 品种:中华田园猫]
* 添加花花二代后的宠物猫信息: **
[姓名:花花, 年龄:12, 品种:英国短毛猫]
[姓名:凡凡, 年龄:3, 品种:中华田园猫]
[姓名:花花二代, 年龄:2, 品种:英国短毛猫]
* 查找花花的宠物猫信息: **
花花找到了
[姓名:花花, 年龄:12, 品种:英国短毛猫]
* 查找名字查找花花的信息: **
花花找到了
[姓名:花花, 年龄:12, 品种:英国短毛猫]
CatTest.java -2
#删除宠溺猫信息
package com.set;import java.util.HashSet;import java.util.Iterator;import java.util.Set;public class CatTest {public static void main(String[] args) {// 定义宠物猫对象Cat huahua = new Cat("花花", 12, "英国短毛猫");Cat fanfan = new Cat("凡凡", 3, "中华田园猫");// 将宠物猫对象放入HashSet中// <Cat>的意思是:往集合中加入的对象类型,必须是Cat类的对象,其他都不允许加入Set<Cat> set = new HashSet<Cat>();set.add(huahua);set.add(fanfan);// 显示宠物猫信息// 同理,这里<Cat>的意思是迭代器中的元素都是Cat类的对象Iterator<Cat> it = set.iterator();while (it.hasNext()) {System.out.println(it.next()); // 自动调用toString()方法}System.out.println();// 再添加一个与花花属性一样的猫Cat huahua01 = new Cat("花花", 12, "英国短毛猫");set.add(huahua01);System.out.println("********* 添加重复数据后的宠物猫信息: **********");it = set.iterator();while (it.hasNext()) {System.out.println(it.next()); // 自动调用toString()方法}System.out.println();// 重新插入一个新宠物猫Cat huahua02 = new Cat("花花二代", 2, "英国短毛猫");set.add(huahua02);System.out.println("********* 添加花花二代后的宠物猫信息: **********");it = set.iterator();while (it.hasNext()) {System.out.println(it.next()); // 自动调用toString()方法}System.out.println();// 在集合中查找花花的信息并输出System.out.println("********* 查找花花的宠物猫信息: **********");if (set.contains(huahua)) {System.out.println("花花找到了");System.out.println(huahua);} else {System.out.println("花花没找到!");}System.out.println();// 在集合中使用名字查找花花的信息System.out.println("********* 查找名字查找花花的信息: **********");boolean flag = false;Cat c = null;it = set.iterator();while (it.hasNext()) {// 由于引入泛型约束,这里不需要强制类型转换,可以直接赋值c = it.next();if (c.getName().equals("花花")) {flag = true;break;}}if (flag) {System.out.println("花花找到了");System.out.println(c);} else {System.out.println("花花没找到");}System.out.println();// 删除花花二代的信息并重新输出// 这里用到增强型for循环,意思是set中的元素依次放到cat对象中System.out.println("********* 删除花花二代的信息: **********");for (Cat cat : set) {if (cat.getName().equals("花花二代")) {set.remove(cat);}}for (Cat cat : set) {System.out.println(cat);}System.out.println();// 删除集合中所有的宠物猫信息System.out.println("********* 删除所有的宠物猫信息: **********");boolean isClear = set.removeAll(set);if(isClear) { // set.isEmpty()也是可以的System.out.println("猫都不见了。。。");}else {System.out.println("猫还在");}}}
[姓名:花花, 年龄:12, 品种:英国短毛猫]
[姓名:凡凡, 年龄:3, 品种:中华田园猫]
* 添加重复数据后的宠物猫信息: **
[姓名:花花, 年龄:12, 品种:英国短毛猫]
[姓名:凡凡, 年龄:3, 品种:中华田园猫]
* 添加花花二代后的宠物猫信息: **
[姓名:花花, 年龄:12, 品种:英国短毛猫]
[姓名:凡凡, 年龄:3, 品种:中华田园猫]
[姓名:花花二代, 年龄:2, 品种:英国短毛猫]
* 查找花花的宠物猫信息: **
花花找到了
[姓名:花花, 年龄:12, 品种:英国短毛猫]
* 查找名字查找花花的信息: **
花花找到了
[姓名:花花, 年龄:12, 品种:英国短毛猫]
* 删除花花二代的信息: **
[姓名:花花, 年龄:12, 品种:英国短毛猫]
[姓名:凡凡, 年龄:3, 品种:中华田园猫]
* 删除所有的宠物猫信息: **
猫都不见了。。。
CatTest.java -3
#删除宠物猫信息过程中可能碰到的问题
package com.set;import java.util.HashSet;import java.util.Iterator;import java.util.Set;public class CatTest {public static void main(String[] args) {// 定义宠物猫对象Cat huahua = new Cat("花花", 12, "英国短毛猫");Cat fanfan = new Cat("凡凡", 3, "中华田园猫");// 将宠物猫对象放入HashSet中// <Cat>的意思是:往集合中加入的对象类型,必须是Cat类的对象,其他都不允许加入Set<Cat> set = new HashSet<Cat>();set.add(huahua);set.add(fanfan);// 显示宠物猫信息// 同理,这里<Cat>的意思是迭代器中的元素都是Cat类的对象Iterator<Cat> it = set.iterator();while (it.hasNext()) {System.out.println(it.next()); // 自动调用toString()方法}System.out.println();// 重新插入一个新宠物猫Cat huahua02 = new Cat("花花二代", 2, "英国短毛猫");set.add(huahua02);System.out.println("********* 添加花花二代后的宠物猫信息: **********");it = set.iterator();while (it.hasNext()) {System.out.println(it.next()); // 自动调用toString()方法}System.out.println();// 删除花花的信息并重新输出// 这里删除花花的信息时会出错的// Java为了保持数据的一致性,在查找数据的过程中是不允许删除数据的// 这里找到花花的时候,查找过程还在继续,所以就出错了// System.out.println("********* 删除花花的信息: **********");// for (Cat cat : set) {// if (cat.getName().equals("花花")) {// set.remove(cat);// }// }// for (Cat cat : set) {// System.out.println(cat);// }// System.out.println();// 解决方案1:找到花花之后直接break,不再继续查找// 适合只删除一个对象的情况// System.out.println("********* 删除花花的信息: **********");// for (Cat cat : set) {// if (cat.getName().equals("花花")) {// set.remove(cat);// break;// }// }// for (Cat cat : set) {// System.out.println(cat);// }// System.out.println();// 解决方案2:使用removeAll()方法// 适合删除多个对象的情况System.out.println("********* 删除月龄小于5的宠物猫信息: **********");Set<Cat> set1 = new HashSet<Cat>();for (Cat cat : set) {if (cat.getMonth() < 5) {set1.add(cat);}}set.removeAll(set1);for (Cat cat : set) {System.out.println(cat);}System.out.println();}}
[姓名:花花, 年龄:12, 品种:英国短毛猫]
[姓名:凡凡, 年龄:3, 品种:中华田园猫]
* 添加花花二代后的宠物猫信息: **
[姓名:花花, 年龄:12, 品种:英国短毛猫]
[姓名:凡凡, 年龄:3, 品种:中华田园猫]
[姓名:花花二代, 年龄:2, 品种:英国短毛猫]
* 删除月龄小于5的宠物猫信息: **
[姓名:花花, 年龄:12, 品种:英国短毛猫]
Map
- Map中的数据是以键值对(key-value)的形式存储的
- key-value以Entry类型的对象实例存在
- 可以公共key值快速的查找value
- 一个映射不能包含重复的键
- 每个键最多只能映射到一个值
- Map是一个接口
HashMap
- 基于哈希表的Map接口的实现
- 允许使用null值和null键
- key值不允许重复
- HashMap中的Entry对象是无序排列的
案例1:字典管理
package com.set;import java.util.HashMap;import java.util.Iterator;import java.util.Map;import java.util.Map.Entry;import java.util.Scanner;import java.util.Set;public class DictionaryDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {Map<String, String> animal = new HashMap<String, String>();System.out.println("请输入三组单词对应的注释,并存放到HashMap中");Scanner console = new Scanner(System.in);// 添加数据int i = 0;while (i < 3) {System.out.println("请输入key值(单词):");String key = console.next();System.out.println("请输入value值(注释):");String value = console.next();animal.put(key, value);i++;}System.out.println();System.out.println("***********************************");// 打印输出value的值(直接使用迭代器)System.out.println("使用迭代器输出所有的value:");Iterator<String> it = animal.values().iterator();while (it.hasNext()) {System.out.print(it.next() + " ");}System.out.println();System.out.println("***********************************");// 打印输出key 和 value 的值// 通过entrySet方法System.out.println("通过entrySet方法得到key - value");// entrySet是一个集合(Set),其中的每一个元素是Entry,Entry是有键值<String,String>对构成的Set<Entry<String, String>> entrySet = animal.entrySet();for (Entry<String, String> entry : entrySet) {System.out.print(entry.getKey() + "-");System.out.println(entry.getValue());}System.out.println();System.out.println("***********************************");// 通过单词找到注释并输出// 使用keySet方法System.out.println("请输入要查找的单词:");String strSearch = console.next();// 1,取得keysetSet<String> keySet = animal.keySet();// 2,遍历keysetfor (String key : keySet) {if (key.equals(strSearch)) {System.out.println("找到了!" + "键值对为:" + key + "-" + animal.get(key));break;}}}}
案例2:商品管理
#输入异常处理,重复key处理
package com.set;import java.util.HashMap;import java.util.Iterator;import java.util.Map;import java.util.Scanner;public class GoodsTest {public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner console = new Scanner(System.in);// 定义HashMap对象Map<String, Goods> goodsMap = new HashMap<String, Goods>();int i = 0;while (i < 3) {System.out.println("请输入第" + (i + 1) + "条商品信息");System.out.println("商品编号:");String goodsId = console.next();// 判断商品编号是否已存在if (goodsMap.containsKey(goodsId)) {System.out.println("该商品编号已经存在!请重新输入!");continue;}System.out.println("商品名称:");String goodsName = console.next();System.out.println("商品价格:");double goodsPrice = 0;try {goodsPrice = console.nextDouble();} catch (Exception e) {System.out.println("商品价格的格式不正确,请输入数值型数据");console.next();continue;}// 将商品信息添加到HashMap中Goods goods = new Goods(goodsId, goodsName, goodsPrice);goodsMap.put(goodsId, goods);i++;}// 遍历Map,输出商品信息System.out.println("商品的全部信息为:");Iterator<Goods> itGoods = goodsMap.values().iterator();while (itGoods.hasNext()) {System.out.println(itGoods.next());}}}
排序
对基本数据类型进行排序
package com.sort;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.Collections;import java.util.List;public class IntSort {public static void main(String[] args) {// 对存储在List中的整型数据进行排序// List中添加的都是对象,所以泛型只能写类的名字// 由于Java中有包装器类的关系,在list中添加的时候会直接把整型封装成对象List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();list.add(5);list.add(9);list.add(3);list.add(1);System.out.println("排序前");for (int n : list) {System.out.print(n + " ");}System.out.println();// 对List中的数据进行排序Collections.sort(list);System.out.println("排序后");for (int n : list) {System.out.print(n + " ");}System.out.println();}}
排序前
5 9 3 1
排序后
1 3 5 9
对字符串类型进行排序
package com.sort;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.Collections;import java.util.List;public class StringSort {public static void main(String[] args) {// 对存放在List中的字符串进行排序List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();list.add("orange");list.add("blue");list.add("yellow");list.add("gray");System.out.println("排序前");for (String n : list) {System.out.print(n + " ");}System.out.println();// 对List中的数据进行排序Collections.sort(list);System.out.println("排序后");for (String n : list) {System.out.print(n + " ");}System.out.println();}}
排序前
orange blue yellow gray
排序后
blue gray orange yellow
Comparator接口
- 强行对某个对象进行整体排序的比较函数
- 可以将Comparator传递给sort方法(如Collecddtions.sort或Arrays.sort)
- int compare(T o1, T o2) 比较用来排序的两个参数
前提o1>o2,想要升序排序,就返回正整数
前提o1>o2,想要降序排序,就返回负整数
Cat.java
package com.sort;public class Cat {private String name;private int month;private String species;// 构造方法public Cat(String name, int month, String species) {super();this.name = name;this.month = month;this.species = species;}// getter与setter方法...// 方便显示输出自定义对象的内容@Overridepublic String toString() {return "[名字:" + name + ", 年龄:" + month + ", 品种:" + species + "]";}}
NameComparator.java
package com.sort;import java.util.Comparator;public class NameComparator implements Comparator<Cat> {@Overridepublic int compare(Cat o1, Cat o2) {// 按名字升序排序String name1 = o1.getName();String name2 = o2.getName();// return name2.compareTo(name1); // 降序return name1.compareTo(name2); // 升序}}
AgeComparator
package com.sort;import java.util.Comparator;public class AgeComparator implements Comparator<Cat> {@Overridepublic int compare(Cat o1, Cat o2) {// 按年龄降序排序int age1 = o1.getMonth();int age2 = o2.getMonth();return age2 - age1;}}
CatTest.java
package com.sort;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.Collections;import java.util.List;public class CatTest {public static void main(String[] args) {// 按名字升序排序Cat huahua = new Cat("huahua", 4, "英国短毛猫");Cat fanfan = new Cat("fanfan", 2, "中华田园猫");Cat maomao = new Cat("maomao", 3, "中华田园猫");List<Cat> catList = new ArrayList<Cat>();catList.add(huahua);catList.add(fanfan);catList.add(maomao);// 排序前System.out.println("排序前:");for (Cat cat : catList) {System.out.println(cat);}// 按名字进行升序排序Collections.sort(catList, new NameComparator());System.out.println("按名字排序后:");for (Cat cat : catList) {System.out.println(cat);}// 按年龄进行降序排序Collections.sort(catList, new AgeComparator());System.out.println("按年龄降序后:");for (Cat cat : catList) {System.out.println(cat);}}}
排序前:
[名字:huahua, 年龄:4, 品种:英国短毛猫]
[名字:fanfan, 年龄:2, 品种:中华田园猫]
[名字:maomao, 年龄:3, 品种:中华田园猫]
按名字排序后:
[名字:fanfan, 年龄:2, 品种:中华田园猫]
[名字:huahua, 年龄:4, 品种:英国短毛猫]
[名字:maomao, 年龄:3, 品种:中华田园猫]
按年龄降序后:
[名字:huahua, 年龄:4, 品种:英国短毛猫]
[名字:maomao, 年龄:3, 品种:中华田园猫]
[名字:fanfan, 年龄:2, 品种:中华田园猫]
Comparable接口
- 此接口强行对实现它的每个类的对象进行整体排序
- 这种排序被成为类的自然排序,类的 compareTo 方法被成为它的自然比较方法
- 对于集合,通过调用Collections.sort方法进行排序
- 对于数组,通过调用Array.sort()方法进行排序
- int compareTo(T o)方法
该对象小于,等于或大于指定对象,则分别返回负整数,零或正整数
Goods.java
package com.sort;public class Goods implements Comparable<Goods> {private String id;private String name;private double price;// 构造方法public Goods(String id, String name, double price) {super();this.id = id;this.name = name;this.price = price;}// getter和setter...public String toString() {return "商品编号:" + id + ",商品名称:" + name + ",商品价格:" + price;}@Overridepublic int compareTo(Goods o) {// 取出商品价格double price1 = this.getPrice();double price2 = o.getPrice();// 当price1和price2的差小于1时,返回结果为0,可以根据需求做进一步判断// 这里只是掩饰compareTo,不再追求这种细节return new Double(price2 - price1).intValue();}}
GoodsTest.java
package com.sort;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.Collections;import java.util.List;public class GoodsTest {public static void main(String[] args) {Goods g1 = new Goods("s0001", "手机", 2000);Goods g2 = new Goods("s0002", "冰箱", 5000);Goods g3 = new Goods("s0003", "电视机", 3000);List<Goods> goodsList = new ArrayList<Goods>();goodsList.add(g1);goodsList.add(g2);goodsList.add(g3);// 排序前System.out.println("排序前:");for (Goods goods : goodsList) {System.out.println(goods);}// 排序后Collections.sort(goodsList);System.out.println("排序后:");for (Goods goods : goodsList) {System.out.println(goods);}}}
排序前:
商品编号:s0001,商品名称:手机,商品价格:2000.0
商品编号:s0002,商品名称:冰箱,商品价格:5000.0
商品编号:s0003,商品名称:电视机,商品价格:3000.0
排序后:
商品编号:s0002,商品名称:冰箱,商品价格:5000.0
商品编号:s0003,商品名称:电视机,商品价格:3000.0
商品编号:s0001,商品名称:手机,商品价格:2000.0
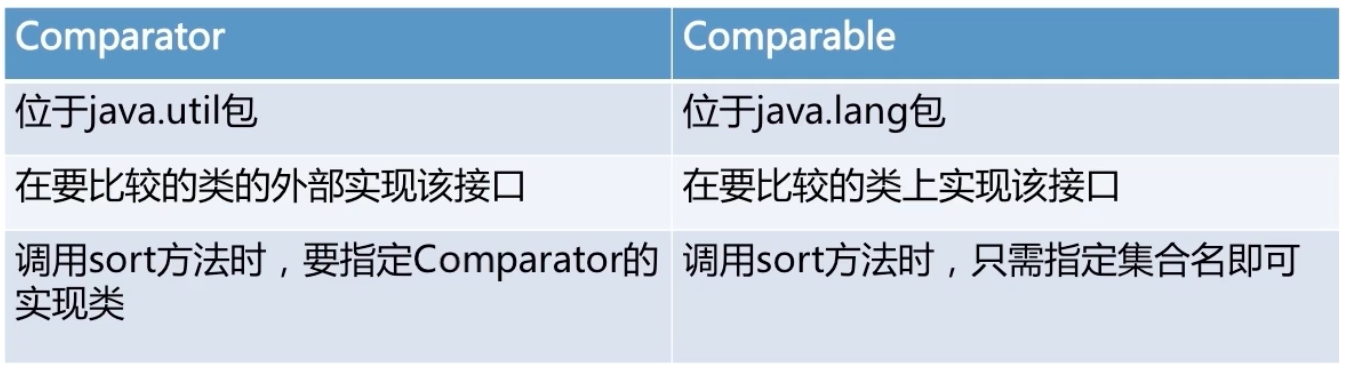
补充:Comparator可以实现多个比较方法,Comparable只能实现一个比较方法

