1. setState
setState更新状态的2种写法
(1). setState(stateChange, [callback])------对象式的setState1.stateChange为状态改变对象(该对象可以体现出状态的更改)2.callback是可选的回调函数, 它在状态更新完毕、界面也更新后(render调用后)才被调用(2). setState(updater, [callback])------函数式的setState1.updater为返回stateChange对象的函数。2.updater可以接收到state和props。3.callback是可选的回调函数, 它在状态更新、界面也更新后(render调用后)才被调用。总结:1.对象式的setState是函数式的setState的简写方式(语法糖).2.使用原则:(1).如果新状态不依赖于原状态 ===> 使用对象方式(2).如果新状态依赖于原状态 ===> 使用函数方式(3).如果需要在setState()执行后获取最新的状态数据, 要在第二个callback函数中读取.生命周期componentWillMountcomponentWillReceivePropscomponentWillUpdate现在使用会出现警告,下一个大版本需要加上UNSAFE_前缀才能使用,以后可能会被彻底废弃,不建议使用。
2. lazyLoad
路由组件的lazyLoad
// 1.通过React的lazy函数配合import()函数动态加载路由组件 ===> 路由组件代码会被分开打包const Login = React.lazy(()=>import('@/pages/Login'))// 2.通过<Suspense>指定在加载得到路由打包文件前显示一个自定义loading界面<Suspense fallback={<h1>loading.....</h1>}><Switch><Route path="/xxx" component={Xxxx}/><Redirect to="/login"/></Switch></Suspense>// 3.当前页面刷新清除路由携带的state数据this.props.history.replaceState(null,'路由地址')
集中式路由配置方式
由于react中的路由编写简单,Route会存在于很多个不同的组件当中,维护难度增加.所以很多时候我们还是需要路由config这种模式来集中式管理我们的路由.
在src根目录下创建一个router文件夹,创建route.js,定义路由配置如下:
import Discover from "../pages/Discover"import Playlist from "../pages/Discover/Playlist"import Toplist from "../pages/Discover/Toplist"import Djradio from "../pages/Discover/Djradio"import Kdp from "../pages/Discover/Djradio/kdp"import Lk from "../pages/Discover/Djradio/lk"import Mine from "../pages/Mine"const routes = [{path: "/discover",component: Discover,children: [{path: "/discover/playlist",component: Playlist},{path: "/discover/toplist",component: Toplist},{path: "/discover/djradio",component: Djradio,children: [{path: "/discover/djradio/kdp",component: Kdp},{path: "/discover/djradio/lk",component: Lk}]}]},{path: "/mine",component: Mine,}]export default routes
在router/创建compireRouter.js 用于编译Route
//这个是个高阶组件 专门负责处理路由逻辑import React, { Component } from "react"import { Route, Redirect } from "react-router-dom"class CompileRouter extends Component {constructor() {super()this.state = {C: null //用于存储通过routes编译好的Route组件的集合}}async renderContent() {//这个方法用于通过配置生成路由let { routes } = this.props;console.log(routes)let C = routes.map(async route => {//处理路由重定向let { redirect } = route;if (redirect) {return <Redirect key={route.path} to={redirect} from={route.path} />}//判断是否是异步组件try {let component = await route.component().then(value => value.default)route.component = component} catch (e) { }//Route中的render属性 和children属性差不多 Render属性可以用于渲染嵌套组件/*** @param {Object} props 路由的三大对象 location history match*/return (<Route path={route.path} exact={route.exact} key={route.path} render={(props) => {return <route.component {...props} routes={route.children} />}} />)})//由于 C得到的数组是Pomiese 所以需要一次执行 等待结果C = await Promise.all(C)//将map得到的值 设置给statethis.setState({C})}componentDidMount() {this.renderContent()}render() {/*** @param {Array} C Route的数组的集合*/let { C } = this.state;return (C)}}export default CompileRouter
React-router-dom里面的render属性讲解:可以渲染子组件 和children不同 render需要路径匹配才会渲染子组件。
3. Hooks
1. React Hook/Hooks是什么?
(1). Hook是React 16.8.0版本增加的新特性/新语法(2). 可以让你在函数组件中使用 state 以及其他的 React 特性
2. 三个常用的Hook
(1). State Hook: React.useState()(2). Effect Hook: React.useEffect()(3). Ref Hook: React.useRef()
3. State Hook
(1). State Hook让函数组件也可以有state状态, 并进行状态数据的读写操作(2). 语法: const [xxx, setXxx] = React.useState(initValue)(3). useState()说明:参数: 第一次初始化指定的值在内部作缓存返回值: 包含2个元素的数组, 第1个为内部当前状态值, 第2个为更新状态值的函数// 改变对象的写法 const [obj, setObj] = useState({name: '李雷'})// setObj({ // 一定要产生新的对象 不然视图会不更新 --- 这个容易踩坑...obj,name: '李四',age: 18, // 给对象添加的新的属性})// 改变数组的写法 const [arr, setArr] = useState([1,2,3])setArr( value => { // 接受一个函数arr.push(4)return [ ...arr ]})// const [func, setFunc] = useState(() => {return {name: '韩梅梅'} // useState内部也可以接受一个函数 必须要有一个返回值 func接受函数的返回值})(4). setXxx()2种写法:setXxx(newValue): 参数为非函数值, 直接指定新的状态值, 内部用其覆盖原来的状态值setXxx(value => newValue): 参数为函数, 接收原本的状态值, 返回新的状态值, 内部用其覆盖原来的状态值
4. Effect Hook
(1). Effect Hook 可以让你在函数组件中执行副作用操作(用于模拟类组件中的生命周期钩子)(2). React中的副作用操作:发ajax请求数据获取设置订阅 / 启动定时器手动更改真实DOM组件更新(3). 语法和说明:useEffect(() => {// 在此可以执行任何带副作用操作return () => { // 在组件卸载前执行// 在此做一些收尾工作, 比如清除定时器/取消订阅等}}, [stateValue])// 如果指定的是[], 回调函数只会在第一次render()后执行, 当里面有stateValue值的时候,当此值发生改变的时候会监听.// 第二个参数不写的时候 会监听所有的状态 -- 只要有状态更新的时候,就会触发useEffect的调用.(4). 可以把 useEffect Hook 看做如下三个函数的组合componentDidMount()componentDidUpdate()componentWillUnmount()
5. Ref Hook
(1). Ref Hook可以在函数组件中存储/查找组件内的标签或任意其它数据(2). 语法: const refContainer = useRef()(3). 作用:保存标签对象,功能与React.createRef()一样 拿到dom元素 或者dom元素的值 存取变量// 用法: import { useRef } from 'react'const inputRef = useRef(null) // 可以单独对 input button 这样的按钮进行绑定---------------------------------------------------------------------如果是想获取子组件的实列对象的话 应该怎样来进行绑定尼?forwardRef useImperativeHandle(ref, createHandle, [deps]) 搭配使用function FancyInput(props, ref) {const inputRef = useRef()useImperativeHandle(ref, () => ({focus: () => { // 此方法就是子组件向父组件向外暴露的方法. 此方法可以直接return 得到子组件定义的变量值.inputRef.current.focus()}}))return <input ref={inputRef} ... />}FancyInput = forwardRef(FancyInput)
6. useContext
import { createContext, useContext } from 'react'const MyContext = createContext()<MyContext.Provider value={123} ><Children> <Children/> // Children是子组件<MyContext.Provider>// 在子组件里面进行接受const value = useContext(MyContext)----------------------------------------------------------------------类组件的写法在子孙组件中:第一种写法:<MyContext.ConSumer>{ value => <div>{ value }</div>}</MyContext.ConSumer>第二种写法:static contextType = MyContextrender() {const value = this.context // 第二种的写法 比较简洁return (<div></div>)}
7. useMemo
1. useMemo---解决组件渲染的性能问题---用到缓存的技术shouldComponentUpdate 类似作用, 在渲染的过程中避免重复渲染的问题当状态或者父组件传来的属性发生变化时,更新组件2. useMemo()是一个函数,有两个参数,第一个参数是个函数,第二个参数是个数组。useMemo(() => {}, [默认可以不写])不写的话回调函数一定会执行默认监控所有的状态 -- 写空数组的话 回调函数不执行 -- 可以监听某个属性的状态值useMemo和Effect执行的时间不同,useEffect是在componentDidMount以后执行的,而useMemo是在组件渲染过程中执行的。let res = useMemo(() => {return { count, num }},[])
8.useCallback
作用: 避免组件的重复渲染,提高性能可以控制组件什么时候更新同样用到缓存技术,和useMemo不同的是useCallback缓存的是个函数, 是个函数就可以执行useCallback(() => {},[可以不写])// 当第二个参数是空数组的时候,只会渲染一次 后面都不会渲染// 当第二个参数不是空数组的时候 只有当依赖项改变的时候 才会进行渲染const callback = useCallback(() => {},[可以不写])callback是个函数 可以直接callback() 执行和useMemo的区别: 前者固定是一个函数, 后者固定的是一个值.
9.useReducer
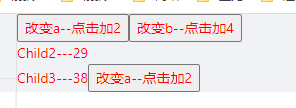
import React, { useContext, useReducer } from 'react';const reducer = (preState: any, action: any) => {const newState = { ...preState };switch (action.type) {case 'change-a':newState.a = newState.a + action.value;return newState;case 'change-b':newState.b = newState.b + action.value;return newState;default:return preState;}};const initailState = {a: 1,b: 2};const GlobalContext = React.createContext({});export default function Usereducer() {const [state, dispatch] = useReducer(reducer, initailState);return (<GlobalContext.Provider value={{ state, dispatch }}><div><Child1 /><Child2 /><Child3 /></div></GlobalContext.Provider>)}function Child1() {const { dispatch }: any = useContext(GlobalContext);return <div><button onClick={() => { dispatch({ type: 'change-a', value: 2 }) }}>改变a--点击加2</button><button onClick={() => { dispatch({ type: 'change-b', value: 4 }) }}>改变b--点击加4</button></div>}function Child2() {const { state }: any = useContext(GlobalContext);return <div>Child2---{state.a}</div>}function Child3() {const { state, dispatch }: any = useContext(GlobalContext);return <div>Child3---{state.b}<button onClick={() => { dispatch({ type: 'change-a', value: 2 }) }}>改变a--点击加2</button></div>}
4. Fragment
使用
<Fragment><Fragment><></>
作用
可以不用必须有一个真实的DOM根标签了
5. Context
理解
一种组件间通信方式, 常用于【祖组件】与【后代组件】间通信
使用
1) 创建Context容器对象:const XxxContext = React.createContext()2) 渲染子组时,外面包裹xxxContext.Provider, 通过value属性给后代组件传递数据:<xxxContext.Provider value={数据}>子组件</xxxContext.Provider>3) 后代组件读取数据://第一种方式:仅适用于类组件static contextType = xxxContext // 声明接收contextthis.context // 读取context中的value数据//第二种方式: 函数组件与类组件都可以<xxxContext.Consumer>{value => ( // value就是context中的value数据要显示的内容)}</xxxContext.Consumer>
注意
在应用开发中一般不用context, 一般都用它的封装react插件
6. 组件优化
Component的2个问题
- 只要执行setState(),即使不改变状态数据, 组件也会重新render() ==> 效率低
- 只当前组件重新render(), 就会自动重新render子组件,纵使子组件没有用到父组件的任何数据 ==> 效率低
效率高的做法
只有当组件的state或props数据发生改变时才重新render()
原因
Component中的shouldComponentUpdate()总是返回true
解决
办法1:重写shouldComponentUpdate()方法比较新旧state或props数据, 如果有变化才返回true, 如果没有返回false办法2:使用PureComponentPureComponent重写了shouldComponentUpdate(), 只有state或props数据有变化才返回true注意:只是进行state和props数据的浅比较, 如果只是数据对象内部数据变了, 返回false不要直接修改state数据, 而是要产生新数据项目中一般使用PureComponent来优化
7. render props
如何向组件内部动态传入带内容的结构(标签) ?
Vue中:使用slot技术, 也就是通过组件标签体传入结构 <A><B/></A>React中:使用children props: 通过组件标签体传入结构使用render props: 通过组件标签属性传入结构,而且可以携带数据,一般用render函数属性
children props
<A><B>xxxx</B></A>{this.props.children}问题: 如果B组件需要A组件内的数据, ==> 做不到
render props
<A render={(data) => <C data={data}></C>}></A> // 相当于传入了render函数给子组件A组件: {this.props.render(内部state数据)}C组件: 读取A组件传入的数据显示 {this.props.data}
8. 错误边界
理解:
错误边界(Error boundary):用来捕获后代组件错误,渲染出备用页面
特点:
只能捕获后代组件生命周期产生的错误,不能捕获自己组件产生的错误和其他组件在合成事件、定时器中产生的错误
使用方式:
getDerivedStateFromError配合componentDidCatch
// 生命周期函数,一旦后台组件报错,就会触发static getDerivedStateFromError(error) {console.log(error);// 在render之前触发// 返回新的statereturn {hasError: true,};}componentDidCatch(error, info) {// 统计页面的错误。发送请求发送到后台去console.log(error, info);}
9. 组件通信方式总结
组件间的关系:
- 父子组件
- 兄弟组件(非嵌套组件)
- 祖孙组件(跨级组件)
几种通信方式:
1.props:(1).children props(2).render props2.消息订阅-发布:pubs-sub、event等等3.集中式管理:redux、dva等等4.conText:生产者-消费者模式
比较好的搭配方式:
父子组件:props兄弟组件:消息订阅-发布、集中式管理祖孙组件(跨级组件):消息订阅-发布、集中式管理、conText(开发用的少,封装插件用的多)

