01_Spring的JdbcTemplate模板类
 A.Spring提供有DAO支持模板类,功能类似于Apache 的DbUtils.
A.Spring提供有DAO支持模板类,功能类似于Apache 的DbUtils. B.常用API
B.常用API
 public int update(String sql, Object… args)
public int update(String sql, Object… args)
执行DML语句.增、删、改语句
 public
public
执行DQL语句.查询单条/多条记录 C.基础实例
C.基础实例
 a.导入jar包
a.导入jar包
// 核 心 包 (4 个 )spring‐beans‐5.1.8.RELEASE.jar spring‐context‐5.1.8.RELEASE.jar spring‐core‐5.1.8.RELEASE.jar spring‐expression‐5.1.8.RELEASE.jar// 日 志 包 (1 个 )spring‐jcl‐5.1.8.RELEASE.jar//jdbc 包 (1 个 )spring‐jdbc‐5.1.8.RELEASE.jar// 事 务 包 (1 个 )spring‐tx‐5.1.8.RELEASE.jar//c3p0包(2个) c3p0‐0.9.5.4.jarmchange‐commons‐java‐0.2.16.jar//mysql 驱 动 包 (1 个 )mysql‐connector‐java‐8.0.11.jar
 b.增删改查
b.增删改查
//增删改ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = applicationContext.getBean("jdbcTemplate", JdbcTemplate.class);jdbcTemplate.update("update tb_account set username = ? where id = ?", "b", 1);//查询单条记录Account account = jdbcTemplate.query("select * from tb_account where id = ?", new ResultSetExtractor < Account > () {@Override public Account extractData(ResultSet resultSet) throws SQLException,DataAccessException {Account existAccount = null;while (resultSet.next()) {existAccount = new Account(resultSet.getInt("id"), resultSet.getString("username"), resultSet.getDoub le("money"));}return existAccount;}},1);System.out.println(account);//查询多条记录List < Account > accountList = jdbcTemplate.query("select * from tb_account", new ResultSetExtractor < List < Account >> () {@Override public List < Account > extractData(ResultSet resultSet) throws SQLException,DataAccessException {List < Account > existAccountList = new ArrayList < >();while (resultSet.next()) {Account existAccount = new Account(resultSet.getInt("id"), resultSet.getString("username"), resultSet.getDoub le("money"));existAccountList.add(existAccount);}return existAccountList;}});System.out.println(accountList);
02_使用xml声明形式开发JDBCTemplate
 前提
前提
 需要导入aop的jar包
需要导入aop的jar包
 需要导入Spring的测试jar包
需要导入Spring的测试jar包 A.在DAO中声明JDBCTemplate变量,提供set方法
A.在DAO中声明JDBCTemplate变量,提供set方法
public class UserDao {public JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;public void setJdbcTemplate(JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate) {this.jdbcTemplate = jdbcTemplate;}public List < User > addUser() {∙∙∙∙∙∙}}
 B.编写外部properties格式文件
B.编写外部properties格式文件 C.将DAO声明为Bean,为其注入JDBCTemplate
C.将DAO声明为Bean,为其注入JDBCTemplate D.声明JDBCTemplate的Bean,为其注入DataSource
D.声明JDBCTemplate的Bean,为其注入DataSource
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF‐8"?><beansxmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema‐instance"xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beanshttp://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring‐beans.xsdhttp://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring‐context.xsd"><bean id="userDao" class="com.qzw.dao.UserDao"><property name="jdbcTemplate" ref="jdbcTemplate"></property></bean><bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate"><property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property></bean><context:property‐placeholder location="classpath:c3p0.properties"></context:property‐placeholder><bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource"><property name="driverClass" value="${c3p0.driverClass}"></property><property name="jdbcUrl" value="${c3p0.jdbcUrl}"></property><property name="user" value="${c3p0.user}"></property><property name="password" value="${c3p0.password}"></property></bean></beans>
 E.代码测试
E.代码测试
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)@ContextConfiguration(locations = {"classpath:spring01.xml"})public class DaoTest {@Resource private UserDao userDao;@Test public void queryAll() {System.out.println(userDao.addUser());}}
03_Spring事务概念
 A.Spring框架处理事务的方式
A.Spring框架处理事务的方式 A,编程式事务管理(TransactionTemplate)
A,编程式事务管理(TransactionTemplate) B,声明式事务管理
B,声明式事务管理
 a,xml声明
a,xml声明
 b,注解声明
b,注解声明
04_Spring编程式事务之PlatformTransactionManager
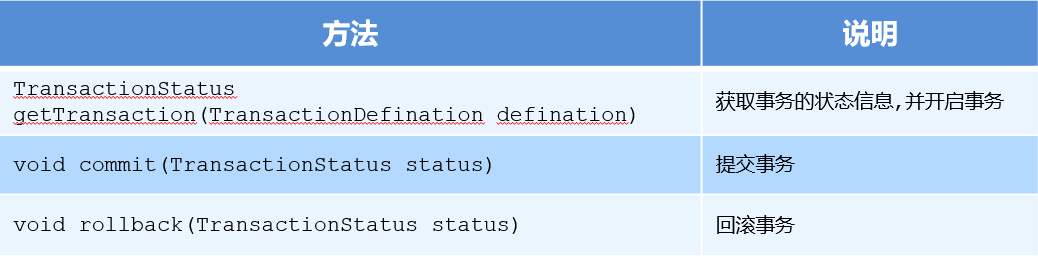
 spring 的事务管理器,提供常用的操作事务的方法
spring 的事务管理器,提供常用的操作事务的方法
 注意事项
注意事项
 PlatformTransactionManager 是接口类型,不同的 Dao 层技术则有不同的实现类
PlatformTransactionManager 是接口类型,不同的 Dao 层技术则有不同的实现类
 Dao 层技术是jdbc 或 mybatis 时:DataSourceTransactionManager
Dao 层技术是jdbc 或 mybatis 时:DataSourceTransactionManager
 Dao 层技术是hibernate时:HibernateTransactionManager
Dao 层技术是hibernate时:HibernateTransactionManager
05_Spring编程式事务之TransactionDefinition
 事务的定义信息对象,里面有如下方法
事务的定义信息对象,里面有如下方法
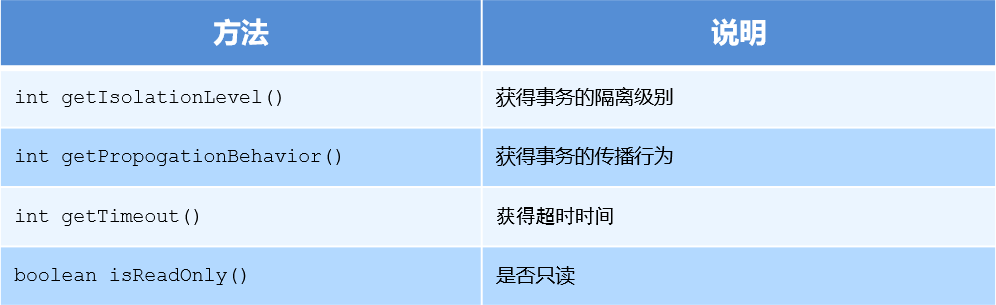
 设置事务隔离级别
设置事务隔离级别 TransactionDefinition是接口,设置操作都在DefaultTransactionDefinition类中
TransactionDefinition是接口,设置操作都在DefaultTransactionDefinition类中
ISOLATION_DEFAULT : 设置成数据库默认的隔离级别,MySQL为REPEATABLE_READ ISOLATION_READ_UNCOMMITTED : 设置为读未提交
ISOLATION_READ_COMMITTED : 设置为读已提交
ISOLATION_REPEATABLE_READ : 设置为可重复读
ISOLATION_SERIALIZABLE : 设置为串行化 设置事务传播行为
设置事务传播行为
 REQUIRED:如果当前没有事务,就新建一个事务,如果已经存在一个事务中,加入到这个事务中。一般的选择(默认值)
REQUIRED:如果当前没有事务,就新建一个事务,如果已经存在一个事务中,加入到这个事务中。一般的选择(默认值)
 SUPPORTS:支持当前事务,如果当前没有事务,就以非事务方式执行(没有事务)
SUPPORTS:支持当前事务,如果当前没有事务,就以非事务方式执行(没有事务)
 MANDATORY:使用当前的事务,如果当前没有事务,就抛出异常
MANDATORY:使用当前的事务,如果当前没有事务,就抛出异常
 REQUERS_NEW:新建事务,如果当前在事务中,把当前事务挂起。
REQUERS_NEW:新建事务,如果当前在事务中,把当前事务挂起。
 NOT_SUPPORTED:以非事务方式执行操作,如果当前存在事务,就把当前事务挂起
NOT_SUPPORTED:以非事务方式执行操作,如果当前存在事务,就把当前事务挂起
 NEVER:以非事务方式运行,如果当前存在事务,抛出异常
NEVER:以非事务方式运行,如果当前存在事务,抛出异常
 NESTED:如果当前存在事务,则在嵌套事务内执行。如果当前没有事务,则执行
NESTED:如果当前存在事务,则在嵌套事务内执行。如果当前没有事务,则执行
REQUIRED 类似的操作 超时时间:默认值是-1,没有超时限制。如果有,以秒为单位进行设置
超时时间:默认值是-1,没有超时限制。如果有,以秒为单位进行设置
是否只读:建议查询时设置为只读
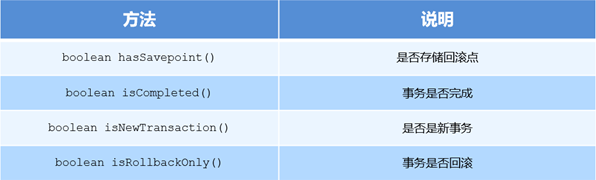
06_Spring编程式事务之TransactionStatus
07_Spring事务环境搭建
 jar包
jar包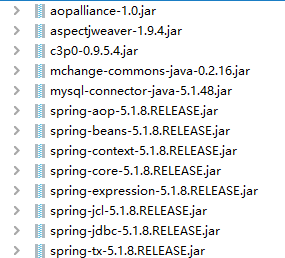
 spring.xml配置文件
spring.xml配置文件
<context:component‐scan base‐package="com.qzw"></context:component‐scan><context:property‐placeholder location="c3p0.properties"></context:property‐ placeholder><bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate"><property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property></bean><bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource"><property name="driverClass" value="${c3p0.driverClass}"></property><property name="jdbcUrl" value="${c3p0.jdbcUrl}"></property><property name="user" value="${c3p0.user}"></property><property name="password" value="${c3p0.password}"></property></bean>
 service层
service层
@Servicepublic class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {@Autowiredprivate AccountDao accoutDao;@Autowired private SelfTransactionManager selfTransactionManager;@Overridepublic void transfer(String outName, String inName, int money) {try {accoutDao.outMoney("张三", 100);int num = 1 / 0;accoutDao.inMoney("李四", 100);} catch(Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}
 dao层
dao层
@Repositorypublic class AccountDaoImpl implements AccountDao {@Autowiredprivate JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;@Overridepublic void inMoney(String inName, int money) throws Exception {jdbcTemplate.update("update tb_account set money = money + ? where username =?", money, inName);}@Overridepublic void outMoney(String outName, int money) throws Exception {jdbcTemplate.update("update tb_account set money = money ‐ ? where username =?", money, outName);}}
08_Spring编程式事务基础版
 spring.xml配置文件中,加入事务管理器: DataSourceTransactionManager
spring.xml配置文件中,加入事务管理器: DataSourceTransactionManager
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager"><property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property></bean>
 自定义事务管理器
自定义事务管理器
@Componentpublic class SelfTransactionManager {@Autowiredprivate DataSourceTransactionManager transactionManager;//手动开启事务public TransactionStatus begin() {DefaultTransactionAttribute attribute = new DefaultTransactionAttribute();TransactionStatus transactionStatus = transactionManager.getTransaction(attribute);return transactionStatus;}//开启事务public void commit(TransactionStatus transactionStatus) {transactionManager.commit(transactionStatus);}//回滚public void rollback(TransactionStatus transactionStatus) {transactionManager.rollback(transactionStatus);}}
 改造service层代码,加入事务管理
改造service层代码,加入事务管理
@Servicepublic class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {@Autowiredprivate AccountDao accoutDao;@Autowiredprivate SelfTransactionManager selfTransactionManager;@Overridepublic void transfer(String outName, String inName, int money) {TransactionStatus status = selfTransactionManager.begin();try {accoutDao.outMoney("张三", 100);int num = 1 / 0;accoutDao.inMoney("李四", 100);} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();selfTransactionManager.rollback(status);}selfTransactionManager.commit(status);}}
09_Spring编程式事务优化版
 在基础版中,如果需要事务管理的业务方法较多,那么就需要考虑将事务管理抽取成一个公 共的环绕通知,这样就只需要维护一处事务管理通知了!
在基础版中,如果需要事务管理的业务方法较多,那么就需要考虑将事务管理抽取成一个公 共的环绕通知,这样就只需要维护一处事务管理通知了!
 自定义事务通知类TxAdvice
自定义事务通知类TxAdvice
public class TxAdvice {@Resourceprivate SelfTransactionManager selfTransactionManager;public void txAround(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) {System.out.println("txAround");TransactionStatus status = selfTransactionManager.begin();try {pjp.proceed();} catch (Throwable throwable) {throwable.printStackTrace();selfTransactionManager.rollback(status);}selfTransactionManager.commit(status);}}
 配置环绕通知
配置环绕通知
.......<aop:config><aop:aspect ref="txAdvice"><aop:around method="txAround" pointcut="execution(* *..*Service.*(..))"></aop:around></aop:aspect></aop:config><bean id="txAdvice" class="com.qzw.tx.TxAdvice"></bean>
 service层代码
service层代码
 注意service层的异常不能使用try方式捕获,要抛出.这样,环绕通知才能截获到发生的异常进行处理!!!
注意service层的异常不能使用try方式捕获,要抛出.这样,环绕通知才能截获到发生的异常进行处理!!!
@Servicepublic class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {@Autowiredprivate AccountDao accoutDao;@Overridepublic void transfer(String outName, String inName, int money)throws Exception {accoutDao.outMoney("张三", 100);int num = 1 / 0;accoutDao.inMoney("李四", 100);}}
10_声明式事务概念及入门
 A.思路分析:
A.思路分析:
 将编程式事务中的通用代码抽取出来,制作成独立的around通知使用AOP工作原理,将事务管理的代码动态织入到原始方法中。由于该功能使用量较大,Spring已经将该通知制作完毕。
将编程式事务中的通用代码抽取出来,制作成独立的around通知使用AOP工作原理,将事务管理的代码动态织入到原始方法中。由于该功能使用量较大,Spring已经将该通知制作完毕。 B.开发步骤:
B.开发步骤:
 a.开启事务tx命名空间
a.开启事务tx命名空间
 b.配置事务通知
b.配置事务通知
 c.将事务通知配置到切入点
c.将事务通知配置到切入点
<!‐‐配置事务通知id:事务通知唯一标识transaction‐manager:事务管理类‐‐><tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction‐manager="transactionManager"><tx:attributes><tx:method name="transfer"/></tx:attributes></tx:advice><!‐‐将事务通知配置到切入点‐‐><aop:config><!‐‐配置事务切面‐‐><aop:advisor advice‐ref="txAdvice" pointcut="execution(* *..*Service.*(..))"></aop:advisor></aop:config>
11_声明式事务属性说明
 read-only: 设置是否只读.增删改为false,查询为true
read-only: 设置是否只读.增删改为false,查询为true propagation: 设置事务传播
propagation: 设置事务传播 isolation: 设置隔离级别
isolation: 设置隔离级别
<tx:advice transaction‐manager="transactionManager" id="txAdvice"><tx:attributes ><tx:method name="transfer" read‐only="false" propagation="REQUIRED" isolation="REPEATABLE_READ" /><tx:method name="add*" read‐only="false" propagation="REQUIRED" isolation="DEFAULT"></tx:method><tx:method name="update*" read‐only="false" propagation="REQUIRED" isolation="DEFAULT"></tx:method><tx:method name="delete*" read‐only="false" propagation="REQUIRED" isolation="DEFAULT"></tx:method><tx:method name="select*" read‐only="true" propagation="REQUIRED" isolation="DEFAULT"></tx:method></tx:attributes></tx:advice>
12,注解式事务
 A.步骤
A.步骤
 a.在配置文件中,开启注解式事务,为其指定事务管理器
a.在配置文件中,开启注解式事务,为其指定事务管理器
<tx:annotation‐driven transaction‐manager="transactionManager"></tx:annotation‐ driven>
 b.对要添加事务的类、接口、方法上方声明@Transactional
b.对要添加事务的类、接口、方法上方声明@Transactional
@Servicepublic class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {@Autowiredprivate AccountDao accoutDao;@Transactional(readOnly = false, isolation = Isolation.DEFAULT, propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)@Overridepublic void transfer(String outName, String inName, int money)throws Exception {accoutDao.outMoney("张三", 100);int num = 1 / 0;accoutDao.inMoney("李四", 100);}}