反射
反射概述
JAVA反射机制是在运行状态中,对于任意一个类,都能知道这个类的所有属性和方法;对于任意一个对象,都能够调用它的任意一个方法和属性;这种动态获取的信息以及动态调用对象的方法的功能称为JAVA的反射机制。
实际上,我们创建的每一个类也都是对象,即类本身是java.lang.Class类的实例对象。这个实例对象称之为类对象,也就是Class对象。
Class对象特点
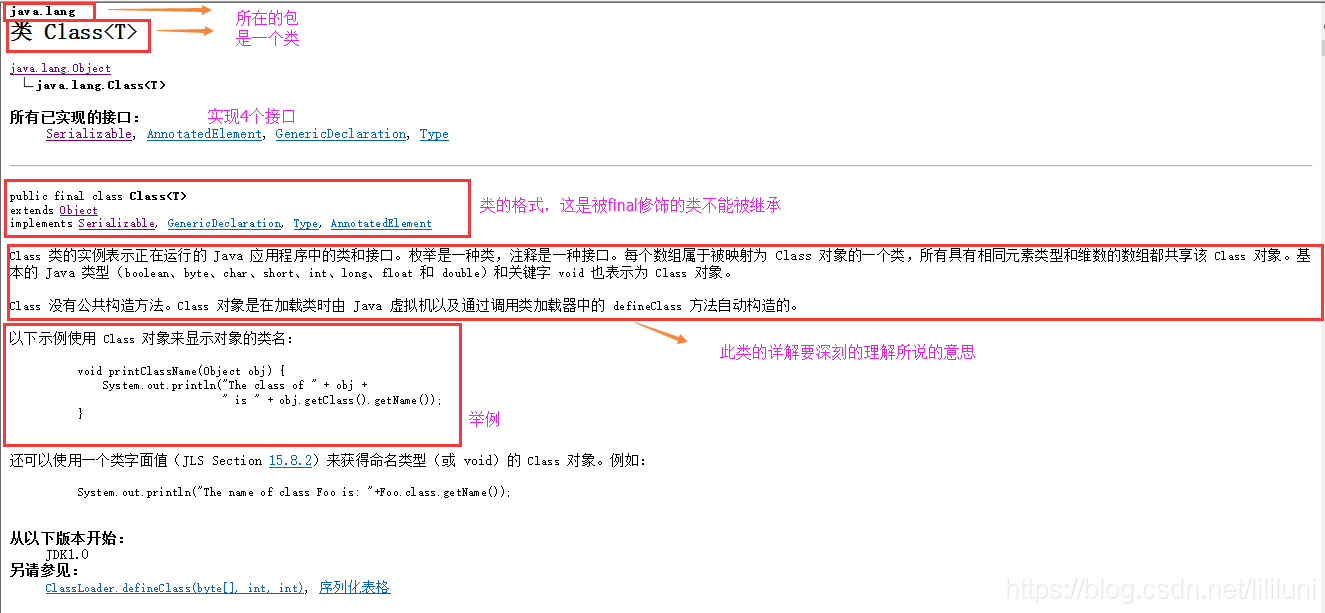
从图中可以得出以下几点:
- Class 类的实例对象表示正在运行的 Java 应用程序中的类和接口。也就是jvm中有很多的实例,每个类都有唯一的Class对象。
- Class 类没有公共构造方法。Class 对象是在加载类时由 Java 虚拟机自动构造的。也就是说我们不需要创建,JVM已经帮我们创建了。
- Class 对象用于提供类本身的信息,比如有几种构造方法, 有多少属性,有哪些普通方法
反射的使用
初步使用
先创建一个类
import org.junit.Test;import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;import java.lang.reflect.Field;import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;import java.lang.reflect.Method;public class Person {private String name;private int age;public Person() {}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Person{" +"name='" + name + '\'' +", age=" + age +'}';}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public int getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(int age) {this.age = age;}public Person(String name, int age) {this.name = name;this.age = age;}public void show(){System.out.println("你好,我是一个人");}public void showNation(){System.out.println("我的国际是");}}
通过反射创建对应的运行时类的对象
import org.junit.Test;import java.util.Random;/*通过反射创建对应的运行时类的对象*/public class NewInstanceTest {@Testpublic void test1() throws IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException {Class<Person> clazz = Person.class;/*newInstance():调用此方法,创建对应的运行时类的对象,内部调用了运行时类的空参构造器*/Person obj = clazz.newInstance();System.out.println(obj);}@SuppressWarnings("SwitchStatementWithoutDefaultBranch")@Testpublic void test2(){int num=new Random().nextInt(3);String classPath="";switch (num){case 0:classPath="java.util.Date";break;case 1:classPath="java.sql.Date";break;case 2:classPath="Person";break;}try {Object obj = getInstance(classPath);System.out.println(obj);} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (InstantiationException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}/*创建一个指定类的对象。classpath:指定类的全类名*/public Object getInstance(String classpath) throws ClassNotFoundException, IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException {Class<?> clazz = Class.forName(classpath);return clazz.newInstance();}}
import org.junit.Test;import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;import java.lang.reflect.Field;import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;import java.lang.reflect.Method;public class ReflectionTest {//反射之前对于Person的操作@Testpublic void test1(){//1、创建Person类的对象Person tom = new Person("Tom", 12);//通过对象,调用其内部的属性、方法tom.setAge(10);System.out.println(tom.toString());tom.show();//再Person类外部,不可以通过Person类的对象调用其内部私有结构。//比如:name,showNation()以及私有的构造器}//反射之后对于Person的操作@Testpublic void test2() throws NoSuchMethodException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException, NoSuchFieldException {Class clazz= Person.class;//1、通过反射来创建Person类的对象Constructor cons=clazz.getConstructor(String.class,int.class);Object obj=cons.newInstance("Tom",12);Person p=(Person)obj;System.out.println(p.toString());//2、通过反射,调用对象指定的属性、方法//调用属性Field age = clazz.getDeclaredField("age");//反射的那个类中构造方法被private权限修饰符修饰了//private修饰的成员(变量和方法)语法上只能在本类中进行访问,// 但是也有例外,如果使用的是反射技术,可以通过setAccessible(true)进行暴力访问。age.setAccessible(true);age.set(p,10);System.out.println(p.toString());//调用方法Method shows = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("show");shows.invoke(p);}//获取class的实例的方式@Testpublic void test3() throws ClassNotFoundException {//方式一、调用运行时类的属性:.classClass clazz1 = Person.class;System.out.println(clazz1);//方式二:通过运行时类的对象,调用getClass()Person p1 = new Person();Class clazz2 = p1.getClass();System.out.println(clazz2);//方式三:调用class的静态方法:forName(String classPath)Class clazz3 = Class.forName("Person");System.out.println(clazz3);}}
反射的进一步使用
首先创建一个接口:
package java1;public interface MyInterface {void info();}
创建一个注解package java1;import java.lang.annotation.Retention;import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;import java.lang.annotation.Target;import static java.lang.annotation.ElementType.*;@Target({TYPE,FIELD,METHOD,PARAMETER,CONSTRUCTOR,LOCAL_VARIABLE})@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)public @interface MyAnnotation {String value() default "hello";}
再创建一个父类:
package java1;import java.io.Serializable;public class Creature<T> implements Serializable {private char gender;public double weight;private void breath(){System.out.println("生物呼吸");}private void eat(){System.out.println("生物吃东西");}}
再创建一个Person类实现接口和继承父类:
package java1;@MyAnnotation(value = "hi")public class Person extends Creature<String> implements Comparable<String>,MyInterface{private String name;int age;public int id;public Person(){}@MyAnnotation(value = "abc")private Person(String name){this.name=name;}Person(String name,int age){this.name=name;this.age=age;}@MyAnnotation(value = "Chinese")private String show(String nation){System.out.println("我的国籍是:"+nation);return nation;}public String display(String interest){return interest;}@Overridepublic void info(){System.out.println("我是一个人");}@Overridepublic int compareTo(String o) {return 0;}}
首先是获取当前运行时类的属性结构:
package java2;import java1.Person;import org.junit.Test;import java.lang.reflect.AnnotatedType;import java.lang.reflect.Field;/** 获取当前运行时类的属性结构* */public class FiledTest {@Testpublic void test1(){Class<Person> clazz = Person.class;//获取属性结构//getFields():获取当前运行时类及其父类中声明为public访问权限的属性Field[] fields = clazz.getFields();for (Field field : fields) {System.out.println(field);}//getDeclaredFields():获取当前运行时类中声明的所有属性。(不包含父类中的属性)Field[] declaredFields = clazz.getDeclaredFields();for (Field declaredField : declaredFields) {System.out.println(declaredField);}}@Testpublic void test2(){Class<Person> clazz = Person.class;Field[] declaredFields = clazz.getDeclaredFields();for (Field f : declaredFields) {//1、权限修饰符int modifiers = f.getModifiers();System.out.println(modifiers);//2、数据类型AnnotatedType annotatedType = f.getAnnotatedType();System.out.println(annotatedType);//3、变量名String name = f.getName();System.out.println(name);}}}
获取运行时类的方法结构:
package java2;import java1.Person;import org.junit.Test;import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;import java.lang.reflect.Method;import java.lang.reflect.Modifier;/*获取运行时类的方法结构*/public class MethodTest {@Testpublic void test1(){Class<Person> clazz = Person.class;//getMethods():获取当前运行时类及其所有父类中声明为public权限的方法。Method[] methods = clazz.getMethods();for (Method method : methods) {System.out.println(method);}System.out.println();//getDeclaredMethods():获取当前运行时类中声明的所有方法。不包含父类中声明的方法。Method[] declaredMethods = clazz.getDeclaredMethods();for (Method declaredMethod : declaredMethods) {System.out.println(declaredMethod);}}@Testpublic void test2(){Class<Person> clazz = Person.class;Method[] declaredMethods = clazz.getDeclaredMethods();for (Method declaredMethod : declaredMethods) {//1、获取方法声明中的注解Annotation[] annos = declaredMethod.getAnnotations();for (Annotation anno : annos) {System.out.println(anno);}//2、权限修饰符System.out.print(Modifier.toString(declaredMethod.getModifiers())+"\t");//3、返回值类型System.out.print(declaredMethod.getReturnType()+"\t");//4、方法名System.out.println(declaredMethod.getName()+"\t");System.out.println();}}}
其他:
package java2;import java1.Person;import org.junit.Test;import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;public class OtherTest {/*获取构造器结构*/@Testpublic void test1(){Class<Person> clazz = Person.class;//getConstructors():当前运行时类中声明为public的构造器Constructor<?>[] constructors = clazz.getConstructors();for (Constructor<?> c : constructors) {System.out.println(c);}Constructor<?>[] declaredConstructors = clazz.getDeclaredConstructors();for (Constructor<?> d : declaredConstructors) {System.out.println(d);}}/*获取运行时类的父类*/@Testpublic void test2(){Class<Person> clazz = Person.class;Class<? super Person> superclass = clazz.getSuperclass();System.out.println(superclass);}/*获取运行时类的接口*/@Testpublic void test3(){Class<Person> clazz = Person.class;Class<?>[] interfaces = clazz.getInterfaces();for (Class<?> anInterface : interfaces) {System.out.println(anInterface);}}/*获取运行时类的包*/@Testpublic void test4(){Class<Person> personClass = Person.class;Package aPackage = personClass.getPackage();System.out.println(aPackage);}}
调用运行时类中指定的结构:属性、方法、构造器:
package java2;import java1.Person;import org.junit.Test;import java.lang.reflect.Field;import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;import java.lang.reflect.Method;/*调用运行时类中指定的结构:属性、方法、构造器*/public class ReflectionTest {@Testpublic void test1() throws Exception {Class<Person> clazz = Person.class;//创建运行时类的对象Person p = (Person) clazz.newInstance();//获取指定的属性Field id = clazz.getField("id");/*设置当前属性的值set():参数1:指明设置哪个对象的属性 参数2:将此属性值设置为多少*/id.set(p,1001);/*获取当前属性的值get():参数1:获取哪个对象的当前属性值*/int pID= (int) id.get(p);System.out.println(pID);}/*如何操作运行时类中的指定的属性*/@Testpublic void test2() throws IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException, NoSuchFieldException {Class<Person> clazz = Person.class;Person p = clazz.newInstance();//getDeclaredField("name"):获取运行时类中指定变量名的属性Field name = clazz.getDeclaredField("name");//保证当前属性是可访问的name.setAccessible(true);//获取,设置指定对象的属性值name.set(p,"Tom");System.out.println(name.get(p));}/*如何操作运行时类中的指定方法*/@Testpublic void test3() throws Exception {Class<Person> clazz = Person.class;//创建运行时类的对象Person p = clazz.newInstance();/*获取指定的方法getDeclaredMethod("show", String.class):参数1:指明获取的方法名称 参数2:指明获取的方法的形参列表,可变形参*/Method show = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("show", String.class);show.setAccessible(true);/*调用方法的invoke():参数1:方法的调用者 参数2:给方法形参赋值的实参*/show.invoke(p,"CHN");}}

