libevent 的基本操作单元是事件。每个事件代表一组条件的集合,这些条件包括:
- 文件描述符已经就绪,可以读取或者写入
- 文件描述符变为就绪状态,可以读取或者写入(仅对于边沿触发 IO)
- 超时事件
- 发生某信号
- 用户触发事件
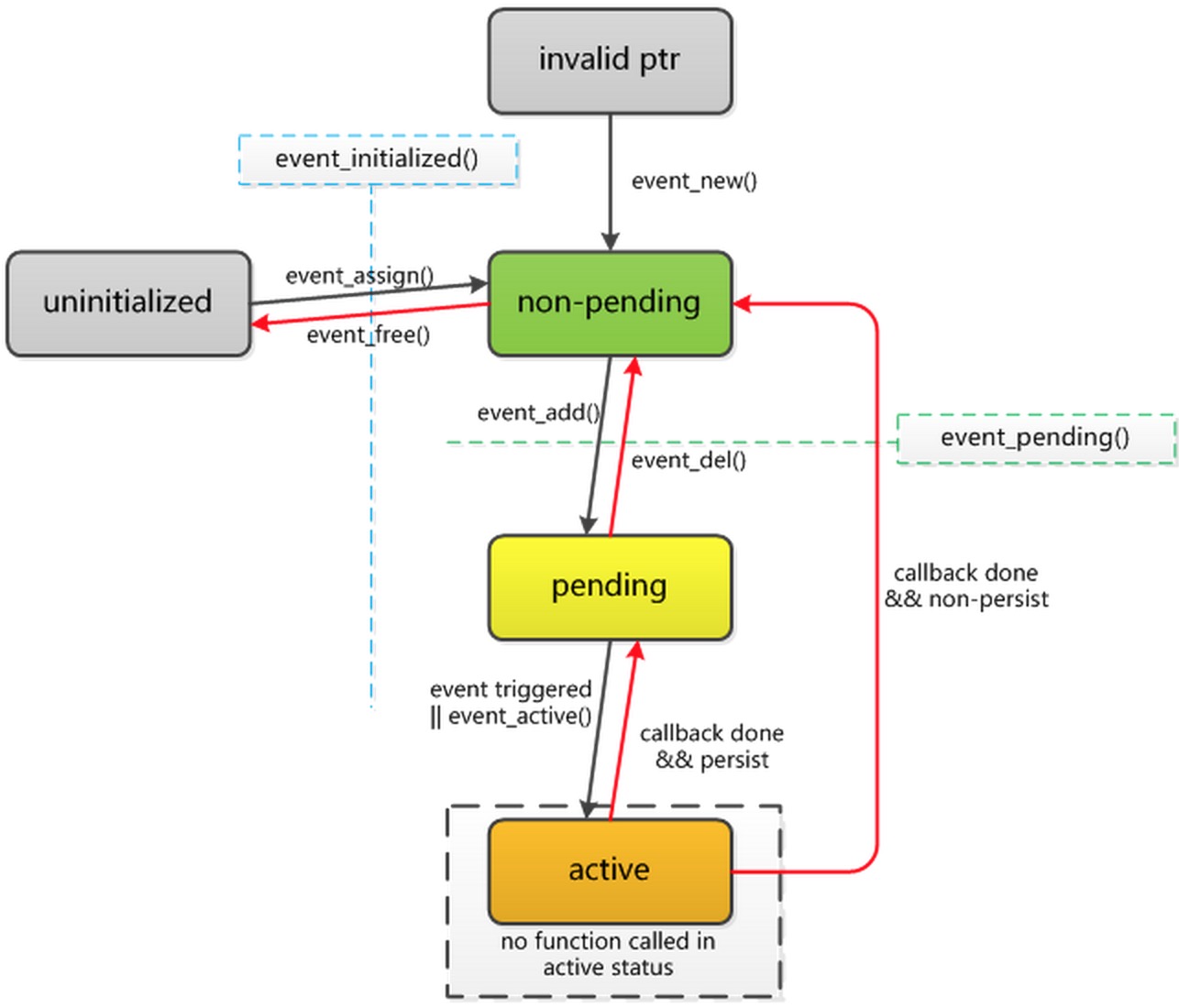
所有事件具有相似的生命周期。调用 libevent 函数设置事件并且关联到 event_base 之后, 事件进入“已初始化(initialized)”状态。此时可以将事件添加到 event_base 中,这使之进入“未决(pending)”状态。在未决状态下,如果触发事件的条件发生(比如说,文件描述 符的状态改变,或者超时时间到达 ),则事件进入“激活(active)”状态,(用户提供的)事件回调函数将被执行。如果配置为“持久的(persistent)”,事件将保持为未决状态。否则, 执行完回调后,事件不再是未决的。删除操作可以让未决事件成为非未决(已初始化)的 ; 添加操作可以让非未决事件再次成为未决的。
6.1 创建事件
6.1.1 生成新事件
使用 event_new()接口创建事件。
#define EV_TIMEOUT 0x01#define EV_READ 0x02#define EV_WRITE 0x04#define EV_SIGNAL 0x08#define EV_PERSIST 0x10#define EV_ET 0x20typedef void (*event_callback_fn)(evutil_socket_t, short, void *);struct event *event_new(struct event_base *base, evutil_socket_t fd,short what, event_callback_fn cb,void *arg);void event_free(struct event *event);
event_new()试图分配和构造一个用于 base 的新的事件。what 参数是上述标志的集合。
如果 fd 非负,则它是将被观察其读写事件的文件。事件被激活时, libevent 将调用 cb 函数,传递这些参数:文件描述符 fd,表示所有被触发事件的位字段 ,以及构造事件时的 arg 参数。发生内部错误,或者传入无效参数时, event_new()将返回 NULL。
所有新创建的事件都处于已初始化和非未决状态 ,调用 event_add()可以使其成为未决的。
要释放事件,调用 event_free()。对未决或者激活状态的事件调用 event_free()是安全 的:在释放事件之前,函数将会使事件成为非激活和非未决的。
实例
#include <event2/event.h>void cb_func(evutil_socket_t fd, short what, void *arg){const char *data = arg;printf("Got an event on socket %d:%s%s%s%s [%s]",(int) fd,(what&EV_TIMEOUT) ? " timeout" : "",(what&EV_READ) ? " read" : "",(what&EV_WRITE) ? " write" : "",(what&EV_SIGNAL) ? " signal" : "",data);}void main_loop(evutil_socket_t fd1, evutil_socket_t fd2){struct event *ev1, *ev2;struct timeval five_seconds = {5,0};struct event_base *base = event_base_new();/* The caller has already set up fd1, fd2 somehow, and make themnonblocking. */ev1 = event_new(base, fd1, EV_TIMEOUT|EV_READ|EV_PERSIST, cb_func,(char*)"Reading event");ev2 = event_new(base, fd2, EV_WRITE|EV_PERSIST, cb_func,(char*)"Writing event");event_add(ev1, &five_seconds);event_add(ev2, NULL);event_base_dispatch(base);}
上述函数定义在
6.1.2 事件标志
- EV_TIMEOUT
这个标志表示某超时时间流逝后事件成为激活的。构造事件的时候,EV_TIMEOUT 标志是 被忽略的:可以在添加事件的时候设置超时 ,也可以不设置。超时发生时,回调函数的 what 参数将带有这个标志。
- EV_READ
表示指定的文件描述符已经就绪,可以读取的时候,事件将成为激活的。
- EV_WRITE
表示指定的文件描述符已经就绪,可以写入的时候,事件将成为激活的。
- EV_SIGNAL
用于实现信号检测,请看下面的 “构造信号事件”节。 - EV_PERSIST
表示事件是“持久的”,请看下面的“关于事件持久性”节。 - EV_ET
表示如果底层的 event_base 后端支持边沿触发事件,则事件应该是边沿触发的。这个标志 影响 EV_READ 和 EV_WRITE 的语义。
从2.0.1-alpha 版本开始,可以有任意多个事件因为同样的条件而未决。比如说,可以有两 个事件因为某个给定的 fd 已经就绪,可以读取而成为激活的。这种情况下,多个事件回调 被执行的次序是不确定的。
这些标志定义在
中。除了 EV_ET 在2.0.1-alpha 版本中引入外,所有标志 从1.0版本开始就存在了。
6.1.3 关于事件持久性
默认情况下,每当未决事件成为激活的(因为 fd 已经准备好读取或者写入,或者因为超时), 事件将在其回调被执行前成为非未决的。如果想让事件再次成为未决的 ,可以在回调函数中 再次对其调用 event_add()。
然而,如果设置了 EV_PERSIST 标志,事件就是持久的。这意味着即使其回调被激活 ,事件还是会保持为未决状态 。如果想在回调中让事件成为非未决的 ,可以对其调用 event_del ()。
每次执行事件回调的时候,持久事件的超时值会被复位。因此,如果具有 EV_READ|EV_PERSIST 标志,以及5秒的超时值,则事件将在以下情况下成为激活的:
- 套接字已经准备好被读取的时候
- 从最后一次成为激活的开始,已经逝去 5秒
6.1.4 信号事件
libevent 也可以监测 POSIX 风格的信号。要构造信号处理器,使用:
#define evsignal_new(base, signum, cb, arg) \event_new(base, signum, EV_SIGNAL|EV_PERSIST, cb, arg)
除了提供一个信号编号代替文件描述符之外,各个参数与 event_new()相同。
实例
struct event *hup_event;struct event_base *base = event_base_new();/* call sighup_function on a HUP signal */hup_event = evsignal_new(base, SIGHUP, sighup_function, NULL);
注意 :信号回调是信号发生后在事件循环中被执行的,所以可以安全地调用通常不能 在 POSIX 风格信号处理器中使用的函数。
**警告**:不要在信号事件上设置超时,这可能是不被支持的。 [待修正:真是这样的吗?]
libevent 也提供了一组方便使用的宏用于处理信号事件:
#define evsignal_add(ev, tv) \event_add((ev),(tv))#define evsignal_del(ev) \event_del(ev)#define evsignal_pending(ev, what, tv_out) \event_pending((ev), (what), (tv_out))
evsignal_*宏从2.0.1-alpha 版本开始存在。先前版本中这些宏叫做 signal_add()、signal_del ()等等。
关于信号的警告
在当前版本的 libevent 和大多数后端中,每个进程任何时刻只能有一个 event_base 可以监 听信号。如果同时向两个 event_base 添加信号事件,即使是不同的信号,也只有一 个 event_base 可以取得信号。
kqueue 后端没有这个限制。
6.2 事件的未决和非未决
构造事件之后,在将其添加到 event_base 之前实际上是不能对其做任何操作的。使用event_add()将事件添加到 event_base。
6.2.1 设置未决事件
int event_add(struct event *ev, const struct timeval *tv);
在非未决的事件上调用 event_add()将使其在配置的 event_base 中成为未决的。成功时 函数返回0,失败时返回-1。
如果 tv 为 NULL,添加的事件不会超时。否则, tv 以秒和微秒指定超时值。
如果对已经未决的事件调用 event_add(),事件将保持未决状态,并在指定的超时时间被重新调度。
注意:不要设置 tv 为希望超时事件执行的时间。如果在 2010 年 1 月 1 日设置 “tv->tv_sec=time(NULL)+10;”,超时事件将会等待40年,而不是10秒。
6.2.2 设置非未决事件
int event_del(struct event *ev);
对已经初始化的事件调用 event_del()将使其成为非未决和非激活的。如果事件不是未决的或者激活的,调用将没有效果。成功时函数返回 0,失败时返回-1。
注意:如果在事件激活后,其回调被执行前删除事件,回调将不会执行。
这些函数定义在
6.3 事件的优先级
多个事件同时触发时,libevent 没有定义各个回调的执行次序。可以使用优先级来定义某些事件比其他事件更重要。
在前一章讨论过,每个 event_base 有与之相关的一个或者多个优先级。在初始化事件之后, 但是在添加到 event_base 之前,可以为其设置优先级。
int event_priority_set(struct event *event, int priority);
事件的优先级是一个在 0和 event_base 的优先级减去1之间的数值。成功时函数返回 0,失 败时返回-1。
多个不同优先级的事件同时成为激活的时候 ,低优先级的事件不会运行 。libevent 会执行高优先级的事件,然后重新检查各个事件。只有在没有高优先级的事件是激活的时候 ,低优先级的事件才会运行。
实例:
#include <event2/event.h>void read_cb(evutil_socket_t, short, void *);void write_cb(evutil_socket_t, short, void *);void main_loop(evutil_socket_t fd){struct event *important, *unimportant;struct event_base *base;base = event_base_new();event_base_priority_init(base, 2);/* Now base has priority 0, and priority 1 */important = event_new(base, fd, EV_WRITE|EV_PERSIST, write_cb, NULL);unimportant = event_new(base, fd, EV_READ|EV_PERSIST, read_cb, NULL);event_priority_set(important, 0);event_priority_set(unimportant, 1);/* Now, whenever the fd is ready for writing, the write callback willhappen before the read callback. The read callback won't happen atall until the write callback is no longer active. */}
如果不为事件设置优先级,则默认的优先级将会是 event_base 的优先级数目除以2。
6.4 检查事件状态
有时候需要了解事件是否已经添加,检查事件代表什么。
int event_pending(const struct event *ev, short what, struct timeval *tv_out);#define event_get_signal(ev) /* ... */evutil_socket_t event_get_fd(const struct event *ev);struct event_base *event_get_base(const struct event *ev);short event_get_events(const struct event *ev);event_callback_fn event_get_callback(const struct event *ev);void *event_get_callback_arg(const struct event *ev);int event_get_priority(const struct event *ev);void event_get_assignment(const struct event *event,struct event_base **base_out,evutil_socket_t *fd_out,short *events_out,event_callback_fn *callback_out,void **arg_out);
event_pending()函数确定给定的事件是否是未决的或者激活的。如果是,而且 what 参 数设置了 EV_READ、EV_WRITE、EV_SIGNAL 或者 EV_TIMEOUT 等标志,则函数会返回事件当前为之未决或者激活的所有标志 。如果提供了 tv_out 参数,并且 what 参数中设置了 EV_TIMEOUT 标志,而事件当前正因超时事件而未决或者激活,则 tv_out 会返回事件 的超时值。
event_get_fd()和 event_get_signal()返回为事件配置的文件描述符或者信号值。 event_get_base()返回为事件配置的 event_base。event_get_events()返回事件的标志(EV_READ、EV_WRITE 等)。event_get_callback()和 event_get_callback_arg() 返回事件的回调函数及其参数指针。
event_get_assignment()复制所有为事件分配的字段到提供的指针中。任何为 NULL 的参数会被忽略。
实例
#include <event2/event.h>#include <stdio.h>/* Change the callback and callback_arg of 'ev', which must not be* pending. */int replace_callback(struct event *ev, event_callback_fn new_callback,void *new_callback_arg){struct event_base *base;evutil_socket_t fd;short events;int pending;pending = event_pending(ev, EV_READ|EV_WRITE|EV_SIGNAL|EV_TIMEOUT,NULL);if (pending) {/* We want to catch this here so that we do not re-assign a* pending event. That would be very very bad. */fprintf(stderr,"Error! replace_callback called on a pending event!\n");return -1;}event_get_assignment(ev, &base, &fd, &events,NULL /* ignore old callback */ ,NULL /* ignore old callback argument */);event_assign(ev, base, fd, events, new_callback, new_callback_arg);return 0;}
6.5 一次触发事件
如果不需要多次添加一个事件,或者要在添加后立即删除事件,而事件又不需要是持久的 , 则可以使用 event_base_once()。
int event_base_once(struct event_base *, evutil_socket_t, short,void (*)(evutil_socket_t, short, void *), void *, const struct timeval *);
除了不支持 EV_SIGNAL 或者 EV_PERSIST 之外,这个函数的接口与 event_new()相同。 安排的事件将以默认的优先级加入到 event_base并执行。回调被执行后,libevent内部将 会释放 event 结构。成功时函数返回0,失败时返回-1。
不能删除或者手动激活使用 event_base_once ()插入的事件:如果希望能够取消事件, 应该使用 event_new()或者 event_assign()。
6.6 手动激活事件
极少数情况下,需要在事件的条件没有触发的时候让事件成为激活的。
void event_active(struct event *ev, int what, short ncalls);
这个函数让事件 ev 带有标志 what(EV_READ、EV_WRITE 和 EV_TIMEOUT 的组合)成 为激活的。事件不需要已经处于未决状态,激活事件也不会让它成为未决的。
6.7 事件状态之间的转换