| 版本 | 日期 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| 1.0 | 2021.12.20 | 文章首发 |
| 1.1 | 2021.12.22 | 错别字修正 |
| 1.2 | 2022.2.24 | 描述错误修正 |
0. 前言
在最初接触到Flink时,是来自于业界里一些头部玩家的分享——大家会用其来处理海量数据。在这种场景下,如何避免JVM GC带来StopTheWorld带来的副作用这样的问题一直盘绕在我心头。直到用了Flink以后,阅读了相关的源码(以1.14.0为基准),终于有了一些答案。在这篇文章里也是会分享给大家。
1. JVM内存管理的不足
除了上述提到的StopTheWorld,JVM的内存管理还会带来以下问题:
- 内存浪费:一个Java对象在内存中存储时会分为三个部分:对象头、实例数据、对齐填充部分。首先,32位和64位的实现中,对象头分别要占用32bit和64bit。而为了提供整体的使用效率,JVM内存中的数据不是连续存储的,而是按照8byte的整数倍进行存储。哪怕你只有1byte,会自动padding7byte。
- 缓存未命中:大家都知道CPU是有L1、2、3级缓存的,当CPU去读取内存中的数据时,会将内存中邻近的数据读到缓存中——这是程序局部性原理的一种实践手段。
最近被CPU访问的数据,短期内CPU还要访问(时间);被CPU访问的数据附近的数据,CPU短期内还要访问(空间)。但我们前面提到,Java对象在堆上存储的时候并不是连续的,所以CPU去读取JVM上的对象时,缓存的邻近内存区域数据往往不是CPU下一步计算所需要的。这时CPU只能空转等待从内存里读取数据(两者的速度不是一个量级)。如果数据恰好被swap到硬盘里,那就是难上加难了。
2. Flink的演进方案
在v0.10之前,Flink使用了堆上内存的实现。简单来说就是通过byte数组的方式来分配连续内存,应用层自己维护类型信息来获取相应的数据。但这样仍然会有问题:
- 在堆内内存过大的情况下,JVM启动时间会很长,而且Full GC会到达分钟级。
- IO效率低:堆上内存写磁盘或网络至少需要1次内存复制。
因此在v0.10后,Flink引入了堆外内存管理功能。见Jira:Add an off-heap variant of the managed memory。除了解决堆内内存的问题,还会带来一些好处:
- 堆外内存可以做成进程之间共享。这意味Flink可以以此来做故障恢复。
当然,凡事都是有双面性的,缺点是:
- 分配短生命周期的对象,比起堆上内存,在堆外内存上分配开销更高。
- 堆外内存出错时排错更为复杂。
这种实现在Spark中也可以找到,它叫做MemoryPool,同时支持堆内和堆外的内存方式,具体见MemoryMode.scala;Kafka也有类似的思路——通过Java NIO的ByteBuffer来保存它的消息。
3. 源码分析
总的来说,Flink在这一块的实现是比较清晰的——和操作系统一样有内存段,也有内存页这样的数据结构。
3.1 内存段
主要实现为MemorySegment。在v1.12前MemorySegment
仅仅为一个接口,它的实现有两个HybridMemorySegment和HeapMemorySegment。在之后的发展中,大家发现HeapMemorySegment基本都没有人用了,而是都用HybridMemorySegment了,为了优化性能——避免运行时每次都去查函数表确认调用的函数,去掉了HeapMemorySegment,并将HybridMemorySegment移到了MemorySegment中——这会见带来近2.7倍的调用速度优化。:Off-heap Memory in Apache Flink and the curious JIT compiler以及Jira:Don’t explicitly use HeapMemorySegment in raw format serde。
MemorySegment主要负责引用内存段,并其中数据进行读写——它对基本类型支持的很好,而复杂类型则需要外部来做序列化。具体的实现还是比较简单的,从field的声明中就可以大致看出实现了。唯一需要讲一下的是LITTLE_ENDIAN:不同的CPU架构会才不同的存储顺序——PowerPC会采用Big Endian方式,低地址存放最低有效字节;而x86会采用Little Endian方式存储数据,低地址存放最高有效字节。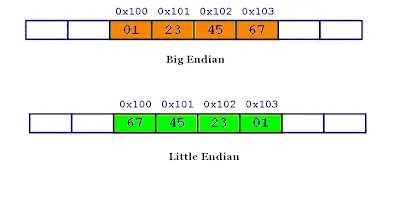
说实话,读到这个代码的时候笔者还是略震惊的,因为写Java这么多年几乎对底层的硬件是无感知的。没想到Java代码还要考虑兼容CPU架构的逻辑。
这个时候就会有同学问了,那这个MemorySegments是如何在Flink中运作的呢?我们可以看个测试用例:BinaryRowDataTest里的testPagesSer:
先是有MemorySegments,通过对应的BinaryRowWriter写入数据到RowData,再用BinaryRowDataSerializer写RowData到RandomAccessOutputView:
@Testpublic void testPagesSer() throws IOException {MemorySegment[] memorySegments = new MemorySegment[5];ArrayList<MemorySegment> memorySegmentList = new ArrayList<>();for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {memorySegments[i] = MemorySegmentFactory.wrap(new byte[64]);memorySegmentList.add(memorySegments[i]);}{// multi memorySegmentsString str = "啦啦啦啦啦我是快乐的粉刷匠,啦啦啦啦啦我是快乐的粉刷匠," + "啦啦啦啦啦我是快乐的粉刷匠。";BinaryRowData row = new BinaryRowData(1);BinaryRowWriter writer = new BinaryRowWriter(row);writer.writeString(0, fromString(str));writer.complete();RandomAccessOutputView out = new RandomAccessOutputView(memorySegments, 64);BinaryRowDataSerializer serializer = new BinaryRowDataSerializer(1);serializer.serializeToPages(row, out);BinaryRowData mapRow = serializer.createInstance();mapRow =serializer.mapFromPages(mapRow, new RandomAccessInputView(memorySegmentList, 64));writer.reset();writer.writeString(0, mapRow.getString(0));writer.complete();assertEquals(str, row.getString(0).toString());BinaryRowData deserRow =serializer.deserializeFromPages(new RandomAccessInputView(memorySegmentList, 64));writer.reset();writer.writeString(0, deserRow.getString(0));writer.complete();assertEquals(str, row.getString(0).toString());}// ignore some code}
3.2 内存页
一个MemorySegment默认对应了32KB大小的内存块。在流处理中,很容易出现超过32KB的数据,这时就需要跨MemorySegment。那么对于编写相应逻辑的人就需要持有多个MemorySegment,因此Flink提供了内存页的实现,它会持有多个MemorySegment实例,方便框架的开发人员来快速的编写Memory相关的代码,而无需关注一个个的MemorySegment。
其抽象为DataInputView和DataOutputView,分别对了数据读取和数据写入。
接下来,还是关联实际的代码看一下。我们以我们最常见的KafkaProducer使用为例:
|-- KafkaProducer#invoke //在这里指定了serializedValue\-- KeyedSerializationSchema#serializeValue //序列化record 的value
我们挑一个实现看看,以TypeInformationKeyValueSerializationSchema为例:
|-- TypeInformationKeyValueSerializationSchema#deserialize //KeyedSerializationSchema的实现类|-- DataInputDeserializer#setBuffer // 这是DataInputView的实现,用内部的byte数组存储数据。这里很奇怪的是并没有使用MemorySegement。|-- TypeSerializer#deserialize // 它的实现会针对不同的类型,从DataInputView里读出数据返回
其实这里的例子不太恰当。因为KeyedSerializationSchema已经被标记为了废弃。社区更建议我们使用KafkaSerializationSchema。第一个原因是因为KeyedSerializationSchema的抽象并不合适Kafka,当Kafka在Record新加字段时,是很难抽象当这个接口里的——这个接口仅仅关注了key、value以及topic。
以KafkaSerializationSchema展开的话,我们可以看典型的实现——KafkaSerializationSchemaWrapper,我们关心的地方很容找到:
@Overridepublic ProducerRecord<byte[], byte[]> serialize(T element, @Nullable Long timestamp) {byte[] serialized = serializationSchema.serialize(element);final Integer partition;if (partitioner != null) {partition = partitioner.partition(element, null, serialized, topic, partitions);} else {partition = null;}final Long timestampToWrite;if (writeTimestamp) {timestampToWrite = timestamp;} else {timestampToWrite = null;}return new ProducerRecord<>(topic, partition, timestampToWrite, null, serialized);}
这个serializationSchema的声明是一个名为SerializationSchema的接口。可以看到它有大量的实现,其中很多对应了DataStream还有SQL API中的format。我们以TypeInformationSerializationSchema为例继续跟踪:
@Publicpublic class TypeInformationSerializationSchema<T>implements DeserializationSchema<T>, SerializationSchema<T> {//ignore some filed/** The serializer for the actual de-/serialization. */private final TypeSerializer<T> serializer;....
又看到我们熟悉的接口TypeSerializer了。就像上面说的,它的实现会针对不同的类型,从DataInputView、DataOutputView进行互动,提供序列化和反序列化的能力。在它的方法签名中也是可以看到的:
/*** Serializes the given record to the given target output view.** @param record The record to serialize.* @param target The output view to write the serialized data to.* @throws IOException Thrown, if the serialization encountered an I/O related error. Typically* raised by the output view, which may have an underlying I/O channel to which it* delegates.*/public abstract void serialize(T record, DataOutputView target) throws IOException;/*** De-serializes a record from the given source input view.** @param source The input view from which to read the data.* @return The deserialized element.* @throws IOException Thrown, if the de-serialization encountered an I/O related error.* Typically raised by the input view, which may have an underlying I/O channel from which* it reads.*/public abstract T deserialize(DataInputView source) throws IOException;/*** De-serializes a record from the given source input view into the given reuse record instance* if mutable.** @param reuse The record instance into which to de-serialize the data.* @param source The input view from which to read the data.* @return The deserialized element.* @throws IOException Thrown, if the de-serialization encountered an I/O related error.* Typically raised by the input view, which may have an underlying I/O channel from which* it reads.*/public abstract T deserialize(T reuse, DataInputView source) throws IOException;/*** Copies exactly one record from the source input view to the target output view. Whether this* operation works on binary data or partially de-serializes the record to determine its length* (such as for records of variable length) is up to the implementer. Binary copies are* typically faster. A copy of a record containing two integer numbers (8 bytes total) is most* efficiently implemented as {@code target.write(source, 8);}.** @param source The input view from which to read the record.* @param target The target output view to which to write the record.* @throws IOException Thrown if any of the two views raises an exception.*/public abstract void copy(DataInputView source, DataOutputView target) throws IOException;
那么TypeSerializer#deserialize到底是怎么被调用到的呢?这些细节并不是这篇文章需要关心的。在这里我们展示一下调用链,有兴趣的读者可以沿着这个调用链看一下具体的代码:
|-- TypeSerializer#deserialize|-- StreamElementSerializer#deserialize|-- TypeInformationKeyValueSerializationSchema#deserialize|-- KafkaDeserializationSchema#deserialize|-- KafkaFetcher#partitionConsumerRecordsHandler //到这里已经很清楚了,这里是由FlinkKafkaConsumer new出来的对象
3.3 缓冲池
还有一个比较有意思的类是LocalBufferPool,封装了MemorySegment。一般用于网络缓冲器(NetworkBuffer),NetworkBuffer是网络交换数据的包装,当结果分区(ResultParition)开始写出数据的时候,需要向LocalBufferPool申请Buffer资源。
写入逻辑:
|-- Task#constructor //构造任务|-- NettyShuffleEnvironment#createResultPartitionWriters // 创建用于写入结果的结果分区|-- ResultPartitionFactory#create\-- ResultPartitionFactory#createBufferPoolFactory //在这里创建了一个简单的BufferPoolFactory|-- PipelinedResultPartition#constructor|-- BufferWritingResultPartition#constructor|-- SortMergeResultPartition#constructor or BufferWritingResultPartition#constructor|-- ResultPartition#constructor\-- ResultPartition#steup // 注册缓冲池到这个结果分区中
另外,NetworkBuffer实现了Netty的AbstractReferenceCountedByteBuf。这意味着这里采用了经典的引用计数算法,当Buffer不再被需要时,会被回收。
4. 其他
4.1 相关Flink Jira
以下是我在写本文时参考过的Jira列表:
- Add an off-heap variant of the managed memory:https://issues.apache.org/jira/browse/FLINK-1320
- Separate type specific memory segments.:https://issues.apache.org/jira/browse/FLINK-21417
- Investigate potential out-of-memory problems due to managed unsafe memory allocation:https://issues.apache.org/jira/browse/FLINK-15758
- Adjust GC Cleaner for unsafe memory and Java 11:https://issues.apache.org/jira/browse/FLINK-14522
- FLIP-49 Unified Memory Configuration for TaskExecutors:https://issues.apache.org/jira/browse/FLINK-13980
- Don’t explicitly use HeapMemorySegment in raw format serde:https://issues.apache.org/jira/browse/FLINK-21236
- Refactor HybridMemorySegment:https://issues.apache.org/jira/browse/FLINK-21375
- use flink’s buffers in netty:https://issues.apache.org/jira/browse/FLINK-7315
- Add copyToUnsafe, copyFromUnsafe and equalTo to MemorySegment:https://issues.apache.org/jira/browse/FLINK-11724

