基础说明
有许多QML元素可用于项目定位。这些称为定位器,其中QtQuick模块提供以下内容:Row,Column,Grid和Flow。在下面的插图中可以看到它们显示了相同的内容。
:::success
我们在详细介绍之前,让我介绍一些辅助元素:红色,蓝色,绿色,较亮和较暗的方块。这些组件中的每一个都包含一个48x48像素凸起的矩形。作为参考,这里是RedSquare的源代码:
:::
// RedSquare.qmlimport QtQuickRectangle {width: 48height: 48color: "#ea7025"border.color: Qt.lighter(color)}//GreenSquare.qmlimport QtQuickRectangle {width: 48height: 48color: "#228B22"border.color: Qt.lighter(color)}//BlueSquare.qmlimport QtQuickRectangle {width: 48height: 48color: "#1E90FF"border.color: Qt.lighter(color)}
请注意,在填充颜色的基础上,使用Qt.llighter(color)来产生一个较浅的边框颜色。在下面的示例中,我们将使用这些辅助程序,使源代码更加紧凑和可读。请记住,每个矩形最初是48x48像素。
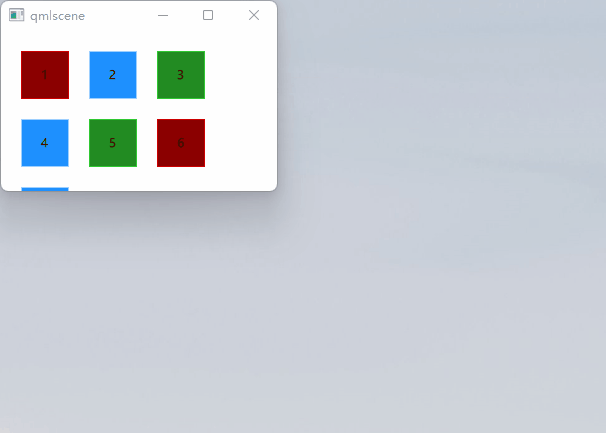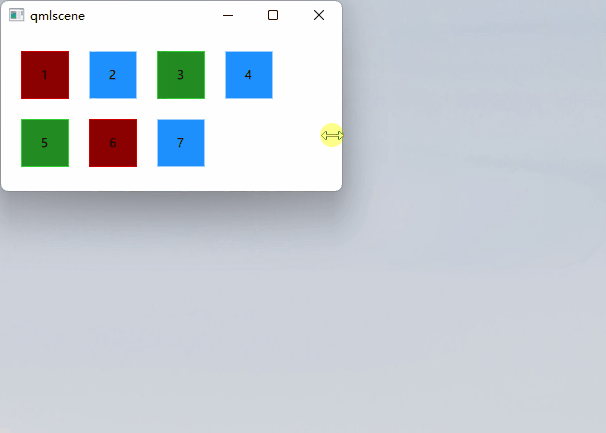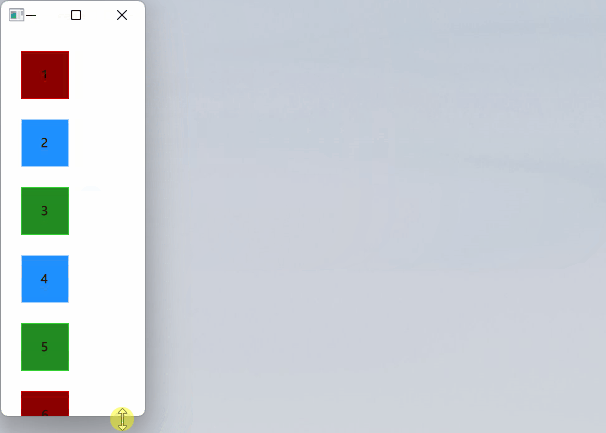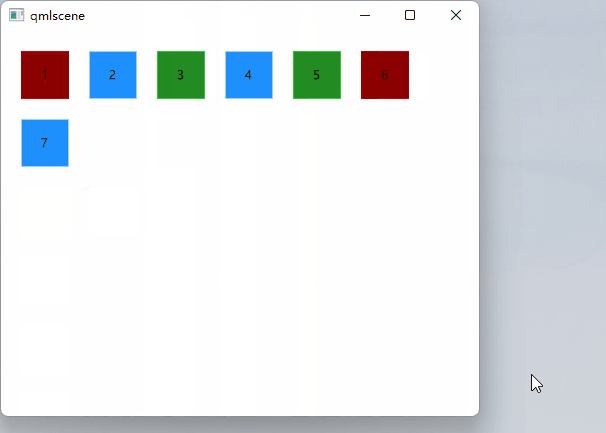
Column定位
// ColumnExample.qmlimport QtQuickRectangle {id: rootwidth: 120height: 240Column {id: rowanchors.centerIn: parentspacing: 8RedSquare { }GreenSquare { width: 96 }BlueSquare { }}}
Row定位
Row元素将其子项目彼此相邻放置,根据layoutDirectio属性从左到右或从右到左。同样,spacing用于分隔子项。
// RowExample.qmlimport QtQuickRectangle {id: rootwidth: 400; height: 120Row {id: rowanchors.centerIn: parentspacing: 20BlueSquare { }GreenSquare { }RedSquare { }}}
Grid定位
Grid元素在网格中排列它的子元素。通过设置Row和Columns属性,可以限制行或列的数量。如果不设置它们中的任何一个,则另一个将根据子项目的数量计算。
例如,将行设置为3并添加6个子项将生成2列。属性flow和layoutDirection用于控制将项目添加到网格中的顺序,而spacing控制子项目之间的间距。
// ColumnExample.qmlimport QtQuickRectangle {id: rootwidth: 160height: 160Grid {id: gridrows: 2columns: 2anchors.centerIn: parentspacing: 8RedSquare { }RedSquare { }RedSquare { }RedSquare { }}}
Flow定位
最后的定位器是Flow。它将其子项添加到流中。使用flow和layoutDirection控制流的方向。它可以横着布局,也可以从上到下。
它也可以从左向右或相反的方向运行。在流中添加项时,将根据需要对它们进行包装以形成新的行或列。为了让流工作,它必须有一个宽度或高度。这可以直接设置,或通过锚布局。
:::success
子元素Sequare做了简单更改,增加了序号,让特性显示的更明显。这里仅列出RedSquare.qml,其他两个也做类型更改,增加Text设置
:::
//RedSquare.qmlimport QtQuickRectangle {id:rootwidth: 48height: 48color: "#8B0000"property string showText: ""Text {id: labelanchors.centerIn: parenttext:root.showText}border.color: Qt.lighter(color)}
// ColumnExample.qmlimport QtQuickRectangle {id: rootwidth: 160height: 160Flow {anchors.fill: parentanchors.margins: 20spacing: 20RedSquare {showText:"1" }BlueSquare { showText:"2" }GreenSquare { showText:"3" }BlueSquare { showText:"4" }GreenSquare { showText:"5" }RedSquare {showText:"6" }BlueSquare { showText:"7" }}}
Repeater
中继器经常和定位器一起使用。它的工作方式类似于for循环,在模型上进行迭代。在最简单的情况下,模型只是一个提供循环次数的值。
// RepeaterExample.qmlimport QtQuickDarkSquare {id: rootwidth: 252height: 252property variant colorArray: ["#00bde3", "#67c111", "#ea7025"]Grid{anchors.fill: parentanchors.margins: 8spacing: 4Repeater {model: 16delegate: Rectangle {required property int indexproperty int colorIndex: Math.floor(Math.random()*3)width: 56; height: 56color: root.colorArray[colorIndex]border.color: Qt.lighter(color)Text {anchors.centerIn: parentcolor: "#f0f0f0"text: "Cell " + parent.index}}}}}
结果: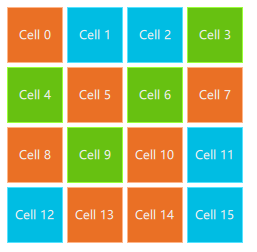
在这个中继器示例中,我们使用了一些新的魔法。我们定义了自己的颜色数组属性,它是一个颜色数组。中继器创建一系列矩形(由模型定义16 个)。
对于每个循环,它创建由转发器的子节点定义的矩形。在矩形中,我们使用 JS 数学函数选择颜色:Math.floor(Math.random()\*3)。这为我们提供了一个范围为0..2 的随机数,我们用它来从颜色数组中选择颜色。如前所述,Java Script 是 Qt Quick 的核心部分,因此我们可以使用标准库。
转发器将index属性注入转发器。它包含当前循环索引。(0,1,..15)。我们可以使用它根据索引做出我们自己的决定,或者在我们的例子中使用 Text元素可视化当前索引。
:::success
虽然index属性被动态注入到Rectangle中,但最好将其声明为必需属性,以简化可读性和帮助工具。这是通过必需的属性required property int index实现的。
:::
:::success
使用更高级的动态委托处理更大的模型和动态视图将在模型视图一章中介绍。当有少量静态数据要显示时,最好使用中继器。
:::