JS的八种内置类型
- boolean
- number
- string
- undefined
- null
- symbol
- bigint
- object
布尔类型
我们用 boolean 来表示布尔类型,注意开头是小写的,如果你在Typescript文件中写成 Boolean 那代表是 JavaScript 中的布尔对象,这是新手常犯的错误。
const isLoading: boolean = false
这里需要提示一下,很多 TypeScript 的原始类型比如 boolean、number、string等等,在JavaScript中都有类似的关键字 Boolean、Number、String,后者是 JavaScript 的构造函数,比如我们用 Number 用于数字类型转化或者构造 Number 对象用的,而 TypeScript 中的 number 类型仅仅是表示类型,两者完全不同。
数字
JavaScript中的二进制、十进制、十六进制等数都可以用 number 类型表示。
const decLiteral: number = 6const hexLiteral: number = 0xf00dconst binaryLiteral: number = 0b1010const octalLiteral: number = 0o744
字符串
const book: string = '深入浅出 Typescript'
Null 和 Undefined
TypeScript 里,undefined 和 null 两者各自有自己的类型分别叫做 undefined 和 null,和void相似,它们的本身的类型用处不是很大:
let u: undefined = undefined;let n: null = null;
注意
默认情况下 null 和 undefined 是所有类型的子类型,就是说你可以把 null 和 undefined 赋值给 number 类型的变量。
但是在正式项目中一般都是开启 --strictNullChecks 检测的,即 null 和 undefined 只能赋值给 void 和它们各自,可以规避非常多的问题。
// null和undefined赋值给stringlet str:string = "666";str = nullstr= undefined// null和undefined赋值给numberlet num:number = 666;num = nullnum= undefined// null和undefined赋值给objectlet obj:object ={};obj = nullobj= undefined// null和undefined赋值给Symbollet sym: symbol = Symbol("me");sym = nullsym= undefined// null和undefined赋值给booleanlet isDone: boolean = false;isDone = nullisDone= undefined// null和undefined赋值给bigintlet big: bigint = 100n;big = nullbig= undefined
Symbol
Symbol 是在ES2015之后成为新的原始类型,它通过 Symbol 构造函数创建:
const sym1 = Symbol('key1');const sym2 = Symbol('key2');
而且 Symbol 的值是唯一不变的:
Symbol('key1') === Symbol('key1') // false
BigInt
BigInt 类型在 TypeScript3.2 版本被内置,使用 BigInt 可以安全地存储和操作大整数,即使这个数已经超出了JavaScript构造函数 Number 能够表示的安全整数范围。
在 JavaScript 中采用双精度浮点数,这导致精度有限,比如 Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER 给出了可以安全递增的最大可能整数,即2**53-1,我们看一下案例:
const max = Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER;const max1 = max + 1const max2 = max + 2max1 === max2 //true
max1与max2居然相等?这就是超过精读范围造成的问题,而BigInt正是解决这类问题而生的:
const max = BigInt(Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER);const max1 = max + 1nconst max2 = max + 2nmax1 === max2 // false
这是在 Chrome 浏览器 console 的结果: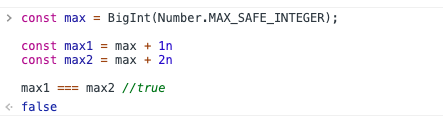
值得注意的是我们需要用 BigInt(number) 把 Number 转化为 BigInt,同时如果类型是 BigInt ,那么数字后面需要加 n ,就如同上面例子的 const max1 = max + 1n 中的 1n。
在TypeScript中,number 类型虽然和 BigInt 都是有表示数字的意思,但是实际上两者类型是不同的:
declare let foo: number;declare let bar: bigint;foo = bar; // error: Type 'bigint' is not assignable to type 'number'.bar = foo; // error: Type 'number' is not assignable to type 'bigint'.