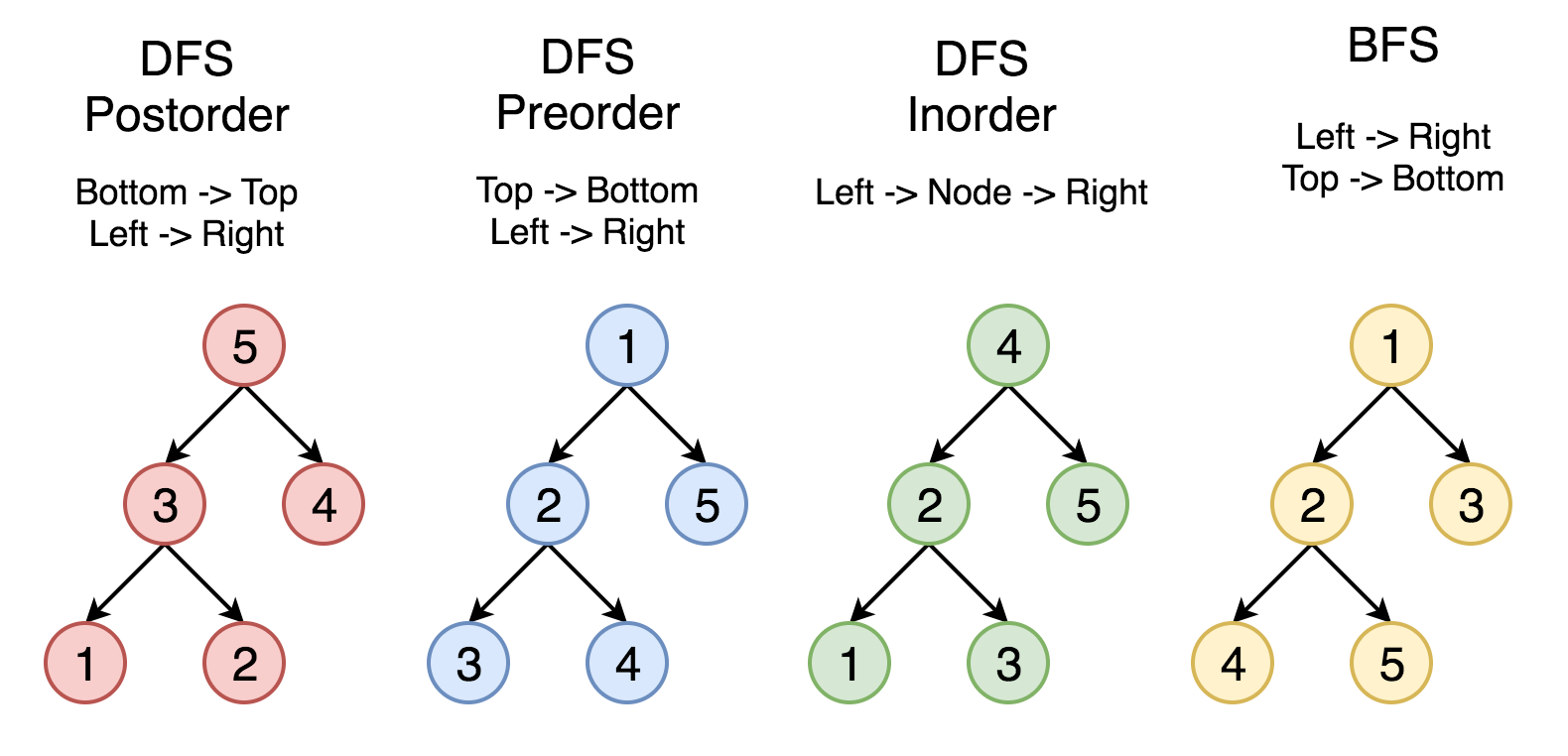
1 DFS
1 定义:
深度优先搜索算法(英语:Depth-First-Search,DFS)是一种用于遍历或搜索树或图的算法。沿着树的深度遍历树的节点,尽可能深的搜索树的分支。当节点v的所在边都己被探寻过,搜索将回溯到发现节点v的那条边的起始节点。这一过程一直进行到已发现从源节点可达的所有节点为止。如果还存在未被发现的节点,则选择其中一个作为源节点并重复以上过程,整个进程反复进行直到所有节点都被访问为止。属于盲目搜索。
深度优先搜索是图论中的经典算法,利用深度优先搜索算法可以产生目标图的相应拓扑排序表,利用拓扑排序表可以方便的解决很多相关的图论问题,如最大路径问题等等。
- 北京大学: 将问题各状态之间的状态转移关系描述成一个图, DFS遍历图的框架
2 按照 1-2-3-4-5 的顺序来比较不同的策略。
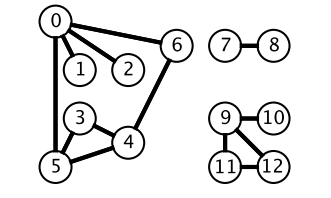
而深度优先搜索在得到一个新节点时立即对新节点进行遍历:从节点 0 出发开始遍历,得到到新节点 6 时,立马对新节点 6 进行遍历,得到新节点 4;如此反复以这种方式遍历新节点,直到没有新节点了,此时返回。返回到根节点 0 的情况是,继续对根节点 0 进行遍历,得到新节点 2,然后继续以上步骤。
从一个节点出发,使用 DFS 对一个图进行遍历时,能够遍历到的节点都是从初始节点可达的,DFS 常用来求解这种 可达性 问题。
在程序实现 DFS 时需要考虑以下问题:
图中
- 栈:用栈来保存当前节点信息,当遍历新节点返回时能够继续遍历当前节点。可以使用递归栈。
-
二叉树中
栈: 用栈来保存当前节点信息,当遍历新节点返回时能够继续遍历当前节点。可以使用递归栈。
- 标记:和 BFS 一样同样需要对已经遍历过的节点进行标记, 递归向stack 加入左右子节点, 因为子节点不会向 上访问, 变形得标记了节点。
1 二叉树的最大深度
给定一个二叉树,找出其最大深度。
二叉树的深度为根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数。
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例:
给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
返回它的最大深度 3 。
- idea: pair 保存节点和深度的值 ```java import javafx.util.Pair; import java.lang.Math;
class Solution {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
Queue
int depth = 0;
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
Pair<TreeNode, Integer> current = stack.poll();
root = current.getKey();
int current_depth = current.getValue();
if (root != null) {
depth = Math.max(depth, current_depth);
stack.add(new Pair(root.left, current_depth + 1));
stack.add(new Pair(root.right, current_depth + 1));
}
}
return depth;
} };
```java
class Solution {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
int left = maxDepth(root.left);
int right = maxDepth(root.right);
return Math.max(left, right)+1;
}
};
2 在每个树行中找最大值
您需要在二叉树的每一行中找到最大的值。
示例:
输入:
1<br /> / \<br /> 3 2<br /> / \ \ <br /> 5 3 9
输出: [1, 3, 9]
- 类似: 右视图, 每一行的值。
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode(int x) { val = x; } * } */ class Solution { public List<Integer> largestValues(TreeNode root) { Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>(); List<Integer> res = new LinkedList<>(); if(root ==null){ return res; } queue.add(root); while(!queue.isEmpty()){ // 比普通bfs多了一层循环, 找出同层的树的最小值 int maxValue = Integer.MIN_VALUE; int count = queue.size(); while(count-- > 0){ // 用count来控制一层循环。 TreeNode temNode = queue.poll(); if(temNode.left != null){ queue.add(temNode.left); } if(temNode.right != null){ queue.add(temNode.right); } maxValue = Math.max(maxValue, temNode.val); } res.add(maxValue); } return res; } }
3 路径总和
给定一个二叉树和一个目标和,判断该树中是否存在根节点到叶子节点的路径,这条路径上所有节点值相加等于目标和。
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例:
给定如下二叉树,以及目标和 sum = 22,
5
/ \
4 8
/ / \
11 13 4
/ \ \
7 2 1
返回 true, 因为存在目标和为 22 的根节点到叶子节点的路径 5->4->11->2。
class Solution {
public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int sum) {
if (root == null)
return false;
// 用 sum_stack 与 node_stack 保持同样的同点同值。
LinkedList<TreeNode> node_stack = new LinkedList();
LinkedList<Integer> sum_stack = new LinkedList();
node_stack.add(root);
sum_stack.add(sum - root.val);
TreeNode node;
int curr_sum;
while ( !node_stack.isEmpty() ) {
node = node_stack.pollLast();
curr_sum = sum_stack.pollLast();
if ((node.right == null) && (node.left == null) && (curr_sum == 0))
return true;
if (node.right != null) {
node_stack.add(node.right);
sum_stack.add(curr_sum - node.right.val);
}
if (node.left != null) {
node_stack.add(node.left);
sum_stack.add(curr_sum - node.left.val);
}
}
return false;
}
}
- 递归
class Solution {
public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int sum) {
if (root == null)
return false;
sum -= root.val;
if ((root.left == null) && (root.right == null))
return (sum == 0);
return hasPathSum(root.left, sum) || hasPathSum(root.right, sum);
}
}
2 BFS
- 广度优先搜索一层一层地进行遍历,每层遍历都以上一层遍历的结果作为起点,遍历一个距离能访问到的所有节点。需要注意的是,遍历过的节点不能再次被遍历。
图中
- 队列:用队列来保存当前节点信息,当遍历新节点返回时能够继续遍历当前节点。可以使用递归队列。
- 标记:和DFS 一样同样需要对已经遍历过的节点进行标记。
树中
- 队列:用队列来保存当前节点信息,当遍历新节点返回时能够继续遍历当前节点。可以使用递归队列。
- 标记:用node.left, node.right向queue中加入节点的最近子节点。
- 相当与mark,不能向上访问父节点, 只能访问子节点。
1 N叉树的层序遍历
给定一个 N 叉树,返回其节点值的层序遍历。 (即从左到右,逐层遍历)。
例如,给定一个 3叉树 :
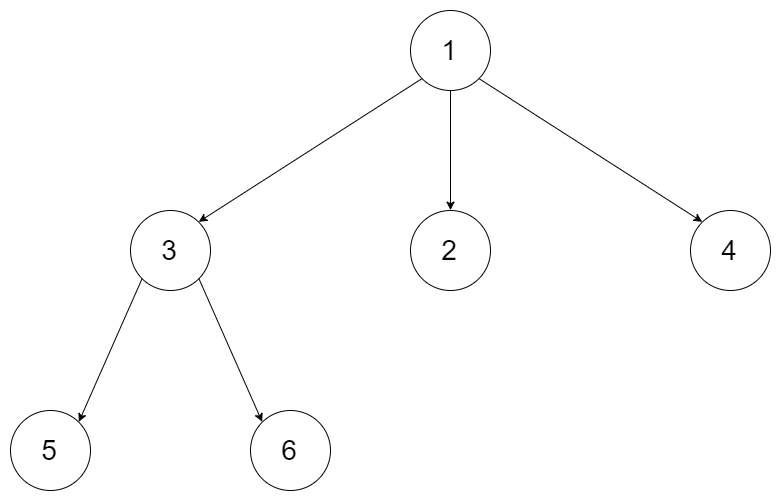
返回其层序遍历:
[
[1],
[3,2,4],
[5,6]
]
idea: 用queue.size()来控制一层的循环
/* // Definition for a Node. class Node { public int val; public List<Node> children; public Node() {} public Node(int _val,List<Node> _children) { val = _val; children = _children; } }; */ class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(Node root) { List<List<Integer>> res= new ArrayList<>(); if(root == null) return res; Queue<Node> queue= new LinkedList<>(); queue.add(root); while(!queue.isEmpty()){ List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(); int cnt = queue.size(); while(cnt-- > 0){ Node cur = queue.poll(); list.add(cur.val); for(Node x: cur.children){ if(x != null){ queue.add(x); } } } res.add(list); } return res; } }
2 对称二叉树
给定一个二叉树,检查它是否是镜像对称的。
例如,二叉树 [1,2,2,3,4,4,3] 是对称的。
1
/ \
2 2
/ \ / \
3 4 4 3
但是下面这个 [1,2,2,null,3,null,3] 则不是镜像对称的:
1
/ \
2 2
\ \
3 3
- idea: 每一层都o
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
Queue<TreeNode> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.add(root);
q.add(root);
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode t1 = q.poll();
TreeNode t2 = q.poll();
if (t1 == null && t2 == null) continue;
if (t1 == null || t2 == null) return false;
if (t1.val != t2.val) return false;
// 树节点加入队列顺序, 使得每次都可以比较对称树节点的值。
q.add(t1.left);
q.add(t2.right);
q.add(t1.right);
q.add(t2.left);
}
return true;
}
}
3 课程表
现在你总共有 n 门课需要选,记为 0 到 n-1。
在选修某些课程之前需要一些先修课程。 例如,想要学习课程 0 ,你需要先完成课程 1 ,我们用一个匹配来表示他们: [0,1]
给定课程总量以及它们的先决条件,判断是否可能完成所有课程的学习?
示例 1:
输入: 2, [[1,0]]
输出: true
解释: 总共有 2 门课程。学习课程 1 之前,你需要完成课程 0。所以这是可能的。
示例 2:
输入: 2, [[1,0],[0,1]]
输出: false
解释: 总共有 2 门课程。学习课程 1 之前,你需要先完成课程 0;并且学习课程 0 之前,你还应先完成课程 1。这是不可能的。
3 DFS&&BFS 双解法
1 岛屿数量
给定一个由 '1'(陆地)和 '0'(水)组成的的二维网格,计算岛屿的数量。一个岛被水包围,并且它是通过水平方向或垂直方向上相邻的陆地连接而成的。你可以假设网格的四个边均被水包围。
示例 1:
输入:
11110
11010
11000
00000
输出: 1
示例 2:
输入:
11000
11000
00100
00011
输出: 3
- 深度优先搜索, 查看当前节点是否为 “1”, 小岛数量加一, 设当前节点为”0”,
- 利用是DFS搜索当前节点四个方向的节点
- 出口条件是, if(r <0 || c < 0 || r >=nr || c >= nc || grid[r][c] == ‘0’)
class Solution {
void dfs(char[][] grid, int r, int c) {
int nr = grid.length;
int nc = grid[0].length;
if(r <0 || c < 0 || r >=nr || c >= nc || grid[r][c] == '0'){
return;
}
grid[r][c] ='0';
dfs(grid, r-1, c);
dfs(grid, r+1, c);
dfs(grid, r, c-1);
dfs(grid, r, c+1);
}
public int numIslands(char[][] grid) {
if (grid == null || grid.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
int nr = grid.length;
int nc = grid[0].length;
int num_islands = 0;
for (int r = 0; r < nr; ++r) {
for (int c = 0; c < nc; ++c) {
if (grid[r][c] == '1') {
++num_islands;
dfs(grid, r, c);
}
}
}
return num_islands;
}
}

