0 性质
树是一种抽象数据类型(ADT)或是实现这种抽象数据类型的数据结构,用来模拟具有树状结构性质的数据集合。它是由 n(n>0)n(n>0) 个有限节点组成一个具有层次关系的集合。
把它叫做「树」是因为它看起来像一棵倒挂的树,也就是说它是根朝上,而叶朝下的。
它具有以下的特点:
每个节点都只有有限个子节点或无子节点;
没有父节点的节点称为根节点;
每一个非根节点有且只有一个父节点;
除了根节点外,每个子节点可以分为多个不相交的子树;
树里面没有环路。
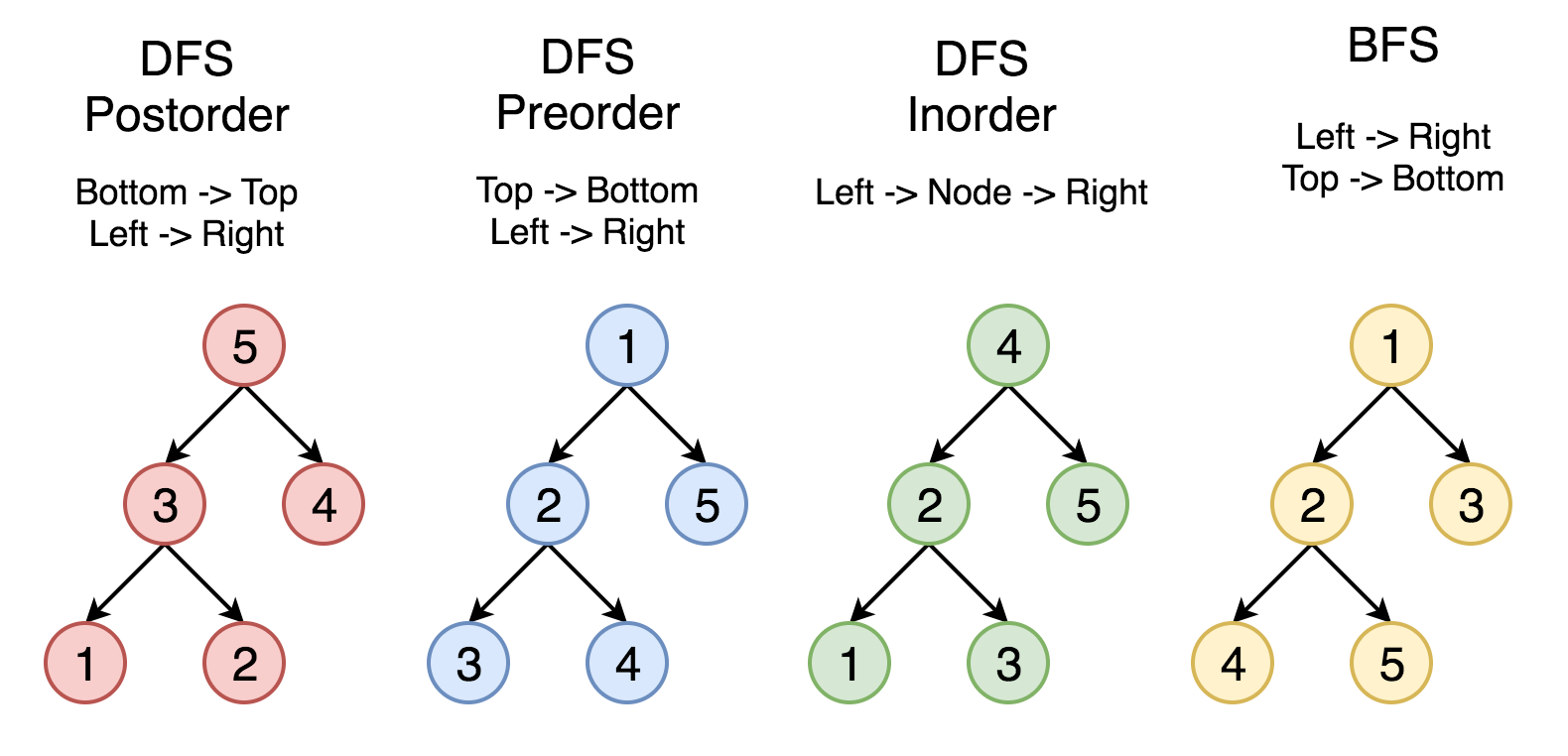
1 树的遍历
1/ \2 3/ \ \4 5 6
1-1 结果
- 层次遍历顺序:[1 2 3 4 5 6]
- 前序遍历顺序:[1 2 4 5 3 6]
- 中序遍历顺序:[4 2 5 1 3 6]
- 后序遍历顺序:[4 5 2 6 3 1]
层次遍历使用 BFS 实现,利用的就是 BFS 一层一层遍历的特性;而前序、中序、后序遍历利用了 DFS 实现。
前序、中序、后序遍只是在对节点访问的顺序有一点不同,其它都相同。
1-2 思想
public List<> list = new LinkedList();
visit(TreeNode root){
if(root.null) return null;
list.add(root.val);
}
① 前序
void dfs(TreeNode root) {
visit(root);
dfs(root.left);
dfs(root.right);
}
② 中序
void dfs(TreeNode root) {
dfs(root.left);
visit(root);
dfs(root.right);
}
③ 后序
void dfs(TreeNode root) {
dfs(root.left);
dfs(root.right);
visit(root);
}
2 DFS
1 定义:
深度优先搜索算法(英语:Depth-First-Search,DFS)是一种用于遍历或搜索树或图的算法。沿着树的深度遍历树的节点,尽可能深的搜索树的分支。当节点v的所在边都己被探寻过,搜索将回溯到发现节点v的那条边的起始节点。这一过程一直进行到已发现从源节点可达的所有节点为止。如果还存在未被发现的节点,则选择其中一个作为源节点并重复以上过程,整个进程反复进行直到所有节点都被访问为止。属于盲目搜索。
深度优先搜索是图论中的经典算法,利用深度优先搜索算法可以产生目标图的相应拓扑排序表,利用拓扑排序表可以方便的解决很多相关的图论问题,如最大路径问题等等。
- 北京大学: 将问题各状态之间的状态转移关系描述成一个图, DFS遍历图的框架
2 按照 1-2-3-4-5 的顺序来比较不同的策略。
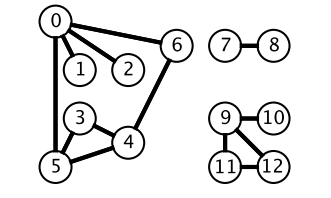
而深度优先搜索在得到一个新节点时立即对新节点进行遍历:从节点 0 出发开始遍历,得到到新节点 6 时,立马对新节点 6 进行遍历,得到新节点 4;如此反复以这种方式遍历新节点,直到没有新节点了,此时返回。返回到根节点 0 的情况是,继续对根节点 0 进行遍历,得到新节点 2,然后继续以上步骤。
从一个节点出发,使用 DFS 对一个图进行遍历时,能够遍历到的节点都是从初始节点可达的,DFS 常用来求解这种 可达性 问题。
在程序实现 DFS 时需要考虑以下问题:
图中
- 栈:用栈来保存当前节点信息,当遍历新节点返回时能够继续遍历当前节点。可以使用递归栈。
-
二叉树中
栈: 用栈来保存当前节点信息,当遍历新节点返回时能够继续遍历当前节点。可以使用递归栈。
- 标记:和 BFS 一样同样需要对已经遍历过的节点进行标记, 递归向stack 加入左右子节点, 因为子节点不会向 上访问, 变形得标记了节点。
3 具体实现
前序遍历
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> ret = new ArrayList<>();
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(root);
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
TreeNode node = stack.pop();
if(node == null){
continue; // root为null的时候
}
ret.add( node.val);
stack.push(node.right);
stack.push(node.left);
}
return ret;
}
- root加入stack
- 当stack不为空时, stack.pop();
- stack.push 右边 => 左边
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> ret = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) {
return;
}
Stack<TreeNode> s = new Stack<TreeNode>();
while (root != null || !s.isEmpty()) {
while (root != null) {
ret.add(root.val);
s.push(root);
root = root.left;
}
root = s.pop();
root = root.right;
}
return ret;
}
后序遍历
- 前序遍历为 root -> left -> right,后序遍历为 left -> right -> root。可以修改前序遍历成为 root -> right -> left,那么这个顺序就和后序遍历正好相反。
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> ret = new ArrayList<>();
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(root);
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
TreeNode node = stack.pop();
if(node == null) continue;
ret.add(node.val);
stack.add(node.left);
stack.add(node.right);
}
Collections.reverse(ret);
return ret;
}
中序遍历
- BST 的中序遍历返回的是有序数组
- (1) BST的rank的问题
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List < Integer > inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode curr = root;
while(curr != null || !stack.isEmpty() ){
while(curr != null){
stack.push(curr);
curr =curr.left;
}
curr = stack.pop();
res.add(curr.val);
curr = curr.right;
}
return res;
}
}
BFS遍历: 关键怎么加元素进queue;
- 最短路径
4 二叉查找树(BST)
根节点大于等于左子树所有节点,小于等于右子树所有节点。
1寻找二叉查找树的第 k 个元素
- Kth Smallest Element in a BST (Medium)
中序遍历解法:
private int cnt = 0;
private int val;
public int kthSmallest(TreeNode root, int k) {
inOrder(root, k);
return val;
}
private void inOrder(TreeNode node, int k) {
if (node == null) return;
inOrder(node.left, k);
cnt++;
if (cnt == k) {
val = node.val;
return;
}
inOrder(node.right, k);
}
2 二叉查找树的最近公共祖先
235. Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Search Tree (Easy)
_______6______
/ \
___2__ ___8__
/ \ / \
0 4 7 9
/ \
3 5
For example, the lowest common ancestor (LCA) of
nodes 2 and 8 is 6. Another example is LCA of nodes 2 and 4 is 2, since
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(root.val > p.val && root.val > q.val) lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);
if(root.val < p.val && root.val < q.val) lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);
return root;
}
3 二叉树的最近公共祖先
236. Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Tree (Medium)
_______3______
/ \
___5__ ___1__
/ \ / \
6 2 0 8
/ \
7 4
For example, the lowest common ancestor (LCA) of
nodes 5 and 1 is 3.
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if (root == null || root == p || root == q) return root;
TreeNode left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);
TreeNode right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);
return left == null ? right : right == null ? left : root;
}
4 将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树
将一个按照升序排列的有序数组,转换为一棵高度平衡二叉搜索树。
本题中,一个高度平衡二叉树是指一个二叉树每个节点 的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过 1。
示例:
给定有序数组: [-10,-3,0,5,9],
一个可能的答案是:[0,-3,9,-10,null,5],它可以表示下面这个高度平衡二叉搜索树:
0
/ \
-3 9
/ /
-10 5
- idea: 中点为root, 左右子节点递归寻找中点
class Solution {
public TreeNode sortedArrayToBST(int[] nums) {
// 左右等分建立左右子树,中间节点作为子树根节点,递归该过程
return nums == null ? null : buildTree(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);
}
private TreeNode buildTree(int[] nums, int l, int r) {
if (l > r) {
return null;
}
int mid = (r+l)/2;
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(nums[mid]);
root.left = buildTree(nums, l, mid-1);
root.right = buildTree(nums, mid+1, r);
return root;
}
}
5 树的递归
- 一棵树要么是空树,要么有两个指针,每个指针指向一棵树。树是一种递归结构,很多树的问题可以使用递归来处理。
1 树的高度
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
return Math.max(maxDepth(root.left),maxDepth(root.right))+1;
}
2两节点的最长路径
543. Diameter of Binary Tree (Easy)
Input:
1
/ \
2 3
/ \
4 5
Return 3, which is the length of the path [4,2,1,3] or [5,2,1,3].
class Solution {
int ans;
public int diameterOfBinaryTree(TreeNode root) {
ans = 1;
depth(root);
return ans - 1;
}
public int depth(TreeNode node) {
if (node == null) return 0; // 访问到空节点了,返回0
int L = depth(node.left); // 左儿子为根的子树的深度
int R = depth(node.right); // 右儿子为根的子树的深度
ans = Math.max(ans, L+R+1); // 计算d_node即L+R+1 并更新ans
return Math.max(L, R) + 1; // 返回该节点为根的子树的深度
}
}
- compute 每个节点的左右最长子树,
- 与max比较, 计算最长距离;max = (max, node.left.height+node.right.height);
3 相同的树
定两个二叉树,编写一个函数来检验它们是否相同。
如果两个树在结构上相同,并且节点具有相同的值,则认为它们是相同的。
示例 1:
输入: 1 1
/ \ / \
2 3 2 3
[1,2,3], [1,2,3]
输出: true
输入: 1 1
/ \
2 2
[1,2], [1,null,2]
输出: false
- idea: 验证是否p, q同时为空节点, 验证是否只有一个为空,
- 比较连个节点的值, 不相等false。 递归比较左右子节点,直到为空节点,都true时返回true;
class Solution { public boolean isSameTree(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) { if( p == null && q== null ) return true; if(p == nul || q == null) return false; if(p.val != q.val ) return false; return isSameTree(p.left, q.left) && isSameTree(p.right, q.right); } }
4 子树
Given tree s:
3
/ \
4 5
/ \
1 2
Given tree t:
4
/ \
1 2
Return true, because t has the same structure and node values with a subtree of s.
- 和相同树的算法差不多, 都要判断树是否相同, 多了判断每个子树是否相同。
public boolean isSubtree(TreeNode s, TreeNode t) {
if (s == null) return false;
return isSubtreeWithRoot(s, t) || isSubtree(s.left, t) || isSubtree(s.right, t);
}
private boolean isSubtreeWithRoot(TreeNode s, TreeNode t) {
if (t == null && s == null) return true;
if (t == null || s == null) return false;
if (t.val != s.val) return false;
return isSubtreeWithRoot(s.left, t.left) && isSubtreeWithRoot(s.right, t.right);
}
5 求根到叶子节点数字之和
给定一个二叉树,它的每个结点都存放一个 0-9 的数字,每条从根到叶子节点的路径都代表一个数字。
例如,从根到叶子节点路径 1->2->3 代表数字 123。
计算从根到叶子节点生成的所有数字之和。
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例 1:
输入: [1,2,3]
1
/ \
2 3
输出: 25
解释:
从根到叶子节点路径 1->2 代表数字 12.
从根到叶子节点路径 1->3 代表数字 13.
因此,数字总和 = 12 + 13 = 25.
- sum返回结果, curr 保存当前的节点的值, 为计算子节点准备
class Solution {
int sum= 0 ;
private void helper(TreeNode root, int fa){
if(root == null) return ;
int cur = fa*10+root.val; // 左右节点的curr不同;
if(root.right == null && root.left == null){
sum += cur;
return;
}
helper(root.left, cur);
helper(root.right, cur);
}
public int sumNumbers(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return sum;
helper(root, 0);
return sum;
}
}
6 找到树左下角的值
给定一个二叉树,在树的最后一行找到最左边的值。
输入:
1
/ \
2 3
/ / \
4 5 6
/
7
输出:
7
- BFS , 注意先加右边节点到队列中。
class Solution { public int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode root) { Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>(); queue.add(root.val); while(!queue.isEmpty()){ root = queue.poll(); if(root.right != null) queue.add(root.right); if(root.left != null) queue.add(root.left); } return root.val; } }
6 树的构建
public class BST<Key extends Comparable<Key>, Value> {
private Node root; // root of BST
private class Node {
private Key key; // sorted by key
private Value val; // associated data
private Node left, right; // left and right subtrees
private int size; // number of nodes in subtree
public Node(Key key, Value val, int size) {
this.key = key;
this.val = val;
this.size = size;
}
}
/**
* Initializes an empty symbol table.
*/
public BST() {
}
/**
* Returns true if this symbol table is empty.
* @return {@code true} if this symbol table is empty; {@code false} otherwise
*/
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size() == 0;
}
/**
* Returns the number of key-value pairs in this symbol table.
* @return the number of key-value pairs in this symbol table
*/
public int size() {
return size(root);
}
// return number of key-value pairs in BST rooted at x
private int size(Node x) {
if (x == null) return 0;
else return x.size;
}
/**
* Does this symbol table contain the given key?
*
* @param key the key
* @return {@code true} if this symbol table contains {@code key} and
* {@code false} otherwise
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code key} is {@code null}
*/
public boolean contains(Key key) {
if (key == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("argument to contains() is null");
return get(key) != null;
}
/**
* Returns the value associated with the given key.
*
* @param key the key
* @return the value associated with the given key if the key is in the symbol table
* and {@code null} if the key is not in the symbol table
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code key} is {@code null}
*/
public Value get(Key key) {
return get(root, key);
}
private Value get(Node x, Key key) {
if (key == null)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("calls get() with a null key");
if (x == null) return null;
int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key);
if (cmp < 0) return get(x.left, key);
else if (cmp > 0) return get(x.right, key);
else return x.val;
}
/**
* Inserts the specified key-value pair into the symbol table, overwriting the old
* value with the new value if the symbol table already contains the specified key.
* Deletes the specified key (and its associated value) from this symbol table
* if the specified value is {@code null}.
*
* @param key the key
* @param val the value
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code key} is {@code null}
*/
public void put(Key key, Value val) {
if (key == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("calls put() with a null key");
if (val == null) {
delete(key);
return;
}
root = put(root, key, val);
assert check();
}
private Node put(Node x, Key key, Value val) {
if (x == null) return new Node(key, val, 1);
int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key);
if (cmp < 0) x.left = put(x.left, key, val);
else if (cmp > 0) x.right = put(x.right, key, val);
else x.val = val;
x.size = 1 + size(x.left) + size(x.right);
return x;
}
/**
* Removes the smallest key and associated value from the symbol table.
*
* @throws NoSuchElementException if the symbol table is empty
*/
public void deleteMin() {
if (isEmpty()) throw new NoSuchElementException("Symbol table underflow");
root = deleteMin(root);
assert check();
}
private Node deleteMin(Node x) {
if (x.left == null) return x.right;
x.left = deleteMin(x.left);
x.size = size(x.left) + size(x.right) + 1;
return x;
}
/**
* Removes the largest key and associated value from the symbol table.
*
* @throws NoSuchElementException if the symbol table is empty
*/
public void deleteMax() {
if (isEmpty()) throw new NoSuchElementException("Symbol table underflow");
root = deleteMax(root);
assert check();
}
private Node deleteMax(Node x) {
if (x.right == null) return x.left;
x.right = deleteMax(x.right);
x.size = size(x.left) + size(x.right) + 1;
return x;
}
/**
* Removes the specified key and its associated value from this symbol table
* (if the key is in this symbol table).
*
* @param key the key
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code key} is {@code null}
*/
public void delete(Key key) {
if (key == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("calls delete() with a null key");
root = delete(root, key);
assert check();
}
private Node delete(Node x, Key key) {
if (x == null) return null;
int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key);
if (cmp < 0) x.left = delete(x.left, key);
else if (cmp > 0) x.right = delete(x.right, key);
else {
if (x.right == null) return x.left;
if (x.left == null) return x.right;
Node t = x;
x = min(t.right);
x.right = deleteMin(t.right);
x.left = t.left;
}
x.size = size(x.left) + size(x.right) + 1;
return x;
}
/**
* Returns the smallest key in the symbol table.
*
* @return the smallest key in the symbol table
* @throws NoSuchElementException if the symbol table is empty
*/
public Key min() {
if (isEmpty()) throw new NoSuchElementException("calls min() with empty symbol table");
return min(root).key;
}
private Node min(Node x) {
if (x.left == null) return x;
else return min(x.left);
}
/**
* Returns the largest key in the symbol table.
*
* @return the largest key in the symbol table
* @throws NoSuchElementException if the symbol table is empty
*/
public Key max() {
if (isEmpty()) throw new NoSuchElementException("calls max() with empty symbol table");
return max(root).key;
}
private Node max(Node x) {
if (x.right == null) return x;
else return max(x.right);
}
/**
* Returns the largest key in the symbol table less than or equal to {@code key}.
*
* @param key the key
* @return the largest key in the symbol table less than or equal to {@code key}
* @throws NoSuchElementException if there is no such key
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code key} is {@code null}
*/
public Key floor(Key key) {
if (key == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("argument to floor() is null");
if (isEmpty()) throw new NoSuchElementException("calls floor() with empty symbol table");
Node x = floor(root, key);
if (x == null) return null;
else return x.key;
}
private Node floor(Node x, Key key) {
if (x == null) return null;
int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key);
if (cmp == 0) return x;
if (cmp < 0) return floor(x.left, key);
Node t = floor(x.right, key);
if (t != null) return t;
else return x;
}
public Key floor2(Key key) {
return floor2(root, key, null);
}
private Key floor2(Node x, Key key, Key best) {
if (x == null) return best;
int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key);
if (cmp < 0) return floor2(x.left, key, best);
else if (cmp > 0) return floor2(x.right, key, x.key);
else return x.key;
}
/**
* Returns the smallest key in the symbol table greater than or equal to {@code key}.
*
* @param key the key
* @return the smallest key in the symbol table greater than or equal to {@code key}
* @throws NoSuchElementException if there is no such key
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code key} is {@code null}
*/
public Key ceiling(Key key) {
if (key == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("argument to ceiling() is null");
if (isEmpty()) throw new NoSuchElementException("calls ceiling() with empty symbol table");
Node x = ceiling(root, key);
if (x == null) return null;
else return x.key;
}
private Node ceiling(Node x, Key key) {
if (x == null) return null;
int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key);
if (cmp == 0) return x;
if (cmp < 0) {
Node t = ceiling(x.left, key);
if (t != null) return t;
else return x;
}
return ceiling(x.right, key);
}
/**
* Return the key in the symbol table whose rank is {@code k}.
* This is the (k+1)st smallest key in the symbol table.
*
* @param k the order statistic
* @return the key in the symbol table of rank {@code k}
* @throws IllegalArgumentException unless {@code k} is between 0 and
* <em>n</em>–1
*/
public Key select(int k) {
if (k < 0 || k >= size()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("argument to select() is invalid: " + k);
}
Node x = select(root, k);
return x.key;
}
// Return key of rank k.
private Node select(Node x, int k) {
if (x == null) return null;
int t = size(x.left);
if (t > k) return select(x.left, k);
else if (t < k) return select(x.right, k-t-1);
else return x;
}
/**
* Return the number of keys in the symbol table strictly less than {@code key}.
*
* @param key the key
* @return the number of keys in the symbol table strictly less than {@code key}
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code key} is {@code null}
*/
public int rank(Key key) {
if (key == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("argument to rank() is null");
return rank(key, root);
}
// Number of keys in the subtree less than key.
private int rank(Key key, Node x) {
if (x == null) return 0;
int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key);
if (cmp < 0) return rank(key, x.left);
else if (cmp > 0) return 1 + size(x.left) + rank(key, x.right);
else return size(x.left);
}
/**
* Returns all keys in the symbol table as an {@code Iterable}.
* To iterate over all of the keys in the symbol table named {@code st},
* use the foreach notation: {@code for (Key key : st.keys())}.
*
* @return all keys in the symbol table
*/
public Iterable<Key> keys() {
if (isEmpty()) return new Queue<Key>();
return keys(min(), max());
}
/**
* Returns all keys in the symbol table in the given range,
* as an {@code Iterable}.
*
* @param lo minimum endpoint
* @param hi maximum endpoint
* @return all keys in the symbol table between {@code lo}
* (inclusive) and {@code hi} (inclusive)
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if either {@code lo} or {@code hi}
* is {@code null}
*/
public Iterable<Key> keys(Key lo, Key hi) {
if (lo == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("first argument to keys() is null");
if (hi == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("second argument to keys() is null");
Queue<Key> queue = new Queue<Key>();
keys(root, queue, lo, hi);
return queue;
}
private void keys(Node x, Queue<Key> queue, Key lo, Key hi) {
if (x == null) return;
int cmplo = lo.compareTo(x.key);
int cmphi = hi.compareTo(x.key);
if (cmplo < 0) keys(x.left, queue, lo, hi);
if (cmplo <= 0 && cmphi >= 0) queue.enqueue(x.key);
if (cmphi > 0) keys(x.right, queue, lo, hi);
}
/**
* Returns the number of keys in the symbol table in the given range.
*
* @param lo minimum endpoint
* @param hi maximum endpoint
* @return the number of keys in the symbol table between {@code lo}
* (inclusive) and {@code hi} (inclusive)
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if either {@code lo} or {@code hi}
* is {@code null}
*/
public int size(Key lo, Key hi) {
if (lo == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("first argument to size() is null");
if (hi == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("second argument to size() is null");
if (lo.compareTo(hi) > 0) return 0;
if (contains(hi)) return rank(hi) - rank(lo) + 1;
else return rank(hi) - rank(lo);
}
/**
* Returns the height of the BST (for debugging).
*
* @return the height of the BST (a 1-node tree has height 0)
*/
public int height() {
return height(root);
}
private int height(Node x) {
if (x == null) return -1;
return 1 + Math.max(height(x.left), height(x.right));
}
/**
* Returns the keys in the BST in level order (for debugging).
*
* @return the keys in the BST in level order traversal
*/
public Iterable<Key> levelOrder() {
Queue<Key> keys = new Queue<Key>();
Queue<Node> queue = new Queue<Node>();
queue.enqueue(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Node x = queue.dequeue();
if (x == null) continue;
keys.enqueue(x.key);
queue.enqueue(x.left);
queue.enqueue(x.right);
}
return keys;
}
/*************************************************************************
* Check integrity of BST data structure.
***************************************************************************/
private boolean check() {
if (!isBST()) StdOut.println("Not in symmetric order");
if (!isSizeConsistent()) StdOut.println("Subtree counts not consistent");
if (!isRankConsistent()) StdOut.println("Ranks not consistent");
return isBST() && isSizeConsistent() && isRankConsistent();
}
// does this binary tree satisfy symmetric order?
// Note: this test also ensures that data structure is a binary tree since order is strict
private boolean isBST() {
return isBST(root, null, null);
}
// is the tree rooted at x a BST with all keys strictly between min and max
// (if min or max is null, treat as empty constraint)
// Credit: Bob Dondero's elegant solution
private boolean isBST(Node x, Key min, Key max) {
if (x == null) return true;
if (min != null && x.key.compareTo(min) <= 0) return false;
if (max != null && x.key.compareTo(max) >= 0) return false;
return isBST(x.left, min, x.key) && isBST(x.right, x.key, max);
}
// are the size fields correct?
private boolean isSizeConsistent() { return isSizeConsistent(root); }
private boolean isSizeConsistent(Node x) {
if (x == null) return true;
if (x.size != size(x.left) + size(x.right) + 1) return false;
return isSizeConsistent(x.left) && isSizeConsistent(x.right);
}
// check that ranks are consistent
private boolean isRankConsistent() {
for (int i = 0; i < size(); i++)
if (i != rank(select(i))) return false;
for (Key key : keys())
if (key.compareTo(select(rank(key))) != 0) return false;
return true;
}
/**
* Unit tests the {@code BST} data type.
*
* @param args the command-line arguments
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
BST<String, Integer> st = new BST<String, Integer>();
for (int i = 0; !StdIn.isEmpty(); i++) {
String key = StdIn.readString();
if ((st.size() > 1) && (st.floor(key) != st.floor2(key)))
throw new RuntimeException("floor() function inconsistent");
st.put(key, i);
}
for (String s : st.levelOrder())
StdOut.println(s + " " + st.get(s));
StdOut.println();
for (String s : st.keys())
StdOut.println(s + " " + st.get(s));
}
}

