什么是B+树
B+ 树是自平衡树的高级形式,其中所有值都位于叶子节点。 在学习B+树之前要理解的一个重要概念是多级索引。在多级索引中,索引的索引创建如下图。它使访问数据更容易、更快。
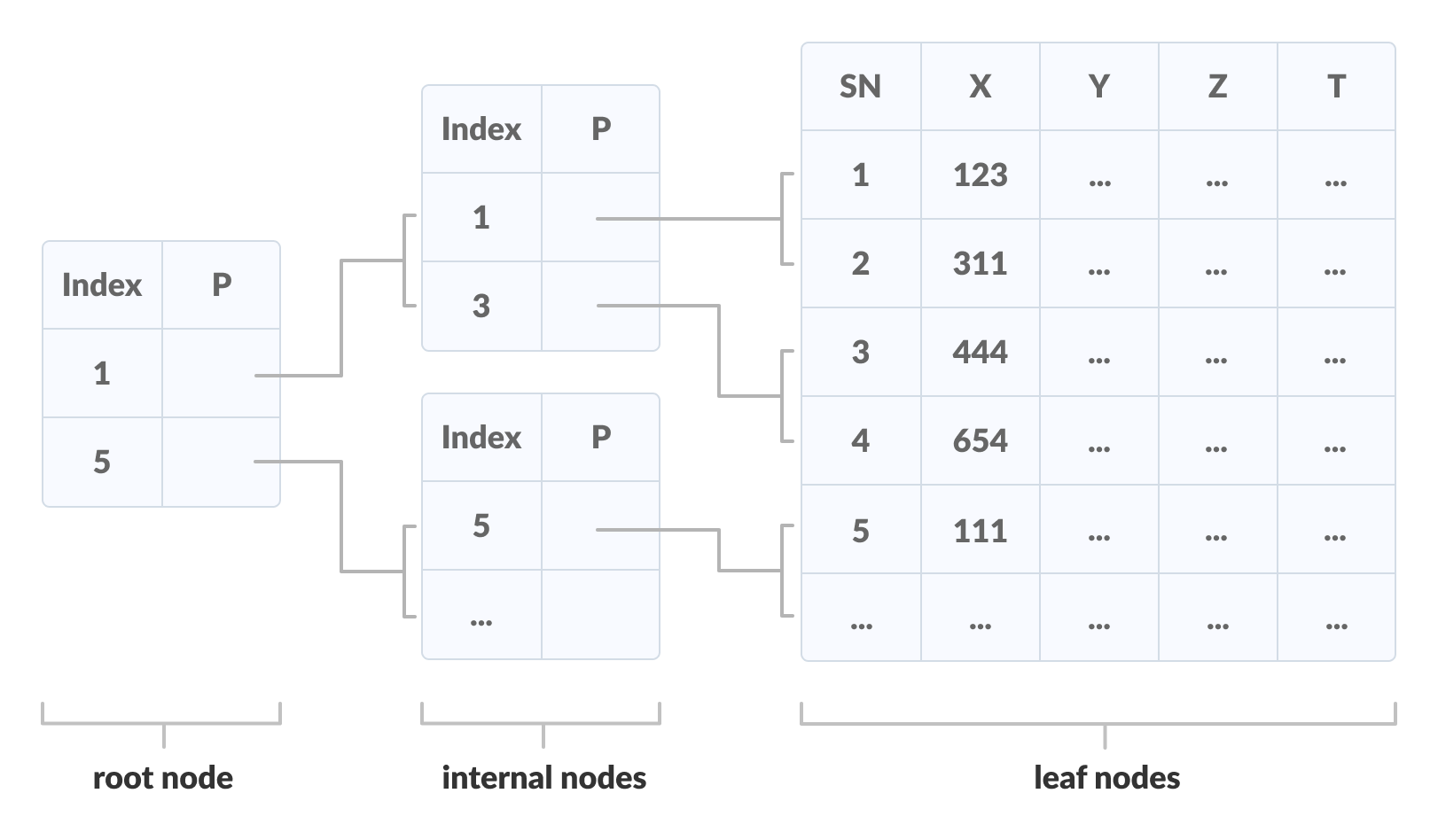 |
|---|
| 使用 B+ 树的多级索引 |
B+树的性质
- 所有的叶子都在同一水平线上。
- 根至少有两个孩子。
- 除根之外的每个节点最多可以有 m 个子节点和至少 m/2 个子节点。
- 每个节点最多可以包含 m - 1 个键和至少 ⌈m/2⌉ - 1 个键。
B树和B+树的比较
数据指针仅存在于 B+树的叶节点中,而数据指针可以存在于B树的内部、叶或根节点中。叶子节点在B树上不相互连接,而它们在B+树上相互连接。B+树上的操作比 B树上的操作快。
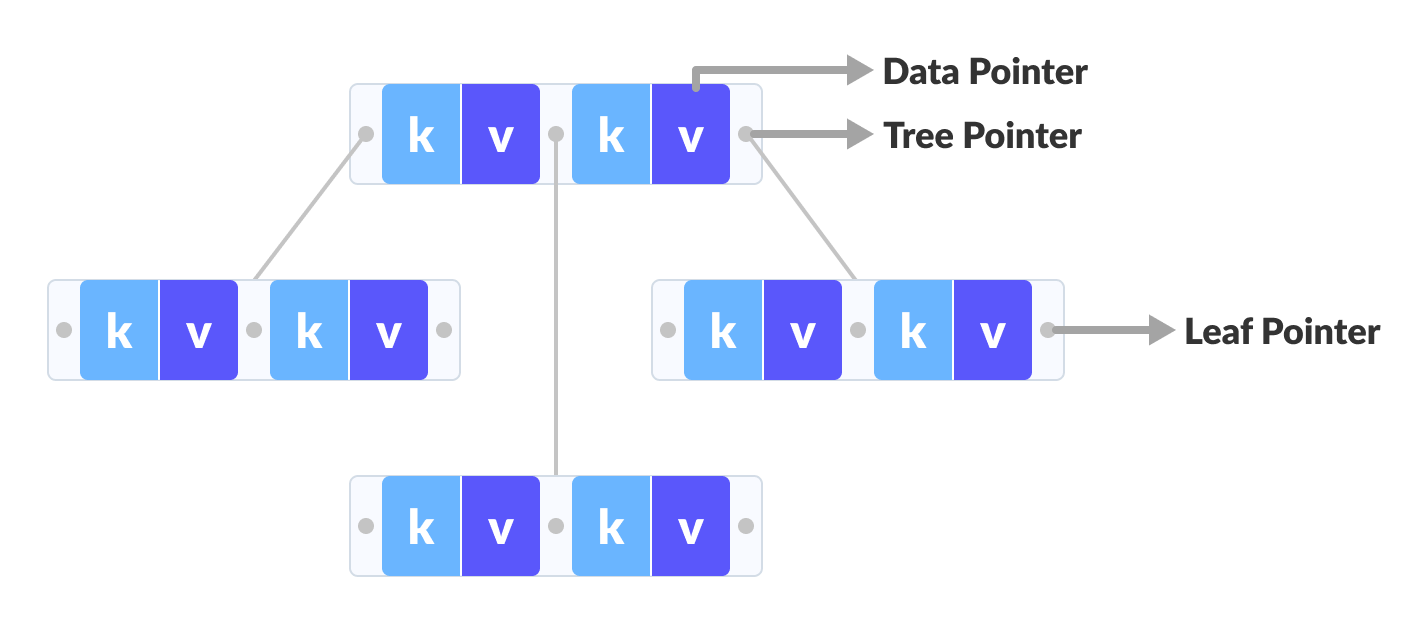 |
|---|
| B树 |
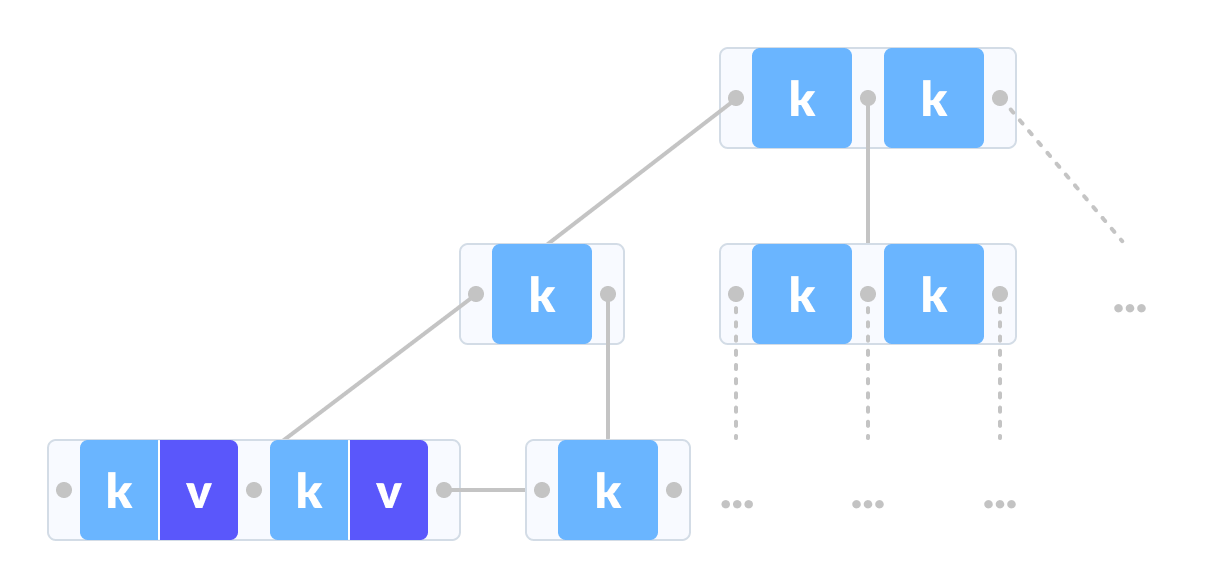 |
|---|
| B+树 |
B+树的操作
B+树的搜索
搜索操作
按照以下步骤在B+序树中搜索的数据为k.
- 从根节点开始。将 k 与根节点的键进行比较 [k1, k2, k3,……km - 1].
- 如果 k < k1,转到根节点的左子节点。
- 否则如果 k == k1, 继续和k2比较. 如果k < k2, 则k 介于k1和 k2之间. 所以搜索k2的左子节点.
- 如果 k > k2, 继续与 k3, k4,…km -1 重复第 2 步和第 3 步。
- 重复以上步骤,直到到达叶子节点。
- 如果 k 存在于叶节点中,则返回 true 否则返回 false。
搜索示例
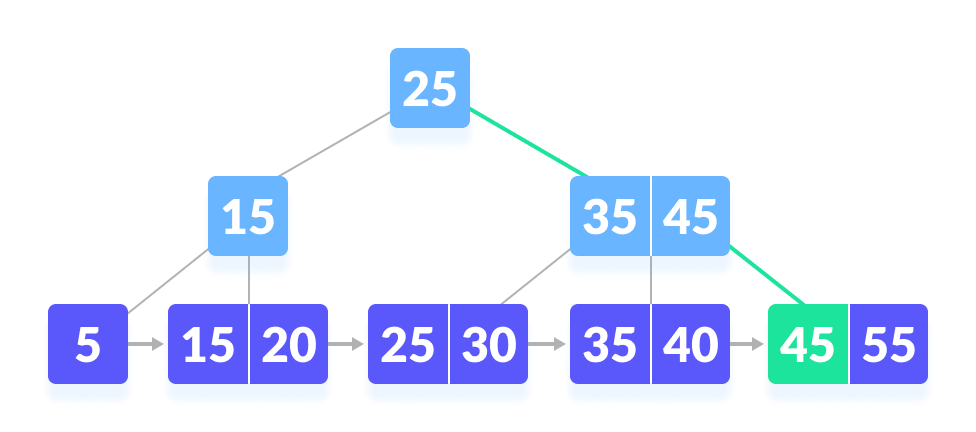
让我们在下面的 B+ 树上搜索 k = 45
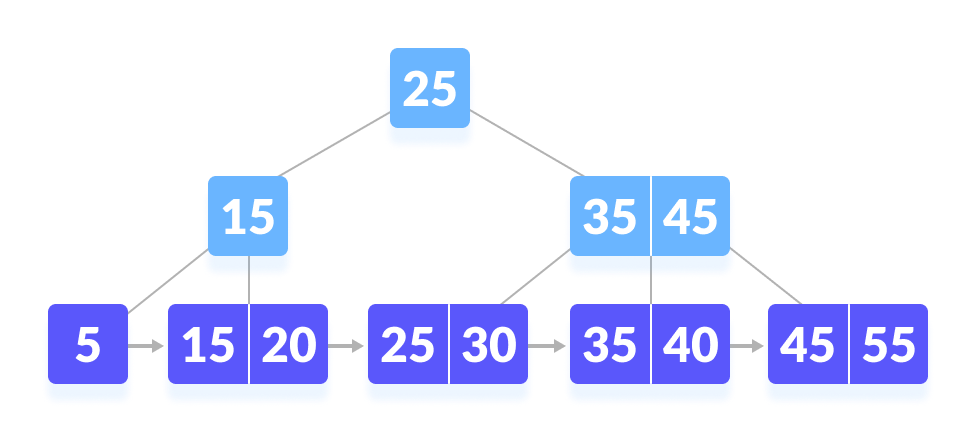 |
|---|
| B+树 |
- 将 k 与根节点进行比较。
|
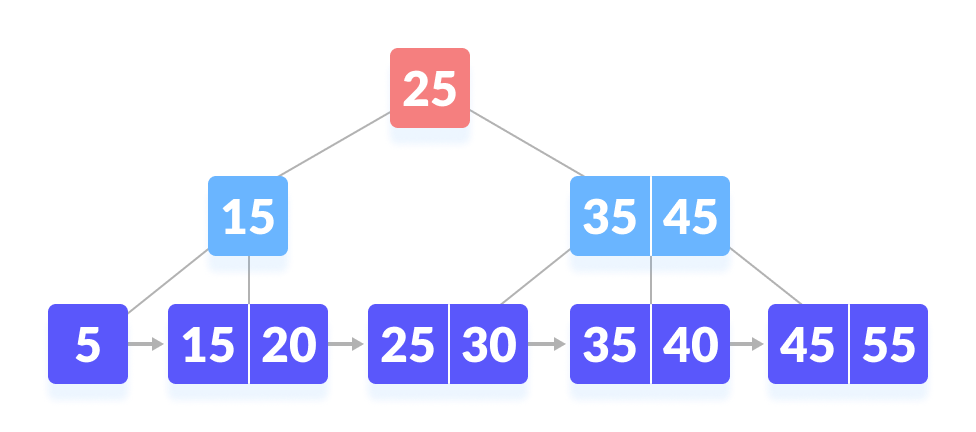 |
| —- |
| 在根处找不到 k |
|
| —- |
| 在根处找不到 k |
- 由于 k > 25,去右孩子。
|
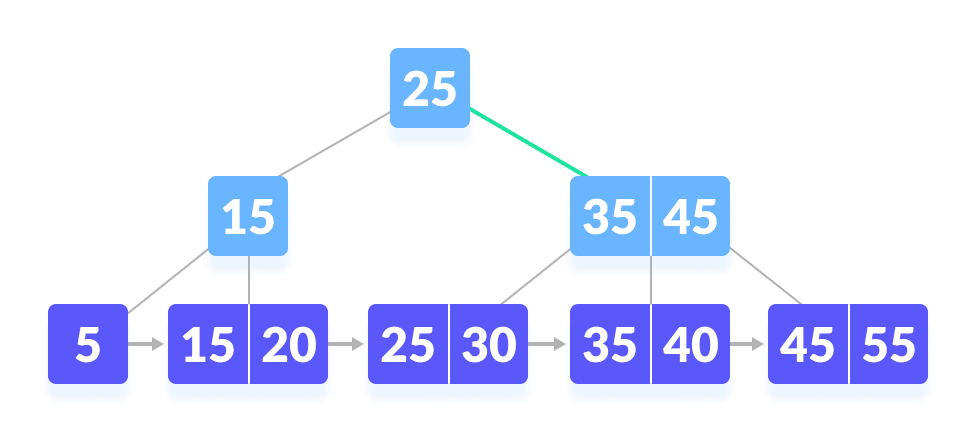 |
| —- |
| 转到根的右侧 |
|
| —- |
| 转到根的右侧 |
- 将 k 与 35 进行比较。由于 k > 30,将 k 与 45 进行比较。
|
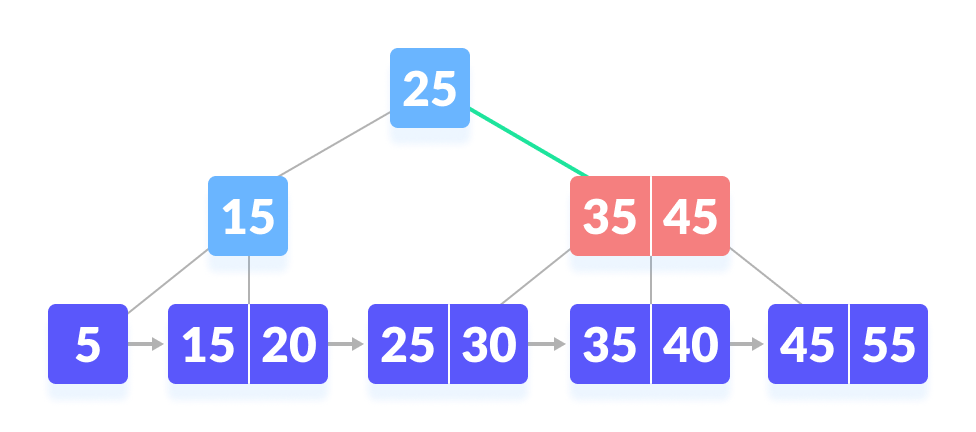 |
| —- |
| 没有找到 |
|
| —- |
| 没有找到 |
- 由于 k ≥ 45,所以继续搜索右孩子。
|
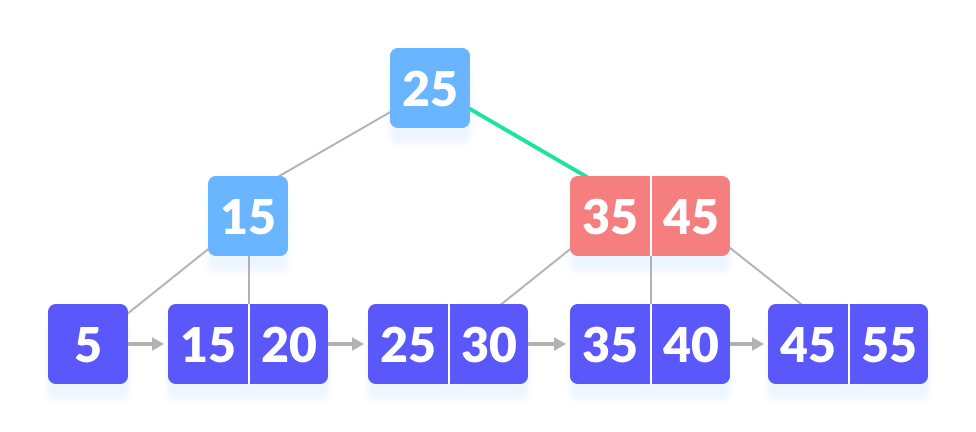 |
| —- |
| 向右走 |
|
| —- |
| 向右走 |
- k 被发现。
|
 |
| —- |
| 找到 k |
|
| —- |
| 找到 k |
搜索时间复杂度
如果在节点内部实现线性搜索,则总复杂度为 Θ(logt n).
如果使用二分查找,则总复杂度为 Θ(log2t.logt n).
B+树的插入
将元素插入B+ 树包括三个主要事件:搜索适当的叶子、插入元素和平衡/分裂树。
插入约束
插入操作在将元素插入 B+ 树之前,必须牢记这些约束:
- 根至少有两个孩子。
- 除根之外的每个节点最多可以有 m 个孩子和至少 m/2 的孩子。
- 每个节点最多可以包含 m - 1 个键和至少 ⌈m/2⌉ - 1 键。
插入算法
按照以下步骤插入元素。
- 由于每个元素都插入到叶节点中,因此请转到相应的叶节点。
- 将key插入叶节点。
案例一:叶子节点未满
- 如果叶子节点未满,则将key按升序插入叶子节点。
案例二:叶子节点已满
- 如果叶子节点已满,则将key按升序插入叶子节点,并按以下方式平衡树。
- 在 m/2 位置断开节点。
- 将m/2位置的key添加到父节点。
- 如果父节点已满,请执行步骤 2 至 3。
插入示例
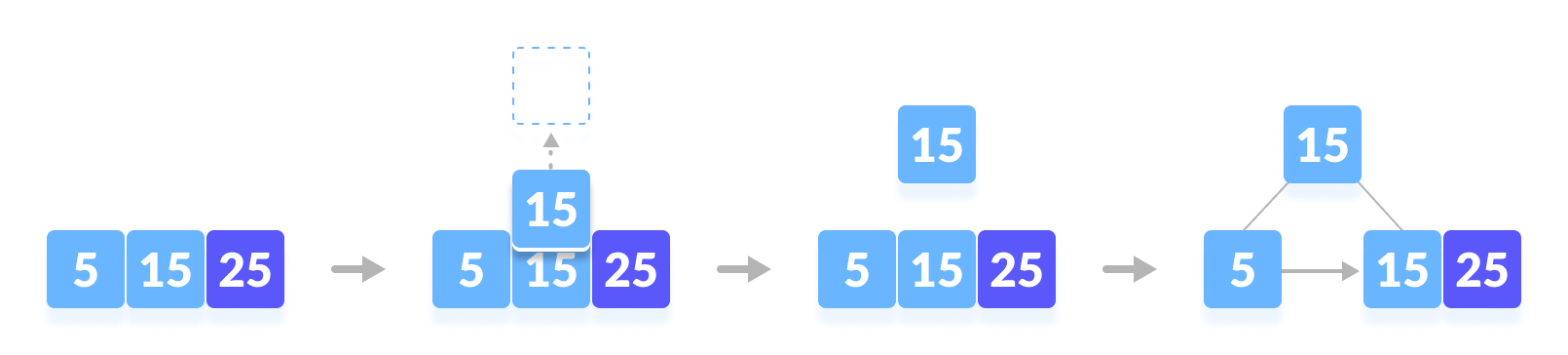
要插入的元素是 5,15, 25, 35, 45。
插入 5 |
 |
| —- |
| 插入 5 |
|
| —- |
| 插入 5 |插入 15 |
 |
| —- |
| 插入 15 |
|
| —- |
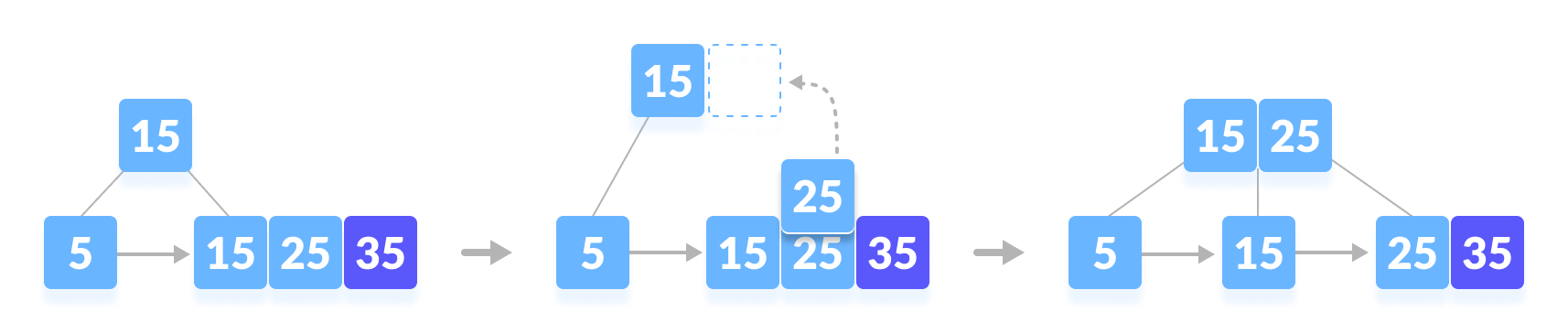
| 插入 15 |插入 25。(在 15 位置分裂成2个节点。 将key 15添加到父节点。) |
 |
| —- |
| 插入 25 |
|
| —- |
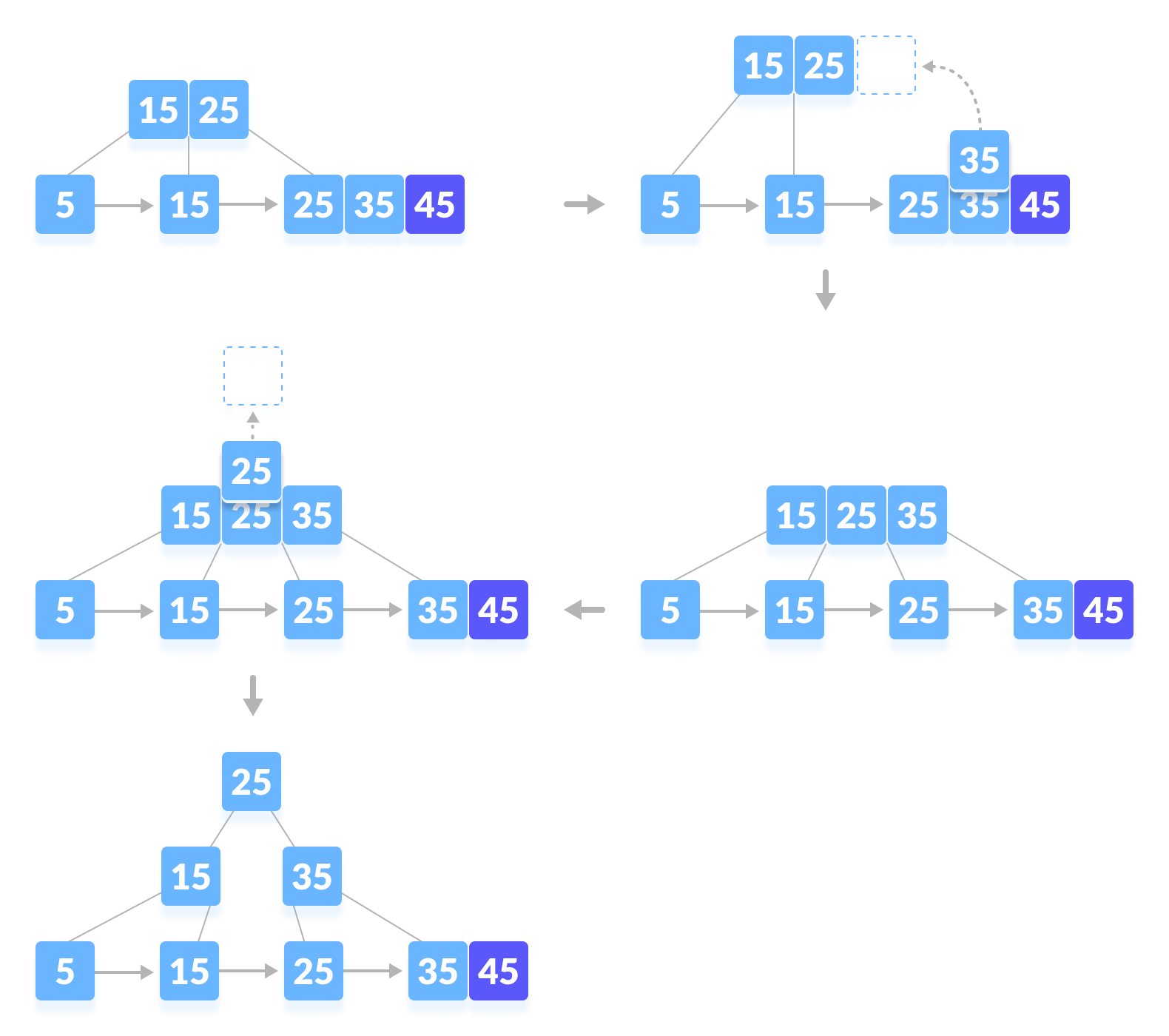
| 插入 25 |插入 35(在 25位置分裂成2个节点。 将key 25添加到父节点。) |
 |
| —- |
| 插入 35 |
|
| —- |
| 插入 35 |插入 45 |
 |
| —- |
| 插入 45 |
|
| —- |
| 插入 45 |
插入复杂度
- 时间复杂度:Θ(t.logt n)
B+树的删除
删除 B+ 树上的元素包括三个主要事件:搜索要删除的键所在的节点,删除键并在需要时平衡树。下溢是一种情况,当节点中的键数少于它应该保存的最小键数时。
删除约束
在进行以下步骤之前,必须了解有关度数为m(例如m=3)的 B+树的这些事实。
- 一个节点最多可以有 m 个子节点。(即 3)
- 一个节点最多可以包含 m - 1 个键。(即 2)
- 一个节点应该有最少的 ⌈m/2⌉ 个子节点。(即 2)
- 一个节点(除了根节点)应该包含最少的⌈m/2⌉ - 1 个键。(即 1)
在删除键时,我们还必须注意内部节点(即索引)中存在的键,因为这些值在 B+ 树中是多余的。搜索要删除的key,然后按照以下步骤操作。
删除算法
案例一:删除的键仅在叶子节点
要删除的键仅存在于叶子节点中,而不存在于索引(或内部节点)中。它有两种情况:
- 节点中的键数超过最少key数量的约束,只需删除key。
|
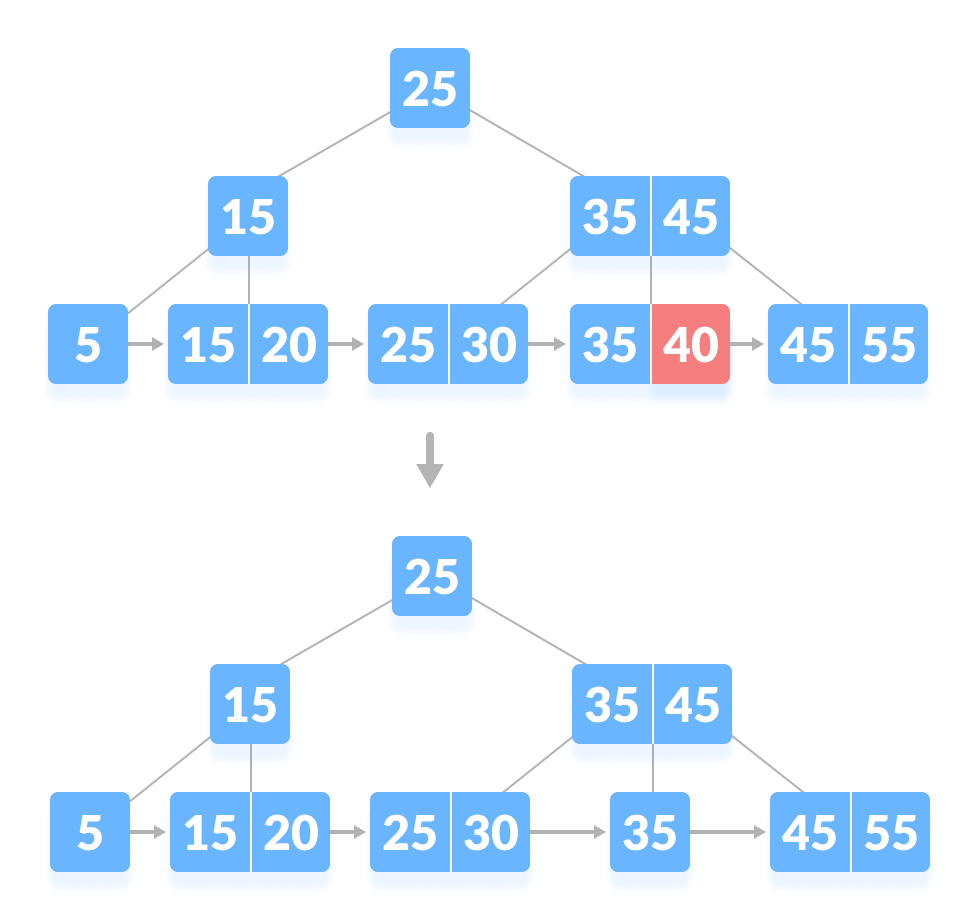 |
| —- |
| 从B+树中删除 40 |
|
| —- |
| 从B+树中删除 40 |
- 节点中的key数量低于最小约束。删除key并从直接兄弟中借用key。将兄弟节点的中间键添加到父节点。
|
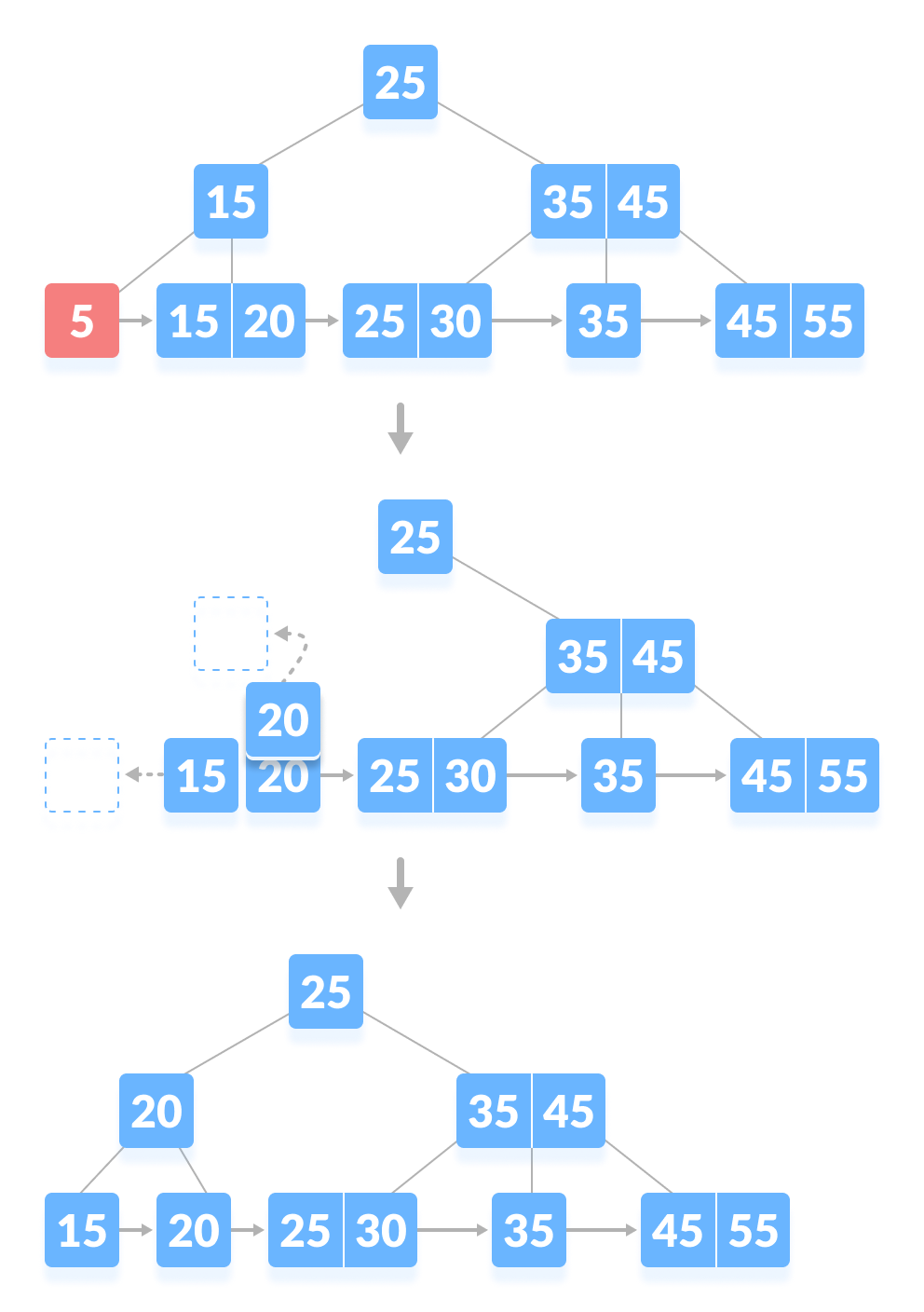 |
| —- |
| 从B+树中删除 5 |
|
| —- |
| 从B+树中删除 5 |
案例二:删除的键也在内部节点
要删除的key即在叶子节点,也存在于内部节点中。然后我们必须从内部节点中删除它们。这种情况有以下几种情况。
- 如果节点中的键数量高于最小数量的约束,只需从叶子节点中删除键并从内部节点中删除键即可。用中序后继填充内部节点中的空白空间。
|
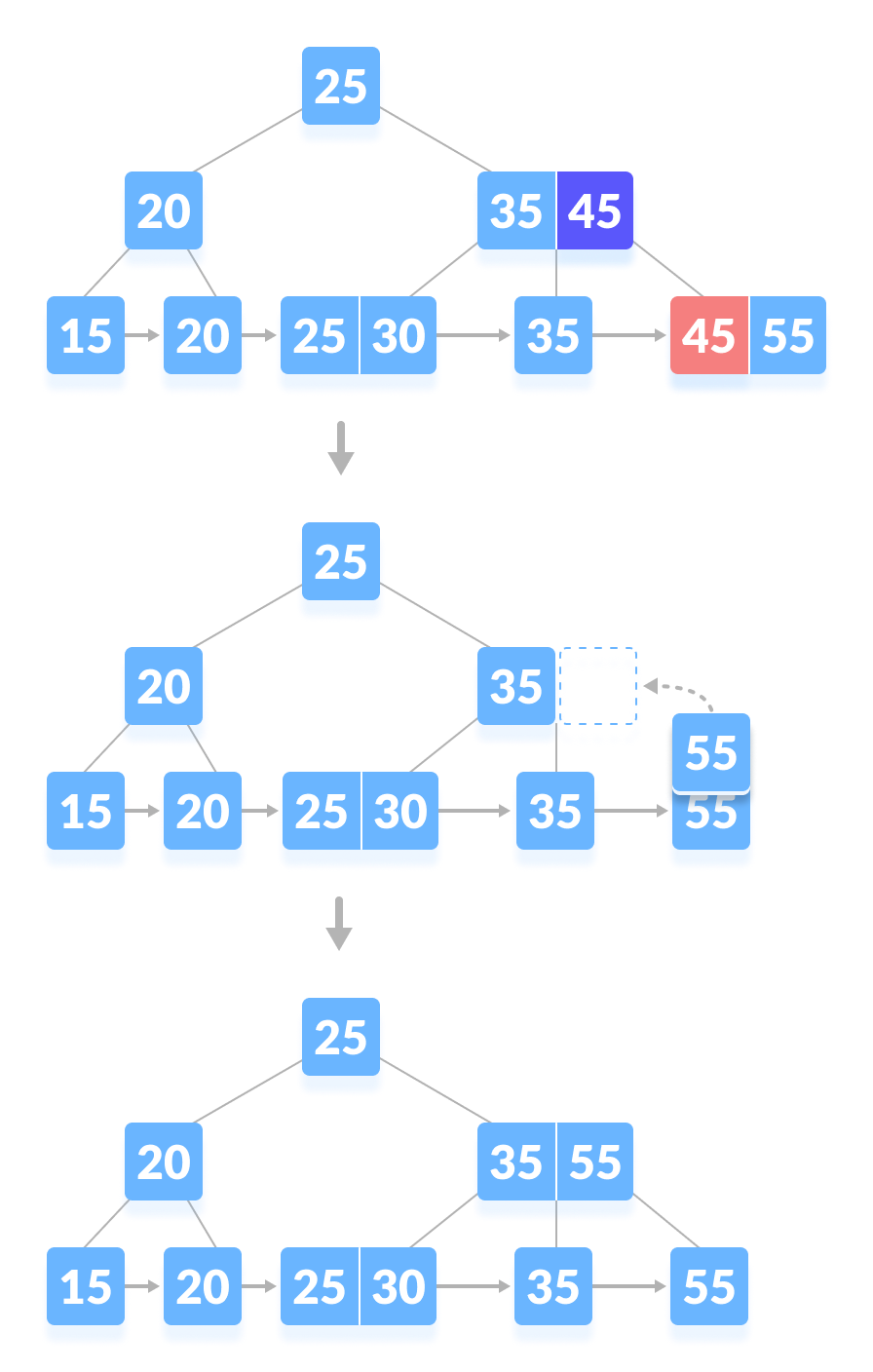 |
| —- |
| 从B+树中删除 45 |
|
| —- |
| 从B+树中删除 45 |
- 如果节点中的键数低于最小数量的约束,则删除该键并从其直接兄弟(通过父级)借用一个键。用借用的键填充索引(内部节点)中创建的空白空间。
|
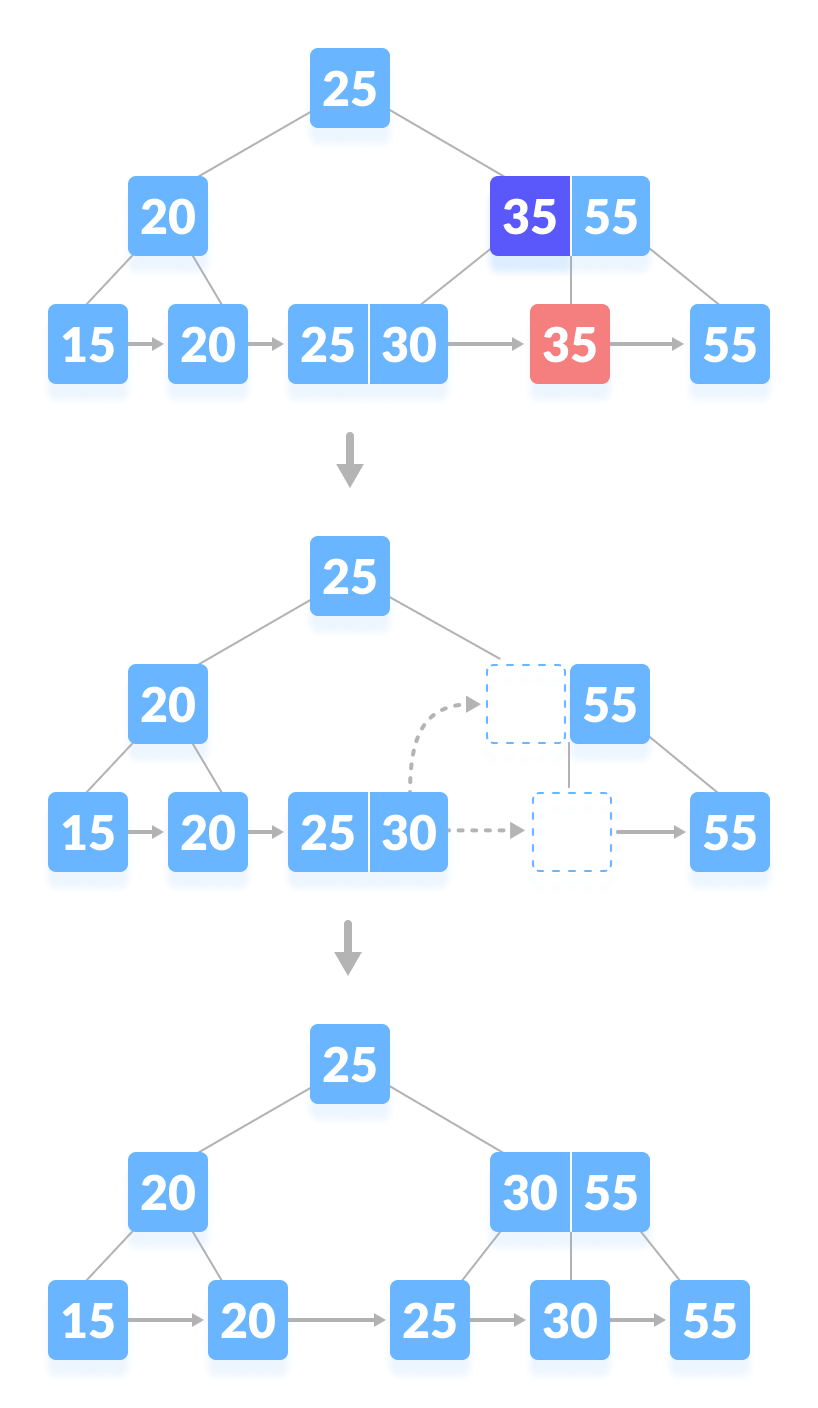 |
| —- |
| 从B+树中删除 35 |
|
| —- |
| 从B+树中删除 35 |
- 这种情况类似于案例二(1),但在这里,在直接父节点上方生成空白空间。删除键后,将空白空间(不一定为空)与其兄弟合并。用中序后继节点填充祖父节点中的空白空间。
|
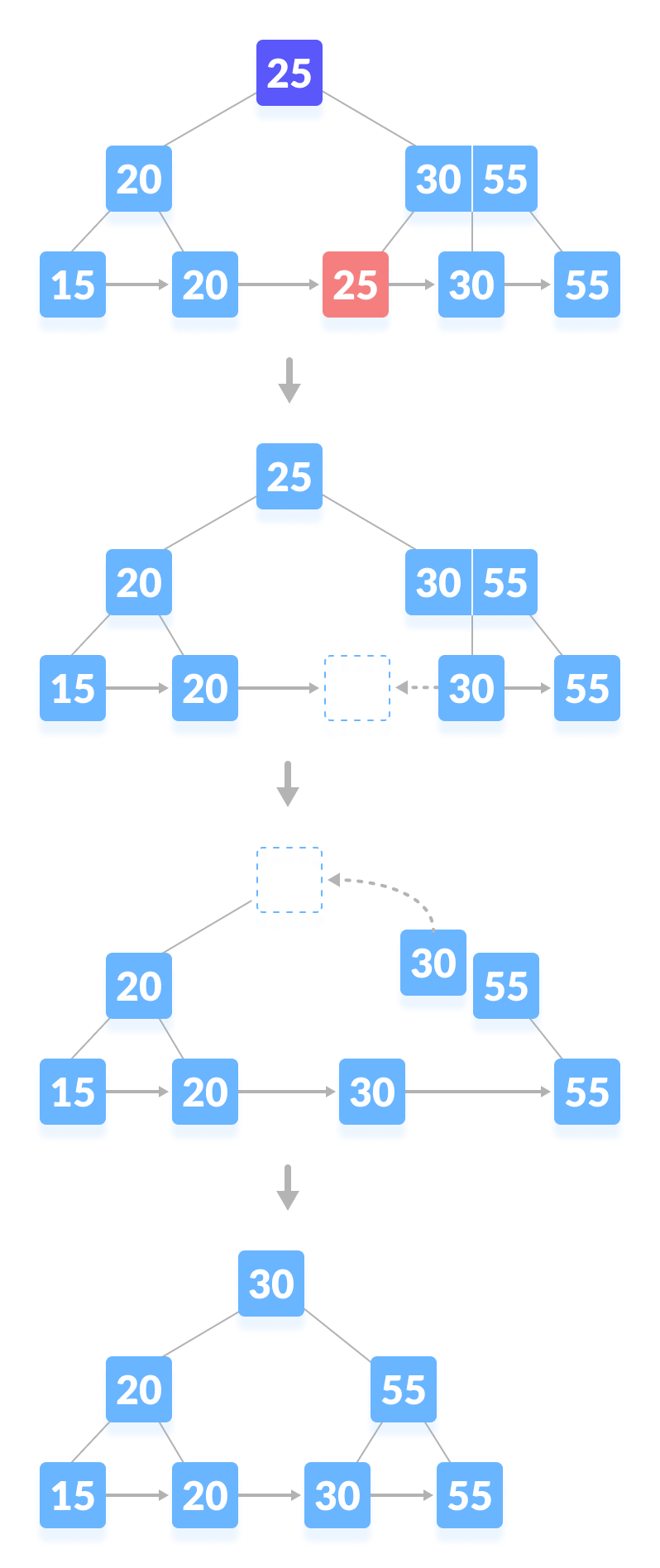 |
| —- |
| 从B+树中删除 25 |
|
| —- |
| 从B+树中删除 25 |
案例三:删除节点导致平衡打破
在这种情况下,树的高度会缩小。有点复杂。从下面的树中删除 55 会导致这种情况。可以在下面的插图中理解。
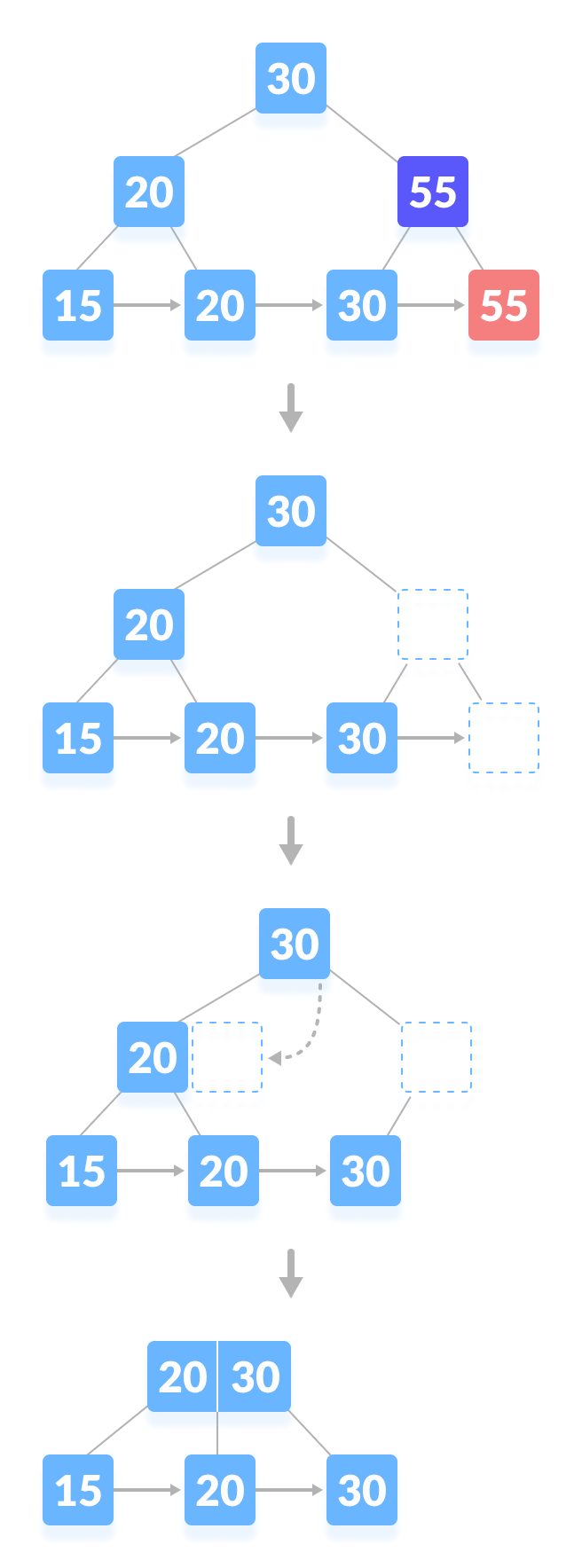 |
|---|
| 从 B 树中删除 55 |
B+树的应用
- 多级索引
- 树上更快的操作(插入、删除、搜索)
- 数据库索引
B+树的实现
// Searching on a B+ tree in Javaimport java.util.*;public class BPlusTree {int m;InternalNode root;LeafNode firstLeaf;// Binary search programprivate int binarySearch(DictionaryPair[] dps, int numPairs, int t) {Comparator<DictionaryPair> c = new Comparator<DictionaryPair>() {@Overridepublic int compare(DictionaryPair o1, DictionaryPair o2) {Integer a = Integer.valueOf(o1.key);Integer b = Integer.valueOf(o2.key);return a.compareTo(b);}};return Arrays.binarySearch(dps, 0, numPairs, new DictionaryPair(t, 0), c);}// Find the leaf nodeprivate LeafNode findLeafNode(int key) {Integer[] keys = this.root.keys;int i;for (i = 0; i < this.root.degree - 1; i++) {if (key < keys[i]) {break;}}Node child = this.root.childPointers[i];if (child instanceof LeafNode) {return (LeafNode) child;} else {return findLeafNode((InternalNode) child, key);}}// Find the leaf nodeprivate LeafNode findLeafNode(InternalNode node, int key) {Integer[] keys = node.keys;int i;for (i = 0; i < node.degree - 1; i++) {if (key < keys[i]) {break;}}Node childNode = node.childPointers[i];if (childNode instanceof LeafNode) {return (LeafNode) childNode;} else {return findLeafNode((InternalNode) node.childPointers[i], key);}}// Finding the index of the pointerprivate int findIndexOfPointer(Node[] pointers, LeafNode node) {int i;for (i = 0; i < pointers.length; i++) {if (pointers[i] == node) {break;}}return i;}// Get the mid pointprivate int getMidpoint() {return (int) Math.ceil((this.m + 1) / 2.0) - 1;}// Balance the treeprivate void handleDeficiency(InternalNode in) {InternalNode sibling;InternalNode parent = in.parent;if (this.root == in) {for (int i = 0; i < in.childPointers.length; i++) {if (in.childPointers[i] != null) {if (in.childPointers[i] instanceof InternalNode) {this.root = (InternalNode) in.childPointers[i];this.root.parent = null;} else if (in.childPointers[i] instanceof LeafNode) {this.root = null;}}}}else if (in.leftSibling != null && in.leftSibling.isLendable()) {sibling = in.leftSibling;} else if (in.rightSibling != null && in.rightSibling.isLendable()) {sibling = in.rightSibling;int borrowedKey = sibling.keys[0];Node pointer = sibling.childPointers[0];in.keys[in.degree - 1] = parent.keys[0];in.childPointers[in.degree] = pointer;parent.keys[0] = borrowedKey;sibling.removePointer(0);Arrays.sort(sibling.keys);sibling.removePointer(0);shiftDown(in.childPointers, 1);} else if (in.leftSibling != null && in.leftSibling.isMergeable()) {} else if (in.rightSibling != null && in.rightSibling.isMergeable()) {sibling = in.rightSibling;sibling.keys[sibling.degree - 1] = parent.keys[parent.degree - 2];Arrays.sort(sibling.keys, 0, sibling.degree);parent.keys[parent.degree - 2] = null;for (int i = 0; i < in.childPointers.length; i++) {if (in.childPointers[i] != null) {sibling.prependChildPointer(in.childPointers[i]);in.childPointers[i].parent = sibling;in.removePointer(i);}}parent.removePointer(in);sibling.leftSibling = in.leftSibling;}if (parent != null && parent.isDeficient()) {handleDeficiency(parent);}}private boolean isEmpty() {return firstLeaf == null;}private int linearNullSearch(DictionaryPair[] dps) {for (int i = 0; i < dps.length; i++) {if (dps[i] == null) {return i;}}return -1;}private int linearNullSearch(Node[] pointers) {for (int i = 0; i < pointers.length; i++) {if (pointers[i] == null) {return i;}}return -1;}private void shiftDown(Node[] pointers, int amount) {Node[] newPointers = new Node[this.m + 1];for (int i = amount; i < pointers.length; i++) {newPointers[i - amount] = pointers[i];}pointers = newPointers;}private void sortDictionary(DictionaryPair[] dictionary) {Arrays.sort(dictionary, new Comparator<DictionaryPair>() {@Overridepublic int compare(DictionaryPair o1, DictionaryPair o2) {if (o1 == null && o2 == null) {return 0;}if (o1 == null) {return 1;}if (o2 == null) {return -1;}return o1.compareTo(o2);}});}private Node[] splitChildPointers(InternalNode in, int split) {Node[] pointers = in.childPointers;Node[] halfPointers = new Node[this.m + 1];for (int i = split + 1; i < pointers.length; i++) {halfPointers[i - split - 1] = pointers[i];in.removePointer(i);}return halfPointers;}private DictionaryPair[] splitDictionary(LeafNode ln, int split) {DictionaryPair[] dictionary = ln.dictionary;DictionaryPair[] halfDict = new DictionaryPair[this.m];for (int i = split; i < dictionary.length; i++) {halfDict[i - split] = dictionary[i];ln.delete(i);}return halfDict;}private void splitInternalNode(InternalNode in) {InternalNode parent = in.parent;int midpoint = getMidpoint();int newParentKey = in.keys[midpoint];Integer[] halfKeys = splitKeys(in.keys, midpoint);Node[] halfPointers = splitChildPointers(in, midpoint);in.degree = linearNullSearch(in.childPointers);InternalNode sibling = new InternalNode(this.m, halfKeys, halfPointers);for (Node pointer : halfPointers) {if (pointer != null) {pointer.parent = sibling;}}sibling.rightSibling = in.rightSibling;if (sibling.rightSibling != null) {sibling.rightSibling.leftSibling = sibling;}in.rightSibling = sibling;sibling.leftSibling = in;if (parent == null) {Integer[] keys = new Integer[this.m];keys[0] = newParentKey;InternalNode newRoot = new InternalNode(this.m, keys);newRoot.appendChildPointer(in);newRoot.appendChildPointer(sibling);this.root = newRoot;in.parent = newRoot;sibling.parent = newRoot;} else {parent.keys[parent.degree - 1] = newParentKey;Arrays.sort(parent.keys, 0, parent.degree);int pointerIndex = parent.findIndexOfPointer(in) + 1;parent.insertChildPointer(sibling, pointerIndex);sibling.parent = parent;}}private Integer[] splitKeys(Integer[] keys, int split) {Integer[] halfKeys = new Integer[this.m];keys[split] = null;for (int i = split + 1; i < keys.length; i++) {halfKeys[i - split - 1] = keys[i];keys[i] = null;}return halfKeys;}public void insert(int key, double value) {if (isEmpty()) {LeafNode ln = new LeafNode(this.m, new DictionaryPair(key, value));this.firstLeaf = ln;} else {LeafNode ln = (this.root == null) ? this.firstLeaf : findLeafNode(key);if (!ln.insert(new DictionaryPair(key, value))) {ln.dictionary[ln.numPairs] = new DictionaryPair(key, value);ln.numPairs++;sortDictionary(ln.dictionary);int midpoint = getMidpoint();DictionaryPair[] halfDict = splitDictionary(ln, midpoint);if (ln.parent == null) {Integer[] parent_keys = new Integer[this.m];parent_keys[0] = halfDict[0].key;InternalNode parent = new InternalNode(this.m, parent_keys);ln.parent = parent;parent.appendChildPointer(ln);} else {int newParentKey = halfDict[0].key;ln.parent.keys[ln.parent.degree - 1] = newParentKey;Arrays.sort(ln.parent.keys, 0, ln.parent.degree);}LeafNode newLeafNode = new LeafNode(this.m, halfDict, ln.parent);int pointerIndex = ln.parent.findIndexOfPointer(ln) + 1;ln.parent.insertChildPointer(newLeafNode, pointerIndex);newLeafNode.rightSibling = ln.rightSibling;if (newLeafNode.rightSibling != null) {newLeafNode.rightSibling.leftSibling = newLeafNode;}ln.rightSibling = newLeafNode;newLeafNode.leftSibling = ln;if (this.root == null) {this.root = ln.parent;} else {InternalNode in = ln.parent;while (in != null) {if (in.isOverfull()) {splitInternalNode(in);} else {break;}in = in.parent;}}}}}public Double search(int key) {if (isEmpty()) {return null;}LeafNode ln = (this.root == null) ? this.firstLeaf : findLeafNode(key);DictionaryPair[] dps = ln.dictionary;int index = binarySearch(dps, ln.numPairs, key);if (index < 0) {return null;} else {return dps[index].value;}}public ArrayList<Double> search(int lowerBound, int upperBound) {ArrayList<Double> values = new ArrayList<Double>();LeafNode currNode = this.firstLeaf;while (currNode != null) {DictionaryPair dps[] = currNode.dictionary;for (DictionaryPair dp : dps) {if (dp == null) {break;}if (lowerBound <= dp.key && dp.key <= upperBound) {values.add(dp.value);}}currNode = currNode.rightSibling;}return values;}public BPlusTree(int m) {this.m = m;this.root = null;}public class Node {InternalNode parent;}private class InternalNode extends Node {int maxDegree;int minDegree;int degree;InternalNode leftSibling;InternalNode rightSibling;Integer[] keys;Node[] childPointers;private void appendChildPointer(Node pointer) {this.childPointers[degree] = pointer;this.degree++;}private int findIndexOfPointer(Node pointer) {for (int i = 0; i < childPointers.length; i++) {if (childPointers[i] == pointer) {return i;}}return -1;}private void insertChildPointer(Node pointer, int index) {for (int i = degree - 1; i >= index; i--) {childPointers[i + 1] = childPointers[i];}this.childPointers[index] = pointer;this.degree++;}private boolean isDeficient() {return this.degree < this.minDegree;}private boolean isLendable() {return this.degree > this.minDegree;}private boolean isMergeable() {return this.degree == this.minDegree;}private boolean isOverfull() {return this.degree == maxDegree + 1;}private void prependChildPointer(Node pointer) {for (int i = degree - 1; i >= 0; i--) {childPointers[i + 1] = childPointers[i];}this.childPointers[0] = pointer;this.degree++;}private void removeKey(int index) {this.keys[index] = null;}private void removePointer(int index) {this.childPointers[index] = null;this.degree--;}private void removePointer(Node pointer) {for (int i = 0; i < childPointers.length; i++) {if (childPointers[i] == pointer) {this.childPointers[i] = null;}}this.degree--;}private InternalNode(int m, Integer[] keys) {this.maxDegree = m;this.minDegree = (int) Math.ceil(m / 2.0);this.degree = 0;this.keys = keys;this.childPointers = new Node[this.maxDegree + 1];}private InternalNode(int m, Integer[] keys, Node[] pointers) {this.maxDegree = m;this.minDegree = (int) Math.ceil(m / 2.0);this.degree = linearNullSearch(pointers);this.keys = keys;this.childPointers = pointers;}}public class LeafNode extends Node {int maxNumPairs;int minNumPairs;int numPairs;LeafNode leftSibling;LeafNode rightSibling;DictionaryPair[] dictionary;public void delete(int index) {this.dictionary[index] = null;numPairs--;}public boolean insert(DictionaryPair dp) {if (this.isFull()) {return false;} else {this.dictionary[numPairs] = dp;numPairs++;Arrays.sort(this.dictionary, 0, numPairs);return true;}}public boolean isDeficient() {return numPairs < minNumPairs;}public boolean isFull() {return numPairs == maxNumPairs;}public boolean isLendable() {return numPairs > minNumPairs;}public boolean isMergeable() {return numPairs == minNumPairs;}public LeafNode(int m, DictionaryPair dp) {this.maxNumPairs = m - 1;this.minNumPairs = (int) (Math.ceil(m / 2) - 1);this.dictionary = new DictionaryPair[m];this.numPairs = 0;this.insert(dp);}public LeafNode(int m, DictionaryPair[] dps, InternalNode parent) {this.maxNumPairs = m - 1;this.minNumPairs = (int) (Math.ceil(m / 2) - 1);this.dictionary = dps;this.numPairs = linearNullSearch(dps);this.parent = parent;}}public class DictionaryPair implements Comparable<DictionaryPair> {int key;double value;public DictionaryPair(int key, double value) {this.key = key;this.value = value;}public int compareTo(DictionaryPair o) {if (key == o.key) {return 0;} else if (key > o.key) {return 1;} else {return -1;}}}public static void main(String[] args) {BPlusTree bpt = null;bpt = new BPlusTree(3);bpt.insert(5, 33);bpt.insert(15, 21);bpt.insert(25, 31);bpt.insert(35, 41);bpt.insert(45, 10);if (bpt.search(15) != null) {System.out.println("Found");} else {System.out.println("Not Found");};}}

