1. 问题出现
使用gin的参数校验,很自然想到参考官方例子https://pkg.go.dev/github.com/gin-gonic/gin#readme-model-binding-and-validation
type Login struct {User string `form:"user" json:"user" xml:"user" binding:"required"`Password string `form:"password" json:"password" xml:"password" binding:"required"`}func main() {router := gin.Default()// Example for binding JSON ({"user": "manu", "password": "123"})router.POST("/loginJSON", func(c *gin.Context) {var json Loginif err := c.ShouldBindJSON(&json); err != nil {c.JSON(http.StatusBadRequest, gin.H{"error": err.Error()})return}if json.User != "manu" || json.Password != "123" {c.JSON(http.StatusUnauthorized, gin.H{"status": "unauthorized"})return}c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{"status": "you are logged in"})})...}
gin参数校验用的是github.com/go-playground/validator库,必须了解一下呀。
官网例子https://github.com/go-playground/validator/blob/master/_examples/simple/main.go
...// User contains user informationtype User struct {FirstName string `validate:"required"`LastName string `validate:"required"`Age uint8 `validate:"gte=0,lte=130"`Email string `validate:"required,email"`FavouriteColor string `validate:"iscolor"` // alias for 'hexcolor|rgb|rgba|hsl|hsla'Addresses []*Address `validate:"required,dive,required"` // a person can have a home and cottage...}...
好家伙,一看就冒出疑惑了,gin中使用的binding tag ,validator的官方例子使用的是validate ,那我到底要用谁?什么情况下该用谁?
2. 源码探究
Go方便就方便在看源码实在太方便了,第一想法就是看看gin中是如何校验的。
首先,从c.ShouldBind()进入看看
context.go
...// ShouldBind checks the Content-Type to select a binding engine automatically,// Depending on the "Content-Type" header different bindings are used:// "application/json" --> JSON binding// "application/xml" --> XML binding// otherwise --> returns an error// It parses the request's body as JSON if Content-Type == "application/json" using JSON or XML as a JSON input.// It decodes the json payload into the struct specified as a pointer.// Like c.Bind() but this method does not set the response status code to 400 and abort if the json is not valid.func (c *Context) ShouldBind(obj interface{}) error {b := binding.Default(c.Request.Method, c.ContentType())return c.ShouldBindWith(obj, b)}...
在进入ShouldBindWith
...// ShouldBindWith binds the passed struct pointer using the specified binding engine.// See the binding package.func (c *Context) ShouldBindWith(obj interface{}, b binding.Binding) error {return b.Bind(c.Request, obj)}...
进入Bind,发现是接口里的方法,
...// Binding describes the interface which needs to be implemented for binding the// data present in the request such as JSON request body, query parameters or// the form POST.type Binding interface {Name() stringBind(*http.Request, interface{}) error}...
然后我们看看该接口有哪些实现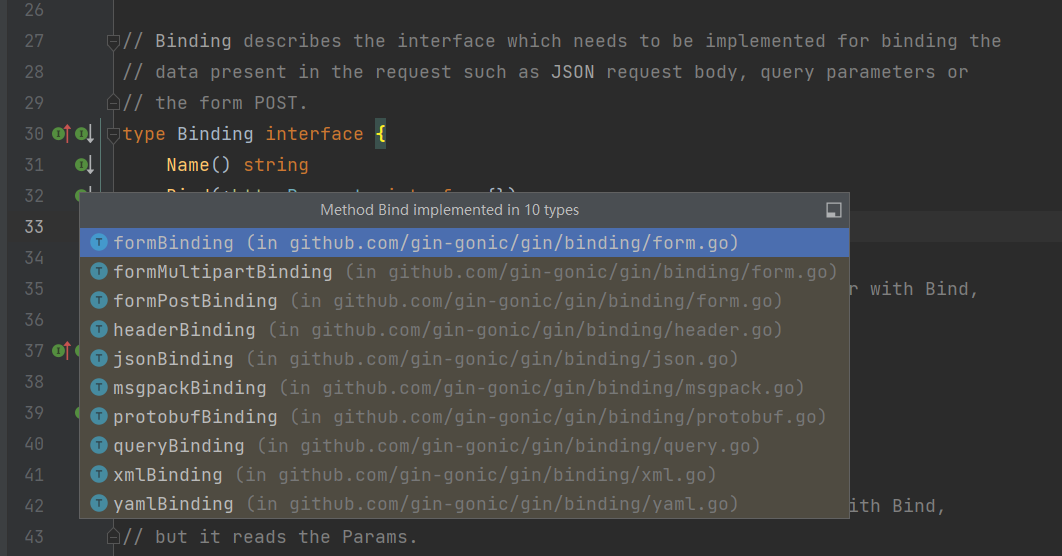
进入formBinding
...func (formBinding) Bind(req *http.Request, obj interface{}) error {if err := req.ParseForm(); err != nil {return err}if err := req.ParseMultipartForm(defaultMemory); err != nil && !errors.Is(err, http.ErrNotMultipart) {return err}if err := mapForm(obj, req.Form); err != nil {return err}return validate(obj)}...
进入validate
...func validate(obj interface{}) error {if Validator == nil {return nil}return Validator.ValidateStruct(obj)}
进入Validator.ValidateStruct,发现也是接口里的方法
...type StructValidator interface {// ValidateStruct can receive any kind of type and it should never panic, even if the configuration is not right.// If the received type is a slice|array, the validation should be performed travel on every element.// If the received type is not a struct or slice|array, any validation should be skipped and nil must be returned.// If the received type is a struct or pointer to a struct, the validation should be performed.// If the struct is not valid or the validation itself fails, a descriptive error should be returned.// Otherwise nil must be returned.ValidateStruct(interface{}) error// Engine returns the underlying validator engine which powers the// StructValidator implementation.Engine() interface{}}...
看看有哪些实现?噢,原来是defaultValidator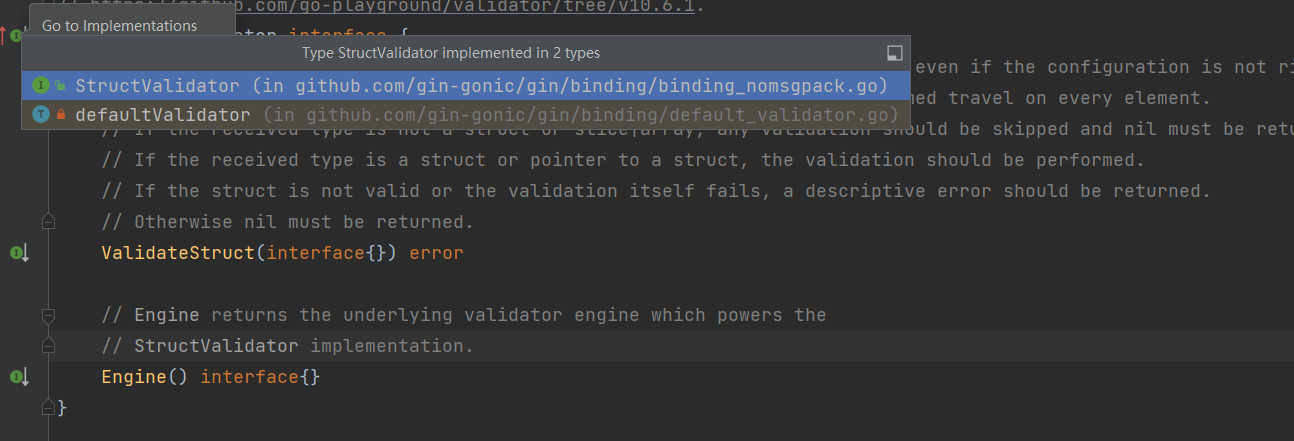
进入defaultValidator的ValidateStruct
...// ValidateStruct receives any kind of type, but only performed struct or pointer to struct type.func (v *defaultValidator) ValidateStruct(obj interface{}) error {if obj == nil {return nil}value := reflect.ValueOf(obj)switch value.Kind() {case reflect.Ptr:return v.ValidateStruct(value.Elem().Interface())case reflect.Struct:return v.validateStruct(obj)case reflect.Slice, reflect.Array:count := value.Len()validateRet := make(SliceValidationError, 0)for i := 0; i < count; i++ {if err := v.ValidateStruct(value.Index(i).Interface()); err != nil {validateRet = append(validateRet, err)}}if len(validateRet) == 0 {return nil}return validateRetdefault:return nil}}...
进入v.validateStruct(obj)
...// validateStruct receives struct typefunc (v *defaultValidator) validateStruct(obj interface{}) error {v.lazyinit()return v.validate.Struct(obj)}// Engine returns the underlying validator engine which powers the default// Validator instance. This is useful if you want to register custom validations// or struct level validations. See validator GoDoc for more info -// https://pkg.go.dev/github.com/go-playground/validator/v10func (v *defaultValidator) Engine() interface{} {v.lazyinit()return v.validate}func (v *defaultValidator) lazyinit() {v.once.Do(func() {v.validate = validator.New()v.validate.SetTagName("binding")})}
找到了找到了,v.validate.SetTagName("binding"),原来是gin封装validator库并设置了标签名;接下来我们看看validator库的默认tag
const (defaultTagName = "validate"...)...// SetTagName allows for changing of the default tag name of 'validate'func (v *Validate) SetTagName(name string) {v.tagName = name}
3. 总结
binding tag 是gin封装validator库后设置的标签名,如果要使用gin封装的校验就使用binding tag ;
如果直接使用validator库就用validate tag

