独立部署
Go 语言支持跨平台交叉编译,也就是说我们可以在 Windows 或 Mac 平台下编写代码,并且将代码编译成能够在 Linux amd64 服务器上运行的程序。
对于简单的项目,通常我们只需要将编译后的二进制文件拷贝到服务器上,然后设置为后台守护进程运行即可。
编译
编译可以通过以下命令或编写 makefile 来操作。
CGO_ENABLED=0 GOOS=linux GOARCH=amd64 go build -o ./bin/bluebell
下面假设我们将本地编译好的 bluebell 二进制文件、配置文件和静态文件等上传到服务器的/data/app/bluebell目录下。
补充一点,如果嫌弃编译后的二进制文件太大,可以在编译的时候加上-ldflags "-s -w"参数去掉符号表和调试信息,一般能减小20%的大小。
CGO_ENABLED=0 GOOS=linux GOARCH=amd64 go build -ldflags "-s -w" -o ./bin/bluebell
如果还是嫌大的话可以继续使用 upx 工具对二进制可执行文件进行压缩。
我们编译好 bluebell 项目后,相关必要文件的目录结构如下:
├── bin│ └── bluebell├── conf│ └── config.yaml├── static│ ├── css│ │ └── app.0afe9dae.css│ ├── favicon.ico│ ├── img│ │ ├── avatar.7b0a9835.png│ │ ├── iconfont.cdbe38a0.svg│ │ ├── logo.da56125f.png│ │ └── search.8e85063d.png│ └── js│ ├── app.9f3efa6d.js│ ├── app.9f3efa6d.js.map│ ├── chunk-vendors.57f9e9d6.js│ └── chunk-vendors.57f9e9d6.js.map└── templates└── index.html
nohup
nohup 用于在系统后台不挂断地运行命令,不挂断指的是退出执行命令的终端也不会影响程序的运行。
我们可以使用 nohup 命令来运行应用程序,使其作为后台守护进程运行。由于在主流的 Linux 发行版中都会默认安装 nohup 命令工具,我们可以直接输入以下命令来启动我们的项目:
sudo nohup ./bin/bluebell conf/config.yaml > nohup_bluebell.log 2>&1 &
其中:
./bluebell conf/config.yaml是我们应用程序的启动命令nohup ... &表示在后台不挂断的执行上述应用程序的启动命令> nohup_bluebell.log表示将命令的标准输出重定向到 nohup_bluebell.log 文件2>&1表示将标准错误输出也重定向到标准输出中,结合上一条就是把执行命令的输出都定向到 nohup_bluebell.log 文件
上面的命令执行后会返回进程 id
[1] 6338
当然我们也可以通过以下命令查看 bluebell 相关活动进程:
ps -ef | grep bluebell
输出:
root 6338 4048 0 08:43 pts/0 00:00:00 ./bin/bluebell conf/config.yamlroot 6376 4048 0 08:43 pts/0 00:00:00 grep --color=auto bluebell
此时就可以打开浏览器输入http://服务器公网ip:端口查看应用程序的展示效果了。
supervisor
Supervisor 是业界流行的一个通用的进程管理程序,它能将一个普通的命令行进程变为后台守护进程,并监控该进程的运行状态,当该进程异常退出时能将其自动重启。
首先使用 yum 来安装 supervisor:
如果你还没有安装过 EPEL,可以通过运行下面的命令来完成安装,如果已安装则跳过此步骤:
sudo yum install epel-release
安装 supervisor
sudo yum install supervisor
Supervisor 的配置文件为:/etc/supervisord.conf ,Supervisor 所管理的应用的配置文件放在 /etc/supervisord.d/ 目录中,这个目录可以在 supervisord.conf 中的include配置。
[include]files = /etc/supervisord.d/*.conf
启动supervisor服务:
sudo supervisord -c /etc/supervisord.conf
我们在/etc/supervisord.d目录下创建一个名为bluebell.conf的配置文件,具体内容如下。
[program:bluebell] ;程序名称user=root ;执行程序的用户command=/data/app/bluebell/bin/bluebell /data/app/bluebell/conf/config.yaml ;执行的命令directory=/data/app/bluebell/ ;命令执行的目录stopsignal=TERM ;重启时发送的信号autostart=trueautorestart=true ;是否自动重启stdout_logfile=/var/log/bluebell-stdout.log ;标准输出日志位置stderr_logfile=/var/log/bluebell-stderr.log ;标准错误日志位置
创建好配置文件之后,重启supervisor服务
sudo supervisorctl update # 更新配置文件并重启相关的程序
查看bluebell的运行状态:
sudo supervisorctl status bluebell
输出:
bluebell RUNNING pid 10918, uptime 0:05:46
最后补充一下常用的supervisr管理命令:
supervisorctl status # 查看所有任务状态supervisorctl shutdown # 关闭所有任务supervisorctl start 程序名 # 启动任务supervisorctl stop 程序名 # 关闭任务supervisorctl reload # 重启supervisor
搭配nginx部署
在需要静态文件分离、需要配置多个域名及证书、需要自建负载均衡层等稍复杂的场景下,我们一般需要搭配第三方的web服务器(Nginx、Apache)来部署我们的程序。
正向代理与反向代理
正向代理可以简单理解为客户端的代理,你访问墙外的网站用的那个属于正向代理。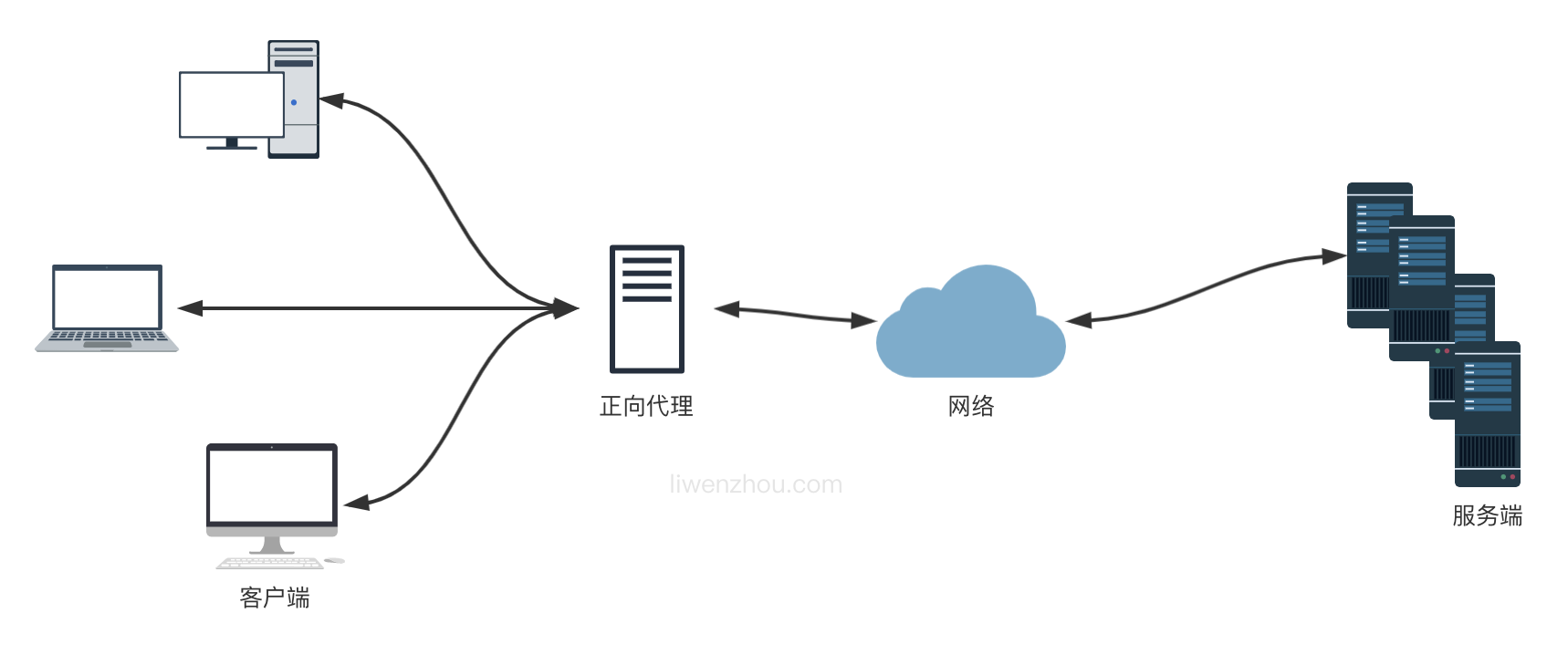
反向代理可以简单理解为服务器的代理,通常说的 Nginx 和 Apache 就属于反向代理。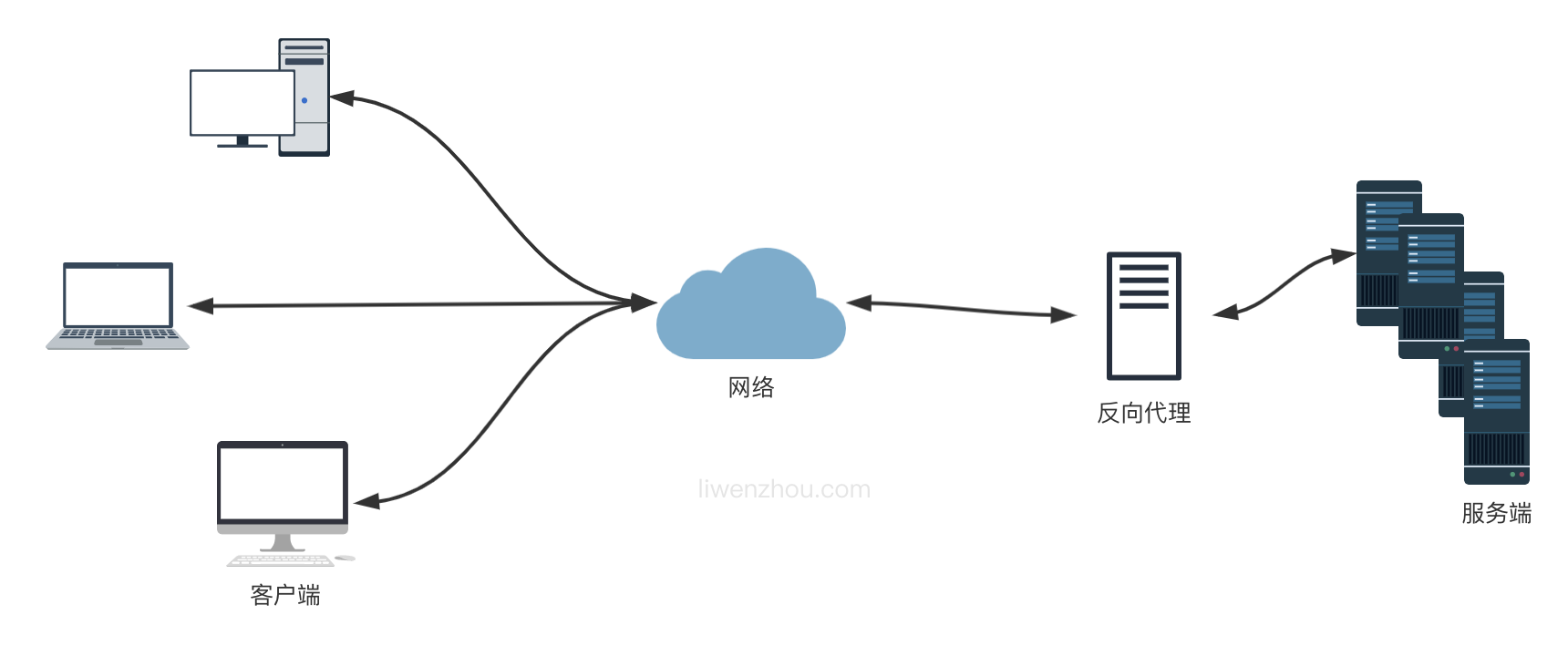
Nginx 是一个免费的、开源的、高性能的 HTTP 和反向代理服务,主要负责负载一些访问量比较大的站点。Nginx 可以作为一个独立的 Web 服务,也可以用来给 Apache 或是其他的 Web 服务做反向代理。相比于 Apache,Nginx 可以处理更多的并发连接,而且每个连接的内存占用的非常小。
使用yum安装nginx
EPEL 仓库中有 Nginx 的安装包。如果你还没有安装过 EPEL,可以通过运行下面的命令来完成安装:
sudo yum install epel-release
安装nginx
sudo yum install nginx
安装完成后,执行下面的命令设置Nginx开机启动:
sudo systemctl enable nginx
启动Nginx
sudo systemctl start nginx
查看Nginx运行状态:
sudo systemctl status nginx
Nginx配置文件
通过上面的方法安装的 nginx,所有相关的配置文件都在 /etc/nginx/ 目录中。Nginx 的主配置文件是 /etc/nginx/nginx.conf。
默认还有一个nginx.conf.default的配置文件示例,可以作为参考。你可以为多个服务创建不同的配置文件(建议为每个服务(域名)创建一个单独的配置文件),每一个独立的 Nginx 服务配置文件都必须以 .conf结尾,并存储在 /etc/nginx/conf.d 目录中。
Nginx常用命令
补充几个 Nginx 常用命令。
nginx -s stop # 停止 Nginx 服务nginx -s reload # 重新加载配置文件nginx -s quit # 平滑停止 Nginx 服务nginx -t # 测试配置文件是否正确
Nginx反向代理部署
我们推荐使用 nginx 作为反向代理来部署我们的程序,按下面的内容修改 nginx 的配置文件。
worker_processes 1;events {worker_connections 1024;}http {include mime.types;default_type application/octet-stream;sendfile on;keepalive_timeout 65;server {listen 80;server_name localhost;access_log /var/log/bluebell-access.log;error_log /var/log/bluebell-error.log;location / {proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8084;proxy_redirect off;proxy_set_header Host $host;proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;}}}
执行下面的命令检查配置文件语法:
nginx -t
执行下面的命令重新加载配置文件:
nginx -s reload
接下来就是打开浏览器查看网站是否正常了。
当然我们还可以使用 nginx 的 upstream 配置来添加多个服务器地址实现负载均衡。
worker_processes 1;events {worker_connections 1024;}http {include mime.types;default_type application/octet-stream;sendfile on;keepalive_timeout 65;upstream backend {server 127.0.0.1:8084;# 这里需要填真实可用的地址,默认轮询#server backend1.example.com;#server backend2.example.com;}server {listen 80;server_name localhost;access_log /var/log/bluebell-access.log;error_log /var/log/bluebell-error.log;location / {proxy_pass http://backend/;proxy_redirect off;proxy_set_header Host $host;proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;}}}
Nginx分离静态文件请求
上面的配置是简单的使用 nginx 作为反向代理处理所有的请求并转发给我们的 Go 程序处理,其实我们还可以有选择的将静态文件部分的请求直接使用 nginx 处理,而将 API 接口类的动态处理请求转发给后端的 Go 程序来处理。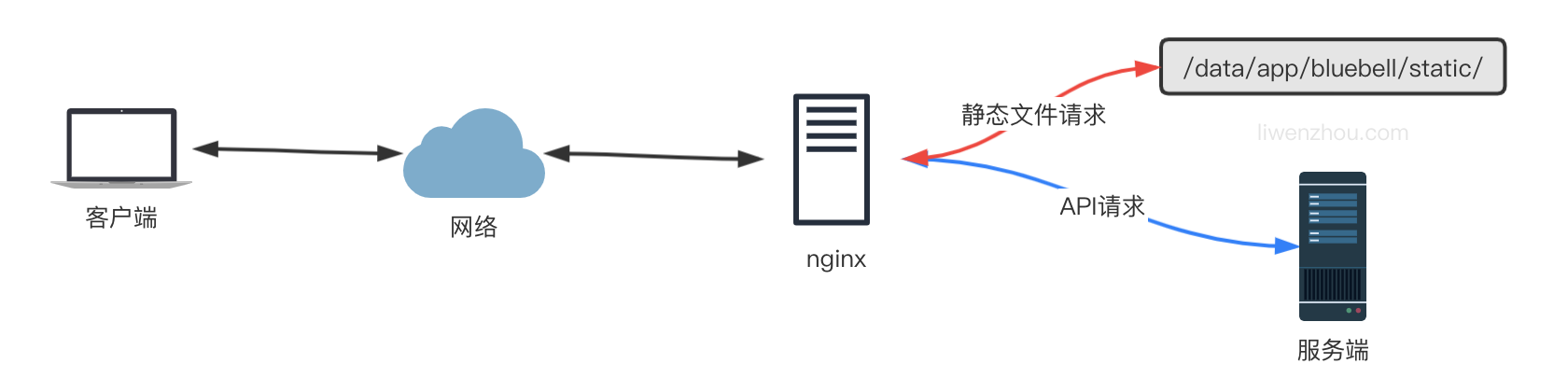
下面继续修改我们的 nginx 的配置文件来实现上述功能。
worker_processes 1;events {worker_connections 1024;}http {include mime.types;default_type application/octet-stream;sendfile on;keepalive_timeout 65;server {listen 80;server_name bluebell;access_log /var/log/bluebell-access.log;error_log /var/log/bluebell-error.log;# 静态文件请求location ~ .*\.(gif|jpg|jpeg|png|js|css|eot|ttf|woff|svg|otf)$ {access_log off;expires 1d;root /data/app/bluebell;}# index.html页面请求# 因为是单页面应用这里使用 try_files 处理一下,避免刷新页面时出现404的问题location / {root /data/app/bluebell/templates;index index.html;try_files $uri $uri/ /index.html;}# API请求location /api {proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8084;proxy_redirect off;proxy_set_header Host $host;proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;}}}
前后端分开部署
前后端的代码没必要都部署到相同的服务器上,也可以分开部署到不同的服务器上,下图是前端服务将 API 请求转发至后端服务的方案。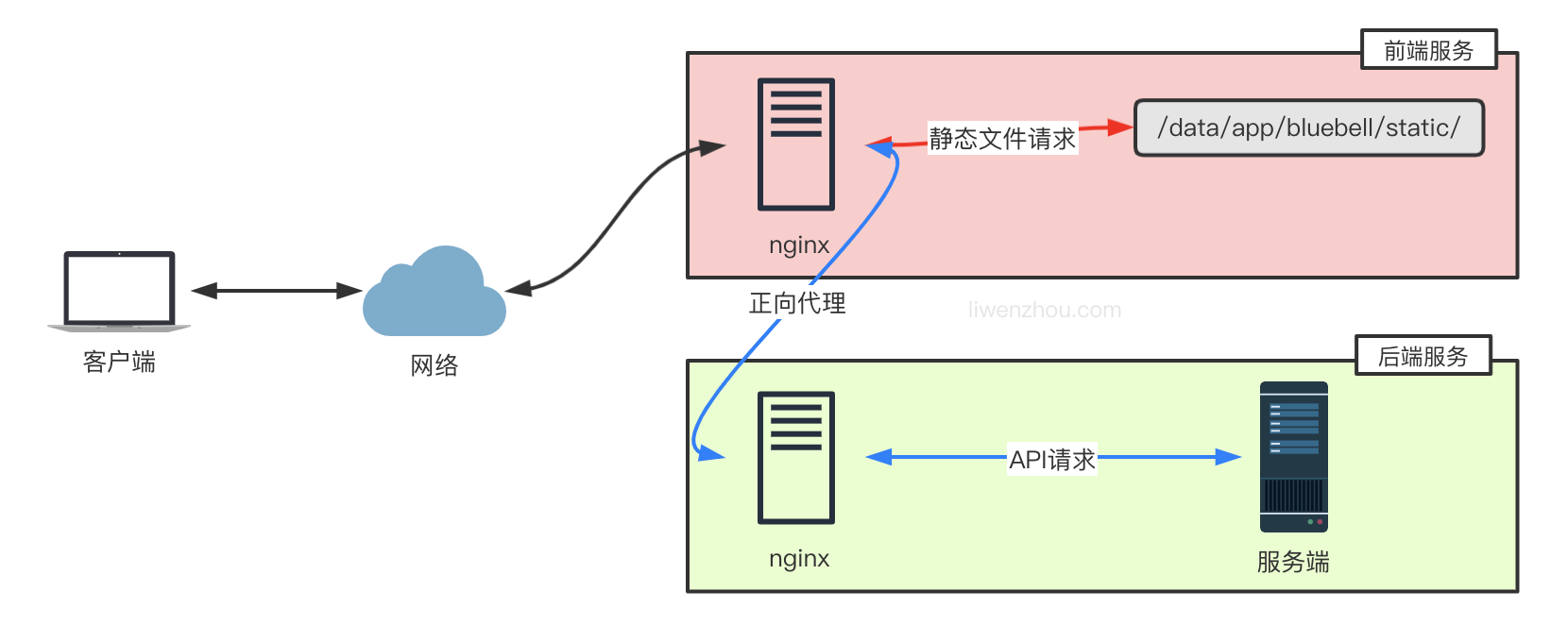
上面的部署方案中,所有浏览器的请求都是直接访问前端服务,而如果是浏览器直接访问后端API服务的部署模式下,如下图。
此时前端和后端通常不在同一个域下,我们还需要在后端代码中添加跨域支持。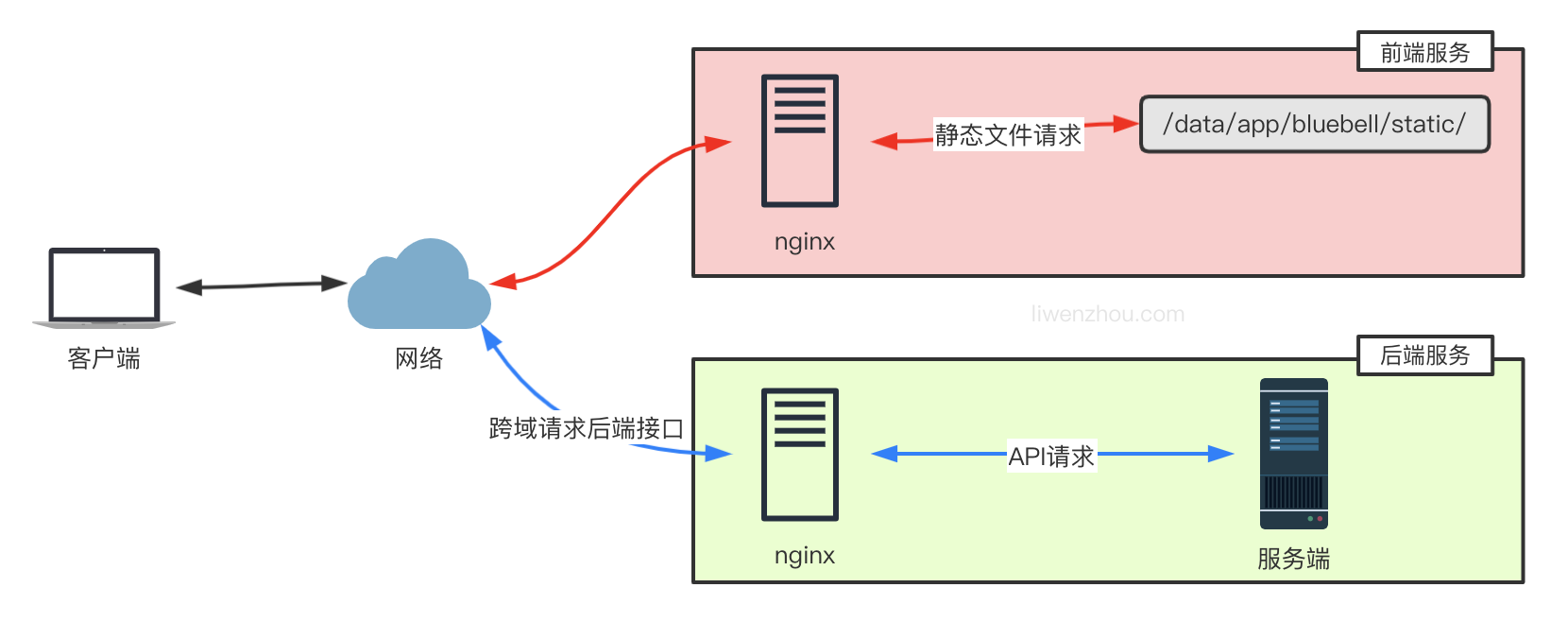
这里使用github.com/gin-contrib/cors库来支持跨域请求。
最简单的允许跨域的配置是使用cors.Default(),它默认允许所有跨域请求。
func main() {router := gin.Default()// same as// config := cors.DefaultConfig()// config.AllowAllOrigins = true// router.Use(cors.New(config))router.Use(cors.Default())router.Run()}
此外,还可以使用cors.Config自定义具体的跨域请求相关配置项:
package mainimport ("time""github.com/gin-contrib/cors""github.com/gin-gonic/gin")func main() {router := gin.Default()// CORS for https://foo.com and https://github.com origins, allowing:// - PUT and PATCH methods// - Origin header// - Credentials share// - Preflight requests cached for 12 hoursrouter.Use(cors.New(cors.Config{AllowOrigins: []string{"https://foo.com"},AllowMethods: []string{"PUT", "PATCH"},AllowHeaders: []string{"Origin"},ExposeHeaders: []string{"Content-Length"},AllowCredentials: true,AllowOriginFunc: func(origin string) bool {return origin == "https://github.com"},MaxAge: 12 * time.Hour,}))router.Run()}

