1 Mysql Collection介绍
MySQL提供NoSQL JSON文档存储(Document Store,mongodb??),从MySQL 5.7版本和MySQL 8.0版本开始,开发者可以在表的一列中存储 JSON 文档。MySQL 5.7 引入的 JSON 数据类型。它允许在表的一行中提供大约1GB大小的列,数据必须是有效的JSON,否则服务器会报错。
MySQL文档存储允许开发者跳过底层数据结构创建、数据规范化和其它使用传统数据库时需要做的工作,直接存储数据。只需创建一个 JSON 文档集合(document collection),接着就可以使用了。通过 X DevAPI,你可以从你的代码中移除令人不爽的结构化查询字符串,改为使用支持现代编程设计的 API 调用。
在Document Store的概念中,collection=table,document=row。
2 collection基本CRUD操作
Collection的基本CRUD函数已经在上一节表中列出:
语雀内容
使用示例如下:
Session sess("localhost", 33060, "barret", "newpasswd");Schema db = sess.getSchema("test");//创建新的collectionCollection coll = db.createCollection("my_collection");//插入几行json documentcoll.add(R"({"name":"barret","age":30})").execute();coll.add(R"({"name":"dandan","age":28})").execute();coll.add(R"({"name":"paopao","age":3})").execute();//查询数据DocResult docs = coll.find("age < :param1").bind("param1", 30).execute();//打印结果cout << docs.fetchOne() << endl;//删除collectiondb.dropCollection("my_collection");
2.1 创建collection
调用DB对象的createCollection()函数,并且可以指定是否覆盖原有同名collection:
// Create a new collection called 'my_collection'Collection myColl = db.createCollection("my_collection");// Create a new collection or reuse existing oneCollection myExistingColl = db.createCollection("my_collection", true)//true表示重用
2.2 获取collection
调用DB对象的getCollection()函数,获取已存在的collection:
// Get a collection object for 'my_collection'Collection myColl = db.getCollection("my_collection");// Get a collection object but also ensure it exists in the databaseCollection myColl = db.getCollection("my_collection", true);//true表示不存在则抛出异常
2.3 collection.add
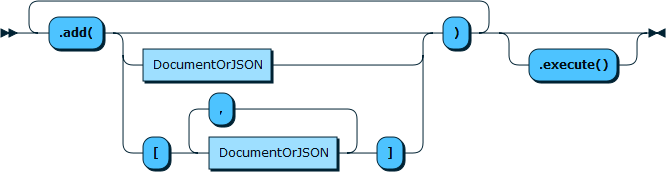
// 插入一条记录coll.add(R"({"name":"Laurie", "age":19})").execute();// 插入多条记录std::list<DbDoc> docs = {DbDoc(R"({"name":"Nadya", "age":54})"),DbDoc(R"({"name":"Lukas", "age":32})")};coll.add(docs).execute();
2.4 collection.find
find函数用于查询json数据,fields(),sort(),skip()和limit()等函数可以用在find之后,作为附加的限定。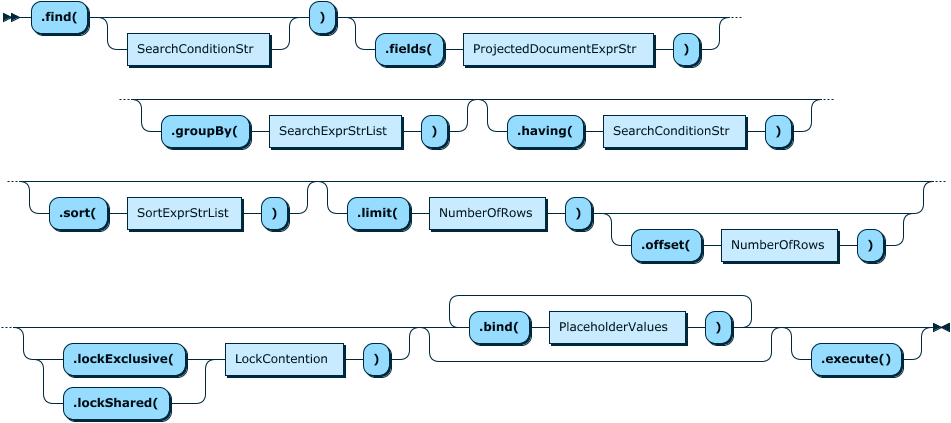
// Find a single document that has a field 'name' that starts with 'L'DocResult docs = myColl.find("name like :param").limit(1).bind("param", "L%").execute();
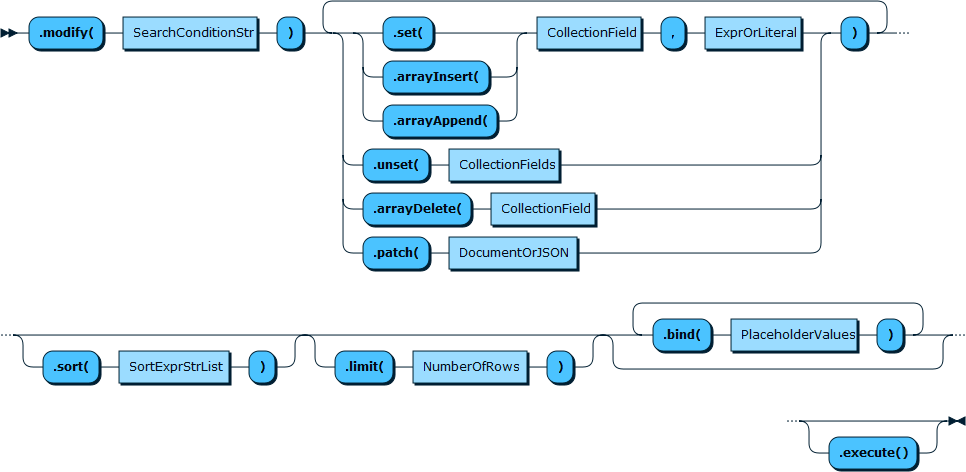
2.4 collection.modify
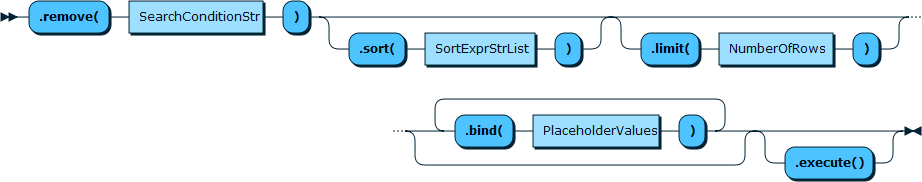
2.5 collection.remove
3 单条记录操作函数
除了上面的基本函数,DevAPI还提供了单独处理一条document记录的函数,前提是必须提供记录的id。
Collection.replaceOne(string id, Document doc)Collection.addOrReplaceOne(string id, Document doc)Collection.getOne(string id)Collection.removeOne(string id)
Document Id唯一标识一个row,在add json数据时,mysql可以自动生成一个名为_id的项,保存随机的id值,并作为add函数的返回值返回。i当然我们也可以在插入数据时,手动指定_id的值(在json数据中,必须使用_id作为key,标识此条记录的id)。
4 将collection当作Table操作
DB的函数getCollectionAsTable可以把collection转换为Table,使用Table的CRUD函数,这样可以统一代码:
// Get the customers collection as a tableTable customers = db.getCollectionAsTable("customers");customers.insert("doc").values(R"({"_id":"001", "name": "Ana", "last_name": "Silva"})").execute();// Now do a find operation to retrieve the inserted documentRowResult result = customers.select("doc->'$.name'", "doc->'$.last_name'").where("doc->'$._id' = '001'").execute();Row record = result.fetchOne();cout << "Name : " << record[0] << endl;cout << "Last Name : " << record[1] << endl;