IO流思维导图
IO知识点多且复杂,对于后期项目优化有重要作用,弄懂IO流是十分必要的
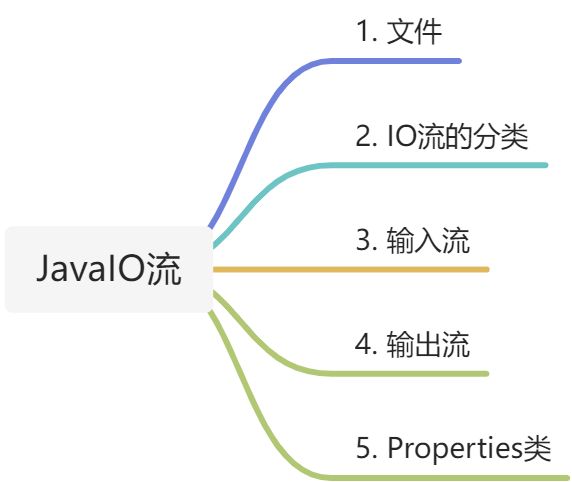
java中的IO流知识梳理
1 文件
1.1 什么是文件?
在生活中可能听到文件的第一反应它可能指是一个文档,但是准确的说文件是一个保存数据的空间,比如音频文件、图片文件、视频文件、文字文件这些统称文件。
1.2 什么是文件流?如何理解流的概念?
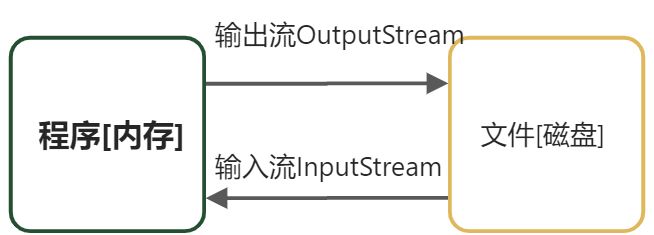
在程序中文件是以流的形式来操作的; 流:指文件与程序(内存)之间的经历路径 输入流:数据从外部存储设备到程序(内存)的路径(只能读) 输出流:数据从程序(内存)到外部存储设备的路径(只能写) 输入输出是针对程序本身而言的,指向程序则为输入流,指向文件则为输出流
1.3 流的作用
作用1:程序读取文件中的数据 作用2:程序把数据写到文件中
2 文件操作
2.1 快速了解File类
- 拿到File类我们发现它在 java.io包下,不在java.lang包下使用时需要导包
File的构造方法有四个 | 构造器 | 说明 | | —- | —- | | File)(File parent, String child) | 从父抽象路径名和子路径名字符串创建新的 File实例。 | | File)(String pathname) | 通过将给定的路径名字符串转换为抽象路径名来创建新的 File实例。 | | File)(String parent, String child) | 从父路径名字符串和子路径名字符串创建新的 File实例。 |
看成员方法; | 方法名 | 说明 | | —- | —- | | String getName)() | 返回此文件或目录的名称。 |
2.2 创建文件
案例1—-创建文件
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {System.out.println("-------------方式1-------------------");// String filePath = "E:\\aba\\test01.txt";// creat02(filePath);System.out.println("---------------方式2-----------------");// String fileName = "test02.txt";// creat01(fileName);System.out.println("----------------方式3----------------");// String parentName = "E:\\aba\\";// String fileNaem = "test03.txt";// creat03(parentName,fileNaem);}//具体方法实现//第一种方式 File(File parent, String child) 创建文件对象public static void creat01(String fileName){File parentFile = new File("E:\\aba\\");File file = new File(parentFile,fileName);try {file.createNewFile();System.out.println("方式1创建成功");} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}//第二种方式 File(String pathname) 创建文件对象private static void creat02(String filePath) {File file = new File(filePath);try {file.createNewFile();System.out.println("方式2创建成功");} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}//第三种方式 File(String parent, String child) 创建文件对象private static void creat03(String parentName, String fileNaem) {File file = new File(parentName,fileNaem);try {file.createNewFile();System.out.println("第3种方式创建成功");} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}
2.3 获取文件相关信息
步骤解析
第一步:创建文件对象 第二步:调用成员方法
案例2—- 获取当前文件对象的文件名
File file = new File("E:\\aba\\testaaa.txt"); //创建文件对象file.createNewFile(); //创建文件System.out.println("获取文件名:"+file.getName()); //用对象调用成员方法,并输出方法名System.out.println("获取文件绝对路径:"+file.getAbsolutePath());System.out.println("获取文件父级目录:"+file.getParent());System.out.println("获取文件大小(字节):"+file.length());System.out.println("判断文件是否存在:"+file.exists());System.out.println("判断是否是一个文件:"+file.isFile());
2.4 目录操作和文件删除
注意:【目录也是一种特殊形式存在的文件】
- mkdir创建一级目录\mkdirs创建多级目录\delete删除空目录或者文件
案例3—- 判断E盘aba目录下是否存在testaaa.txt,如果存在删掉
String filepath = "E:\\aba\\testaaa.txt"; //定义好文件路径File file1 = new File(filepath); //创建文件对象if (file1.exists()){ //判断文件是否存在,再接着往下做if (file1.delete()){System.out.println(filepath+"删除成功!");}else {System.out.println(filepath+"删除失败!");}}else {System.out.println("文件不存在!");}
案例4—-判断e盘下atest目录是否存在,如果存在删除
String documentpath = "E:\\atest"; //定义好文件路径File file2 = new File(documentpath); //创建文件对象if (file2.exists()){ //判断文件是否存在,再接着往下做if (file2.delete()){System.out.println(documentpath+"删除成功!");}else {System.out.println(documentpath+"删除失败!");}}else {System.out.println("目录不存在!");}
3 javaIO流原理及分类
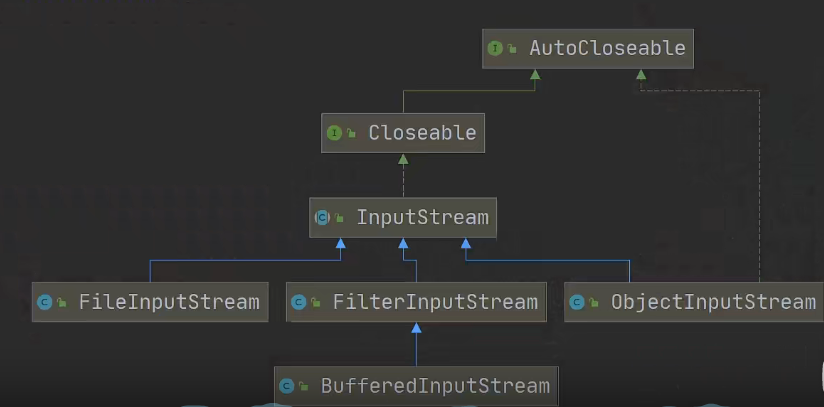
3.1 InputStream的常见子类
| 子类 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| FileInputStream | 文件字节流输入流 |
| BufferedInputStreanm | 缓冲输入流 |
| ObjectInputStream | 对象输入流 |
案例5—-FileInputStream读取文件数据
int read() 从此输入流中读取一个字节的数据。当内容读取结束返回 -1;
//读取E盘下aba目录下test03.txt文件内容String str = "E:\\aba\\test03.txt";FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(str);int count =0;while ((count=fileInputStream.read()) != -1){System.out.print((char) count);}fileInputStream.close();
int read(byte[] b) 从此输入流 b.length最多 b.length字节的数据读 b.length字节数组。最终读取结束后也会返回-1
String str = "E:\\aba\\test03.txt";byte ch [] = new byte[8];int cout = 0;FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(str);while ((cout = fileInputStream.read(ch)) !=-1){String st = new String(ch,0,cout);System.out.print(st);}fileInputStream.close();
3.2 OutputStream的常见子类
- FileOutputStream | 文件字节流输出流
案例6—- 写入文件案例
String filePath = "E:\\aba\\write.txt"; //定义写入路径FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(filePath); //创建文件输出流对象fileOutputStream.write("hello,word".getBytes()); //通过write方法写入文件
注意:【此处创建对象时,在文件路径后加true,则写入数据追加在文件原内容之后,不加true这每次执行都会新写】
书摘
- 该书的金句摘录…
- 该书的金句摘录…
- 该书的金句摘录… | 主页连接 | https://juejin.cn/user/2485331028089560 | | —- | —- | | 姓名: | 左松龙 | | 电话: | 18219899001 | | 地址: | 福建省泉州市南安市康美镇康元路181号 | | | |
相关资料
可通过“⌘+K”插入引用链接,或使用“本地文件”引入源文件。

