NIO解释
NIO模型
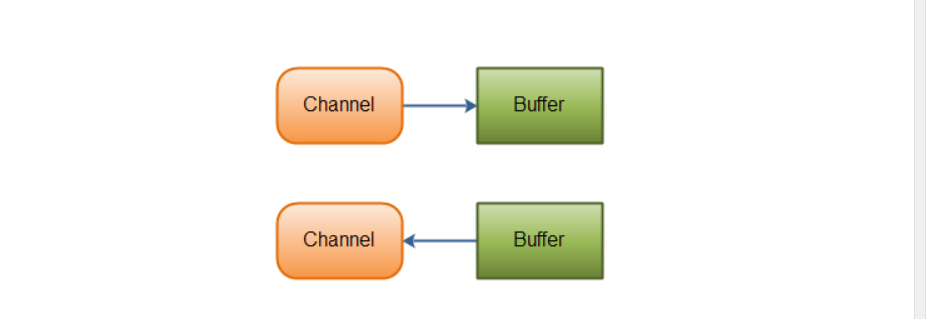
相比经典io基于流的传输,NIO采用的是缓冲区的方式,基于块的传输
Channel分类
- FileChannel
- FileChannnel允许你向文件里读写内容
- DatagramChannel
- DatagramChannel允许你通过UDP协议读写网络上的内容
- SocketChannel
- SocketChannel允许你通过TCP协议读写网络上的内容
ServerSocketChannel
allows you to listen for incoming TCP connections, like a web server does. For each incoming connection a
SocketChannelis created.NIO读写文件Demo
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {RandomAccessFile afile=new RandomAccessFile("E:\\Nio.txt","rw");//使用RandomAccessFile创建文件对象FileChannel fileChannel=afile.getChannel();//获取channelByteBuffer byteBuffer=ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);//创建bufferString mess="fighting for beatiful girl";int j=fileChannel.read(byteBuffer);//这个j代表了一次读出来的字符个数while (j!=-1){System.out.println("reads: "+j);// byteBuffer.flip();//这个flip很重要,修改buffer的模式,由写模式转换为读模式// while (byteBuffer.hasRemaining()){//把字符读完// System.out.print((char)byteBuffer.get());// }// byteBuffer.clear();//本次独处的字符输出完了,清空bytebuffer。j=fileChannel.read(byteBuffer);//buffer此时又是写模式}byte[] we=mess.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8);byteBuffer.put(we);byteBuffer.flip();//将buffer切换为读模式fileChannel.write(byteBuffer);//将buffer里的东西写入文件afile.close();//关闭文件资源}
Buffer
buffer的使用步骤
Using a
Bufferto read and write data typically follows this little 4-step process:
- Write data into the Buffer
- Call
buffer.flip() - Read data out of the Buffer
- Call
buffer.clear()orbuffer.compact()buffer的三个参数
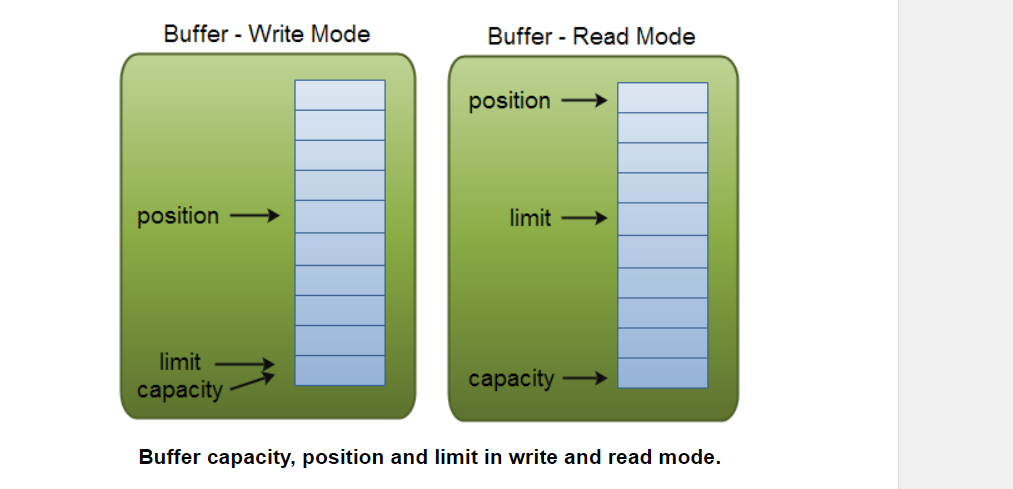
- capacity
- position
- limit
Capacity
Being a memory block, a Buffer has a certain fixed size, also called its “capacity”. You can only write capacity bytes, longs, chars etc. into the Buffer. Once the Buffer is full, you need to empty it (read the data, or clear it) before you can write more data into it.
Position
When you write data into the
Buffer, you do so at a certain position. Initially the position is 0. When a byte, long etc. has been written into theBufferthe position is advanced to point to the next cell in the buffer to insert data into. Position can maximally becomecapacity - 1.When you read data from a
Bufferyou also do so from a given position. When you flip aBufferfrom writing mode to reading mode, the position is reset back to 0. As you read data from theBufferyou do so fromposition, andpositionis advanced to next position to read.Limit
In write mode the limit of a
Bufferis the limit of how much data you can write into the buffer. In write mode the limit is equal to the capacity of theBuffer.
When flipping the Buffer into read mode, limit means the limit of how much data you can read from the data. Therefore, when flipping a Buffer into read mode, limit is set to write position of the write mode. In other words, you can read as many bytes as were written (limit is set to the number of bytes written, which is marked by position).
buffer的类别
- ByteBuffer
- MappedByteBuffer
- CharBuffer
- DoubleBuffer
- FloatBuffer
- IntBuffer
- LongBuffer
- ShortBuffer
初始化buffer
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(48);//用的最多的BufferCharBuffer buf = CharBuffer.allocate(1024);
向buffer中写入数据
int bytesRead = inChannel.read(buf); //read into buffer.从channel中读取数据,写入到bufferbuf.put(127); //直接往buffer里put数据
flip()
The flip() method switches a Buffer from writing mode to reading mode. Calling flip() sets the position back to 0, and sets the limit to where position just was.
In other words, position now marks the reading position, and limit marks how many bytes, chars etc. were written into the buffer - the limit of how many bytes, chars etc. that can be read.
将buffer从写模式切换到读模式。limit为buffer中有多少数据,position切换为0;
从buffer中读取数据
There are two ways you can read data from a Buffer.
- Read data from the buffer into a channel.
- Read data from the buffer yourself, using one of the get() methods. ```java
int bytesWritten = inChannel.write(buf);//从buffer中读取数据,并写入channel,返回一个int,代表写入了多少数据 byte aByte = buf.get();//获取一个字符
There are many other versions of the `get()` method, allowing you to read data from the `Buffer` in many different ways. For instance, reading at specific positions, or reading an array of bytes from the buffer. See the JavaDoc for the concrete buffer implementation for more details.<a name="W6OgH"></a>## rewind()The `Buffer.rewind()` sets the `position` back to 0, so you can reread all the data in the buffer. The `limit` remains untouched, thus still marking how many elements (bytes, chars etc.) that can be read from the `Buffer`.> 将buffer的position设置为0;这样就可以从0开始读取数据。limit不改变<a name="ZgPEo"></a>## clear() and compact()Once you are done reading data out of the `Buffer` you have to make the `Buffer` ready for writing again. You can do so either by calling `clear()` or by calling `compact()`.<br />If you call `clear()` the `position` is set back to 0 and the `limit` to `capacity`. In other words, the `Buffer` is cleared. The data in the `Buffer` is not cleared. Only the markers telling where you can write data into the `Buffer` are.<br />If there is any unread data in the `Buffer` when you call `clear()` that data will be "forgotten", meaning you no longer have any markers telling what data has been read, and what has not been read.<br />If there is still unread data in the `Buffer`, and you want to read it later, but you need to do some writing first, call `compact()` instead of `clear()`.<br />`compact()` copies all unread data to the beginning of the `Buffer`. Then it sets `position` to right after the last unread element. The `limit` property is still set to `capacity`, just like `clear()` does. Now the `Buffer` is ready for writing, but you will not overwrite the unread data.> 当你读了数据之后,应该调用clear方法或者compact方法来使buffer重新可读。> 1. clear方法会将position设置为0;limit设置为capacity大小。但是数据并不会清空。同时你也不会知道是否还有数据没有读,有未读的数据你也读不出来。> 1. compact方法,会将未读的数据移到buffer的开头,并将position置为未读的数据的最后一位,limit依然设置为capacity,但是你不会覆写未读的数据。<a name="x9zil"></a>## mark() and reset()You can mark a given position in a `Buffer` by calling the `Buffer.mark()` method. You can then later reset the position back to the marked position by calling the `Buffer.reset()` method. Here is an example:```javabuffer.mark();//call buffer.get() a couple of times, e.g. during parsing.buffer.reset(); //set position back to mark.
你可以调用 mark方法。将buffer此时的position标记起来。并可通过reset方法,恢复到标记的位点