1、分支结构
1.if
- 根据判定的结果(真或假)决定执行某个分支代码。 ```java //if循环语句格式 //格式1: if(条件表达式){ 语句体; }
//格式2: if(条件表达式){ 语句体; }else{ 语句体; }
//格式3: if(条件表达式1){ 语句体1; }else if(条件表达式2){ 语句体2; }else if(条件表达式3){ 语句体3; } …… else{ 语句体n+1; }
<a name="O28xG"></a>### 2.switch- **是匹配条件去执行分支,适合做值匹配的分支选择,结构清晰,格式良好。****switch分支注意事项:**1. **表达式只能是byte、short、int、char,JDK5开始支持枚举,JDK7开始支持String、不支持double、float、long。**1. **case给出的值不允许重复,且只能是字面量,不能是变量。**1. **不能忘记写break,否则会出现穿透现象。**```java//switch循环语句格式switch(表达式){case 值1:执行代码……;break;case 值2:执行代码……break;……case 值n-1:执行代码……;break;default:执行代码……;}
执行流程:
- 先执行表达式的值,拿着这个值去与case后的值进行匹配。
- 匹配哪个case的值为true就执行哪个case,遇到break就跳出switch分支。
- 如果casae后的值都不能匹配则执行default代码。 ```java switch (weekday){ case “周一”: System.out.println(“今天周一”); break; case “周二”: System.out.println(“今天周二”); break; case “周三”: System.out.println(“今天周三”); break; case “周四”: System.out.println(“今天周四”); break; case “周五”: System.out.println(“今天周五”); break; case “周六”: System.out.println(“今天周六”); break; case “周日”: System.out.println(“今天周日”); break; default: System.out.println(“错误”); }
<a name="zAPZh"></a>### 3.switch穿透性- **存在多个case分支的功能代码是一样时,可以用穿透性把流程集中到同一处处理,这样可以简化代码**```java//穿透前switch(month){case 1:System.out,println("31天");break;case 3:System.out.println("31天");break;case 5:System.out.println("31天");break;case 7:System.out.println("31天");break;case 8:System.out.println("31天");break;case 10:System.out.println("31天");break;case 12:System.out.println("31天");break;default:System.out.println("其他");
//穿透后switch(month){case 1:case 3:case 5:case 7:case 8:case 10:case 12:System.out.println("31天");break;default:System.out.println("其他");
2、循环结构
三种循环的区别
- for循环和while循环(先判断后执行)。
- do…while(第一次先执行后判断)。
for 和 while 的区别
- for循环和while循环的执行流程是一摸一样的。
- 如果已知循环次数建议用for循环,如果不清楚要循环多少次建议用while循环。
- for循环中,控制循环的变量只在循环中可以使用。while循环中,控制循环的变量在循环后还可以继续使用。
1.for循环
- 控制一段代码反复执行很多次。
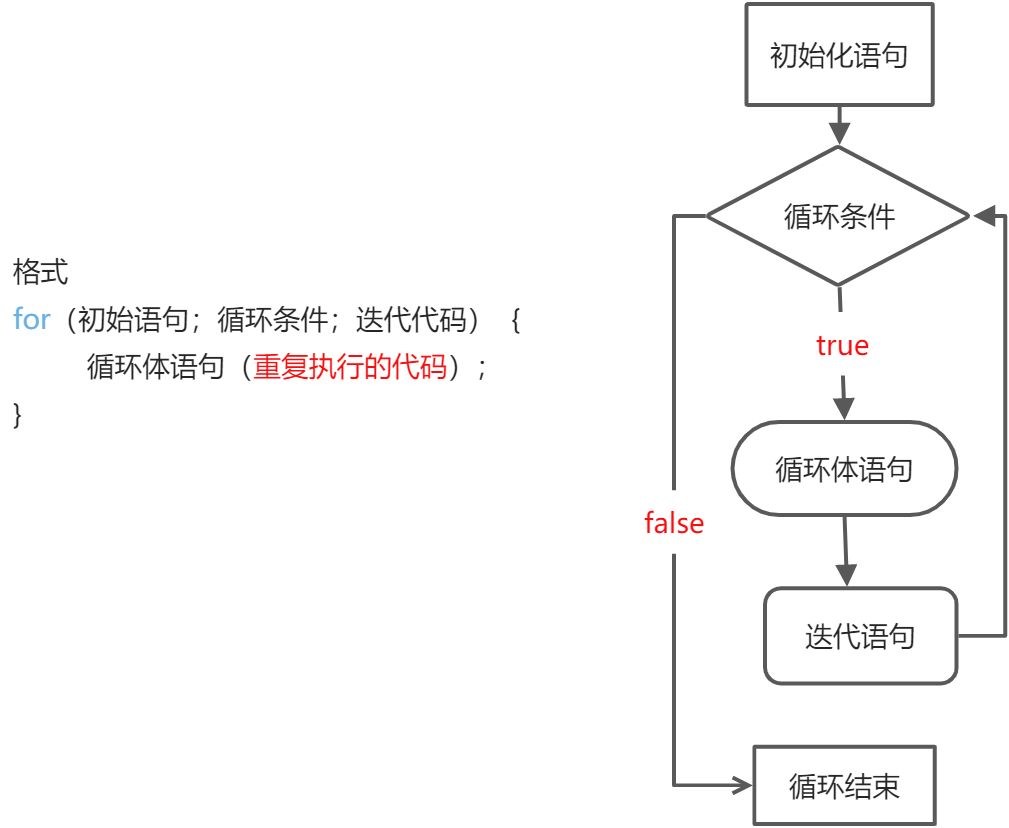
//求和int sum = 0;for (int i = 1; i < 6; i++) {sum +=i;}
//求奇数和int sum = 0;for (int i = 1;i <=10;i++) {if (i % 2 == 1) {sum += i;}}———————————————————————————————int sum = 0;for (int i = 1;i <= 10;i += 2) {sum += i;}
//水仙花数for (i = 100;i <= 999;i++){int ge = i % 10;int shi = i / 10 % 10;int bai = i / 100;if (ge*ge*ge + shi*shi*shi + bai*bai*bai == i) {System.out.print(i+" ");}}
2.while循环
- 当知道循环几次时使用for循环;不知道时可以使用while循环。
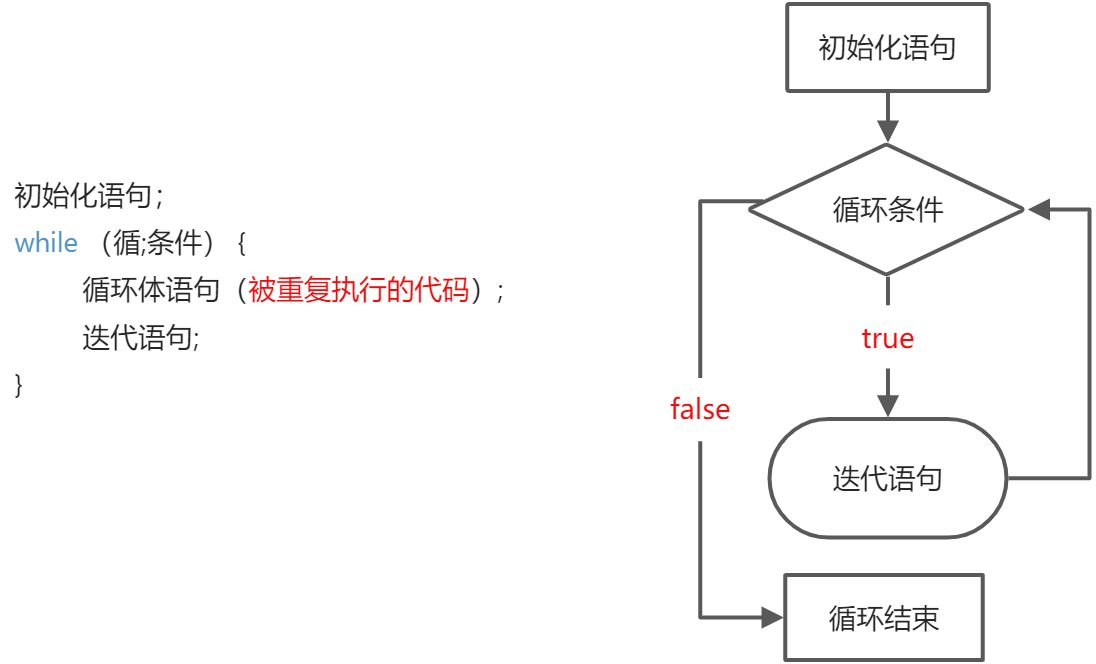
int i = 0;while (i < 3){System.out.println("Hello World");i++;}
double peakHeight = 8848860;double paperThickness = 0.1;int count = 0;while (paperThickness < peakHeight){paperThickness *= 2;count++;}System.out.println("折叠的次数:"+count);System.out.println("纸张的厚度:"+paperThickness);
3.do-while循环
- 特点:一定会先执行一次循环体。
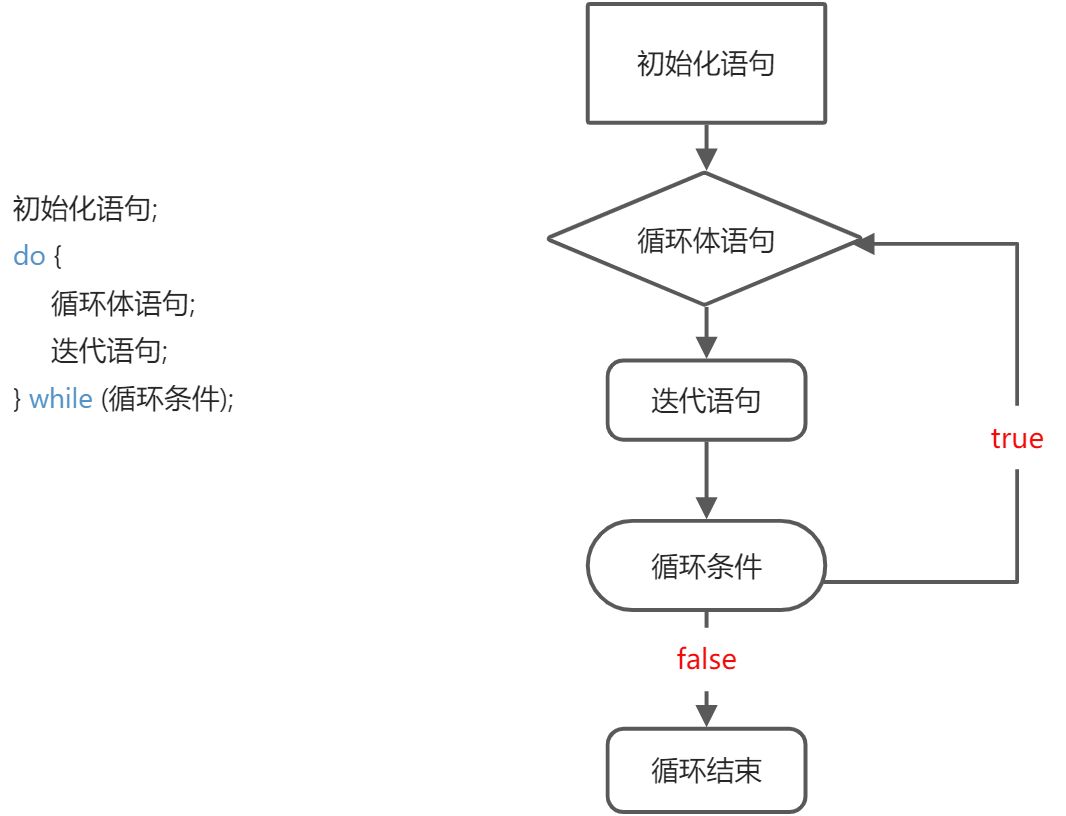
int i = 0;do {System.out.priintln("Hello World");i++;} while (i < 3);
4.死循环
- 一直循环执行下去,如果没有干预不会停止。 ```java for ( ; ; ) { System.out.println(“Hello World”); }
while (true) { System.out.println(“Hello World”); }
do { System.out.println(“Hello World”); } while (true);
<a name="U0dVV"></a>### 5.嵌套循环- **特点:外部循环一次,内部循环全部执行完一次。**```javafor (int i = 0; i < 3;i++) {for (int j = 0;j < 5;j++) {System.out.println("Hello World");}}
3、跳转关键字
- break :跳出并结束当前所在循环的执行。(只能用于结束所在循环,或者所在switch分支的执行)
- continue :用于跳出当前循环的当前执行,进入下一次循环。(只能在循环中进行使用)
- return; : 可以立即跳出并结束当前方法的执行;return关键字可以放在任何方法中。

