线程池使用FutureTask的时候如果拒绝策略设置为了DiscardPolicy和DiscardOldestPolicy
并且在被拒绝的任务的Future对象上调用无参get方法那么调用线程会一直被阻塞。
阿里巴巴手册
【强制】线程池不允许使用 Executors 去创建,而是通过 ThreadPoolExecutor 的方式,这样的处理方式让写的同学更加明确线程池的运行规则,规避资源耗尽的风险
因为:
该任务队列是LinkedBlockingQueue,是无界队列,如果任务数量特别多,可能会导致内存不足
是无界队列
线程池的四种池
1、FixedThreadPool 和 SingleThreadPool:
允许的请求队列长度为 Integer.MAX_VALUE,可能会堆积大量的请求,从而导致 OOM。
2、CachedThreadPool 和 ScheduledThreadPool:
允许的创建线程数量为 Integer.MAX_VALUE,可能会创建大量的线程,从而导致 OOM
自定义线程池的重要参数含义
1.corePoolSize 指定了线程池里的线程数量
2.maximumPoolSize 指定了线程池里的最大线程数量
3.keepAliveTime 当线程池线程数量大于corePoolSize时候,多出来的空闲线程,多长时间会被销毁。
4.unit 时间单位
5.workQueue 任务队列,用于存放提交但是尚未被执行的任务。
6.threadFactory 线程工厂,用于创建线程,一般可以用默认的
7.handler 拒绝策略,当任务过多时候,如何拒绝任务。
corePoolSize and maximumPoolSize 解释意义流程图

corePoolSize:核心线程数;maximunPoolSize:最大线程数
每当有新的任务到线程池时,
第一步: 先判断线程池中当前线程数量是否达到了corePoolSize,若未达到,则新建线程运行此任务,且任务结束后将该线程保留在线程池中,不做销毁处理,若当前线程数量已达到corePoolSize,则进入下一步;
第二步: 判断工作队列(workQueue)是否已满,未满则将新的任务提交到工作队列中,满了则进入下一步;
第三步: 判断线程池中的线程数量是否达到了maxumunPoolSize,如果未达到,则新建一个工作线程来执行这个任务,如果达到了则使用饱和策略来处理这个任务。
[
](https://blog.csdn.net/qq_33323054/article/details/106923732)
keepAliveTime
如果一个线程处在空闲状态的时间超过了该属性值,就会因为超时而退出。
举个例子,如果线程池的核心大小corePoolSize=5,而当前大小poolSize =8,那么超出核心大小的线程,会按照keepAliveTime的值判断是否会超时退出。
如果线程池的核心大小corePoolSize=5,而当前大小poolSize =5,那么线程池中所有线程都是核心线程,这个时候线程是否会退出,取决于allowCoreThreadTimeOut。
队列workQueue
缓冲队列有三种通用策略:直接提交、有界队列、无界队列
SynchronousQueue、ArrayBlockingQueue、LinkedBlockingQueue、
SynchronousQueue:
由于该Queue本身的特性,在某次添加元素后必须等待其他线程取走后才能继续添加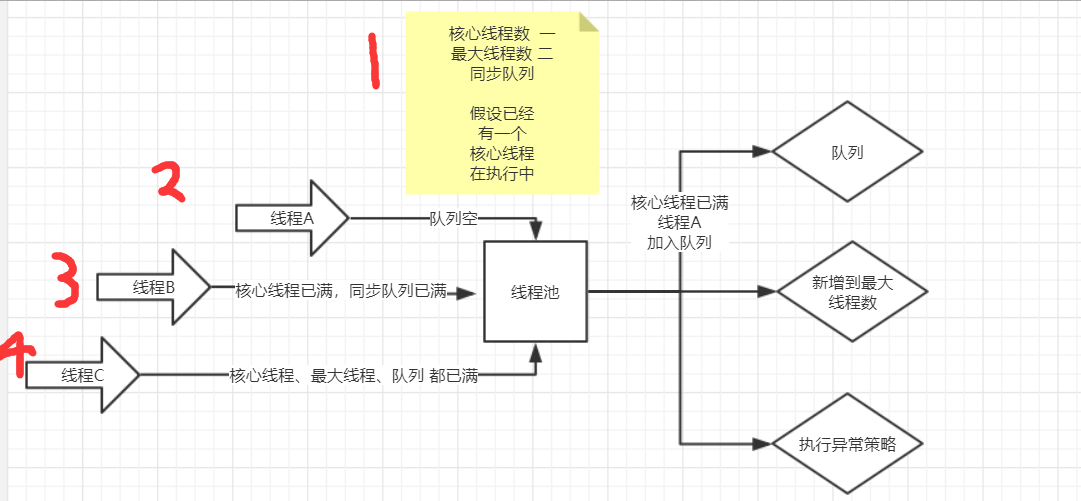
ArrayBlockingQueue:
有界队列,特点可以防止资源耗尽, 默认有界长度 2147483647(二十一亿 四千七百四十八万多)
LinkedBlockingQueue:
无界队列,会造成资源耗尽
handler 拒绝策略JDK 提供了四种内置拒绝策略,我们要理解并记住,有如下的四种:
ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy:丢弃任务并抛出RejectedExecutionException异常。ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardPolicy:也是丢弃任务,但是不抛出异常。ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardOldestPolicy:丢弃队列最前面的任务,然后重新尝试执行任务(重复此过程)ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy:由调用线程处理该任务 极大概率是main线程去执行
https://www.jianshu.com/p/aa420c7df275
ThreadFactory来定义我们自己的线程工厂,比如说自定义线程名称,组,优先级等信息,可以跟着线程池究竟在何时创建了多少线程等等。
使用Executors 创建线程池
newCachedThreadPool 创建一个可缓存线程池,如果线程池长度超过处理需要,可灵活回收空闲线程,若无可回收,则新建线程。
public static void main(String[] args) {Date time = Calendar.getInstance().getTime();// Single();//Scheduled(time);System.out.println(time);//开始时间//可缓存的线程池 核心线程数无限大,所以即使线程输出完成 休眠十秒,十个线程也是在一瞬间执行完成的ExecutorService cachedThreadPool = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {final int index = i;cachedThreadPool.execute(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":"+index);System.out.println(Calendar.getInstance().getTime());try {Thread.sleep(10000);//休眠十秒} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}});}}
newFixedThreadPool 创建一个定长线程池,可控制线程最大并发数,超出的线程会在队列中等待。
public static void main(String[] args) {Date time = Calendar.getInstance().getTime();// Single();//Scheduled(time);//CaChed(time);ExecutorService fixedThreadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {fixedThreadPool.execute(() -> {try {System.out.println(Calendar.getInstance().getTime() + ";当前线程名称" + Thread.currentThread().getName());Thread.sleep(3000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}});}/*Sat Apr 13 11:03:37 CST 2019;当前线程名称pool-1-thread-3Sat Apr 13 11:03:37 CST 2019;当前线程名称pool-1-thread-2Sat Apr 13 11:03:37 CST 2019;当前线程名称pool-1-thread-1Sat Apr 13 11:03:40 CST 2019;当前线程名称pool-1-thread-3Sat Apr 13 11:03:40 CST 2019;当前线程名称pool-1-thread-2Sat Apr 13 11:03:40 CST 2019;当前线程名称pool-1-thread-1Sat Apr 13 11:03:43 CST 2019;当前线程名称pool-1-thread-3Sat Apr 13 11:03:43 CST 2019;当前线程名称pool-1-thread-2Sat Apr 13 11:03:43 CST 2019;当前线程名称pool-1-thread-1Sat Apr 13 11:03:46 CST 2019;当前线程名称pool-1-thread-3*/}
newScheduledThreadPool 创建一个定长线程池,支持定时及周期性任务执行。
public static void main(String[] args) {// Single();Date time = Calendar.getInstance().getTime();System.out.println(time);//核心线程数量 2ScheduledExecutorService scheduledThreadPool = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(2);for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {scheduledThreadPool.schedule(() -> {System.out.println("三秒后执行,每次间隔两秒" + Calendar.getInstance().getTime() + ";当前线程名称" + Thread.currentThread().getName());try {Thread.sleep(2000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}, 3, TimeUnit.SECONDS);}/*Sat Apr 13 10:28:51 CST 2019三秒后执行,每次间隔两秒Sat Apr 13 10:28:54 CST 2019;当前线程名称pool-1-thread-1三秒后执行,每次间隔两秒Sat Apr 13 10:28:54 CST 2019;当前线程名称pool-1-thread-2三秒后执行,每次间隔两秒Sat Apr 13 10:28:56 CST 2019;当前线程名称pool-1-thread-1三秒后执行,每次间隔两秒Sat Apr 13 10:28:56 CST 2019;当前线程名称pool-1-thread-2三秒后执行,每次间隔两秒Sat Apr 13 10:28:58 CST 2019;当前线程名称pool-1-thread-2*/}
newSingleThreadExecutor 创建一个单线程化的线程池,它只会用唯一的工作线程来执行任务,保证所有任务按照指定顺序(FIFO, LIFO, 优先级)执行。
public static void main(String[] args) {//单例的线程ExecutorService service = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();for (int i = 0; i < 5 ; i++) {service.execute(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+ " : " + "查看线程是否是单例的");try {Thread.sleep(2000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}});}}--------------------------------------pool-1-thread-1 : 查看线程是否是单例的pool-1-thread-1 : 查看线程是否是单例的pool-1-thread-1 : 查看线程是否是单例的pool-1-thread-1 : 查看线程是否是单例的pool-1-thread-1 : 查看线程是否是单例的
private final BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue; // 阻塞队列private final ReentrantLock mainLock = new ReentrantLock(); // 互斥锁private final HashSet<Worker> workers = new HashSet<Worker>();// 线程集合.一个Worker对应一个线程private final Condition termination = mainLock.newCondition();// 终止条件private int largestPoolSize; // 线程池中线程数量曾经达到过的最大值。private long completedTaskCount; // 已完成任务数量private volatile ThreadFactory threadFactory; // ThreadFactory对象,用于创建线程。private volatile RejectedExecutionHandler handler;// 拒绝策略的处理句柄private volatile long keepAliveTime; // 线程池维护线程所允许的空闲时间private volatile boolean allowCoreThreadTimeOut;private volatile int corePoolSize; // 线程池维护线程的最小数量,哪怕是空闲的private volatile int maximumPoolSize; // 线程池维护的最大线程数量

