window
- 获取窗口大小
- window.innerWidth ( 获取窗口宽度 )
- window.innerHeight ( 获取窗口的高度 )
- 与 document.body.clientWidth / document.body.clientHeight 大致相同的作用
- 向下/向上滚动
- 滚动到相应位置(to)window.scrollTo( posX,posY )
- 接收两个参数,一个是 X轴 (向右为正),一个是 Y轴 (向下为正)
- 滚动相应距离(By) window.scrollBy( posX,posY )
- 参数与上面的相同,但是是滚动到的具体位置
- 滚动到相应位置(to)window.scrollTo( posX,posY )
- 除此以外,还有
moveTo和moveBy两个函数,但是现在好像用的比较少。
HTMLElement
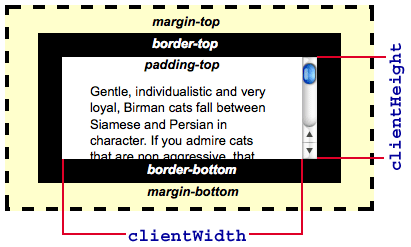
获取元素大小(不包含外边框 border)
- Element.clientWidth (获取元素 比如某个div 的宽度)
- Element.clientHeight (获取元素的宽度)
let myDiv = document.querySelector("div")console.log(myDiv.clientWidth)
获取元素大小(包含外边框 border)
返回值的类型和上面的clientWidth等相同- Element.offsetWidth
- Element.offsetHeight
除此以外,不论是 clientWidth 还是 offsetWidth,它们都包含元素的 宽度(width)、内边距(padding) ,都不包括元素的外边距(margin) 。
获取距离页面左端和上端的距离
- Element.offsetTop (获取元素距离页面上端的距离)
- Element.offsetLeft (获取元素距离页面左端的距离)
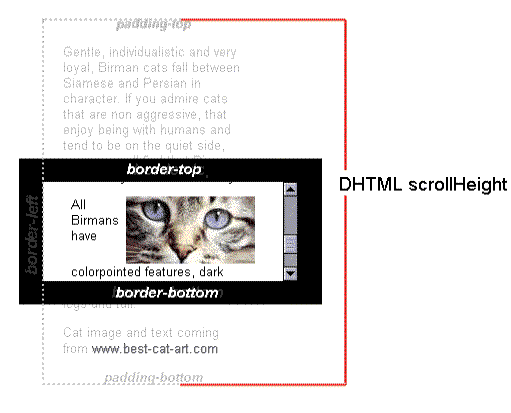
- 获取自身滚动的距离
- Element.scrollTop
- Element.scrollLeft
- 获取距离视窗上和左端的距离
- Element.getBoundingClientRect()
- 返回一个 DOMRect 对象,是与该元素相关的 CSS 集合
let {top,left} = obj.getBoundingClientRect(); // 获取 obj 相对上侧与左侧的距离
- 返回一个 DOMRect 对象,是与该元素相关的 CSS 集合
- Element.getBoundingClientRect()
**解决方案** : 判断元素是否滑动到底
function isScrollToBottom(Element){if(Element.scrollHeight - Element.scrollTop === Element.clientHeight){return true}else{return false}}
**解决方案**:判断元素是否在视口中
var viewportHeight = Math.max(document.documentElement.clientHeight, document.body.clientHeight);var {top, bottom} = targetEle.getBoundingClientRect();if (bottom > 0 && top < viewportHeight) {// 现在出现在视口中}

