前言
前两天和朋友探讨一个react-render 通过map循环一个列表性能问题,主要讨论了一个争议点: map循环state中的一个数组,为了提高性能加key的重要性,由于常见的应用场景如下来分页加载,根据测试在[].length比较庞大,其中key的设置:
- 为map的index属性
- 为数组中的对象的唯一恒定不变的属性值
以上两种设置在实验证明有a比b的循环输出要慢100ms, 其中由于我猜想:在数组中不会存在元素的顺序的变化,key设置为index是一个唯一的索引,应该不会执行深度diff, 会有性能的提高,但是同等情况下,设置成数组中的唯一不变属性值确实会快一些。 我看了官方的解释给出的清晰解释: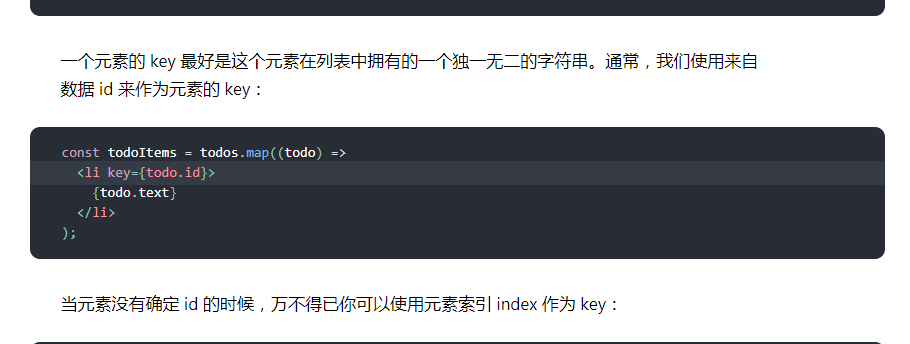

https://medium.com/@robinpokorny/index-as-a-key-is-an-anti-pattern-e0349aece318
其实并没有解决我的问题: 因为我的数组是没有顺序变化的, 但是性能还是有一点小的偏差,此时我猜想是不是map的index有什么特殊的设置???
1. for循环(ES5)
最基本的循环,应该不需要解释了
2. for…in(ES5) obj遍历,并且只能访问允许枚举的属性
以任意顺序遍历一个对象的可枚举属性。对于每个不同的属性,语句都会被执行。
强调一下: 一个obj通过 Object.defineProperty 创建的属性中必须将enumerable设置为true才能被循环
其中也包括从父元素继承来的元素
另外[for...in](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Statements/for...in)迭代中不能枚举符号。另外,Object.getOwnPropertyNames()不会返回符号对象属性
2.1语法
- variable
在每次迭代时,将不同的属性名分配给变量。
- object
被迭代枚举其属性的对象。
无返回值,不支持链式操作
for (variable in object) {...}
2.2 特点
- 最好是不要用于数组的循环,可能导致索引无序,
- 可以遍历自己的允许枚举及继承的父对象上允许枚举的属性,如果需要只是自己对象上的则可以通过
hasOwnProperty(),getOwnPropertyNames()
3.3 举例
var obj = {a:1, b:2, c:3};for (var prop in obj) {console.log("obj." + prop + " = " + obj[prop]);}下面的函数说明了hasOwnProperty()的用法:继承的属性不显示。var triangle = {a: 1, b: 2, c: 3};function ColoredTriangle() {this.color = 'red';}ColoredTriangle.prototype = triangle;var obj = new ColoredTriangle();for (var prop in obj) {if (obj.hasOwnProperty(prop)) {console.log(`obj.${prop} = ${obj[prop]}`);}}// Output:// "obj.color = red"
3. forEach( ES5 ) []
方法对数组的每个元素执行一次提供的函数。
3.1 语法
callback:传入三个参数1.数组当前项的值2. 数组当前项的索引3. 数组对象本身thisArg: 指定this 如果使用箭头函数表达式来传入函数参数,thisArg 参数会被忽略,因为箭头函数在词法上绑定了 this 值。arr.forEach(callback[, thisArg]);
3.2 特点
1.没有返回值,不支持链式操作
2. 没有办法中止或者跳出 forEach() 循环,除了抛出一个异常。如果你需要这样,使用 forEach() 方法是错误的。
若你需要提前终止循环,你可以使用:
- 简单循环- [for...of](https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Statements/for...of) 循环- [`Array.prototype.every()`](https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Array/every)- [`Array.prototype.some()`](https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Array/some)- [`Array.prototype.find()`](https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Array/find)- [`Array.prototype.findIndex()`](https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Array/findIndex)
3.如果数组中存在某一个索引下的值不存在直接就跳过
3.3 示例
const items = ['item1', 'item2',, 'item3'];const copy = [];// afteritems.forEach(function(item,index){copy.push(item);console.log(`${index}`, item);});//0 item1//1 item2//3 item3在数组循环中修改了数组的值结构, 可能造成的后果var words = ['one', 'two', 'three', 'four'];words.forEach(function(word) {console.log(word);if (word === 'two') {words.shift(); //移除数组中的第一项,导致数组前移,'three'丢失}});// one// two// four
Polyfill
// Production steps of ECMA-262, Edition 5, 15.4.4.18// Reference: http://es5.github.io/#x15.4.4.18if (!Array.prototype.forEach) {Array.prototype.forEach = function(callback, thisArg) {var T, k;if (this == null) {throw new TypeError(' this is null or not defined');}// 1. Let O be the result of calling toObject() passing the// |this| value as the argument.var O = Object(this); //创建一个对象// 2. Let lenValue be the result of calling the Get() internal// method of O with the argument "length".// 3. Let len be toUint32(lenValue).var len = O.length >>> 0; //验证数组长度大于0// 4. If isCallable(callback) is false, throw a TypeError exception.// See: http://es5.github.com/#x9.11//callback 必须是数组if (typeof callback !== "function") {throw new TypeError(callback + ' is not a function');}// 5. If thisArg was supplied, let T be thisArg; else let// T be undefined.if (arguments.length > 1) {T = thisArg;}// 6. Let k be 0k = 0;// 7. Repeat, while k < lenwhile (k < len) {var kValue;// a. Let Pk be ToString(k).// This is implicit for LHS operands of the in operator// b. Let kPresent be the result of calling the HasProperty// internal method of O with argument Pk.// This step can be combined with c// c. If kPresent is true, thenif (k in O) {// i. Let kValue be the result of calling the Get internal// method of O with argument Pk.kValue = O[k];// ii. Call the Call internal method of callback with T as// the this value and argument list containing kValue, k, and O.//Function.prototype.call(); 改变this,传入值//kValue:当前值//k 索引//o 对象callback.call(T, kValue, k, O);}// d. Increase k by 1.k++;}// 8. return undefined};}
3. for…of [] | Symbol
在可迭代对象(包括 Array,Map,Set,String,TypedArray,arguments 对象等等)上创建一个迭代循环,调用自定义迭代钩子,并为每个不同属性的值执行语句
3.1 语法
variable
在每次迭代中,将不同属性的值分配给变量。
iterable
被迭代枚举其属性的对象。
for (variable of iterable) {//statements}
3.1 特点
- 可以终止
break,throw continue或return终止
3.2示例
可以被迭代的数据类型
1.Array
2.string
3.TypesArray
4.Map对象
5.Set对象
6.arguments
7.DOM集合
8.Symbol
1.let iterable = [10, 20, 30];for (let value of iterable) {value += 1;console.log(value);}// 11// 21// 312.let iterable = "boo";for (let value of iterable) {console.log(value);}// "b"// "o"// "o"3.let iterable = new Uint8Array([0x00, 0xff]);for (let value of iterable) {console.log(value);}// 0// 2554.let iterable = new Map([["a", 1], ["b", 2], ["c", 3]]);for (let entry of iterable) {console.log(entry);}// ["a", 1]// ["b", 2]// ["c", 3]for (let [key, value] of iterable) {console.log(value);}// 1// 2// 35.let iterable = new Set([1, 1, 2, 2, 3, 3]);for (let value of iterable) {console.log(value);}// 1// 2// 36.(function() {for (let argument of arguments) {console.log(argument);}})(1, 2, 3);// 1// 2// 37.//注意:这只能在实现了NodeList.prototype[Symbol.iterator]的平台上运行let articleParagraphs = document.querySelectorAll("article > p");for (let paragraph of articleParagraphs) {paragraph.classList.add("read");}8.var iterable = {[Symbol.iterator]() {return {i: 0,next() {if (this.i < 3) {return { value: this.i++, done: false };}return { value: undefined, done: true };}};}};for (var value of iterable) {console.log(value);}// 0// 1// 2
3.4 for..of 与for…in的区别
以下示例显示了与Array一起使用时,for...of循环和for...in循环之间的区别。
Object.prototype.objCustom = function() {};Array.prototype.arrCustom = function() {};let iterable = [3, 5, 7];iterable.foo = 'hello';//原型链上可以被枚举的所有属性keyfor (let i in iterable) {console.log(i); // 0, 1, 2, "foo", "arrCustom", "objCustom"}for (let i in iterable) {if (iterable.hasOwnProperty(i)) {console.log(i); // 0, 1, 2, "foo"}}//迭代的属性值for (let i of iterable) {console.log(i); // 3, 5, 7}
4. Array.map []
map()方法创建一个新数组,其结果是该数组中的每个元素都调用一个提供的函数后返回的结果。
4.1 特点:
- 会返回一个新数组
2. 数组对象遍历
3. 默认不会修改原来数组的值
4. 数组元素的范围在callback被第一个调用时就已经确定
5. 在map循环中,修改原数组的值,原数组中新增加的元素将不会被 callback 访问到
6. 若已经存在的元素被改变或删除了,则它们的传递到 callback 的值是 map 方法遍历到它们的那一时刻的值;而被删除的元素将不会被访问到。
4.2用法
/** curentObj: 正在处理的当前元素。index:数组中正在处理的当前元素的索引。currentOrigin: 方法被调用的数组,也就是athisArg :每次 callback 函数被调用的时候,this 都会指向 thisArg 参数上的这个对象,如果省略了 thisArg 参数,或者赋值为 null 或 undefined,则 this 指向全局对象 。*/let a = [1,2,3];let thisArg = this;let _a = a.map((curentObj, index, currentOrigin)=>{}, thisArg ) //会返回一个新值
4.3 ES5兼容写法(查看MDN)
// 实现 ECMA-262, Edition 5, 15.4.4.19(如果不支持map的浏览器)// 参考: http://es5.github.com/#x15.4.4.19if (!Array.prototype.map) {Array.prototype.map = function(callback, thisArg) {var T, A, k;if (this == null) {throw new TypeError(" this is null or not defined");}// 1. 将O赋值为调用map方法的数组.var O = Object(this);// 2.将len赋值为数组O的长度.var len = O.length >>> 0;// 3.如果callback不是函数,则抛出TypeError异常.if (Object.prototype.toString.call(callback) != "[object Function]") {throw new TypeError(callback + " is not a function");}// 4. 如果参数thisArg有值,则将T赋值为thisArg;否则T为undefined.if (thisArg) {T = thisArg;}// 5. 创建新数组A,长度为原数组O长度lenA = new Array(len);// 6. 将k赋值为0k = 0;// 7. 当 k < len 时,执行循环.while(k < len) {var kValue, mappedValue;//遍历O,k为原数组索引if (k in O) {//kValue为索引k对应的值.kValue = O[ k ];// 执行callback,this指向T,参数有三个.分别是kValue:值,k:索引,O:原数组.mappedValue = callback.call(T, kValue, k, O);// 返回值添加到新数组A中.A[ k ] = mappedValue;}// k自增1k++;}// 8. 返回新数组Areturn A;};}
5.array.prototype.filter(callback(element, index, array), thisArg)
方法创建一个新数组, 其包含通过所提供函数实现的测试的所有元素。 filter 不会改变原数组,它返回过滤后的新数组。
5.1 语法
element:当前元素
index:索引
array:当前被轮训的对象
thisArg: 执行 callback 时,用于 this 的值。
var newArray = arr.filter(callback(element[, index[, array]])[, thisArg])
5.2 返回值
一个新的、由通过测试的元素组成的数组,如果没有任何数组元素通过测试,则返回空数组。
5.3 应用示例
1. 筛选排除所有满足条件的值function isBigEnough(element) {return element >= 10; //过滤出大于10的数,为 true 则返回}var filtered = [12, 5, 8, 130, 44].filter(isBigEnough);// filtered is [12, 130, 44]2. 过滤 JSON 中的无效条目以下示例使用 filter() 创建具有非零(NaN, undefined, 0,不存在) id 的元素的 json。var arr = [{ id: 15 },{ id: -1 },{ id: 0 },{ id: 3 },{ id: 12.2 },{ },{ id: null },{ id: NaN },{ id: 'undefined' }];var invalidEntries = 0;function isNumber(obj) {return obj !== undefined && typeof(obj) === 'number' && !isNaN(obj);}function filterByID(item) {if (isNumber(item.id) && item.id !== 0) {return true;}invalidEntries++;return false;}var arrByID = arr.filter(filterByID);console.log('Filtered Array\n', arrByID);// Filtered Array// [{ id: 15 }, { id: -1 }, { id: 3 }, { id: 12.2 }]3. 在数组中搜索下例使用 filter() 根据搜索条件来过滤数组内容。var fruits = ['apple', 'banana', 'grapes', 'mango', 'orange'];function filterItems(query) {return fruits.filter(function(el) {return el.toLowerCase().indexOf(query.toLowerCase()) > -1;})}console.log(filterItems('ap')); // ['apple', 'grapes']console.log(filterItems('an')); // ['banana', 'mango', 'orange']
5.4 兼容写法
if (!Array.prototype.filter){Array.prototype.filter = function(func, thisArg) {'use strict';if ( ! ((typeof func === 'Function' || typeof func === 'function') && this) )throw new TypeError();var len = this.length >>> 0,res = new Array(len), // preallocate arrayt = this, c = 0, i = -1;//没有传入thisArgif (thisArg === undefined){while (++i !== len){// checks to see if the key was setif (i in this){//t[i]: 当前值//i:索引//t:当前对象//如果满足条件则放入新建res的数组中if (func(t[i], i, t)){res[c++] = t[i];}}}}else{while (++i !== len){// checks to see if the key was setif (i in this){//指定了this对象if (func.call(thisArg, t[i], i, t)){res[c++] = t[i];}}}}//最后返回一个数组重新处理res的长度res.length = c; // shrink down array to proper size//返回resreturn res;};}
6. find(满足条件的第一值即返回) []
6.1 概念
方法返回数组中满足提供的测试函数的第一个元素的值。否则返回 undefined。
其中与[findIndex()](https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Array/findIndex) 返回满足条件的第一个值的索引
如果支持判断一个值是否存在在一个数组中可以用Array.prototype.indexOf() 或 Array.prototype.includes()。find方法不会改变数组。
6.2 返回值
数组中第一个满足所提供测试函数的元素的值,否则返回 undefined。
6.3 示例
1.用对象的属性查找数组里的对象var inventory = [{name: 'apples', quantity: 2},{name: 'bananas', quantity: 0},{name: 'cherries', quantity: 5}];console.log(inventory.find((fruit)=>{return fruit.name === 'cherries';})); // { name: 'cherries', quantity: 5 }2. 寻找数组中的质数下面的例子展示了如何从一个数组中寻找质数(如果找不到质数则返回undefined)function isPrime(element, index, array) {var start = 2;while (start <= Math.sqrt(element)) {if (element % start++ < 1) {return false;}}return element > 1;}console.log([4, 6, 8, 12].find(isPrime)); // undefined, not foundconsole.log([4, 5, 8, 12].find(isPrime)); // 5
6.4 兼容写法
// https://tc39.github.io/ecma262/#sec-array.prototype.findif (!Array.prototype.find) {Object.defineProperty(Array.prototype, 'find', {value: function(predicate) {// 1. Let O be ? ToObject(this value).if (this == null) {throw new TypeError('"this" is null or not defined');}var o = Object(this);// 2. Let len be ? ToLength(? Get(O, "length")).var len = o.length >>> 0;// 3. If IsCallable(predicate) is false, throw a TypeError exception.if (typeof predicate !== 'function') {throw new TypeError('predicate must be a function');}// 4. If thisArg was supplied, let T be thisArg; else let T be undefined.var thisArg = arguments[1];// 5. Let k be 0.var k = 0;// 6. Repeat, while k < lenwhile (k < len) {// a. Let Pk be ! ToString(k).// b. Let kValue be ? Get(O, Pk).// c. Let testResult be ToBoolean(? Call(predicate, T, « kValue, k, O »)).// d. If testResult is true, return kValue.var kValue = o[k];if (predicate.call(thisArg, kValue, k, o)) {return kValue;}// e. Increase k by 1.k++;}// 7. Return undefined.return undefined;}});}
7. Array.prototype.every []
**every()** 方法测试数组的所有元素是否都通过了指定函数的测试。(只有所有的满足条件才会返回true),只要有一个不满足则返回false
7.1 语法
element:当前元素
index:索引
array:当前被轮训的对象
thisArg: 执行 callback 时,用于 this 的值
arr.every(callback[curentValue,[index,[arr,] ,thisArg])
7.2 特点
- 不会改变原来的数组
- 不能用于链式操作,因为返回的是一个true/false
7.3 示例
下例检测数组中的所有元素是否都大于 10。function isBigEnough(element, index, array) {return (element >= 10);}var passed = [12, 5, 8, 130, 44].every(isBigEnough);// passed is falsepassed = [12, 54, 18, 130, 44].every(isBigEnough);// passed is true
7.4 兼容写法
if (!Array.prototype.every){Array.prototype.every = function(fun /*, thisArg */){'use strict';if (this === void 0 || this === null)throw new TypeError();var t = Object(this);var len = t.length >>> 0;if (typeof fun !== 'function')throw new TypeError();var thisArg = arguments.length >= 2 ? arguments[1] : void 0;for (var i = 0; i < len; i++){//只要有一个不满足则返回falseif (i in t && !fun.call(thisArg, t[i], i, t))return false;}return true;};}
8. some []
**some()** 方法测试是否至少有一个元素通过由提供的函数实现的测试。
只要有一个元素满足条件则通过 注意:对于放在空数组上的任何条件,此方法返回false。
8.1 返回值
返回值为true/false; 不能用于链式操作
用法同every; some是整体,every是局部
8.2 兼容写法
// Production steps of ECMA-262, Edition 5, 15.4.4.17// Reference: http://es5.github.io/#x15.4.4.17if (!Array.prototype.some) {Array.prototype.some = function(fun/*, thisArg*/) {'use strict';if (this == null) {throw new TypeError('Array.prototype.some called on null or undefined');}if (typeof fun !== 'function') {throw new TypeError();}var t = Object(this);var len = t.length >>> 0;var thisArg = arguments.length >= 2 ? arguments[1] : void 0;for (var i = 0; i < len; i++) {//只要有一个满足条件则返回trueif (i in t && fun.call(thisArg, t[i], i, t)) {return true;}}return false;};}
9. reduce []
方法对数组中的每个元素执行一个由您提供的reducer函数(升序执行),将其结果汇总为单个返回值。
9.1 语法
reducer两个参数
- callback 函数接收4个参数:
- Accumulator (acc) (累计器) :每一次累计后的结果
- Current Value (cur) (当前值): 正在处理的元素
- Current Index (idx) (当前索引)
- Source Array (src) (源数组)
2. initialValue
作为第一次调用 callback函数时的第一个参数的值。 如果没有提供初始值,则将使用数组中的第一个元素。 在没有初始值的空数组上调用 reduce 将报错。
您的 reducer 函数的返回值分配给累计器,该返回值在数组的每个迭代中被记住,并最后成为最终的单个结果值。
注意:
如果数组为空且没有提供initialValue,会抛出TypeError 。如果数组仅有一个元素(无论位置如何)并且没有提供initialValue, 或者有提供initialValue但是数组为空,那么此唯一值将被返回并且callback不会被执行。
用一个示例体现展示一下返回的结过
var maxCallback = ( acc, cur ) => Math.max( acc.x, cur.x );var maxCallback2 = ( max, cur ) => Math.max( max, cur );// reduce() 没有初始值[ { x: 22 }, { x: 42 } ].reduce( maxCallback ); // 42[ { x: 22 } ].reduce( maxCallback ); // { x: 22 }[ ].reduce( maxCallback ); // TypeError// map/reduce; 这是更好的方案,即使传入空数组或更大数组也可正常执行[ { x: 22 }, { x: 42 } ].map( el => el.x ).reduce( maxCallback2, -Infinity ); //传入了一个初始值
9.2 返回值
函数累计处理的结果;如果返回的是一个数组则支持链式操作
9.3 示例
let arr = [1,2,1,2,3,5,4,5,3,4,4,4,4];let result = arr.sort().reduce((init, current)=>{if(init.length===0 || init[init.length-1]!==current){init.push(current);}return init;}, []);console.log(result); //[1,2,3,4,5]
9.4 兼容性写法
// Production steps of ECMA-262, Edition 5, 15.4.4.21// Reference: http://es5.github.io/#x15.4.4.21// https://tc39.github.io/ecma262/#sec-array.prototype.reduceif (!Array.prototype.reduce) {Object.defineProperty(Array.prototype, 'reduce', {value: function(callback /*, initialValue*/) {if (this === null) {throw new TypeError( 'Array.prototype.reduce ' +'called on null or undefined' );}if (typeof callback !== 'function') {throw new TypeError( callback +' is not a function');}// 1. Let O be ? ToObject(this value).var o = Object(this);// 2. Let len be ? ToLength(? Get(O, "length")).var len = o.length >>> 0;// Steps 3, 4, 5, 6, 7var k = 0;var value;if (arguments.length >= 2) {value = arguments[1];} else {//不存在继续while (k < len && !(k in o)) {k++;}// 3. If len is 0 and initialValue is not present,// throw a TypeError exception.if (k >= len) {throw new TypeError( 'Reduce of empty array ' +'with no initial value' );}value = o[k++];}// 8. Repeat, while k < lenwhile (k < len) {// a. Let Pk be ! ToString(k).// b. Let kPresent be ? HasProperty(O, Pk).// c. If kPresent is true, then// i. Let kValue be ? Get(O, Pk).// ii. Let accumulator be ? Call(// callbackfn, undefined,// « accumulator, kValue, k, O »).if (k in o) {//value:计算的第一次结果//o[k]:当前需要操作的元素value = callback(value, o[k], k, o);}// d. Increase k by 1.k++;}// 9. Return accumulator.return value;}});}
10.include [] / 类数组arguments对象
**includes()** 方法用来判断一个数组是否包含一个指定的值,根据情况,如果包含则返回 true,否则返回false。
10.1 语法
valueToFind
需要查找的元素值。fromIndex 可选 如果为负数,则是从后面的第一个为开始搜索
从fromIndex 索引处开始查找 valueToFind。如果为负值,则按升序从 array.length + fromIndex 的索引开始搜 (即使从末尾开始往前跳 fromIndex 的绝对值个索引,然后往后搜寻)。默认为 0。
arr.includes(valueToFind[, fromIndex])
10.2 返回值
返回一个布尔值 Boolean ,如果在数组中找到了(如果传入了 fromIndex ,表示在 fromIndex 指定的索引范围中找到了)则返回 true 。
10.3 示例
[1, 2, 3].includes(2); // true[1, 2, 3].includes(4); // false[1, 2, 3].includes(3, 3); // false[1, 2, 3].includes(3, -1); // true[1, 2, NaN].includes(NaN); // true如果 fromIndex 大于等于数组的长度,则会返回 false,且该数组不会被搜索。var arr = ['a', 'b', 'c'];arr.includes('c', 3); // falsearr.includes('c', 100); // falsevar arr = ['a', 'b', 'c'];如果 fromIndex 为负值,计算出的索引将作为开始搜索searchElement的位置。如果计算出的索引小于 0,则整个数组都会被搜索。var arr = ['a', 'b', 'c'];arr.includes('a', -100); // truearr.includes('b', -100); // truearr.includes('c', -100); // truearr.includes('a', -2); // falseincludes() 方法有意设计为通用方法。它不要求this值是数组对象,所以它可以被用于其他类型的对象 (比如类数组对象)。下面的例子展示了 在函数的 arguments 对象上调用的 includes() 方法(function() {console.log([].includes.call(arguments, 'a')); // trueconsole.log([].includes.call(arguments, 'd')); // false})('a','b','c');
10.4 兼容写法
// https://tc39.github.io/ecma262/#sec-array.prototype.includesif (!Array.prototype.includes) {Object.defineProperty(Array.prototype, 'includes', {value: function(valueToFind, fromIndex) {if (this == null) {throw new TypeError('"this" is null or not defined');}// 1. Let O be ? ToObject(this value).var o = Object(this);// 2. Let len be ? ToLength(? Get(O, "length")).var len = o.length >>> 0;// 3. If len is 0, return false.if (len === 0) {return false;}// 4. Let n be ? ToInteger(fromIndex).// (If fromIndex is undefined, this step produces the value 0.)var n = fromIndex | 0;// 5. If n ≥ 0, then// a. Let k be n.// 6. Else n < 0,// a. Let k be len + n.// b. If k < 0, let k be 0.var k = Math.max(n >= 0 ? n : len - Math.abs(n), 0);function sameValueZero(x, y) {//值的相等如果为NAN的验证return x === y || (typeof x === 'number' && typeof y === 'number' && isNaN(x) && isNaN(y));}// 7. Repeat, while k < lenwhile (k < len) {// a. Let elementK be the result of ? Get(O, ! ToString(k)).// b. If SameValueZero(valueToFind, elementK) is true, return true.if (sameValueZero(o[k], valueToFind)) {return true;}// c. Increase k by 1.k++;}// 8. Return falsereturn false;}});}
11. 总结
| 名称 | 语法 | 返回值 | 是否支持链式 | 针对类型 | 是够可以终止 | 是够会修改原数组 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| for | for(let i=0; i<= len;i++) | 无 | no | 数组,对象(string),类数组 | 可以; break; continue;return | no |
| for…in | for(o in obj) o:代表key 属性循环 |
无 | no | 对象中可以枚举的属性(包括原型链) 数组最好不要用,索引可能不是整数 |
no | |
| for…of | for(v of obj) v:代表值 值循环 |
无 | no | Array,Map,Set,String,TypedArray,arguments, symbal |
可以; break; continue;return | no |
| forEach | [].forEach(function(item,index){ }) item:当前值 index:当前值对应的索引 |
无 | no | 数组 | 不能中断,如果需要中断则只能抛异常 | no |
| map | [].map(function(curentObj, index,currentOrigin){}, this) curentObj: 正在处理的当前元素。 index:数组中正在处理的当前元素的索引。 currentOrigin: 方法被调用的数组,也就是a thisArg :每次 callback 函数被调用的时候,this 都会指向 thisArg 参数上的这个对象 |
返回一个新数组; | yes | 数组, arguments | no 不能中断 | no |
| filter | var newArray = arr.filter(callback(element[, index[, array]])[, thisArg]) element:当前元素 index:索引 array:当前被轮训的对象 thisArg: 执 callback 时,用于 this 的值。 |
1.返回新数组 2.如果没有任何元素则返回空数组 |
yes | 数组,数组对象 | no | |
| find | var newArray = arr.find(callback(element[, index[, array]])[, thisArg]) | 1.返回第一个满足条件的值 2. 否则返回undefined |
no | 数组 | yes return |
no |
| every | arr.every(callback[curentValue,[index,[arr,] ,thisArg]) | true/false 全部满足条件则返回true |
no | 数组 | yes return |
no |
| some | arr.some(callback[curentValue,[index,[arr,] ,thisArg]) | true/false 只要有一个不满足则返回false |
no | 数组 | yes return |
no |
| reduce | [],reduce(callback(Accumulator CurrentValue,index, Array ),initialValue) | 返回一个累计处理的结果,可以是值类型,所以是引用类型 | yes | 数组 | yes return |
no |
| includes | arr.includes(valueToFind[, fromIndex]) valueToFind:包含的值fromIndex: 索引 |
true/false 找到就为true |
no | 数组 | yes return |
no |

