集合不安全解决办法
package com.lyj.demo;import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;import java.util.List;import java.util.UUID;import java.util.concurrent.CopyOnWriteArrayList;/*** @program: java-test-demo* @Date: 2021/8/11 7:34* @Author: 凌兮* @Description:*/@SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.NONE)public class JUCTest {/*** List非线程安全的,底层add方法没有synchronized* JUC:就是java.util.concurrent包*/public static void main(String [] args) {// 方式1:list arrayList是非线程安全集合// 报错:Exception in thread "1" Exception in thread "2"// Exception in thread "0" java.util.ConcurrentModificationException// List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();//方式2:使用vector线程安全的集合,底层add方法有synchronized,该方式比较古老,jdk1.0时就有了。// List<String> list = new Vector<>();// 方式3:使用Collections.synchornizedList方式创建,入参传入一个集合,// 线程安全的,底层也是用的synchronized,该方式比较古老,jdk1.2就有了// List<String> list = Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList<>());// 方式4:使用JUC 里的CopyOnWriteArrayList,采用的是写时复制技术,底层采用lock方式List<String> list = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>();for (int i = 0; i < 30; i++) {new Thread(() -> {list.add(UUID.randomUUID().toString().substring(0, 8));System.out.println(list);}, String.valueOf(i)).start();}/** ============hashSet线程不安全测试======== */// hashset非线程安全,报错:Exception in thread "15" Exception// in thread "19" java.util.ConcurrentModificationException// Set<String> set = new HashSet<>();// 解决方式1:CopyOnWriteArraySet,线程安全的,底层用的是lockSet<String> set = new CopyOnWriteArraySet<>();// for (int i = 0; i < 30; i++) {// new Thread(() -> {// set.add(UUID.randomUUID().toString().substring(0, 8));// System.out.println(set);// }, String.valueOf(i)).start();// }/** ============hashMap线程不安全测试======== */// hashmap线程不安全的,报错:Exception in thread "3" java.util.ConcurrentModificationException// Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();// 解决方式1:ConcurrentHashMap 线程安全的Map<String, String> map = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();for (int i = 0; i < 30; i++) {String key = String.valueOf(i);new Thread(() -> {map.put(key, UUID.randomUUID().toString().substring(0, 8));System.out.println(map);}, String.valueOf(i)).start();}}}
juc的三个辅助工具类
countDown测试:
需求:5个学生都必须先离开后,才能锁门。相当于多个线程都执行完后
/*** countDown测试 :* 5个学生都必须先离开后,才能锁门。相当于多个线程都执行完后,* countdown值减为0才执行await之后的代码。* @throws InterruptedException*/@Testpublic void countDownLatchTest() throws InterruptedException {CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(5);for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {new Thread(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "我离开教室了");countDownLatch.countDown();}, String.valueOf(i)).start();}countDownLatch.await();System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "班长锁门了,所有人都离开教室了");}
这个是只有当countdown值减为0才执行await之后的代码
一个线程A可使用CountDownLatch.await()方法阻塞等待,其他线程可调用CountDownLatch.countDown()方法使CountDownLatch数值减1,当CountDownLatch数值为0的时候,线程A可以继续往下执行
循环栅栏cyclicBarrier测试
需求:集齐7个龙珠召唤神龙
/*** 循环栅栏cyclicBarrier测试* 案例:集齐7个龙珠召唤神龙*/@Testpublic void cyclicBarrierTest() {// 创建循环栅栏CyclicBarrier cyclicBarrier = new CyclicBarrier(7, () -> {// 只有parties达到7,才会执行该线程,召唤神龙System.out.println("集齐了7个龙珠召唤神龙");});// 集齐龙珠过程,如果i的最大值改为6,则cyclicBarrier会一直等待,不会召唤神龙for (int i = 1; i <= 7; i++) {new Thread(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "龙珠");try {// 等待,parties加1,未达到7个线程时,cyclicBarrier一直会等待。cyclicBarrier.await();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (BrokenBarrierException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}, String.valueOf(i)).start();}}
Semaphore信号量测试
需求:6辆汽车,3个停车位
/*** Semaphore信号量测试:* 6辆汽车,3个停车位*/@Testpublic void semaphoreTest() {// 创建信号量,具有3个许可证Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(3);for (int i = 1; i <= 6; i++) {new Thread(() -> {try {// 抢占许可证semaphore.acquire();System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "获得了许可证并停车了");// 设置随机停车时间TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(new Random().nextInt(5));System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "归还了许可证并离开车库");} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {// 释放许可证,并离开semaphore.release();}}, String.valueOf(i)).start();}}
读写锁:
static class MapCache {// 创建缓存器 由于是经常进行读写操作,所以设置为volatilepublic static volatile Map<String, Object> cache = new HashMap<>();// 创建读写锁public static ReadWriteLock lock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock();// 读锁public static Lock readLock = lock.readLock();// 写锁public static Lock writeLock = lock.writeLock();/*** 写操作* @param key* @param value*/public static void put(String key, Object value) {writeLock.lock();// 暂停一会try {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "正在进行写操作" + key);TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(300);cache.put(key, value);System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "写入完毕" + key);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {writeLock.unlock();}}/*** 读操作* @param key* @return* @throws InterruptedException*/public static Object get(String key) {readLock.lock();Object result = null;// 暂停一会try {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "正在进行读操作" + key);TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(300);result = cache.get(key);System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "读取完毕" + key);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {readLock.unlock();}return result;}}// 测试public static void main(String[] args) {// 多线程写for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {final int key = i;new Thread(() -> {JUCTest.MapCache.put(key + "", key + "");}, String.valueOf(i)).start();}// 多线程读for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {final int key = i;new Thread(() -> {JUCTest.MapCache.get(key + "");}, String.valueOf(i)).start();}}
ReadWriteLock提供了一个读写锁(也称为共享锁和排他锁)的机制,多个线程可以同时获取到读锁(共享锁),而同一时刻只能有一个线程获取到写锁(排他锁)。
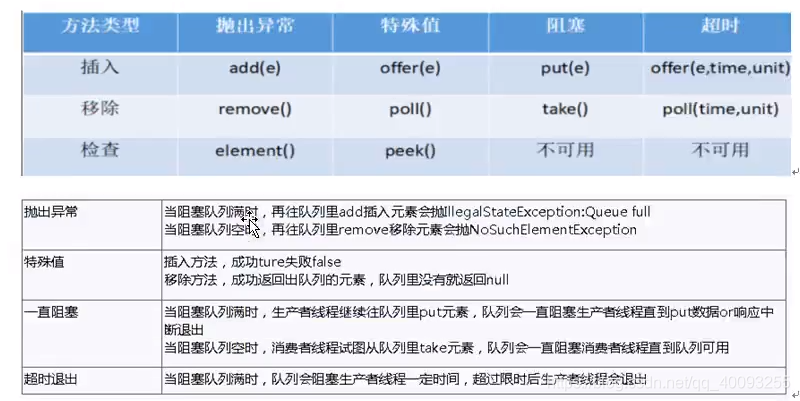
阻塞队列
/*** 阻塞队列测试1--抛出异常*/@Testpublic void blockingQueueTest() {// 创建数组类型的阻塞队列BlockingQueue<String> queue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(3);System.out.println(queue.add("a"));System.out.println(queue.add("b"));System.out.println(queue.add("c"));// 数组类型的阻塞队列,检查元素时,默认是第一个元素System.out.println(queue.element());// 再次添加会报错,queue full// System.out.println(queue.add("d"));System.out.println(queue.remove());System.out.println(queue.remove());System.out.println(queue.remove());// 再次移除会报错,Nosuchemenet// System.out.println(queue.remove());}/*** 阻塞队列测试2--特殊值*/@Testpublic void blockingQueueTest2() {// 创建数组类型的阻塞队列BlockingQueue<String> queue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(3);System.out.println(queue.offer("a"));System.out.println(queue.offer("b"));System.out.println(queue.offer("c"));// 数组类型的阻塞队列,检查元素时,默认是第一个元素System.out.println(queue.peek());// 再次添加返回false, 添加成功返回trueSystem.out.println(queue.offer("d"));System.out.println(queue.poll());System.out.println(queue.poll());System.out.println(queue.poll());// 再次移除会返回nullSystem.out.println(queue.poll());}/*** 阻塞队列测试3--阻塞*/@Testpublic void blockingQueueTest3() throws InterruptedException {// 创建数组类型的阻塞队列BlockingQueue<String> queue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(3);queue.put("a");queue.put("b");queue.put("c");// 再放程序会阻塞,直到队列空出一个位置。// queue.put("d");System.out.println("检测程序是否执行完");System.out.println(queue.take());System.out.println(queue.take());System.out.println(queue.take());// 再取程序会阻塞,直到队列里有值,获得值System.out.println(queue.take());System.out.println("检测程序是否执行完");}/*** 阻塞队列测试4--超时*/@Testpublic void blockingQueueTest4() throws InterruptedException {// 创建数组类型的阻塞队列BlockingQueue<String> queue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(3);System.out.println(queue.offer("a", 10, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS));System.out.println(queue.offer("b", 10, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS));System.out.println(queue.offer("c", 10, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS));// 再次添加,如果添加不进去,并且超时时间到了,会放弃添加System.out.println(queue.offer("d", 10, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS));System.out.println("检测程序是否执行完");System.out.println(queue.poll(10, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS));System.out.println(queue.poll(10, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS));System.out.println(queue.poll(10, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS));// 再次移除,如果没有移除的值,并且超时时间到了,会放弃移除,并返回nullSystem.out.println(queue.poll(10, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS));System.out.println("检测程序是否执行完");}
Phaser
public class TestPhaser {static Random r = new Random();static MarriagePhaser phaser = new MarriagePhaser();public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {phaser.bulkRegister(7);for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {new Person("person" + i).start();}new Person("新郎").start();new Person("新娘").start();}static class Person extends Thread {String name;public Person(String name) {this.name = name;}public void arrive() throws InterruptedException {Thread.sleep(r.nextInt(1000));System.out.printf("%s 到达现场!\n", name);phaser.arriveAndAwaitAdvance();}public void eat() throws InterruptedException {Thread.sleep(r.nextInt(1000));System.out.printf("%s 吃完!\n", name);phaser.arriveAndAwaitAdvance();}public void leave() throws InterruptedException {if (name.equals("新郎") || name.equals("新娘")) {phaser.arriveAndAwaitAdvance();} else {Thread.sleep(r.nextInt(1000));System.out.printf("%s 离开!\n", name);phaser.arriveAndAwaitAdvance();}}private void hug() throws InterruptedException {if (name.equals("新郎") || name.equals("新娘")) {Thread.sleep(r.nextInt(1000));System.out.printf("%s 抱抱!\n", name);phaser.arriveAndDeregister();} else {phaser.arriveAndDeregister();}}@Overridepublic void run() {try {arrive();eat();leave();hug();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}}class MarriagePhaser extends Phaser {@Overrideprotected boolean onAdvance(int phase, int registeredParties) {switch (phase) {case 0:System.out.println("所有人到齐");System.out.println("----------");return false;case 1:System.out.println("所有人吃完");System.out.println("----------");return false;case 2:System.out.println("所有人离开");System.out.println("----------");return false;case 3:System.out.println("婚礼结束");System.out.println("----------");return true;default:return true;}}}
phaser.getPhase() 初始值为0,如果全部线程到达集合点这个Phase+1,如果phaser.getPhase()达到Integer的最大值,这重新清空为0,在这里表示第几次集合了
phaser.arriveAndDeregister(); 表示这个线程到达集合点,就离开这个团体
phaser.arriveAndAwaitAdvance(); 表示这个线程在到某个达集合点,在等待其他线程
phaser.bulkRegister(friendNum); 表示这个线程在某个集合点遇到了friendNum个线程,他们要加入这个团体。
上述代码的意思是一共有7个人,5个person加上新郎新娘一共7个。当phaser.getPhase()为0时代码往下执行,每执行一个线程则加1,加到7后重新置为0,就可以继续向下执行了
Exchanger
public static void testExchanger() {Exchanger<String> exchanger = new Exchanger<>();new Thread(() -> {String name = "Tom";try {name = exchanger.exchange(name);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " " + name);}, "t1").start();new Thread(() -> {String name = "Jack";try {name = exchanger.exchange(name);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " " + name);}, "t2").start();}
输出结果:
t1 Jack
t2 Tom
从上面的程序可以看出,线程t1和t2内部的变量name发生了交换。Exchanger可用于两个线程之间交换数据,也是线程通信的一种方式。
LockSupport
public static void testLockSupport() throws InterruptedException {Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {System.out.println("t1 start and park...");LockSupport.park();System.out.println("t1 continue and end...");}, "t1");t1.start();Thread.sleep(3000);System.out.println("3 second later, unpark t1");LockSupport.unpark(t1);}
LockSupport相比于wait()和notify()更具有灵活性,notify()是随机唤醒一个正在等待的线程,而LockSupport可以唤醒一个特定的线程。
- 其实park/unpark的设计原理核心是“许可”:park是等待一个许可,unpark是为某线程提供一个许可。
如果某线程A调用park,那么除非另外一个线程调用unpark(A)给A一个许可,否则线程A将阻塞在park操作上。
线程的run()方法是由java虚拟机直接调用的,如果我们没有启动线程(没有调用线程的start()方法)而是在应用代码中直接调用run()方法,那么这个线程的run()方法其实运行在当前线程(即run()方法的调用方所在的线程)之中,而不是运行在其自身的线程中,从而违背了创建线程的初衷;
1.直接调用 run 是在主线程中执行了 run,没有启动新的线程(t1)
2.使用 start 是启动新的线程(t1),通过新的线程(t1)间接执行 run 中的代码
线程中的join()方法
演示示例:
public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {Counter counter = new Counter();Thread tA = new Thread(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {counter.printA();}});Thread tB = new Thread(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {counter.printB();}});Thread tC = new Thread(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {counter.printC();}});tA.start();tB.start();tC.start();}static class Counter {public void printA() {try {Thread.currentThread().sleep(500);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {System.out.println("A");}}public void printB() {try {Thread.currentThread().sleep(500);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {System.out.println("B");}}public void printC() {try {Thread.currentThread().sleep(500);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {System.out.println("C");}}}}
join()方法的源码
public final synchronized void join(long millis)throws InterruptedException {long base = System.currentTimeMillis();long now = 0;if (millis < 0) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("timeout value is negative");}if (millis == 0) {while (isAlive()) {wait(0);}} else {while (isAlive()) {long delay = millis - now;if (delay <= 0) {break;}wait(delay);now = System.currentTimeMillis() - base;}}}
因此在tA.join()当中的wait(0)方法是让main线程陷入了无尽的等待中。正是因为如此,在tA.join()之前的代码都会正常从上往下执行,而在tA.join()之后的代码都随着main线程陷入等待而无法继续执行。这样便达到了网上说的 “t.join()方法会使所有线程都暂停并等待t的执行完毕后再执行”。