什么是设计模式,它的作用是什么?
所谓设计模式,就是一套被反复使用的代码设计经验的总结(情境中一个问题经
过证实的一个解决方案)。使用设计模式是为了可重用代码、让代码更容易被他
人理解、保证代码可靠性。设计模式使人们可以更加简单方便的复用成功的设计
和体系结构。将已证实的技术表述成设计模式也会使新系统开发者更加容易理解
其设计思路。
Spring的核心容器:
spring code,spring context,spring exception language,spring bean
什么是spring IOC
IOC又叫依赖注入,主要的作用就是将对象的创建交给spring容器,容器通过读取配置文件,来创建bean对象并实例化。
ApplicationContext和BeanFactory的区别
//方式一:BeanFactory bf=new XmlBeanFactory(new ClassPathResource("applicationContext.xml"));Students student1=ac.getBean("student");//方式二:ApplicationContext ac=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");Students student1=ac.getBean("student");
- applicationContext在加载配置文件时就将配置文件中配置的bean全部创建,而beanFactory只有在调用getbean()方法时才会创建对应的bean。
这样的机制造成了applicationContext启动较慢,而且耗费资源。beanFactory第一次请求获取对应对象较慢。
Bean的装配方式
xml配置
spring提供了两种装配方式:设值注入、构造注入
设值注入要求Bean必须满足一下要求:Bean类必须提供一个默认的无参构造方法;
- Bean类必须为需要注入的属性提供对应的setter方法;
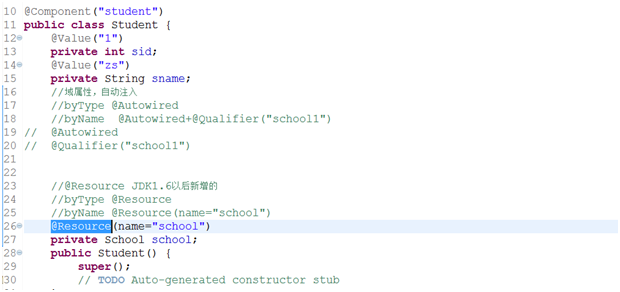
设值注入
构造注入
常用的注入属性值
基于Annotation的装配
Spring常用注解如下:
| Component | 描述Spring中的Bean,但是它是一个泛化的概念,仅仅表示一个组件(Bean)并且可以作用在任何层次; |
|---|---|
| Repository | 用于将数据访问层(DAO层)的类标识为Spring中的Bean |
| Service | 作用在业务层(service层),用于将业务层的类标识为Spring中的Bean |
| Controller | 作用在控制层(如Spring MVC 的 controller层),用于将控制层的类标识为Spring中的Bean |
| Autowired | 用于对Bean的属性变量、属性setter方法及构造方法进行标注,配合对应的注解处理器完成Bean的自动配置工作 |
| Resourse | 作用与Autowired一样。Resourse两个重要的属性:name和type。Spring将name解析为Bean实例名称,type解析为Bean实例类型 |
自动装配
就是将一个bean自动地注入到其他Bean的property中。可以按类型自动注入或者按名称自动注入。
srpingBean的生命周期

参考地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/zrtqsk/p/3735273.html
Bean的作用域
什么是AOP?
AOP: (Aspect Oriented Programming) 面向切面编程。是目前软件开发中的一个热点。利用AOP可以对业务逻辑的各个部分进行隔离,从而使得业务逻辑各部分之间的耦合度降低,提高程序的可重用性,同时提高了开发的效率。主要的功能是:日志记录,性能统计,安全控制,事务处理,异常处理等等。
动态代理和静态代理
静态代理(装配者模式)
package com.woniuxy.wrapper;class Coffee{public String getCoffee() {return "coffee";}}//是你还有你,一切拜托你////是你class MilkCoffee extends Coffee{//还有你Coffee coffee;public MilkCoffee(Coffee coffee) {this.coffee = coffee;}public String getCoffee() {//一切拜托你return "milk"+coffee.getCoffee();}}class SugarCoffee extends Coffee{Coffee coffee;public SugarCoffee(Coffee coffee) {this.coffee = coffee;}public String getCoffee() {return "sugar"+coffee.getCoffee();}}public class MyTest {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {Coffee coffee=new Coffee();System.out.println(coffee.getCoffee());MilkCoffee milkCoffee=new MilkCoffee(coffee);System.out.println(milkCoffee.getCoffee());//SugarCoffee sugarCoffee=new SugarCoffee(coffee);SugarCoffee sugarCoffee=new SugarCoffee(milkCoffee);System.out.println(sugarCoffee.getCoffee());}}
动态代理
package com.woniuxy.dynamicproxy;import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;import java.lang.reflect.Method;import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;public class MyTest {//动态代理有两种实现://Proxy:JDK内置,要求目标类,必须要有接口//cglib:第三方jar包,有没有接口都可以增强public static void main(String[] args) {//目标对象SomeService someService=new SomeServiceImpl();//返回值是一个代理对象:目标对象增强以后的对象// ClassLoader loader,类加载器// Class<?>[] interfaces,目标类的所有接口// InvocationHandler h,接口,需要用这个接口的实现类完成对目标对象的增强SomeService obj = (SomeService) Proxy.newProxyInstance(someService.getClass().getClassLoader(),someService.getClass().getInterfaces(),new InvocationHandler() {//Object proxy, 代理对象//Method method, 目标方法//Object[] args,目标方法的参数@Overridepublic Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {//切面---织入--前置通知System.out.println("前置增强:记录日志");//调用目标对象的方法Object result = method.invoke(someService, args);//切面---织入--后置通知System.out.println("后置增强:记录日志");return result;}});obj.doSome();}}