一、总体结构图
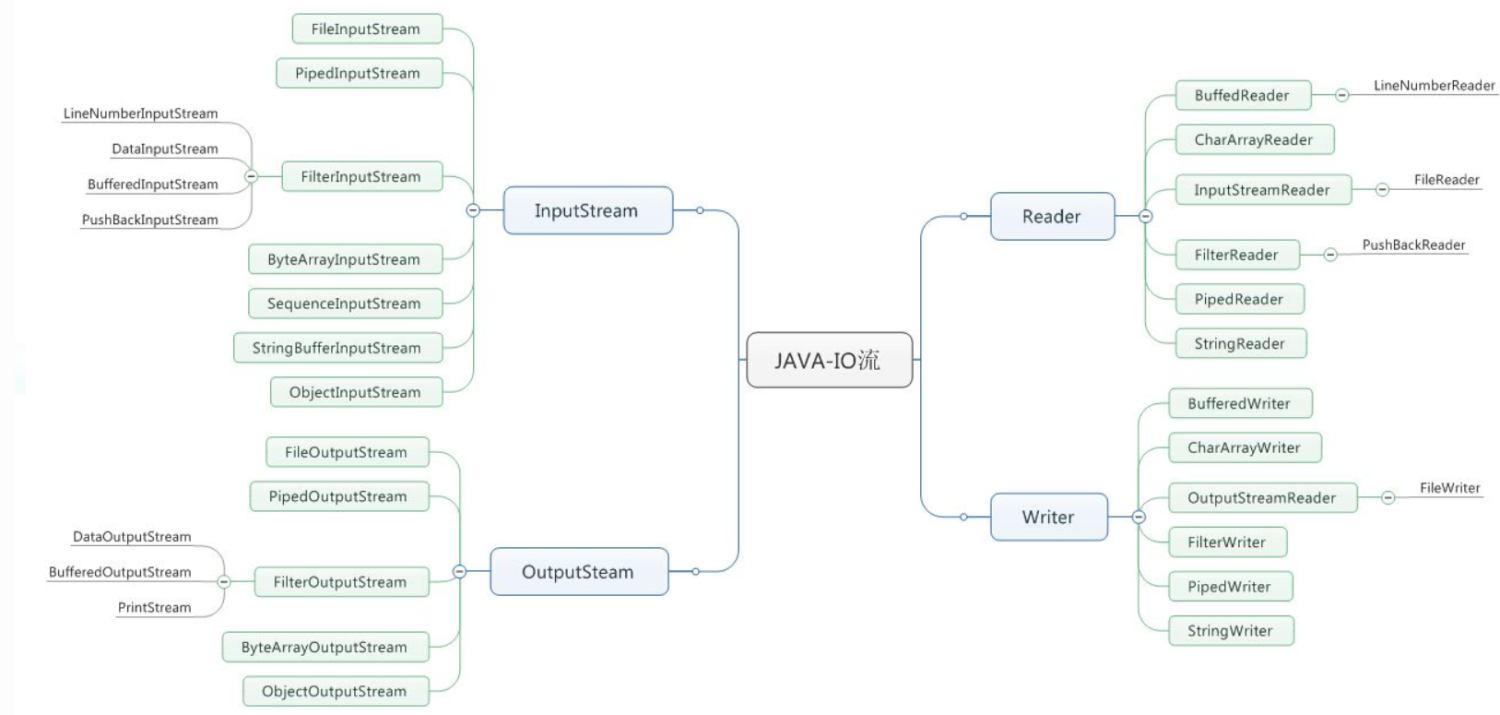
二、概念
流是什么:流是一组有顺序的,有起点和终点的字节集合,是对数据传输的抽象,即数据在两设备间的传输称为流。
三、分类
按照处理数据类型的分为:字符流和字节流
按照数据流向分为:输入流和输出流
1. 字符流和字节流
字节流:InputStream和OutputStream是java中可以按照最小字节单位读取的流,即每次读写一个字节,字节流是直接连接到输入源的流。
字符流:是以字符为单位进行数据处理的IO流。本质是基于字节流读取时,去查找指定的码表。
两者的区别:
- 读写单位不同:字节流以字节(
8bit)为单位,字符流以字符为单位,根据码表映射字符,一次可能读多个字节。 - 处理对象不同:字节流能处理所有类型的数据(如图片等),而字符流只能处理字符类型的数据。
- 字节流:一次读入或读出是
8位二进制。 - 字符流:一次读入或读出是
16位二进制。
结论:只要是处理纯文本数据,就优先考虑使用字符流。 除此之外都使用字节流。
2. 输入流和输出流
输入流:只能进行读操作,
输出流:只能进行写操作。
输入字节流 InputStream
InputStream是所有的输入字节流的父类,是一个抽象类。ByteArrayInputStream、StringBufferInputStream、FileInputStream是三种基本的介质流,分别从Byte数组、StringBuffer、和本地文件中读取数据。- PipedInputStream 是从与其它线程共用的管道中读取数据。
4.ObjectInputStream 和所有FilterInputStream 的子类都是装饰流(装饰器模式的主角)。
输出字节流 OutputStream OutputStream是所有的输出字节流的父类,是一个抽象类。ByteArrayOutputStream、FileOutputStream是两种基本的介质流,它们分别向Byte 数组、和本地文件中写入数据。PipedOutputStream是向与其它线程共用的管道中写入数据。ObjectOutputStream和所有FilterOutputStream的子类都是装饰流。
总结:
输入流:InputStream或者Reader:从文件中读到程序中;
输出流:OutputStream或者Writer:从程序中输出到文件中;
3. 节点流
节点流:直接与数据源相连,读入或读出。
直接使用节点流,读写不方便,为了更快的读写文件,才有了处理流。
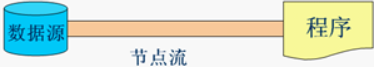
常用的节点流
- 父 类 :
InputStream、OutputStream、Reader、Writer - 文件类型 :
FileInputStream、FileOutputStrean、FileReader、FileWriter文件进行处理的节点流 - 数组类型 :
ByteArrayInputStream、ByteArrayOutputStream、CharArrayReader、CharArrayWriter对数组进行处理的节点流 - 字符串 :
StringReader、StringWriter对字符串进行处理的节点流 - 管 道 :
PipedInputStream、PipedOutputStream、PipedReader、PipedWriter对管道进行处理的节点流
4. 处理流
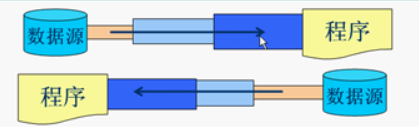
处理流和节点流一块使用,在节点流的基础上,再套接一层,套接在节点流上的就是处理流。如BufferedReader.处理流的构造方法总是要带一个其他的流对象做参数。一个流对象经过其他流的多次包装,称为流的链接。
常用的处理流
- 缓冲流:BufferedInputStrean 、BufferedOutputStream、 BufferedReader、 BufferedWriter 增加缓冲功能,避免频繁读写硬盘。
- 转换流:
InputStreamReader、OutputStreamReader实现字节流和字符流之间的转换。 - 数据流:
DataInputStream、DataOutputStream等提供将基础数据类型写入到文件中,或者读取出来。 - 转换流:
InputStreamReader、OutputStreamWriter要InputStream或OutputStream作为参数,实现从字节流到字符流的转换。
构造函数
//使用的是本系统默认的编码表GBK。InputStreamReader(InputStream)//可指定编码表。InputStreamReader(InputStream,String charSet)//使用的是本系统默认的编码表GBK。OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream)//可以指定编码表。OutputStreamwriter(OutputStream,String charSet)
5. ByteArrayInputStream、ByteArrayOutputStream
继承关系
ByteArrayInputStream entends InputStreamByteArrayOutputStream entends OutputStream
ByteArrayInputStream 可以将字节数组转化为输入流 。ByteArrayOutputStream可以捕获内存缓冲区的数据,转换成字节数组。
ByteArrayInputStream
构造函数:
public ByteArrayInputStream(byte buf[])public ByteArrayInputStream(byte buf[], int offset, int length)
常用方法:
// 关闭该流并释放与之关联的所有资源void close()//返回此流使用的字符编码的名称String getEncoding()//读取单个字符int read()//将字符读入数组中的某一部分int read(char[] cbuf, int offset, int length)//判断此流是否已经准备好用于读取。boolean ready()
ByteArrayOutputStream
构造函数
public ByteArrayOutputStream()public ByteArrayOutputStream(int size)
常用方法
void write(int b)void write(byte b[], int off, int len)void writeTo(OutputStream out)byte toByteArray()[]void close()
举个栗子
将ByteArrayOutputStream读出的字节流用FileOutputStream写入文件
public static void main(String[] args) {String mes = "helloworld" ;byte[] b = mes.getBytes() ;ByteArrayOutputStream byteArrayOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream() ;try {byteArrayOutputStream.write( b );FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream( new File( "D:/123.txt" ) ) ;byteArrayOutputStream.writeTo( fileOutputStream ) ;fileOutputStream.flush();} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {e.printStackTrace();}catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}finally{try {byteArrayOutputStream.close();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}}
6. File常用方法
创建目录
boolean file.mkdir()
如果创建成功,返回 true , 创建失败,返回false。如果这个文件夹已经存在,则返回false.
只能创建一级目录,如果父目录不存在,返回false.
创建多级目录
boolean file.mkdirs()
创建多级目录,创建成功,返回true,创建失败,返回false。如果父目录不存在,就创建,并且返回true.
创建一个新的文件
boolean file.createNewFile()
如果文件不存在就创建该文件,创建成功,返回 true ;创建失败,返回false。如果这个文件已经存在,则返回false.
判断方法
//文件是否存在boolean file.exists()//是否是文件boolean file.isFile()//是否是目录boolean file.isDirectory()//是否隐藏(windows上可以设置某个文件是否隐藏)boolean file.isHidden()//是否为绝对路径boolean file.isAbsolute()//是否可读boolean file.canRead()//是否可写boolean file.canWrite()//是否可执行boolean file.canExecute()
获取文件的信息
//获取文件的名字String file.getName()//获取父目录的绝对路径String file.getParent()//获取父文件,返回值是一个File对象File file.getParentFile()//返回文件最后一次修改的时间long time = file.lastModified() ;Date dt = new Date(time);//文件命名boolean renameTo(File file)//返回文件的大小,单位字节long file.length()//删除文件boolean file.delete()//获取该目录下的所有的文件的名字String[] file.list()//获取该目录下的所有的文件File[] file.listFiles()
注意:如果file为文件,返回值为null,在使用时记得判空;但是如果file为目录,那么返回这个目录下所有文件的名字,只是名字,不含路径;如果file是一个空目录,返回一个长度为0的数组;list() 方法,只是对file为目录时有效,当file为一个文件的时候,没有意义,listFiles()同理。
7. 栗子
使用FileInputStream类读取文件内容
public static void main(String [] args) throws IOException{int i=0;FileInputStream in=null;try {//从文件外读数据in=new FileInputStream("D:\\aaaa.txt");} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {// TODO: handle exceptionSystem.out.println("找不到文件");System.exit(-1);}try {//用于字节个数的计数int num=0;while((i=in.read())!=-1){//将得到的ASCII码值转换成字符型System.out.println((char)i);num++;}in.close();System.out.println("传输字节个数:"+num);} catch (Exception e) {// TODO: handle exceptionSystem.out.println("读取文件错误");}}
使用FileOutputStream写入文件
public static void main(String []args){int i=0;FileInputStream in=null;FileOutputStream out=null;try {//实例化FileInputStream,FileOutputStream对象in=new FileInputStream("D:\\aaaa.txt");out=new FileOutputStream("D:\\bbbb.txt");while((i=in.read())!=-1){out.write(i);System.out.println((char)i);}in.close();out.close();System.out.println("文件已复制");} catch (Exception e) {// TODO: handle exceptionSystem.out.println("文件复制错误");System.exit(-1);}}

