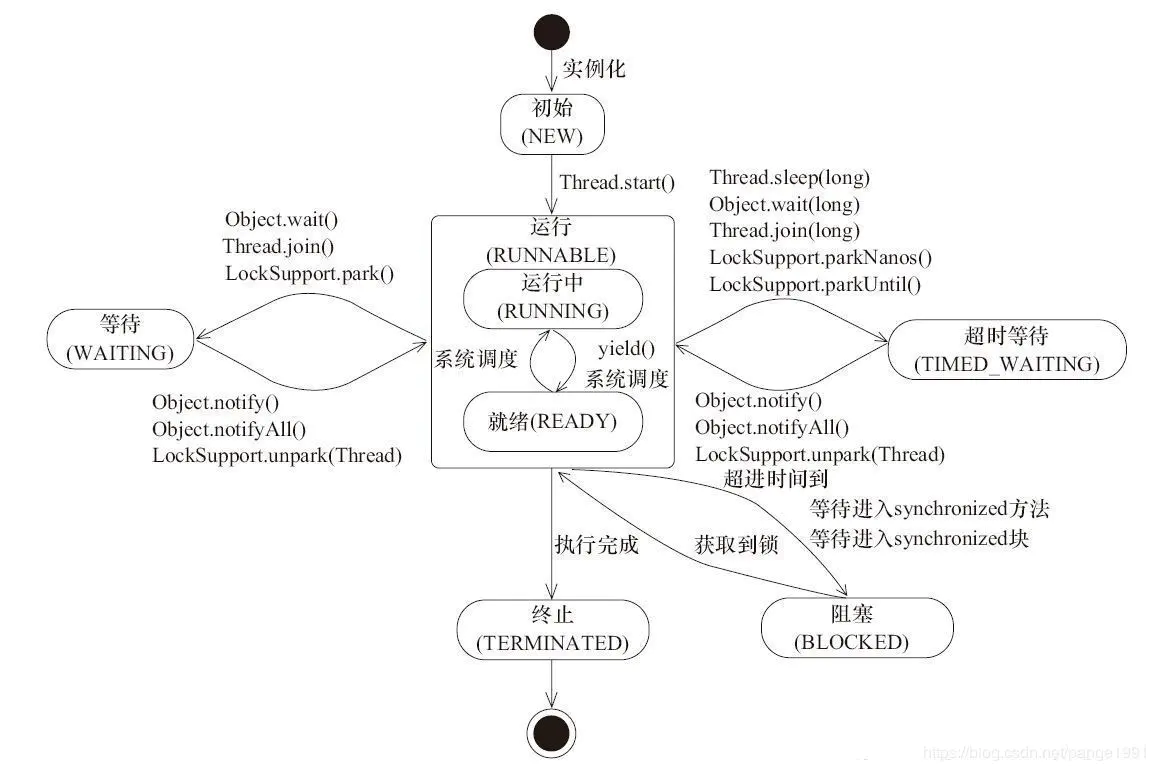
1、线程的6种状态
Thread类中有个线程状态的枚举类型
public class Thread implements Runnable {public enum State {NEW,RUNNABLE,BLOCKED,WAITING,TIMED_WAITING,TERMINATED;}}
线程状态图
2、NEW(新建状态)
线程对象被创建后,还没有调用start方法,就进入了新建状态
Thread thread = new Thread();System.out.println(thread.getState());
3、Runnable(可运行状态)
这个状态的线程,其正在JVM中执行,但是这个”执行”,不一定是真的在运行, 也有可能是在等待CPU资源。所以,在网上,有人把这个状态区分为READY和RUNNING两个,一个表示的start了,资源一到位随时可以执行,另一个表示真正的执行中
Thread thread = new Thread();thread.start();System.out.println(thread.getState());
4、Blocked(阻塞状态)
- 这个状态,一般是线程等待获取一个锁,来继续执行下一步的操作,比较经典的就是synchronized关键字,这个关键字修饰的代码块或者方法,均需要获取到对应的锁,在未获取之前,其线程的状态就一直未BLOCKED,如果线程长时间处于这种状态下,我们就是当心看是否出现死锁的问题了
- 下例输出结果
Thread-0: start TIMED_WAITING BLOCKED Thread-0: end Thread-1: start Thread-1: end
public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {Object obj = new Object();MyThread thread1 = new MyThread(obj);thread1.start();MyThread thread2 = new MyThread(obj);thread2.start();try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}// TIMED_WAITINGSystem.out.println(thread1.getState());// BLOCKEDSystem.out.println(thread2.getState());}public static class MyThread extends Thread {private Object obj;public MyThread(Object obj) {this.obj = obj;}@Overridepublic void run() {synchronized (obj){System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+": start");try {Thread.sleep(10000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+": end");}}}}
5、WAITING(无限等待)
- WAITING状态的线程不再活动,不会浪费CPU资源,也不会去竞争锁;此状态下会等待别的线程执行notify通知,重新进入调度队列中
一个线程进入WAITING无限等待状态,一定是执行了如下的代码
Object.wait()
当一个线程执行了Object.wait()的时候,它一定在等待另一个线程执行Object.notify()或者Object.notifyAll()。
Thread.join()
一个线程thread,其在主线程中被执行了thread.join()的时候,主线程即会等待该线程执行完成。
LockSupport.park()
当一个线程执行了LockSupport.park()的时候,其在等待执行LockSupport.unpark(thread)。
需要关注的是,这边的等待是没有时间限制的,当发现有这种状态的线程的时候,若其长时间处于这种状态,也需要关注下程序内部有无逻辑异常
Object.wait()
代码执行效果
Thread-0: start 0 1 wait WAITING notify 2 3 4 Thread-0: end
public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {Object obj = new Object();MyThread thread1 = new MyThread(obj);thread1.start();Thread.sleep(4000);// WAITINGSystem.out.println(thread1.getState());synchronized (obj){obj.notify();System.out.println("notify");}}public static class MyThread extends Thread {private Object obj;public MyThread(Object obj) {this.obj = obj;}@Overridepublic void run() {synchronized (obj){System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+": start");for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {try {if (i == 2){System.out.println("wait");obj.wait();}Thread.sleep(1000);System.out.println(i);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+": end");}}}}
thread.join()
- 执行结果
thread1 start thread2 start thread1.join()后 , thread2 等待 thread1 执行完毕
thread1 end
thread1 执行完毕,thread2继续执行
thread2 end
public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {Thread1 thread1 = new Thread1();thread1.setName("thread1");thread1.start();Thread2 thread2 = new Thread2(thread1);thread2.setName("thread2");thread2.start();}public static class Thread1 extends Thread {public Thread1() {}@Overridepublic void run() {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" start");try {Thread.sleep(3000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" end");}}public static class Thread2 extends Thread {private Thread thread1;public Thread2(Thread thread1) {this.thread1 = thread1;}@Overridepublic void run() {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" start");try {System.out.println("thread1.join()后 , thread2 等待 thread1 执行完毕");// 等待thread1执行完毕后,当前线程(就是thread2)才会执行后续thread1.join();System.out.println("thread1 执行完毕,thread2继续执行");} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" end");}}}
LockSupport.park()
- 代码执行结果
Thread-0 start
WAITING
Thread-0 end
TERMINATED
public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {MyThread thread1 = new MyThread();thread1.start();Thread.sleep(100);// WAITINGSystem.out.println(thread1.getState());// 唤醒线程LockSupport.unpark(thread1);Thread.sleep(100);// TERMINATEDSystem.out.println(thread1.getState());}public static class MyThread extends Thread {@Overridepublic void run() {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" start");// 阻塞线程LockSupport.park();System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" end");}}}
6、TIMED_WAITING(计时等待)
- 这个状态和WAITING状态的区别就是,这个状态的等待是有一定时效的,即可以理解为WAITING状态等待的时间是永久的,即必须等到某个条件符合才能继续往下走,否则线程不会被唤醒。但是TIMED_WAITING,等待一段时间之后,会唤醒线程去重新获取锁。当执行如下代码的时候,对应的线程会进入到TIMED_WAITING状态
以下这几个方法都会导致线程进入TIMED_WAITING
下面代码执行结果
Thread-0: start TIMED_WAITING
Thread-0: end
TERMINATED
Thread thread = new Thread(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+": start");try {Thread.sleep(3000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+": end");}});thread.start();try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}// TIMED_WAITINGSystem.out.println(thread.getState());try {Thread.sleep(3000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}// TERMINATEDSystem.out.println(thread.getState());
obj.wait(long)
- 代码执行结果
Thread-0: start
0
1
wait sart
TIMED_WAITING
wait end
2
3
4
Thread-0: end
public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {Object obj = new Object();MyThread thread1 = new MyThread(obj);thread1.start();Thread.sleep(2000);// WAITINGSystem.out.println(thread1.getState());}public static class MyThread extends Thread {private Object obj;public MyThread(Object obj) {this.obj = obj;}@Overridepublic void run() {synchronized (obj){System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+": start");for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {try {if (i == 2){System.out.println("wait sart");obj.wait(3000);System.out.println("wait end");}System.out.println(i);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+": end");}}}}
7、TERMINATED(终止)
- 线程执行结束之后的状态