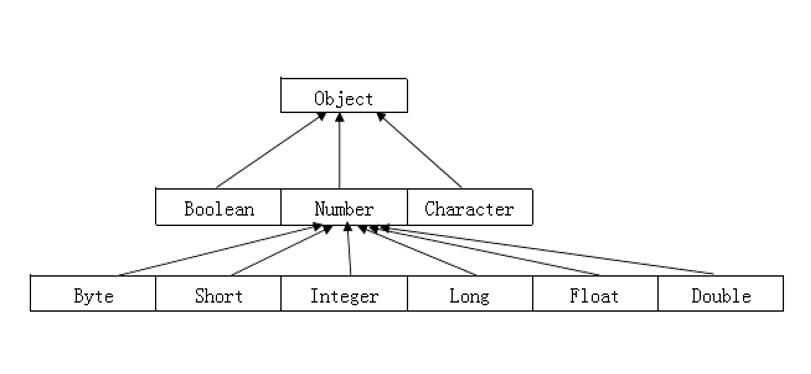
实用类:
包装类的作用:
提供了一系列使用的方法
在某些需要使用包装类来表示的情况下使用,比如集合
构造方法:(已废弃)
所有的包装类,都可以用对应的基本类型作为参数来创建实例
int a=1;Integer b=new Integer(a);char c='a';Character c2=new Character(c);
注意事项:
1.Boolean类型只有给true(不区分大小写)才是true,其他值都是false
boolean b1=new Boolean("true");//trueboolean b2=new Boolean("tRue");//trueboolean b3=new Boolean("ert");//false
2.当Number包装类构造方法参数为String 类型时,字符串不能为null,且该字符串必须可解析为相应的基本数据类型的数据,否则编译不通过,运行时会抛出NumberFormatException异常
Integer a=new Integer("100");//正确Integer b=new Integer("a");//报错
常用方法:
4个方法:Value()、toString()、parse()、valueOf()
*value():
将包装类型装换为基本类型
Integer a=new Integer(12);int b=a.intValue();//int b=a;Character c=new Character('v');char c2=c.charValue();//char c2=c;;
toString:
将基本类型转换成字符串类型(基本类型—->字符串)
//将基本类型转换为字符串//方法一int a=10;String s=Integer.toString(a);System.out.println(s);//方法二String s2=a+"";
parse*():
把字符串类型转换为相应的基本数据类型(Character除外)(字符串—->基本类型)
//字符串转基本数据类型String s="100";//方法一int a=new Integer(s);//方法二int b=Integer.parseInt(s);double d=Double.parseDouble("99.9");
valueOf():
将基本类型转换为包装类(Character除外)(基本类型———>包装类)
注意事项:除Character类外,其他包装类都可以使用如下重载方法 public static Type valueOf(String s)
//基本类型装换为包装类int i=10;//方法一Integer b=Integer.valueOf(i);//方法二Integer c=i;
基本类型和包装类的自动转换:
//自动装箱Integer i=10;//自动拆箱int a=i;
自动装箱:将基本数据类型赋值给包装类
自动拆箱:将包装类装换为基本数据类型
Math类:
Math提供了常用的数学运算方法和两个静态常量(E:double值比其他任何一个都更接近 e ,自然对数的基数)和(PI:double值比任何其他的更接近 pi ,圆周长与其直径的比率)
floor向下取整
ceil向上取整
round四舍五入
abs求绝对值
random随机数
Math.pow(a,b)a的b次方
Math.pow(x,2)就是平方
Math.pow(x,3)就是立方
Math.sqrt(num)num的平方根
double d=Math.floor(9.9);System.out.println("9.9向下取整:"+d);double d1=Math.ceil(9.9);System.out.println("9.9向上取整:"+d1);double d2=Math.round(9.9);System.out.println("9.9四舍五入::"+d);int a=Math.abs(-2);System.out.println("-2绝对值:"+a);double x=Math.pow(2,4);System.out.println("2的4次方:"+x);double y=Math.sqrt(64);System.out.println("64的算术平方根:"+y);//9.9向下取整:9.0//9.9向上取整:10.0//9.9四舍五入::9.0//-2绝对值:2//2的4次方:16.0//64的算术平方根:8.0
String类:
常用方法:
length():返回字符串的长度
equals():比较两个字符串
equalslgnoreCase():忽略大小写进行比较
== 和 equals 的区别
当大家看了上面的内容,相信大家对这两种方式比较对象的区别应该有点了解
对于基本类型:
- == 比较的是具体的值
- equals 无法用于基本类型的比较,要注意
对于引用类型:
- == 比较的是地址值
- equals 一般情况下比较的也是地址值,除非重写 equals 方法,自定义比较规则
concat():字符串拼接
String str=1.concat(2):将字符串2拼接的字符串1的后面形成新的字符字符串提取查询方法:
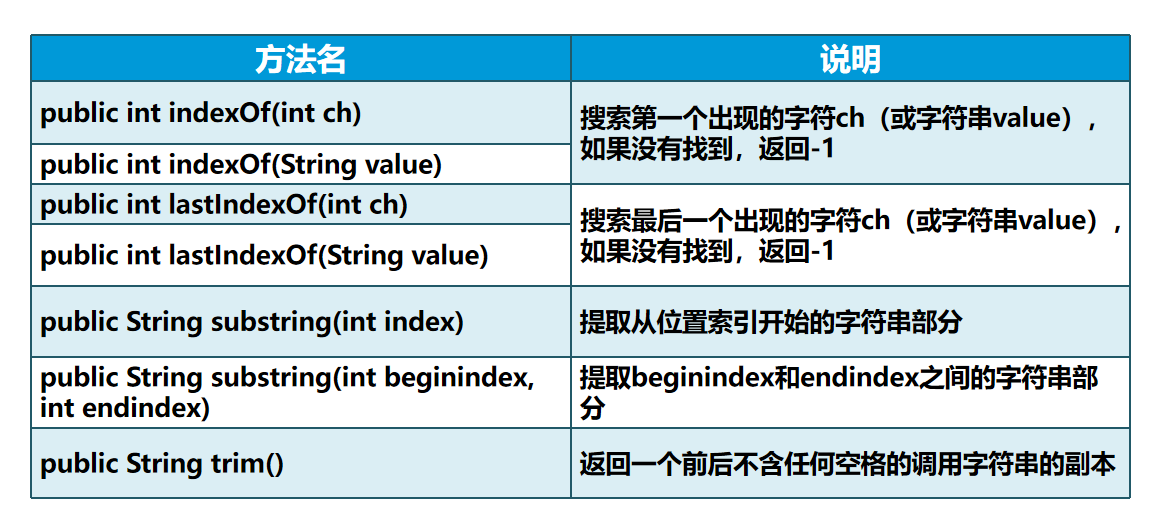
| public int indexOf(int ch) | 搜索并返回第一个出现字符ch(或字符串value)的位置处 如果没有找到返回-1 |
|---|---|
| public int indexOf(String value) | |
| String str=”abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz”; int a=str.indexOf(‘x’);//23 |
|
| public int lastIndexOf(int ch) | 搜索并返回最后出现字符ch(或字符串value)的位置处 如果没有找到返回-1 |
| public int lastIndexOf(String value) | |
| String str=”xabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz”; int a=str.lastIndexOf(‘x’);//24 |
|
| public String substring(int index) | 提取指定索引位置开始的部分字符串 |
| String str=”abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz”; String newstr=str.substring(_5)_;//fghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz |
|
| public String substring(int beginindex,int endindx) | 提取beginindex和endindex之间的字符串 |
| String str=”abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz”; String newstr=str.substring(_5,10)_;//fghij(截取时左包含,右不包含) |
|
| public String trim() | 截取字符串前后的空格后返回新的字符串 |
| String str=” asdfg”; String newstr=str.trim(); System.out.println(_str.length());//10 System._out.println(_newstr.length())_;//5 |
|
| public String replace() | 替换指定字符 |
| String s = “a a a a a “; String s2=s.replace(“ “,””);//aaaaa |
|
| public String[] split() | 字符串分割 |
| String s = “a-a-a-a-a”; String[] _s2 = s.split(“-“)_;//[a, a, a, a, a] |
StringBuffer:
常用方法:
| toString() | 将stringBuffer类装换为string类 |
|---|---|
| StringBuffer stringBuffer=new StringBuffer(“1234”); String str=stringBuffer.toString();//1234 |
|
| append(参数) | 将参数连接到字符串后并返回 |
| String str=”12345”; StringBuffer strb=new StringBuffer(_str); strb.append(“6789”); str=strb.toString();//123456789_ |
|
| insert() | 将指定内容插入到指定位置处 |
| String str=”12345”; StringBuffer strb=new StringBuffer(_str); strb.insert(3,”,”); str=strb.toString();//123,45_ |
String类是不可变的对象
经常改变内容的字符串最后好不要使用string
StringBuffer是可变的字符串
字符串经常改变的情况下使用StringBuffer更高效
jdk5.0后提供了StringBuilder,StringBuffer线程安全,StringBuilder线程更安全,但更快
Date类:
| yyyy | 年 |
|---|---|
| MM | 月 |
| dd | 日 |
| HH/hh | 24小时制/12小时制 |
| mm | 分 |
| ss | 秒 |
| //创建时间对象,当前时间 _Date date=new Date(); //创建格式化对象 DateFormat df=new SimpleDateFormat(“yyyy年MM月dd日 hh:mm:ss”); String s=df.format(date)_;//2021年05月20日 03:40:47 |
Calendar类:
| YEAR | 年 |
|---|---|
| MONTH | 月,美国月份从0开始,中国月份需要加1 |
| DAY_OF_MONTH | 日 |
| HOUR_OF_MONTH/HOUR | HOUR:12小时制HOUR_OF_DAY:24小时制 |
| MINUTE | 分 |
| SECOND | 秒 |
| //获得日历对象 _Calendar c=Calendar._getInstance(); System.out.println(_c.get(Calendar._YEAR));//年 _System._out.println(_c.get(Calendar._MONTH)+1);//美国月份从0开始,中国月份需加1 _System._out.println(_c.get(Calendar._DAY_OF_MONTH));//日 _System._out.println(_c.get(Calendar._HOUR_OF_DAY));//HOUR:12小时制HOUR_OF_DAY:24小时制 _System._out.println(_c.get(Calendar._MINUTE));//分 _System._out.println(_c.get(Calendar._SECOND));//秒 |
|
| DAY_OF_WEEK | 星期几 |
| AM_PM | 上午下午 |
| WEEK_OF_YEAR | 当年第几周 |
| WEEK_OF_MONTH | 当月有几周 |
| DAY_OF_WEEK_IN_MONTH | 当月第几周 |
| DAY_OF_YEAR | 本年第几天 |