let声明—-let a=123
let demo = (a) => {console.log(a);}demo(123)//123
- 没有变量提升—必须先声明,再使用
- 不可重复定义—重复声明报错
- 块级作用域—-如:if(){},for(){},function(){}这样的代码块
箭头函数—-let demo=(x,y)=>{ }
- 语法改变,从function (){ }——->()=>{ }
如果函数只有一个参数可以省略括号()
let demo = a => {console.log(a);}demo(123)//123
如果函数只有一个参数且执行语句只有一条可省略{ }花括号
let demo = a => console.log(a);demo(123)
this指向问题
旧函数:谁调用this指向谁,而箭头函数是创建时就确定了this指向
function fun() {let demo = () => {console.log(this);}demo()}let obj2 = {user: 111,pwd: 222,fun: fun}obj2.fun()//{user: 111, pwd: 222, fun: ƒ}//this指向fun(),fun的this指向的obj2
function fun() {console.log(this);}let obj = {name: 123,sex: 'nv',fun: fun}obj.fun()//{name: 123, sex: 'nv', fun: ƒ}//this指向obj
let demo = () => {console.log(this);}let obj = {name: 123,sex: 'nv',demo: demo}obj.demo()//Window {window: Window, self: Window, document: document, name: '', location: Location, …}//指向window
不可通过call( ),apply( )更改this指向
let demo = () => {console.log(this);}let obj2 = {user: 111,pwd: 222,fun: fun}demo.call(obj2)//指向window
let demo = () => {console.log(this);}let obj2 = {user: 111,pwd: 222,fun: fun}demo.apply(obj2)//指向window
1
- 2
- 3
模板字符串
旧时拼接
let str1 = 123let str2 = str1 + 'xiaoming'console.log(str2);//123xioaming
ES6拼接
let str1 = 123let str2 = `${str1}xioaming`console.log(str2);//123xioaming
class类——就是一个语法糖
定义
class stu1{constructor(name,sex){this.name=namethis.sex=sexthis.grade=function () {console.log(123)}}mood(){console.log(234)}}let class1=new stu1('xiaoming','男')
静态属性和静态方法——-该方法不能通过实例调用/
class stu1 {constructor(name, sex) {this.name = namethis.sex = sexthis.grade = function () {console.log(123)}}mood() {console.log(234)}//静态方法static getXingGe() {console.log('性格')}//静态属性static name='女'}let class1 = new stu1('xiaoming', '男')console.log(class1);class1.mood()// class1.getXingGe()---//class1.getXingGe is not a functionstu1.getXingGe()//只能通过类名调用,不能通过实例对象调用
class类继承

- 私有属性和私有方法
- for…of循环
- for…in循环
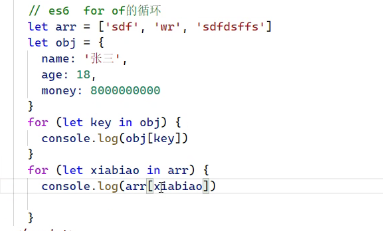
- for…of循环

