
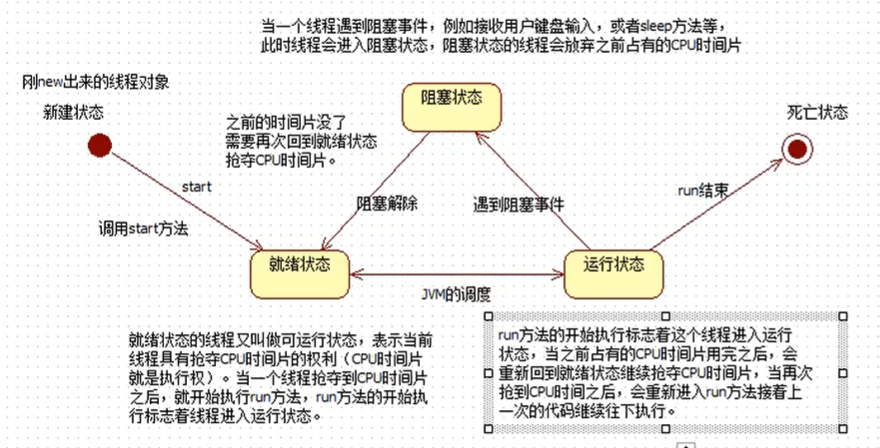


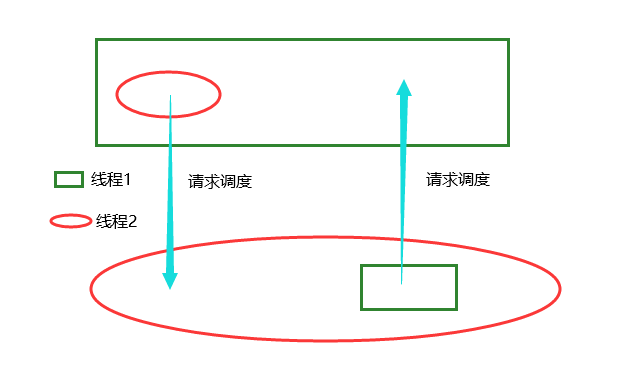
死锁:
//死锁public class Synchronized { public static void main(String[] args) { MyThread thread = new MyThread(); MyThread thread1 = new MyThread(); thread.start(); thread1.start(); }}class MyThread extends Thread { static Object object1 = new Object(); static Object object2 = new Object(); @Override public void run() { while (true){ test01(); test02(); } } public static void test01(){ synchronized(object1){ System.out.println("1"); synchronized(object2){ System.out.println("2"); } } } public static void test02(){ synchronized(object2){ System.out.println("3"); synchronized(object1){ System.out.println("4"); } } }}
死锁原理:
生产消费者线程
import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.Iterator;import java.util.List;//生产消费者线程public class Synchronized { public static void main(String[] args) { //运输媒介 List<Integer> storage = new ArrayList<>(100); new Thread(new Product(storage)).start(); new Thread(new Consumer(storage)).start(); }}class Product implements Runnable { private List<Integer> storage; public Product(List<Integer> storage) { this.storage = storage; } @Override public void run() { while (true) { synchronized (storage) { if (storage.size() < 10) { storage.add(1); System.out.println("生产一个"); } else { try { //唤醒所有在使用storage对象的线程 storage.notifyAll(); //让出当前使用storage对象并抢占了锁的线程,总之就是让出当前线程占用的锁 storage.wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } }}class Consumer implements Runnable { List<Integer> storage; public Consumer(List<Integer> storage) { this.storage = storage; } @Override public void run() { while (true) { synchronized (storage) { if (storage.size() > 0) { Iterator it = storage.iterator(); while (it.hasNext()){ System.out.println("消费:"+it.next()); it.remove(); } }else { try { storage.notifyAll(); storage.wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } }}
例:奇数偶数交换输出
import com.sun.scenario.effect.impl.sw.sse.SSEBlend_SRC_OUTPeer;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.List;public class HomeWork { public static void main(String[] args) { List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(1); Integer i = 1; list.add(i); new Thread(new Even(list)).start(); new Thread(new Odd(list)).start(); }}class Even implements Runnable { private List<Integer> list; public Even(List<Integer> list) { this.list = list; } @Override public void run() { while (true) { try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } synchronized (list) { if (list.get(0) % 2 != 0) { System.out.println("奇数:"+list.get(0)); list.set(0,list.get(0)+1); }else { list.notifyAll(); try { list.wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } }}class Odd implements Runnable { private List<Integer> list; public Odd(List<Integer> list) { this.list = list; } @Override public void run() { while (true) { synchronized (list) { try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } if (list.get(0) % 2 == 0) { System.out.println("偶数:"+list.get(0)); list.set(0,list.get(0)+1); }else { list.notifyAll(); try { list.wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } }}
 ">
">




