剑指 Offer 13. 机器人的运动范围
地上有一个m行n列的方格,从坐标 [0,0] 到坐标 [m-1,n-1] 。一个机器人从坐标 [0, 0] 的格子开始移动,它每次可以向左、右、上、下移动一格(不能移动到方格外),也不能进入行坐标和列坐标的数位之和大于k的格子。例如,当k为18时,机器人能够进入方格 [35, 37] ,因为3+5+3+7=18。但它不能进入方格 [35, 38],因为3+5+3+8=19。请问该机器人能够到达多少个格子?
示例 1:输入:m = 2, n = 3, k = 1输出:3示例 2:输入:m = 3, n = 1, k = 0输出:1提示:1 <= n,m <= 1000 <= k <= 20
BFS
class Solution {int getSum(int x) {int res = 0;for (; x != 0; x /= 10) {res += x % 10;}return res;}public int movingCount(int m, int n, int k) {if (k == 0) {return 1;}Queue<Pair<Integer, Integer>> queue = new LinkedList<>();int[] dx = {0, 1};int[] dy = {1, 0};boolean[][] visited = new boolean[m][n];queue.offer(new Pair<>(0, 0));visited[0][0] = true;int ans = 1;while (!queue.isEmpty()) {Pair<Integer, Integer> pair = queue.poll();int x = pair.getKey();int y = pair.getValue();for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {int tx = dx[i] + x;int ty = dy[i] + y;if (tx < 0 || tx >= m || ty < 0 || ty >= n || visited[tx][ty] || getSum(tx) + getSum(ty) > k) {continue;}queue.offer(new Pair<>(tx, ty));visited[tx][ty] = true;ans++;}}return ans;}}
DFS
class Solution {int getSum(int x) {int res = 0;for (; x != 0; x /= 10) {res += x % 10;}return res;}public int movingCount(int m, int n, int k) {if (k == 0) {return 1;}boolean[][] visited = new boolean[m][n];return dfs(0, 0, m, n, k, visited);}private int dfs(int i, int j, int m, int n, int k, boolean[][] visited) {if (i < 0 || i >= m || j < 0 || j >= n || getSum(i) + getSum(j) > k || visited[i][j]) {return 0;}visited[i][j] = true;return 1 + dfs(i + 1, j, m, n, k, visited) + dfs(i, j + 1, m, n, k, visited);}}
695. 岛屿的最大面积
给定一个包含了一些 0 和 1的非空二维数组 grid , 一个 岛屿 是由四个方向 (水平或垂直) 的 1 (代表土地) 构成的组合。你可以假设二维矩阵的四个边缘都被水包围着。
找到给定的二维数组中最大的岛屿面积。(如果没有岛屿,则返回面积为0。)
示例 1:
[[0,0,1,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0],
[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,1,0,0,0],
[0,1,1,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0],
[0,1,0,0,1,1,0,0,1,0,1,0,0],
[0,1,0,0,1,1,0,0,1,1,1,0,0],
[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0],
[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,1,0,0,0],
[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,0,0,0,0]]
对于上面这个给定矩阵应返回 6。注意答案不应该是11,因为岛屿只能包含水平或垂直的四个方向的‘1’。
示例 2:
[[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0]]
对于上面这个给定的矩阵, 返回 0。
注意: 给定的矩阵grid 的长度和宽度都不超过 50。
DFS
思路分析:基于回溯法思路
1、max 记录最大岛屿面积
2、visited[][] 记录当前坐标是否已被访问
3、当遍历一个未被访问过的 1 时,向上下左右进行遍历,每遍历一个 1岛屿面积+1
class Solution {int[][] move = {{1, 0}, {-1, 0}, {0, 1}, {0, -1}};private boolean isValid(int[][] grid, boolean[][] visited, int x, int y){if(x < 0 || x >= grid.length || y < 0 || y >= grid[0].length || visited[x][y] || grid[x][y] != 1){return false;}return true;}private int dfs(int[][] grid, boolean[][] visited, int x, int y, int count){if(!isValid(grid, visited, x, y)){return count;}visited[x][y] = true;for(int i = 0; i < move.length; ++i){count = dfs(grid, visited, x + move[i][0], y + move[i][1], count);}return count + 1;}public int maxAreaOfIsland(int[][] grid) {int max = 0, row = grid.length, col = grid[0].length;boolean[][] visited = new boolean[row][col];for(int i = 0; i < row; ++i){for(int j = 0; j < col; ++j){if(grid[i][j] == 1){int count = dfs(grid, visited, i, j, 0);max = max > count ? max : count;}}}return max;}}
200. 岛屿数量
给定一个由 ‘1’(陆地)和 ‘0’(水)组成的的二维网格,计算岛屿的数量。一个岛被水包围,并且它是通过水平方向或垂直方向上相邻的陆地连接而成的。你可以假设网格的四个边均被水包围。
示例 1:
输入:
11110
11010
11000
00000
输出: 1
示例 2:
输入:
11000
11000
00100
00011
输出: 3
DFS
跟上一题思路一致,上题是求最大面积,这题是求个数。
class Solution {
int[][] move = {{1, 0}, {-1, 0}, {0, 1}, {0, -1}};
private int dfs(char[][] grid, boolean[][] visited, int x, int y, int count){
if(x < 0 || x >= grid.length || y < 0 || y >= grid[0].length || grid[x][y] != '1' || visited[x][y])
return count;
visited[x][y] = true;
for(int i = 0; i < move.length; ++i){
count = dfs(grid, visited, x + move[i][0], y + move[i][1], count);
}
return count+1;
}
public int numIslands(char[][] grid) {
if(grid.length == 0)
return 0;
int total = 0, row = grid.length, col = grid[0].length;
boolean[][] visited = new boolean[row][col];
int count = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < row; ++i){
for(int j = 0; j < col; ++j){
if(grid[i][j] == '1'){
count = dfs(grid, visited, i, j, 0);
if(count >= 1){
total++;
}
}
}
}
return total;
}
}
BFS
线性扫描整个二维网格,如果一个结点包含 1,则以其为根结点启动广度优先搜索。将其放入队列中,并将值设为 0 以标记访问过该结点。迭代地搜索队列中的每个结点,直到队列为空。
class Solution {
public int numIslands(char[][] grid) {
if(grid == null || grid.length == 0){
return 0;
}
int total = 0, row = grid.length, col = grid[0].length;
for(int i = 0; i < row; ++i){
for(int j = 0; j < col; ++j){
if(grid[i][j] == '1'){
++total;
grid[i][j] = '0';
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(i * col + j);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int id = queue.remove();
int r = id / col;
int c = id % col;
if(r - 1 >= 0 && grid[r - 1][c] == '1'){
queue.add((r - 1) * col + c);
grid[r - 1][c] = '0';
}
if(r + 1 < row && grid[r + 1][c] == '1'){
queue.add((r + 1) * col + c);
grid[r + 1][c] = '0';
}
if(c - 1 >= 0 && grid[r][c - 1] == '1'){
queue.add(r * col + c - 1);
grid[r][c - 1] = '0';
}
if(c + 1 < col && grid[r][c + 1] == '1'){
queue.add(r * col + c + 1);
grid[r][c + 1] = '0';
}
}
}
}
}
return total;
}
}
并查集
class Solution {
class UnionFind{
int count;
int[] parent;
public UnionFind(char[][] grid){
count = 0;
int m = grid.length;
int n = grid[0].length;
parent = new int[m * n];
for(int i = 0; i < m; ++i){
for(int j = 0; j < n; ++j){
if(grid[i][j] == '1'){
parent[i * n + j] = i * n + j;
++count;
}
}
}
}
public int find(int i){
if(parent[i] != i) parent[i] = find(parent[i]);
return parent[i];
}
public void union(int x, int y){
int rootx = find(x);
int rooty = find(y);
if(rootx != rooty){
parent[rootx] = rooty;
--count;
}
}
public int getCount(){
return count;
}
}
public int numIslands(char[][] grid) {
if(grid == null || grid.length == 0){
return 0;
}
int total = 0, row = grid.length, col = grid[0].length;
UnionFind uf = new UnionFind(grid);
for(int i = 0; i < row; ++i){
for(int j = 0; j < col; ++j){
if(grid[i][j] == '1'){
grid[i][j] = '0';
int old = i * col + j;
if(i - 1 >= 0 && grid[i - 1][j] == '1'){
uf.union(old, (i - 1) * col + j);
}
if(i + 1 < row && grid[i + 1][j] == '1'){
uf.union(old, (i + 1) * col + j);
}
if(j - 1 >= 0 && grid[i][j - 1] == '1'){
uf.union(old, i * col + j - 1);
}
if(j + 1 < col && grid[i][j + 1] == '1'){
uf.union(old, i * col + j + 1);
}
}
}
}
return uf.getCount();
}
}
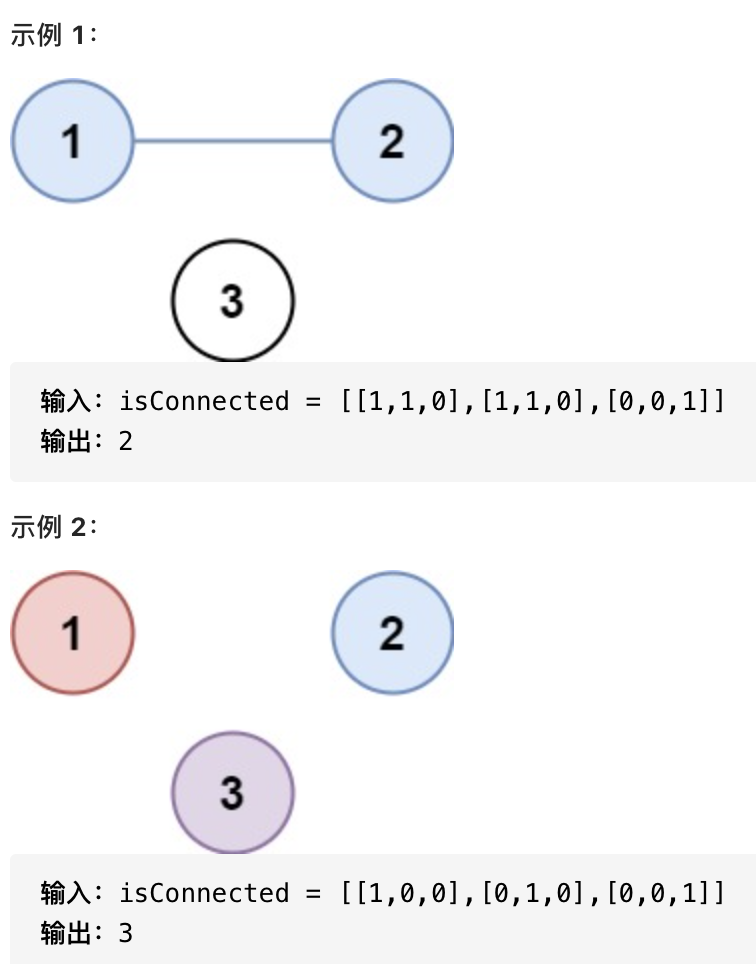
547. 省份数量
有 n 个城市,其中一些彼此相连,另一些没有相连。如果城市 a 与城市 b 直接相连,且城市 b 与城市 c 直接相连,那么城市 a 与城市 c 间接相连。
省份 是一组直接或间接相连的城市,组内不含其他没有相连的城市。
给你一个 n x n 的矩阵 isConnected ,其中isConnected[i][j]= 1表示第 i 个城市和第 j 个城市直接相连,而isConnected[i][j] = 0 表示二者不直接相连。
返回矩阵中 省份 的数量。
DFS
直接DFS
class Solution {
void dfs(int[][] isConnected, int i, boolean[] visited) {
visited[i] = true;
int m = isConnected.length;
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if (!visited[j] && isConnected[i][j] == 1) {
dfs(isConnected, j, visited);
}
}
}
public int findCircleNum(int[][] isConnected) {
if (isConnected == null || isConnected.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
int m = isConnected.length;
int total = 0;
boolean[] visited = new boolean[m];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
if (!visited[i]) {
dfs(isConnected, i, visited);
total++;
}
}
return total;
}
}
BFS
class Solution {
public int findCircleNum(int[][] M) {
int m = M.length;
int total = 0;
boolean[] visited = new boolean[m];
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
if (!visited[i]){
queue.add(i);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int s = queue.remove();
visited[s] = true;
for (int j = 0; j < m; ++j){
if (!visited[j] && M[s][j] == 1){
queue.add(j);
}
}
}
total++;
}
}
return total;
}
}
并查集
class Solution {
private int find(int[] a, int i){
if (a[i] == -1){
return i;
}
return find(a, a[i]);
}
private void union(int[] a, int i, int j){
int x = find(a, i);
int y = find(a, j);
if (x != y){
a[x] = y;
}
}
public int findCircleNum(int[][] M) {
int m = M.length;
int total = 0;
int[] a = new int[m];
Arrays.fill(a, -1);
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++){
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++){
if (M[i][j] == 1 && i != j){
union(a, i, j);
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i){
if (a[i] == -1){
total++;
}
}
return total;
}
}
130. 被围绕的区域
给定一个二维的矩阵,包含 ‘X’ 和 ‘O’(字母 O)。
找到所有被 ‘X’ 围绕的区域,并将这些区域里所有的 ‘O’ 用 ‘X’ 填充。
示例:
X X X X
X O O X
X X O X
X O X X
运行你的函数后,矩阵变为:
X X X X
X X X X
X X X X
X O X X
解释:
被围绕的区间不会存在于边界上,换句话说,任何边界上的 ‘O’ 都不会被填充为 ‘X’。 任何不在边界上,或不与边界上的 ‘O’ 相连的 ‘O’ 最终都会被填充为 ‘X’。如果两个元素在水平或垂直方向相邻,则称它们是“相连”的。
DFS
将边界上的O和与边界上的O相邻的O替换为T,这些T是不符合填充为X的条件的,再遍历整个矩阵,将剩余的O替换为X,并将T替换为O.
class Solution {
private int m, n;
private int[][] direction = {{1, 0}, {-1, 0}, {0, 1}, {0, -1}};
private void dfs(char[][] board, int i, int j){
if (i < 0 || i >= m || j < 0 || j >= n || board[i][j] != 'O'){
return;
}
board[i][j] = 'T';
for (int[] d : direction){
dfs(board, i + d[0], j + d[1]);
}
return;
}
public void solve(char[][] board) {
if (board == null || board.length == 0){
return;
}
m = board.length;
n = board[0].length;
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i){
dfs(board, i, 0);
dfs(board, i, n - 1);
}
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j){
dfs(board, 0, j);
dfs(board, m - 1, j);
}
for(int i = 0; i < m; ++i){
for(int j = 0; j < n; ++j){
if (board[i][j] == 'T'){
board[i][j] = 'O';
}else if (board[i][j] == 'O'){
board[i][j] = 'X';
}
}
}
}
}
417. 太平洋大西洋水流问题
给定一个 m x n 的非负整数矩阵来表示一片大陆上各个单元格的高度。“太平洋”处于大陆的左边界和上边界,而“大西洋”处于大陆的右边界和下边界。
规定水流只能按照上、下、左、右四个方向流动,且只能从高到低或者在同等高度上流动。
请找出那些水流既可以流动到“太平洋”,又能流动到“大西洋”的陆地单元的坐标。
提示:
输出坐标的顺序不重要
m 和 n 都小于150
示例:
给定下面的 5x5 矩阵:
太平洋 ~ ~ ~ ~ ~
~ 1 2 2 3 (5) *
~ 3 2 3 (4) (4) *
~ 2 4 (5) 3 1 *
~ (6) (7) 1 4 5 *
~ (5) 1 1 2 4 *
* * * * * 大西洋
返回:
[[0, 4], [1, 3], [1, 4], [2, 2], [3, 0], [3, 1], [4, 0]] (上图中带括号的单元).
DFS
class Solution {
private int m, n;
private int[][] direction = {{1, 0}, {-1, 0}, {0, 1}, {0, -1}};
private boolean in_area(int x, int y){
return 0 <= x && x < m && 0 <= y && y < n;
}
private void dfs(int[][] matrix, int x, int y, int[][] po, int[][] ao, boolean flag){
if (flag){
po[x][y] = 1;
}else {
ao[x][y] = 1;
}
for (int[] d : direction) {
int newx = x + d[0];
int newy = y + d[1];
if (!in_area(newx, newy) || matrix[x][y] > matrix[newx][newy] || (flag && po[newx][newy] == 1) || (!flag && ao[newx][newy] == 1)){
continue;
}
dfs(matrix, newx, newy, po, ao, flag);
}
}
public List<List<Integer>> pacificAtlantic(int[][] matrix) {
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
if (matrix == null || matrix.length == 0)
return ans;
m = matrix.length;
n = matrix[0].length;
int[][] po = new int[m][n], ao = new int[m][n]; //po 太平洋,ao 大西洋
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i){
dfs(matrix, 0, i, po, ao, true);
dfs(matrix, m - 1, i, po, ao, false);
}
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i){
dfs(matrix, i, 0, po, ao, true);
dfs(matrix, i, n - 1, po, ao, false);
}
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (po[i][j] == 1 && ao[i][j] == 1){
ans.add(Arrays.asList(i, j));
}
}
}
return ans;
}
}
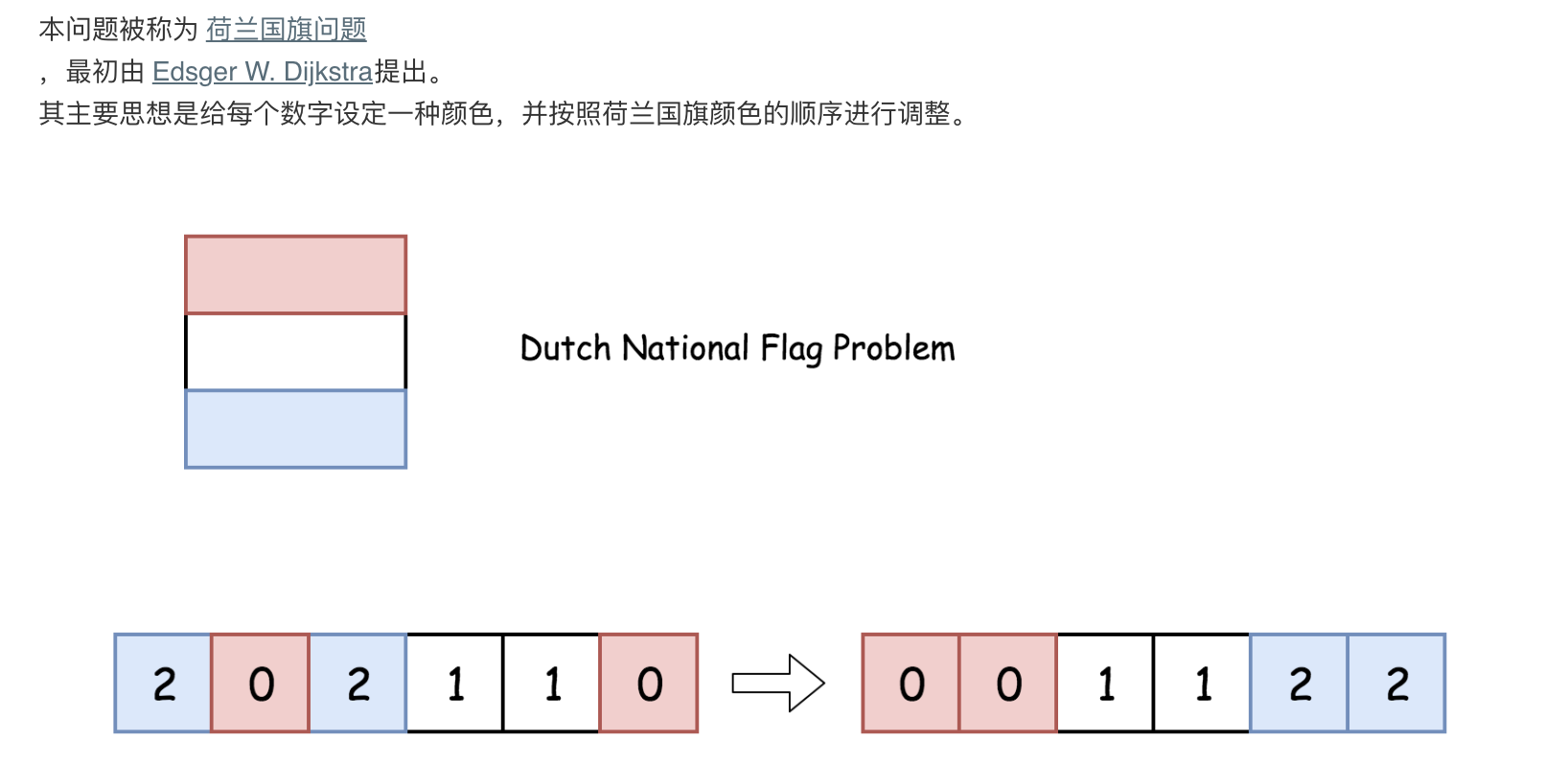
75. 颜色分类
给定一个包含红色、白色和蓝色,一共 n 个元素的数组,原地对它们进行排序,使得相同颜色的元素相邻,并按照红色、白色、蓝色顺序排列。
此题中,我们使用整数 0、 1 和 2 分别表示红色、白色和蓝色。
注意:
不能使用代码库中的排序函数来解决这道题。
示例:
输入: [2,0,2,1,1,0]
输出: [0,0,1,1,2,2]
进阶:
一个直观的解决方案是使用计数排序的两趟扫描算法。
首先,迭代计算出0、1 和 2 元素的个数,然后按照0、1、2的排序,重写当前数组。
你能想出一个仅使用常数空间的一趟扫描算法吗?
直接解决
class Solution {
public:
void sortColors(vector<int>& nums) {
vector<int> v(3);
for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); ++i)
v[nums[i]]++;
vector<int>::iterator n1 = nums.begin();
for(int j = 0; j < 3; ++j)
for(int i = 0; i < v[j]; ++i)
*n1++ = j;
}
};
一次遍历
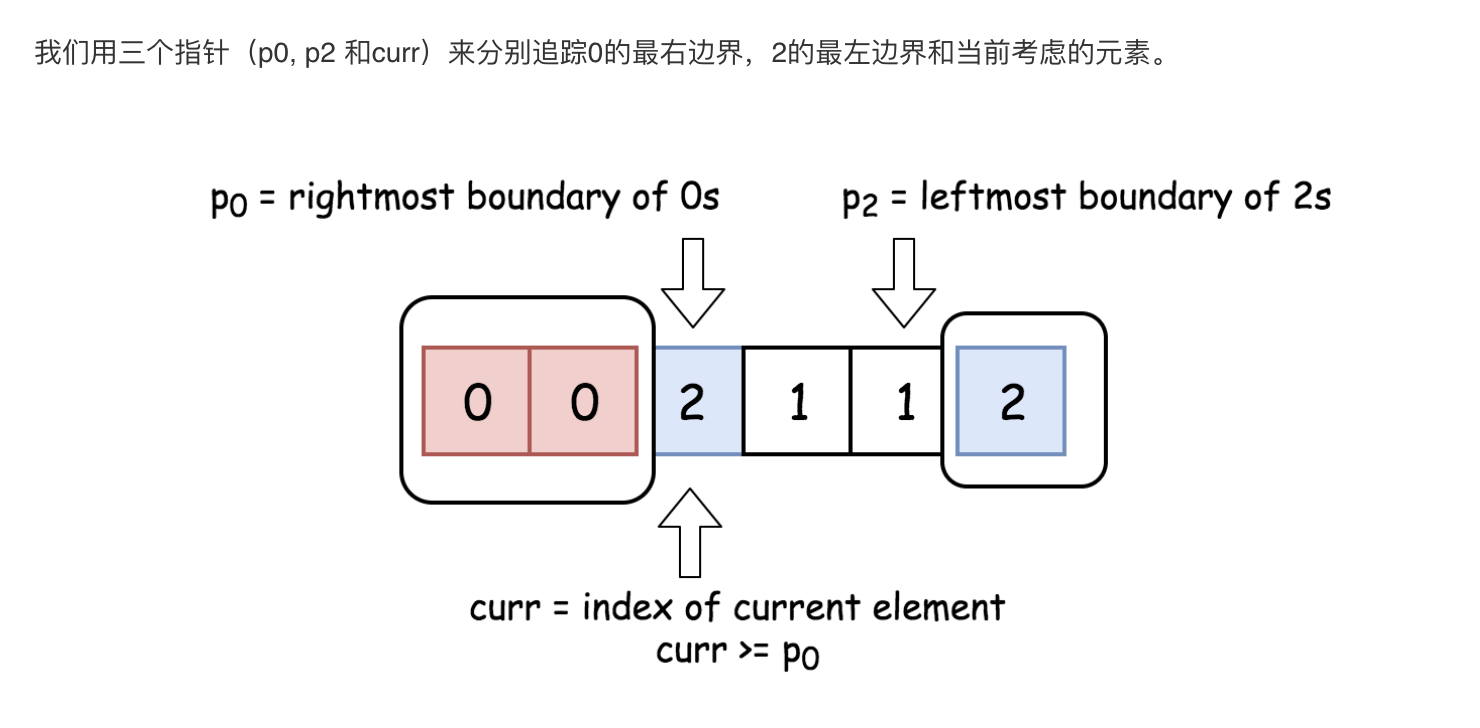
本解法的思路是沿着数组移动 curr 指针,若nums[curr] = 0,则将其与 nums[p0]互换;若 nums[curr] = 2 ,则与 nums[p2]互换。
算法
初始化0的最右边界:p0 = 0。在整个算法执行过程中 nums[idx < p0] = 0.
初始化2的最左边界 :p2 = n - 1。在整个算法执行过程中 nums[idx > p2] = 2.
初始化当前考虑的元素序号 :curr = 0.
While curr <= p2 :
若 nums[curr] = 0 :交换第 curr个 和 第p0个 元素,并将指针都向右移。
若 nums[curr] = 2 :交换第 curr个和第 p2个元素,并将 p2指针左移 。
若 nums[curr] = 1 :将指针curr右移。
class Solution {
public void sortColors(int[] nums) {
int p0 = 0, p2 = nums.length - 1, cur = 0;
while (cur <= p2) {
if (nums[cur] == 1) {
cur++;
} else if (nums[cur] == 0) {
int tmp = nums[p0];
nums[p0++] = nums[cur];
nums[cur++] = tmp;
} else {
int tmp = nums[p2];
nums[p2--] = nums[cur];
nums[cur] = tmp;
}
}
}
}
1091. 二进制矩阵中的最短路径


BFS
class Solution {
public int shortestPathBinaryMatrix(int[][] grid) {
int m = grid.length;
int n = grid[0].length;
int[][] state = new int[m][n];
Deque<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
if (grid[0][0] == 1) {
return -1;
}
if (grid[0][0] == 0 && m == 1 && n == 1) {
return 1;
}
state[0][0] = 1;
queue.addLast(0);
int[][] direction = {{0,1},{1,0},{0,-1},{-1,0},{1,1},{-1,-1},{1,-1},{-1,1}};
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int tmp = queue.removeFirst();
int row = tmp / m;
int col = tmp % m;
for (int[] d : direction) {
int newRow = row + d[0];
int newCol = col + d[1];
if (newRow >= 0 && newRow < m && newCol >= 0 && newCol < n && grid[newRow][newCol] == 0 && state[newRow][newCol] == 0) {
state[newRow][newCol] = state[row][col] + 1;
queue.add(newRow * m + newCol);
if (newRow == m - 1 && newCol == n - 1) {
return state[newRow][newCol];
}
}
}
}
return -1;
}
}
279. 完全平方数
给定正整数 n,找到若干个完全平方数(比如 1, 4, 9, 16, …)使得它们的和等于 n。你需要让组成和的完全平方数的个数最少。
示例 1:
输入: n = 12
输出: 3
解释: 12 = 4 + 4 + 4.
示例 2:
输入: n = 13
输出: 2
解释: 13 = 4 + 9.
动态规划
首先初始化长度为n+1的数组dp,每个位置都为0
如果n为0,则结果为0
对数组进行遍历,下标为i,每次都将当前数字先更新为最大的结果,即dp[i]=i,比如i=4,最坏结果为4=1+1+1+1即为4个数字
动态转移方程为:dp[i] = MIN(dp[i], dp[i - j _ j] + 1),i表示当前数字,j_j表示平方数
时间复杂度:O(n*sqrt(n)),sqrt为平方根
class Solution {
public int numSquares(int n) {
int[] dp = new int[n + 1];
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i){
dp[i] = i;
for(int j = 1; i - j * j >= 0; ++j){
dp[i] = Math.min(dp[i], dp[i - j * j] + 1);
}
}
return dp[n];
}
}
BFS

import javafx.util.Pair;
class Solution {
public int numSquares(int n) {
if(n == 0)
return 0;
LinkedList<Pair<Integer, Integer> > queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.addLast(new Pair<>(n, 0));
boolean[] visited = new boolean[n + 1];
visited[n] = true;
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
Pair<Integer, Integer> front = queue.removeFirst();
int num = front.getKey();
int step = front.getValue();
if(num == 0){
return step;
}
for(int i = 1; num - i * i >= 0; ++i){
int a = num - i * i;
if(!visited[a]){
if(a == 0)
return step + 1;
queue.addLast(new Pair(a, step + 1));
visited[a] = true;
}
}
}
return -1;
}
}
127. 单词接龙
给定两个单词(beginWord 和 endWord)和一个字典,找到从 beginWord 到 endWord 的最短转换序列的长度。转换需遵循如下规则:
每次转换只能改变一个字母。
转换过程中的中间单词必须是字典中的单词。
说明:
如果不存在这样的转换序列,返回 0。
所有单词具有相同的长度。
所有单词只由小写字母组成。
字典中不存在重复的单词。
你可以假设 beginWord 和 endWord 是非空的,且二者不相同。
示例 1:
输入:
beginWord = "hit",
endWord = "cog",
wordList = ["hot","dot","dog","lot","log","cog"]
输出: 5
解释: 一个最短转换序列是 "hit" -> "hot" -> "dot" -> "dog" -> "cog",
返回它的长度 5。
示例 2:
输入:
beginWord = "hit"
endWord = "cog"
wordList = ["hot","dot","dog","lot","log"]
输出: 0
解释: endWord "cog" 不在字典中,所以无法进行转换。
BFS
我们将问题抽象在一个无向无权图中,每个单词作为节点,差距只有一个字母的两个单词之间连一条边。问题变成找到从起点到终点的最短路径,如果存在的话。因此可以使用广度优先搜索方法。
算法中最重要的步骤是找出相邻的节点,也就是只差一个字母的两个单词。为了快速的找到这些相邻节点,我们对给定的 wordList 做一个预处理,将单词中的某个字母用 * 代替。
利用广度优先搜索搜索从 beginWord 到 endWord 的路径。
对给定的 wordList 做预处理,找出所有的通用状态。将通用状态记录在字典中,键是通用状态,值是所有具有通用状态的单词。
将包含 beginWord 和 1 的元组放入队列中,1 代表节点的层次。我们需要返回 endWord 的层次也就是从 beginWord 出发的最短距离。
为了防止出现环,使用访问数组记录。
当队列中有元素的时候,取出第一个元素,记为 current_word。
找到 current_word 的所有通用状态,并检查这些通用状态是否存在其它单词的映射,这一步通过检查 all_combo_dict 来实现。
从 all_combo_dict 获得的所有单词,都和 current_word 共有一个通用状态,所以都和 current_word 相连,因此将他们加入到队列中。
对于新获得的所有单词,向队列中加入元素 (word, level + 1) 其中 level 是 current_word 的层次。
最终当你到达期望的单词,对应的层次就是最短变换序列的长度。
标准广度优先搜索的终止条件就是找到结束单词。
class Solution {
public int ladderLength(String beginWord, String endWord, List<String> wordList) {
int m = beginWord.length();
HashMap<String, ArrayList<String>> dict = new HashMap<>();
wordList.forEach(
word -> {
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
String newWord = word.substring(0, i) + '*' + word.substring(i + 1, m);
ArrayList<String> trans = dict.getOrDefault(newWord, new ArrayList<String>());
trans.add(word);
dict.put(newWord, trans);
}
}
);
Queue<Pair<String, Integer>> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(new Pair(beginWord, 1));
HashMap<String, Boolean> visited = new HashMap<>();
visited.put(beginWord, true);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Pair<String, Integer> node = queue.remove();
String word = node.getKey();
Integer level = node.getValue();
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
String newWord = word.substring(0, i) + '*' + word.substring(i + 1, m);
for (String adj : dict.getOrDefault(newWord, new ArrayList<String>())) {
if (adj.equals(endWord)) {
return level + 1;
}
if (!visited.containsKey(adj)) {
visited.put(adj, true);
queue.add(new Pair(adj, level + 1));
}
}
}
}
return 0;
}
}
双向广度优先搜索
如果使用两个同时进行的广搜可以有效地减少搜索空间。一边从 beginWord 开始,另一边从 endWord 开始。我们每次从两边各扩展一个节点,当发现某一时刻两边都访问了某一顶点时就停止搜索。这就是双向广度优先搜索,它可以可观地减少搜索空间大小,从而降低时间和空间复杂度。
算法与之前描述的标准广搜方法相类似。
唯一的不同是我们从两个节点同时开始搜索,同时搜索的结束条件也有所变化。
我们现在有两个访问数组,分别记录从对应的起点是否已经访问了该节点。
如果我们发现一个节点被两个搜索同时访问,就结束搜索过程。因为我们找到了双向搜索的交点。过程如同从中间相遇而不是沿着搜索路径一直走。
双向搜索的结束条件是找到一个单词被两边搜索都访问过了。
最短变换序列的长度就是中间节点在两边的层次之和。因此,我们可以在访问数组中记录节点的层次。
import javafx.util.Pair;
class Solution {
private int L;
private HashMap<String, ArrayList<String>> dict;
Solution(){
this.L = 0;
this.dict = new HashMap<String, ArrayList<String>>();
}
private int visitWordNode(Queue<Pair<String, Integer>> Q, HashMap<String, Integer> visited1, HashMap<String, Integer> visited2){
Pair<String, Integer> node = Q.remove();
String word = node.getKey();
int level = node.getValue();
for(int i = 0; i < this.L; ++i){
String newWord = word.substring(0, i) + '*' + word.substring(i + 1, L);
for(String adj : this.dict.getOrDefault(newWord, new ArrayList<String>())){
if(visited2.containsKey(adj)){
return level + visited2.get(adj);
}
if(!visited1.containsKey(adj)){
visited1.put(adj, level + 1);
Q.add(new Pair(adj, level + 1));
}
}
}
return -1;
}
public int ladderLength(String beginWord, String endWord, List<String> wordList) {
if(!wordList.contains(endWord)){
return 0;
}
this.L = beginWord.length();
wordList.forEach(
word -> {
for(int i = 0; i < L; i++){
String newWord = word.substring(0, i) + '*' + word.substring(i+1, L);
ArrayList<String> trans = this.dict.getOrDefault(newWord, new ArrayList<String>());
trans.add(word);
this.dict.put(newWord, trans);
}
}
);
Queue<Pair<String, Integer>> qbegin = new LinkedList<Pair<String, Integer>>();
Queue<Pair<String, Integer>> qend = new LinkedList<Pair<String, Integer>>();
qbegin.add(new Pair(beginWord, 1));
qend.add(new Pair(endWord, 1));
HashMap<String, Integer> visited1 = new HashMap<String, Integer>();
HashMap<String, Integer> visited2 = new HashMap<String, Integer>();
visited1.put(beginWord, 1);
visited2.put(endWord, 1);
while(!qbegin.isEmpty() && !qend.isEmpty()){
int ans = visitWordNode(qbegin, visited1, visited2);
if(ans > -1){
return ans;
}
ans = visitWordNode(qend, visited2, visited1);
if(ans > -1){
return ans;
}
}
return 0;
}
};
329. 矩阵中的最长递增路径
给定一个 m x n 整数矩阵 matrix ,找出其中 最长递增路径 的长度。
对于每个单元格,你可以往上,下,左,右四个方向移动。 你 不能 在 对角线 方向上移动或移动到 边界外(即不允许环绕)。
输入:matrix = [[9,9,4],[6,6,8],[2,1,1]]
输出:4
解释:最长递增路径为 [1, 2, 6, 9]。
Dfs
由于同一个单元格对应的最长递增路径的长度是固定不变的,因此可以使用记忆化的方法进行优化。用矩阵
memo 作为缓存矩阵,已经计算过的单元格的结果存储到缓存矩阵中。
class Solution {
public int[][] dirs = {{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {0, 1}};
public int rows, columns;
public int longestIncreasingPath(int[][] matrix) {
if (matrix == null || matrix.length == 0 || matrix[0].length == 0) {
return 0;
}
rows = matrix.length;
columns = matrix[0].length;
int[][] memo = new int[rows][columns];
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < rows; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < columns; ++j) {
ans = Math.max(ans, dfs(matrix, i, j, memo));
}
}
return ans;
}
public int dfs(int[][] matrix, int row, int column, int[][] memo) {
if (memo[row][column] != 0) {
return memo[row][column];
}
++memo[row][column];
for (int[] dir : dirs) {
int newRow = row + dir[0], newColumn = column + dir[1];
if (newRow >= 0 && newRow < rows && newColumn >= 0 && newColumn < columns && matrix[newRow][newColumn] > matrix[row][column]) {
memo[row][column] = Math.max(memo[row][column], dfs(matrix, newRow, newColumn, memo) + 1);
}
}
return memo[row][column];
}
}

