简单工厂(Simple Factory)
Intent
在创建一个对象时不向客户暴露内部细节,并提供一个创建对象的通用接口。
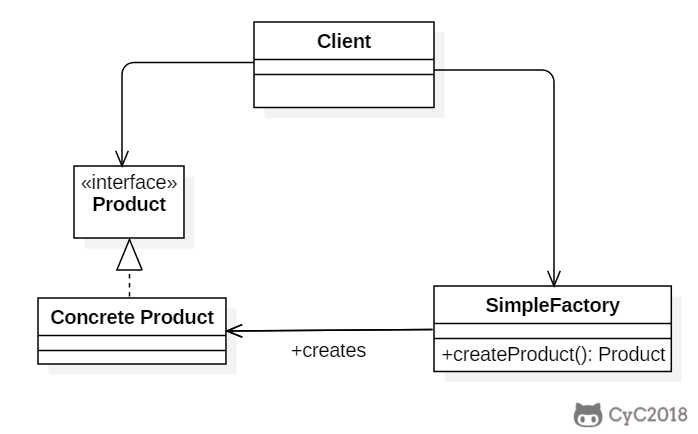
Class Diagram
简单工厂把实例化的操作单独放到一个类中,这个类就成为简单工厂类,让简单工厂类来决定应该用哪个具体子类来实例化。
这样做能把客户类和具体子类的实现解耦,客户类不再需要知道有哪些子类以及应当实例化哪个子类。客户类往往有多个,如果不使用简单工厂,那么所有的客户类都要知道所有子类的细节。而且一旦子类发生改变,例如增加子类,那么所有的客户类都要进行修改。
Implementation
public interface Product {}
public class ConcreteProduct implements Product {}
public class ConcreteProduct1 implements Product {}
public class ConcreteProduct2 implements Product {}
以下的 Client 类包含了实例化的代码,这是一种错误的实现。如果在客户类中存在这种实例化代码,就需要考虑将代码放到简单工厂中。
public class Client {public static void main(String[] args) {int type = 1;Product product;if (type == 1) {product = new ConcreteProduct1();} else if (type == 2) {product = new ConcreteProduct2();} else {product = new ConcreteProduct();}// do something with the product}}
以下的 SimpleFactory 是简单工厂实现,它被所有需要进行实例化的客户类调用。
public class SimpleFactory {public Product createProduct(int type) {if (type == 1) {return new ConcreteProduct1();} else if (type == 2) {return new ConcreteProduct2();}return new ConcreteProduct();}}
public class Client {public static void main(String[] args) {SimpleFactory simpleFactory = new SimpleFactory();Product product = simpleFactory.createProduct(1);// do something with the product}}


