9.1 如何控制并发流程?
9.1.1 什么是控制并发流程?
◆控制并发流程的工具类,作用就是帮助我们程序员更容易得让线程之间合作.
◆让线程之间相互配合,来满足业务逻辑
◆比如让线程A等待线程B执行完毕后再执行等合作策略
9.1.2 常见并发工具类
9.2 倒计时门闩,一等多
CountDownLatch类的作用两个典型用法
并发流程控制的工具
◆倒数门闩
◆例子:购物拼团;大巴(游乐园坐过山车排队) ,人满发车。
◆流程:倒数结束之前,一直处于等待状态,直到倒计时结束了此线程才继续工作。

类的主要方法介绍
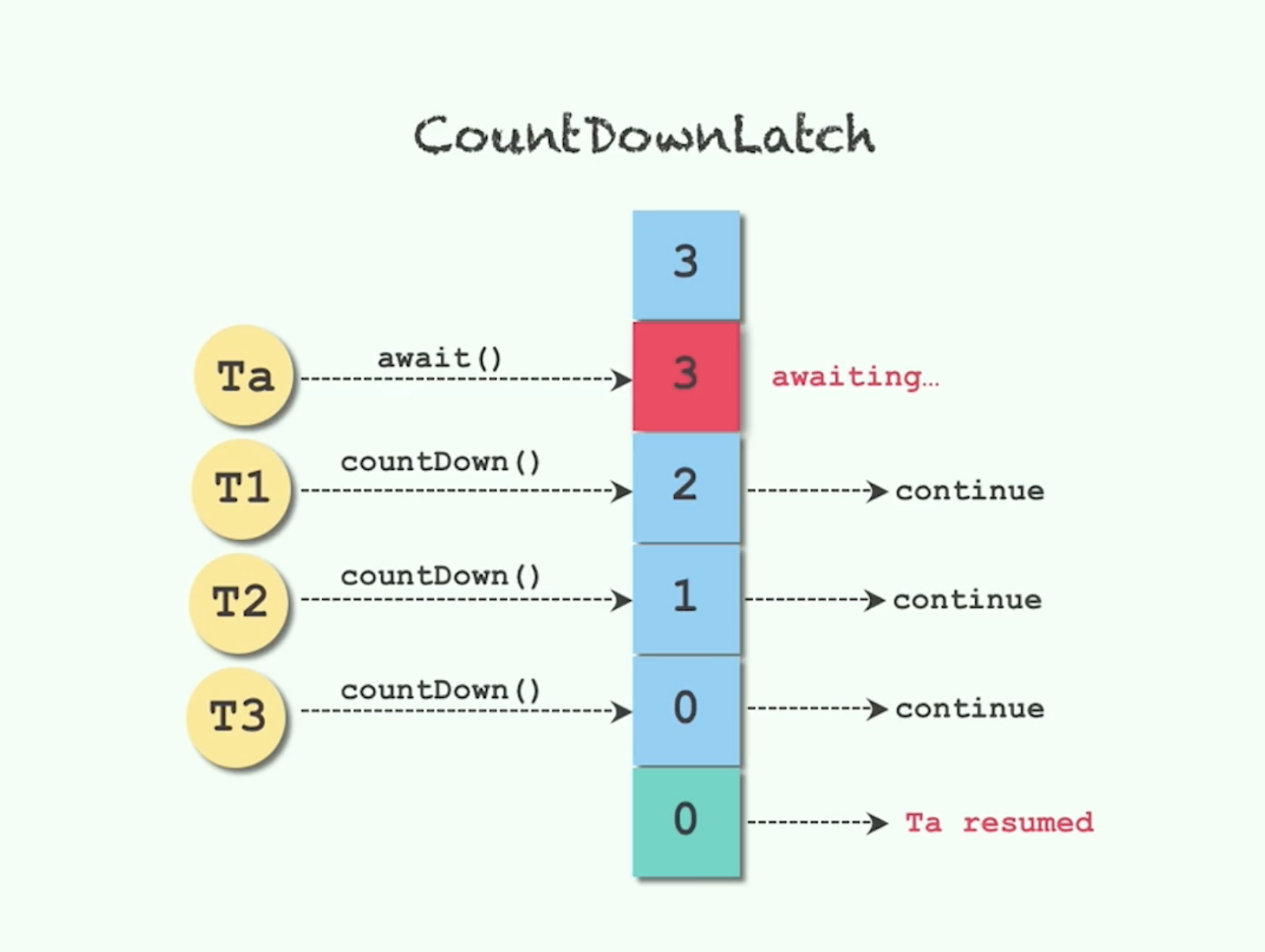
- CountDownLatch(int count) :仅有一个构造函数,参数count为需要倒数的数值。
- await( :调用await()方法的线程会被挂起,它会等待直到count值为0才继续执行。
- countDown() :将count值减1 ,直到为0时,等待的线程会被唤起。
图解await和countDown方法
两个典型用法
用法一:一个线程等待多个线程都执行完毕,在继续自己的工作。
代码示例:
/**** 描述:工厂中,质检,5个工人检查,所有人都认为通过才通过*/public class CountDownLatchDemo1 {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(5);ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {final int no = i + 1;Runnable runnable = new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {try {Thread.sleep((long) (Math.random() * 10000));System.out.println("No." + no + "完成了检查");} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {latch.countDown();}}};service.submit(runnable);}System.out.println("等待5个人检查完成...");latch.await();System.out.println("所有人都完成工作,进入下一个环节");service.shutdown();}}
执行结果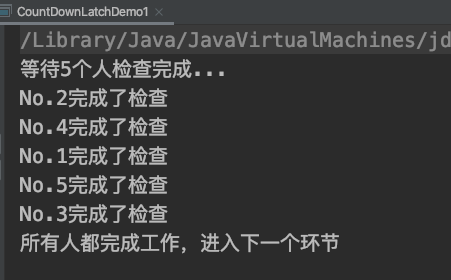
9.3 综合用法
9.3.1 用法二
用法二:多个线程等待某一个线程的信号,同时开始执行
比如对服务器进行压测,尽量在同一时刻打过去。
代码演示
/**
* 描述:
* 模拟100米跑步,5名选手都准备好了,只等裁判员一声令下,所有人同
* 时开始跑步。
*/
public class CountDownLatchDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
CountDownLatch begin = new CountDownLatch(1);
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
final int no = i + 1;
Runnable runnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("No." + no + ",准备完毕等待发令枪");
try {
begin.await();
System.out.println("No." + no + "开始跑步了");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
};
executorService.submit(runnable);
}
//裁判员检查发令枪
Thread.sleep(5000);
System.out.println("发令枪响,比赛开始!");
begin.countDown();
}
}
执行结果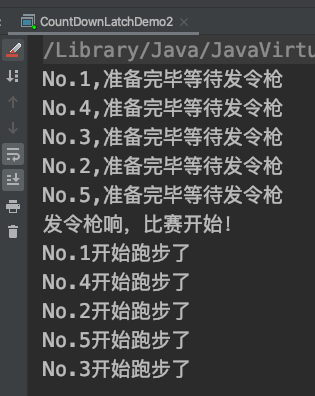
9.3.2 综合案例
假设所有选手到达终点,比赛结束
package com.wzy.flowcontrol.countdownlatch;
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
/**
* 描述:
* 模拟100米跑步,5名选手都准备好了,只等裁判员一声令下,所有人同
* 时开始跑步。
*
* 等待最后一名运动员到达,宣布本场比赛结束。
*/
public class CountDownLatchDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
CountDownLatch begin = new CountDownLatch(1);
CountDownLatch end = new CountDownLatch(5);
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
final int no = i + 1;
Runnable runnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("No." + no + ",准备完毕等待发令枪");
try {
begin.await();
System.out.println("No." + no + "开始跑步了");
Thread.sleep((long) (Math.random() * 10000));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
end.countDown();
}
}
};
executorService.submit(runnable);
}
//裁判员检查发令枪
Thread.sleep(5000);
System.out.println("发令枪响,比赛开始!");
begin.countDown();
end.await();
System.out.println("所有运动员都到达终点,比赛结束!");
}
}
执行结果:
9.3.3 注意点
- 扩展用法:多个线程等多个线程完成执行后,再同时执行
- CountDownLatch是不能够重用的,如果需要重新计数,可以考虑使用CyclicBarrier或者创建新的CountDownLatch实例。
9.3.4总结
- 两个典型用法:一等多和多等一
- CountDownLatch类在创建实例的时候,需要传递倒数次数。倒数到0的时候,之前等待的线程会继续运行
-
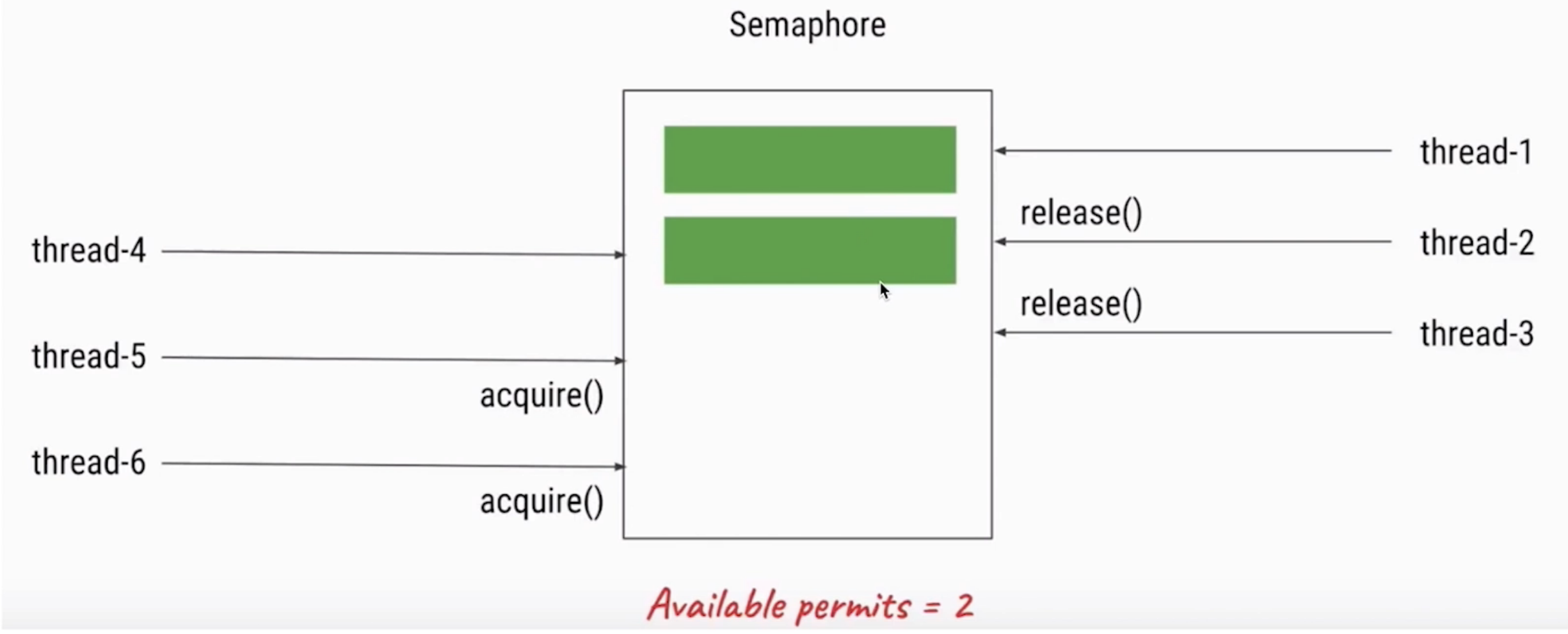
9.4 Semaphore颁发许可证
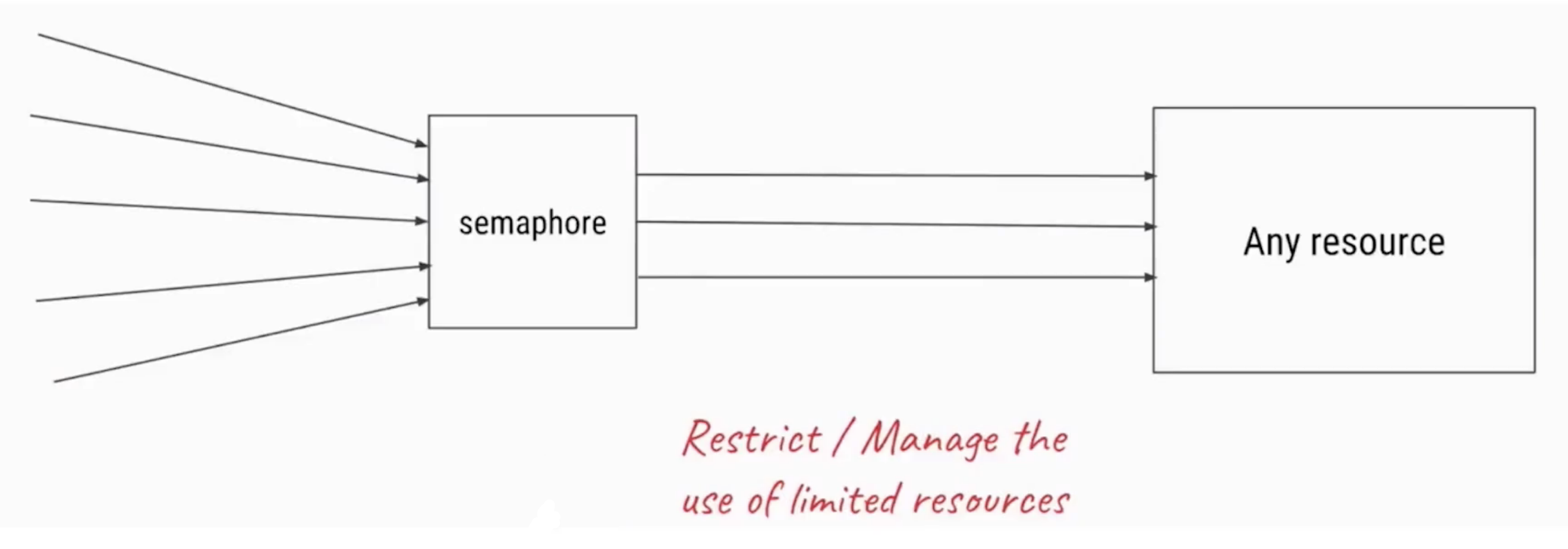
Semaphore信号量
Semaphore可以用来限制或管理数量有限的资源的使用情况。
- 污染不能太多,污染许可证只能发3张
- 信号量的作用是维护一个“许可证”的计数,线程可以“获取”许可证,那信号量剩余的许可证就减一, 线程也可以“是否”一个许可证,那信号量剩余的许可证就加一- ,当信号量所拥有的许可证数量为0 ,那么下一个还想要获取许可证的线程,就需要等待,直到有另外的线程释放了许可证
特别耗时耗费资源的服务。
semaphore应用场景,比如说很多请求都要去执行某一个很耗时的操作,可以使用semphonre去限制,同时有几个线程同时执行。
正常情况下获取许可证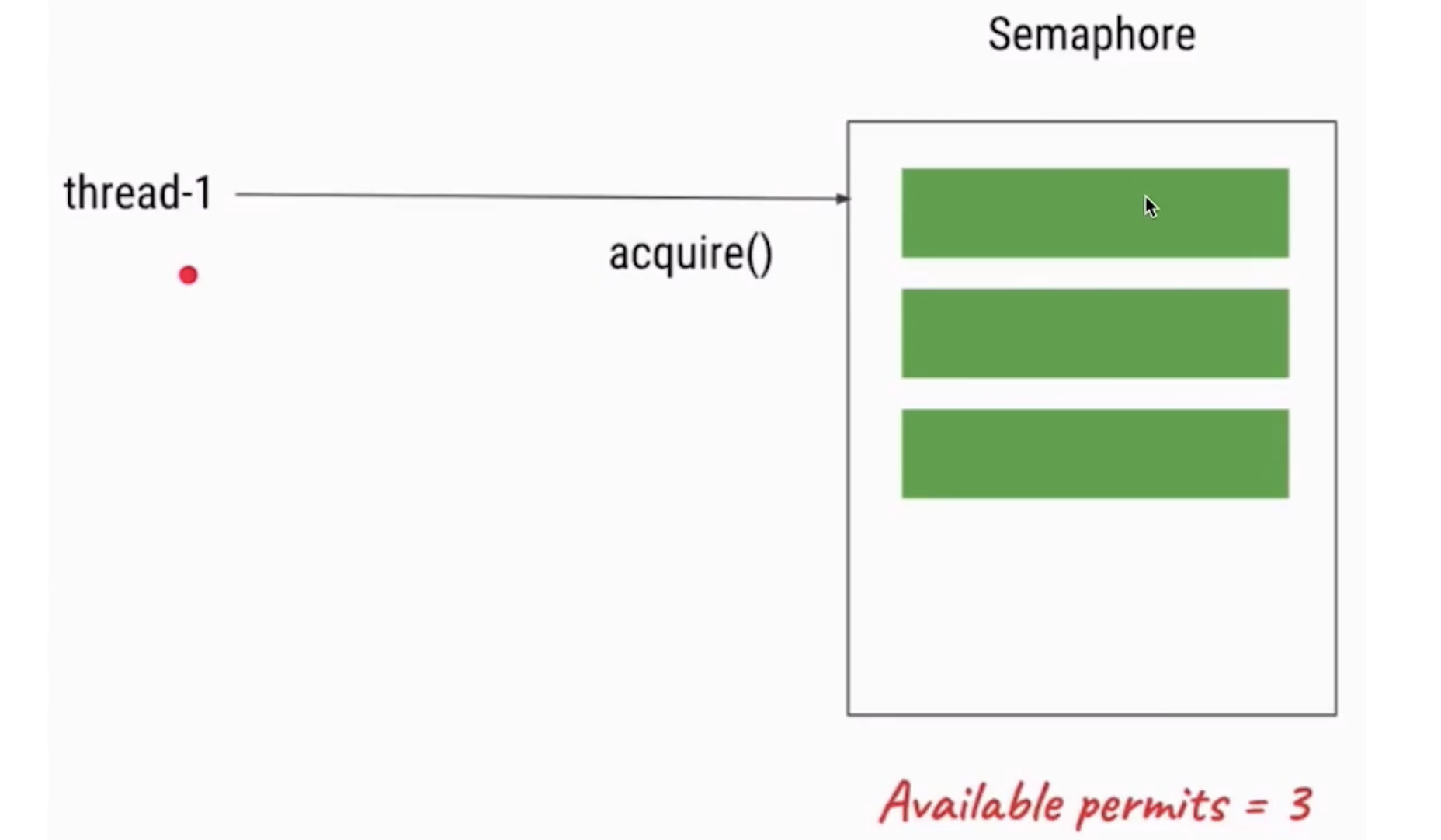

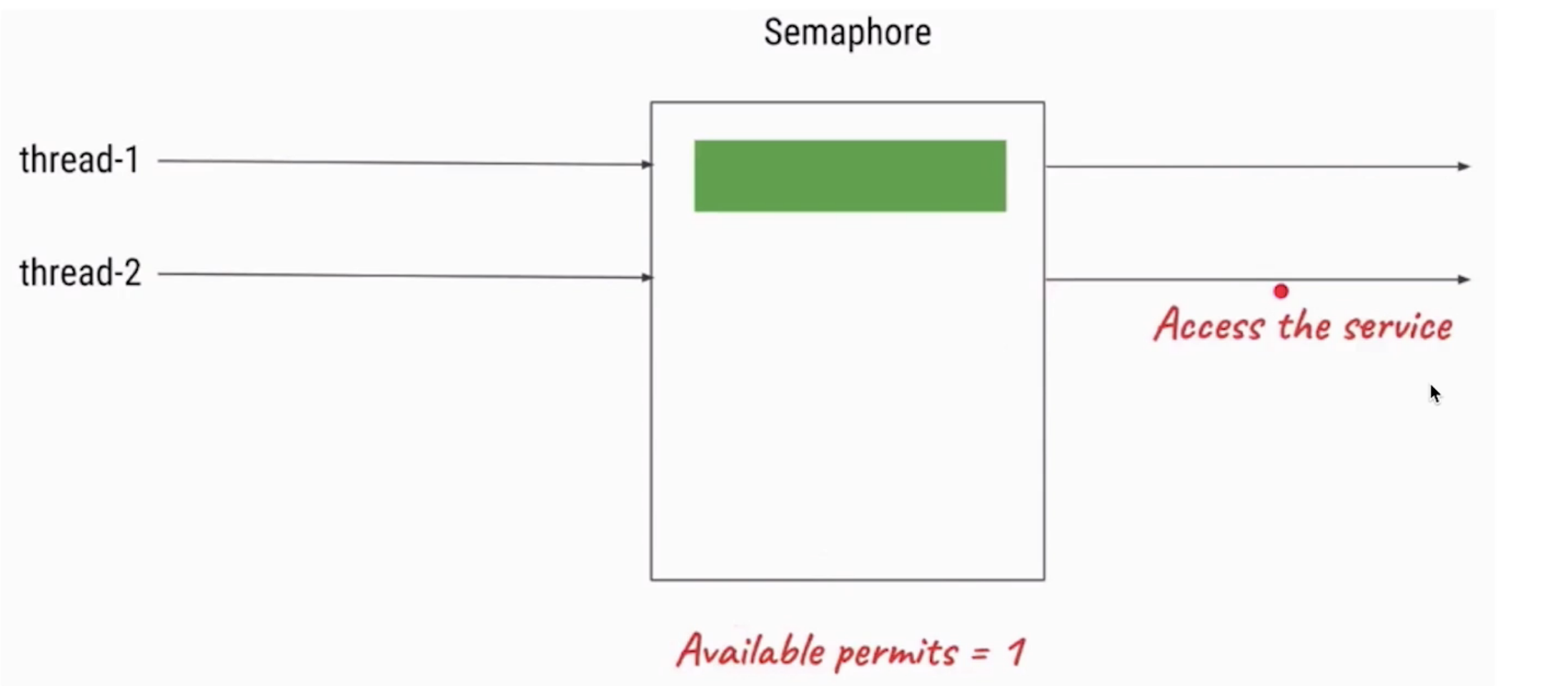

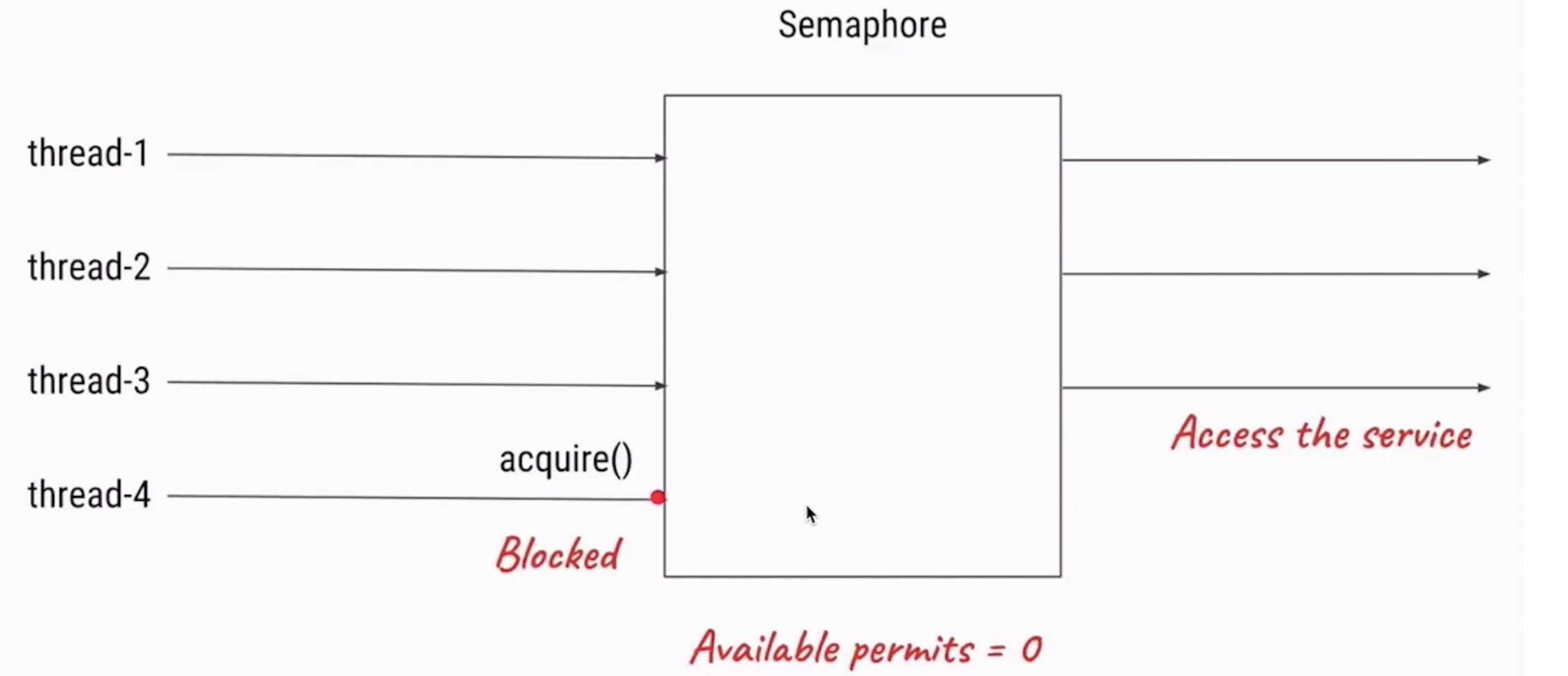
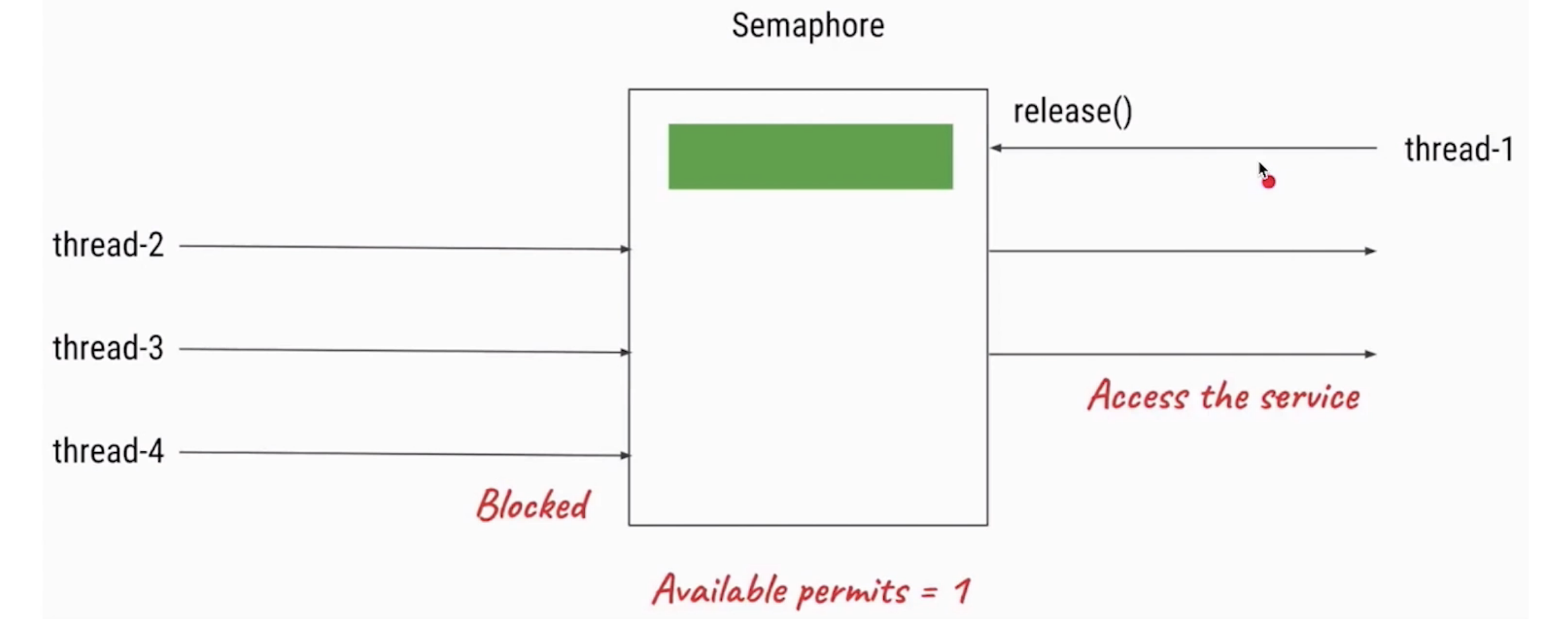
总结



9.5 Semaphore用法和注意点
package com.wzy.flowcontrol.semaphore;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.Semaphore;
/**
* @author wzy
* @version 1.0
* @date 2022/6/30 9:56 上午
*/
public class SemaphoreDemo {
public static Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(3, true);
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(50);
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
service.submit(new Task());
}
service.shutdown();
}
static class Task implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
semaphore.acquire();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "拿到了许可证");
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "释放了许可证");
semaphore.release();
}
}
}
执行结果,三个一起获取,三个一起释放。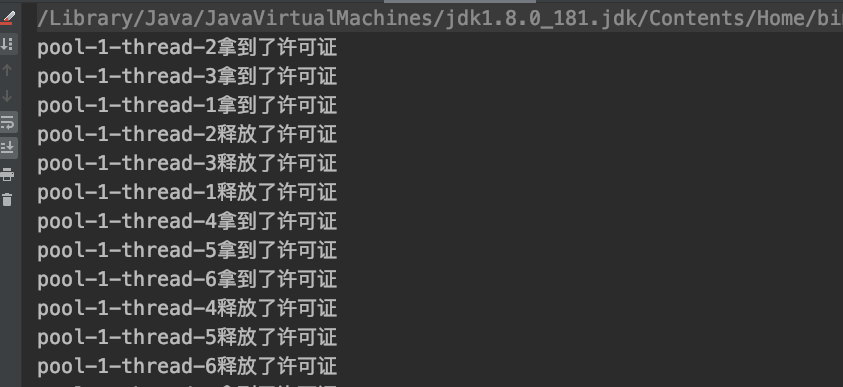
信号量可以获得多个令牌



9.6 Condition条件对象的作用和用法演示




9.7 循环栅栏的作用


第三点不同,就是都到了,可以去做一个统一的工作。



