Function
A return keyword without an expression after it will cause the function to return undefined. Functions that don’t have a return statement at all, similarly return undefined.
Bingdings
Bindings declared with let and const are in fact local to the block that they are declared in, so if you create one of those inside of a loop, the code before and after the loop cannot “see” it.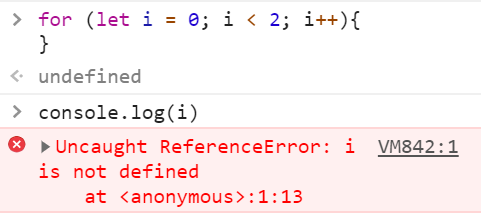
在for()内用let声明的变量,其scope在{}内
函数提升
console.log("The future says:", future());function future() {return "You'll never have flying cars";}
Arrow functions
const power = (base, exponent) => {let result = 1;for (let count = 0; count < exponent; count++) {result *= base;}return result;};// 下面两个等价const square1 = (x) => { return x * x; };const square2 = x => x * x;
Optional arguments
function fn(a, b) {do something}fn(a,b,c,d) // 传多的参数会被忽略fn(a) // 少传的参数为undefinedfunction fn(a, b = 2) // 设置默认值{do something}
The call stack
function chicken() {return egg();}function egg() {return chicken();}console.log(chicken() + " came first.");// → ??
Closure闭包
function wrapValue(n) {let local = n;return () => local;}// wrap1和wrap2是wrapValue返回的函数let wrap1 = wrapValue(1);let wrap2 = wrapValue(2);console.log(wrap1());// → 1console.log(wrap2());// → 2function multiplier(factor) {return number => number * factor;}let twice = multiplier(2);console.log(twice(5));// → 10
This feature—being able to reference a specific instance of a local binding in an enclosing scope—is called closure. A function that references bindings from local scopes around it is called a closure.
A good mental model is to think of function values as containing both the code in their body and the environment in which they are created. When called, the function body sees the environment in which it was created, not the environment in which it is called.
Recursion递归
function findSolution(target) {function find(current, history) {if (current == target) {return history;} else if (current > target) {return null;} else {return find(current + 5, `(${history} + 5)`) ||find(current * 3, `(${history} * 3)`);}}return find(1, "1");}console.log(findSolution(24));// → (((1 * 3) + 5) * 3)
exercises
1. minimum
let min = (a,b) => a > b ? b : a;console.log(min(0, 10));console.log(min(0, -10));
2. isEven
function isEven(x) {if (x === 0) return trueelse if (x === 1) return falseelse if (x < 0) return isEven(-x)else return isEven(x - 2)}console.log(isEven(50));// → trueconsole.log(isEven(75));// → falseconsole.log(isEven(-1));
3. Bean counting
function countBs(str) {return countChar(str, 'B')}function countChar(str, char) {let count = 0for (let i = 0; i < str.length; i++)if (str[i] === char) count += 1return count}console.log(countBs("BBC"));// → 2console.log(countChar("kakkerlak", "k"));// → 4

