转载:https://www.cnblogs.com/yzhmj/p/14923416.html?ivk_sa=1024320u
List
基础类型 List 排序
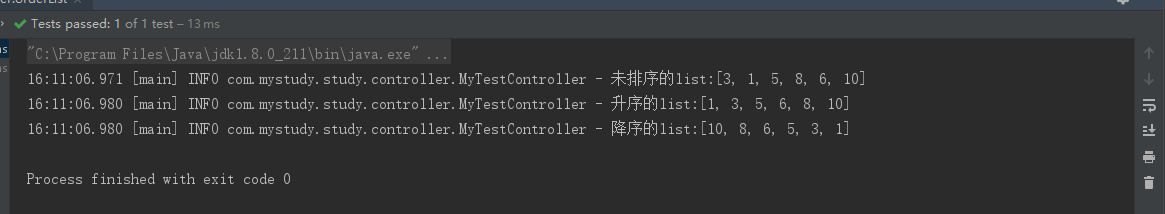
List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(3,1,5,8,6,10);log.info("未排序的list:{}",list);// 升序list.sort(Comparator.naturalOrder());log.info("升序的list:{}",list);// 降序list.sort(Comparator.reverseOrder());log.info("降序的list:{}",list);
对 List 的某个属性排序
Student student1 = new Student("张三",19,175);Student student2 = new Student("李四",18,165);Student student3 = new Student("王五",20,170);List<Student> studentList = Lists.newArrayList();studentList.add(student1);studentList.add(student2);studentList.add(student3);log.info("未排序的list:{}",studentList);//对年龄降序排序List<Student> orderAgeDescList = studentList.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparing(Student::getAge).reversed()).collect(Collectors.toList());log.info("对年龄降序排序后:{}",orderAgeDescList);//对年龄升序排序List<Student> orderAgeAscList = studentList.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparing(Student::getAge)).collect(Collectors.toList());log.info("对年龄升序排序后:{}",orderAgeAscList);//对年龄降序排序,对身高升序排序List<Student> orderAgeDescAndHeightAscList = studentList.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparing(Student::getAge).reversed().thenComparing(Student::getHeight)).collect(Collectors.toList());log.info("对年龄降序排序,对身高升序排序后:{}",orderAgeDescAndHeightAscList);
结果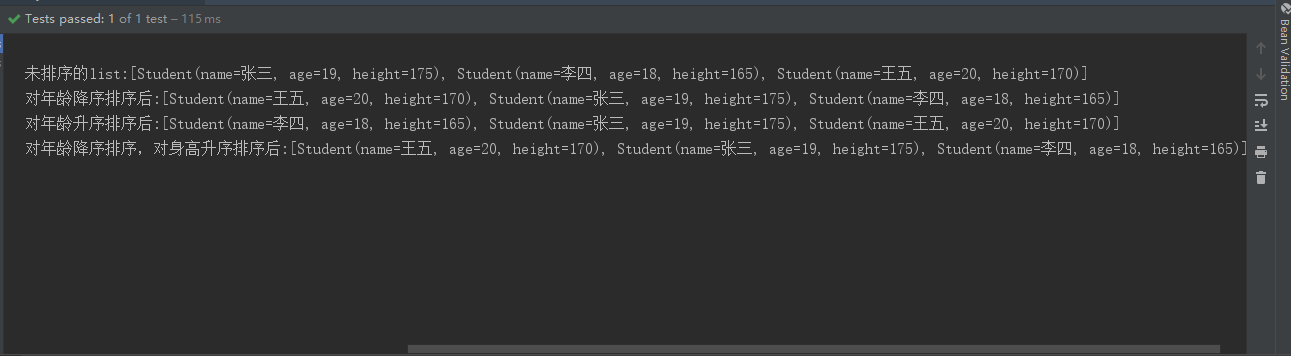
注意:当有多个属性排序时,先满足前一个排序,再对后一个排序
最大值、最小值、平均值、总数
// 最大值Double max = doubleList.stream().max(Comparator.comparingDouble(Double::doubleValue)).orElse(null);Double min = doubleList.stream().min(Comparator.comparingDouble(Double::doubleValue)).orElse(null);// 最小值Double max = doubleList.stream().mapToDouble(Double::doubleValue).max().getAsDouble();Double min = doubleList.stream().mapToDouble(Double::doubleValue).min().getAsDouble();// 平均值Double avg = doubleList.stream().mapToDouble(Double::doubleValue).average().getAsDouble();// 总数Double sum = doubleList.stream().mapToDouble(Double::doubleValue).sum();
去重
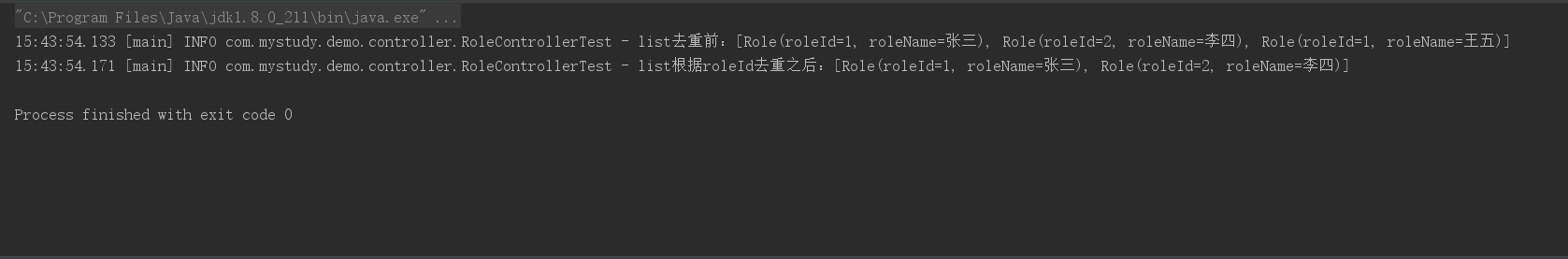
@Testpublic void myTest1(){List<Role> list = Lists.newArrayList();list.add(new Role(1,"张三"));list.add(new Role(2,"李四"));list.add(new Role(1,"王五"));log.info("list去重前:{}",list);//根据roleId去重list = list.stream().collect(Collectors.collectingAndThen(Collectors.toCollection(()->new TreeSet<>(Comparator.comparing(Role::getRoleId))), ArrayList::new));log.info("list根据roleId去重之后:{}",list);}
List、String、String[]的互相转换
// String转List// 方式一String ids= "1,2,3,4,5,6";List<String> result = Arrays.asList(ids.split(","));// 方式二List<String> result = Arrays.asList(ids.split("[,.]"));// 方式三String[] result = ids.split(",");List<String> list = Arrays.asList(result);// List转String// 方式一List<String> result = new ArrayList<>();result.add("a");result.add("b");result.add("c");String ids = String.join(",", result);// 方式二List<String> idsList = Arrays.asList("1", "2", "3","4", "5", "6");String ids = idsList.stream().collect(Collectors.joining(","));// List转String[]String[] array = result.toArray(new String[]{});
将一组数据平均分成 n 组
/*** 将一组数据平均分成n组** @param source 要分组的数据源* @param n 平均分成n组* @param <T>* @return*/public static <T> List<List<T>> averageAssign(List<T> source, int n) {List<List<T>> result = new ArrayList<>();int remainder = source.size() % n; // (先计算出余数)int number = source.size() / n; // 然后是商int offset = 0; // 偏移量for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {List<T> value;if (remainder > 0) {value = source.subList(i * number + offset, (i + 1) * number + offset + 1);remainder--;offset++;} else {value = source.subList(i * number + offset, (i + 1) * number + offset);}result.add(value);}return result;}
将一组数据固定分组,每组 n 个元素
/*** 将一组数据固定分组,每组n个元素* @param source 要分组的数据源* @param n 每组n个元素* @param <T>* @return*/public static <T> List<List<T>> fixedGrouping(List<T> source, int n) {if (null == source || source.size() == 0 || n <= 0)return null;List<List<T>> result = new ArrayList<>();int sourceSize = source.size();int size = (source.size() / n) + 1;for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {List<T> subset = new ArrayList<T>();for (int j = i * n; j < (i + 1) * n; j++) {if (j < sourceSize) {subset.add(source.get(j));}}result.add(subset);}return result;}
Map
对 Map 的 key 或 value 进行排序(升序、降序)
// 先定义 MapMap<Integer,Integer> map = Maps.newHashMap();map.put(2,11);map.put(1,33);map.put(3,22);
按 key 降序排序
//注意:此处初始化map时,若定义为Maps.newHashMap();会使排序失效。因HashMap本身结构是不具备排序的Map<Integer,Integer> descOrderKeyMap = Maps.newLinkedHashMap();map.entrySet().stream().sorted(Map.Entry.<Integer,Integer>comparingByKey().reversed()).forEachOrdered(e->descOrderKeyMap.put(e.getKey(),e.getValue()));log.info("按key降序排序:{}",descOrderKeyMap);
按 key 升序排序
Map<Integer,Integer> ascOrderKeyMap = Maps.newLinkedHashMap();map.entrySet().stream().sorted(Map.Entry.comparingByKey()).forEachOrdered(e->ascOrderKeyMap.put(e.getKey(),e.getValue()));log.info("按key升序排序:{}",ascOrderKeyMap);
按 value 降序排序
Map<Integer,Integer> descOrderValueMap = Maps.newLinkedHashMap();map.entrySet().stream().sorted(Map.Entry.<Integer,Integer>comparingByValue().reversed()).forEachOrdered(e->descOrderValueMap.put(e.getKey(),e.getValue()));log.info("按value降序排序:{}",descOrderValueMap);
按 value 升序排序
Map<Integer,Integer> ascOrderValueMap = Maps.newLinkedHashMap();map.entrySet().stream().sorted(Map.Entry.comparingByValue()).forEachOrdered(e->ascOrderValueMap.put(e.getKey(),e.getValue()));log.info("按value升序排序:{}",ascOrderValueMap);
结果如下