一、FileInputStream
1.可将读取的数据以byte数组的形式保存
package javase.day31.io;import java.io.FileInputStream;import java.io.FileNotFoundException;import java.io.IOException;public class FileInputStreamTest04 {public static void main(String[] args) {FileInputStream fis = null;try {fis = new FileInputStream("io/src/tram");//准备一个byte数组byte [] bytes = new byte[4];/*while (true){int readCount = fis.read(bytes);if (readCount == -1){break;}System.out.println(new String(bytes,0,readCount));}*///好方法int readCount = 0;while ((readCount = fis.read(bytes))!=-1){System.out.println(new String(bytes,0,readCount));}} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {try {fis.close();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}}
2.返回剩余没读到的字节数量
int available()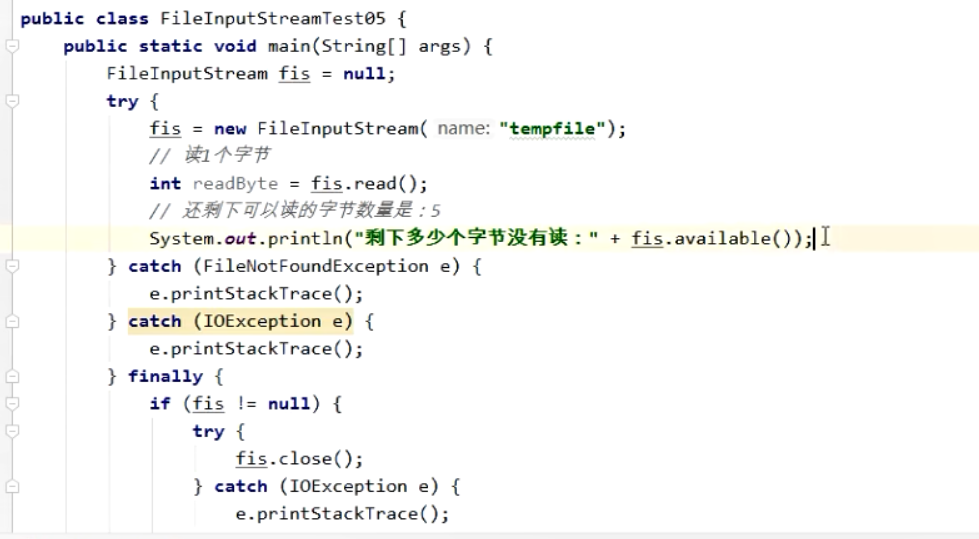
3.跳过几个字节不读取

二、FileOutputStream
package javase.day31.io;import java.io.FileNotFoundException;import java.io.FileOutputStream;import java.io.IOException;public class FileOutputStreamTest01 {public static void main(String[] args) {FileOutputStream fos = null;try {fos = new FileOutputStream("myfile",true);//加true加在原文件后面,不会清空byte[] bytes = {97,98,99,100,101};fos.write(bytes);//字符串String s ="我是在你的";//将字符串转换为byte数组byte[] bs = s.getBytes();fos.write(bs);//写完后一定要刷新fos.flush();} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {if (fos != null){try {fos.close();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}}}
三、复制文件(FileInputStream+FileOutputStream)
package javase.day31.io;import java.io.FileInputStream;import java.io.FileNotFoundException;import java.io.FileOutputStream;import java.io.IOException;public class Copy01 {public static void main(String[] args) {FileInputStream fis = null;FileOutputStream fos = null;try {fis = new FileInputStream("myfile");fos = new FileOutputStream("copymyfile");byte [] bytes = new byte[1024];int readCount=0;while ((readCount = fis.read(bytes)) != -1){fos.write(bytes,0,readCount);}//刷新fos.flush();} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {if (fis !=null){try {fis.close();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}if (fos !=null){try {fos.close();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}}}
四、FileReader
package javase.day31.io;import java.io.FileNotFoundException;import java.io.FileReader;import java.io.IOException;public class FileReaderTest {public static void main(String[] args) {FileReader reader = null;try {reader = new FileReader("io/src/readerfile");//开始读char[] chars = new char[4];//一次4个字符int readCount = 0;while ((readCount = reader.read(chars))!=-1){System.out.println(new String(chars,0,readCount));}} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {if (reader !=null){try {reader.close();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}}}
五、FileWriter
- 文件字符输出流(只能输出普通文本)
- 可以直接写入字符串 ```java package javase.day31.io;
import java.io.FileWriter; import java.io.IOException;
/**
文件字符输出流。只能输出普通文本 */ public class FileWriterTest01 { public static void main(String[] args) {
FileWriter out = null;try {out = new FileWriter("writerfile");//开始写char[] chars = {'我','是','中','国','人'};out.write(chars);out.write(chars,2,3);out.write("我是java工程师");//刷新out.flush();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}finally {if (out !=null){try {out.close();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}
} }
<a name="k11B4"></a># 六、复制2(FileReader+FileWrite)```javapackage javase.day31.io;import java.io.FileNotFoundException;import java.io.FileReader;import java.io.FileWriter;import java.io.IOException;public class Copy02 {public static void main(String[] args) {FileReader in =null;FileWriter out = null;try {in=new FileReader("writerfile");out=new FileWriter("copymyfile2");char[] chars = new char[1024 * 1024];int readCount = 0;while ((readCount = in.read(chars))!= -1){out.write(chars,0,readCount);}//刷新out.flush();} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}finally {try {in.close();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}try {out.flush();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}}
七、BufferedReader
package javase.day31.io;import java.io.BufferedReader;import java.io.FileNotFoundException;import java.io.FileReader;import java.io.IOException;public class BufferedReaderTest01 {public static void main(String[] args) {FileReader reader = null;BufferedReader br = null;try {reader = new FileReader("io/src/javase/day31/io/le.java");br = new BufferedReader(reader);String s = null;//br.readline()方法获取一个文本行,但不带换行符while ((s = br.readLine())!= null){System.out.println(s);}} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {try {//对于包装流来说,只需要关闭最外层流就行,里面的节点流会自动关闭(看源代码)br.close();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}}
八、BufferedWriter
package javase.day31.io;import java.io.*;public class BufferedWriterTest {public static void main(String[] args) {BufferedWriter out = null;try {//out = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("BufferedWriterCopy"));out = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("BufferedWriterCopy02",true)));} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}finally {try {if (out !=null){out.close();}} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}}
九、DataOutputStream
package javase.day31.io;import java.io.DataOutputStream;import java.io.FileNotFoundException;import java.io.FileOutputStream;import java.io.IOException;public class DataOutputStreamTest {public static void main(String[] args) {DataOutputStream dos= null;try {//创建数据专属的字节输出流dos = new DataOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("data"));//写数据byte b =100;short s =200;int i =300;long l = 400;float f =3.0f;double d =3.14;boolean sex =false;char c= 'a';//写dos.writeByte(b);dos.writeShort(s);dos.writeInt(i);dos.writeLong(l);dos.writeFloat(f);dos.writeDouble(d);dos.writeBoolean(sex);dos.writeChar(c);//刷新dos.flush();} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {if (dos !=null){try {dos.close();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}}}
十、DataInputStream
package javase.day31.io;import java.io.DataInputStream;import java.io.FileInputStream;import java.io.FileNotFoundException;import java.io.IOException;/*DataInputStream:数据字节输入流DataOutputStream:写的文件,只能用DataInputStream去读。并且读的时候你需要提前知道写入的顺序读的顺序需要和写的顺序一致。才可以正常取出数据*/public class DataInputStreamTest {public static void main(String[] args) {DataInputStream dis =null;try {dis = new DataInputStream(new FileInputStream("data"));} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {e.printStackTrace();}finally {if (dis !=null){try {dis.close();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}}}
十一、PrintStream(标准输出流)
可以改变输出方向吗?可以。
package javase.day31.io;import java.io.FileNotFoundException;import java.io.FileOutputStream;import java.io.PrintStream;public class PrintStreamTest {public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException {System.out.println("hello world!");PrintStream ps = System.out;ps.println("zhangsan");//标准输出流不需要手动close()关闭//之前System类使用的方法和属性// System.gc();// System.currentTimeMillis();// PrintStream ps2 = System.out;// System.exit(0);// System.arraycopy(...)//标准输出流不再指向控制台,指向“log”文件PrintStream printStream = new PrintStream(new FileOutputStream("log"));//修改输出方向,将输出方向修改到“log”文件System.setOut(printStream);//再输出System.out.println("hello world");System.out.println("hello litty");}}
十二、序列化和反序列化(两个流)
1.ObjectOutputStream和ObjectInputStream
package bean;import java.io.Serializable;public class Student implements Serializable {private int no;private String name;public Student(){}public Student(int no, String name) {this.no = no;this.name = name;}public int getNo() {return no;}public void setNo(int no) {this.no = no;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Student{" +"no=" + no +", name='" + name + '\'' +'}';}}
package bean;import java.io.FileOutputStream;import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;/*1.Student对象不支持序列化2.参与序列化和反序列化的对象,必须实现Serializable接口。3.注意:通过源代码发现,这个接口只是一个标志性接口:标识的作用,虚拟机看到这个类实现了这个接口,可能会对这个类特殊待遇*/public class ObjectOutputStreamTest01 {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {Student s = new Student(111,"zhangsan");//序列化ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("students"));//序列化对象oos.writeObject(s);//刷新oos.flush();oos.close();}}
package bean;import java.io.*;public class ObjectInputStreamTest01 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("students"));Object obj = ois.readObject();System.out.println(obj);ois.close();}}
2.重点:
参与序列化的类型必须实现java.io.Serializable接口。<br /> **并且建议**将序列化版本号手动的写出来。<br /> private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
3.一次序列化多个对象
- transient(修饰的属性不参与序列化)
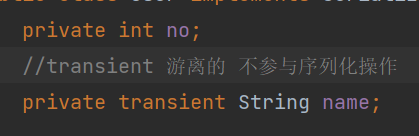
- user ```java package bean;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class User implements Serializable { private int no; //transient 游离的 不参与序列化操作 private transient String name;
public User() {}public User(int no, String name) {this.no = no;this.name = name;}public int getNo() {return no;}public void setNo(int no) {this.no = no;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "User{" +"no=" + no +", name='" + name + '\'' +'}';}
}
将多个序列化对象放到集合中,```javapackage bean;import java.io.FileNotFoundException;import java.io.FileOutputStream;import java.io.IOException;import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.List;public class ObjectOutputStreamTest02 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {List<User> userList = new ArrayList<>();userList.add(new User(111,"zhangsan"));userList.add(new User(122,"lucy"));userList.add(new User(133,"jack"));ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("users"));//序列化对象oos.writeObject(userList);oos.flush();oos.close();}}
package bean;import java.io.FileInputStream;import java.io.ObjectInputStream;import java.util.LinkedList;import java.util.List;public class ObjectInputStreamTest02 {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("users"));// Object obj = ois.readObject();// System.out.println(obj instanceof List);List<User> userList = (List<User>) ois.readObject();for (User user : userList){System.out.println(user);}ois.close();}}
4.序列化版本号


