优先级队列
PriorityBlockingQueue(线程安全)/priorityQueue(非线程安全)
内部维护了一个数组,初始容量是11
小顶堆:
入队的时候向上浮(入队的时候先把元素放到最后,然后向上浮)
出队向下沉(出队的时候吧最后一个元素放到出队元素的地方然后向下沉)
数组的第一个元素为空目的就是快速根据子节点找到父节点的位置 index/2 向下取整 = 父节点下标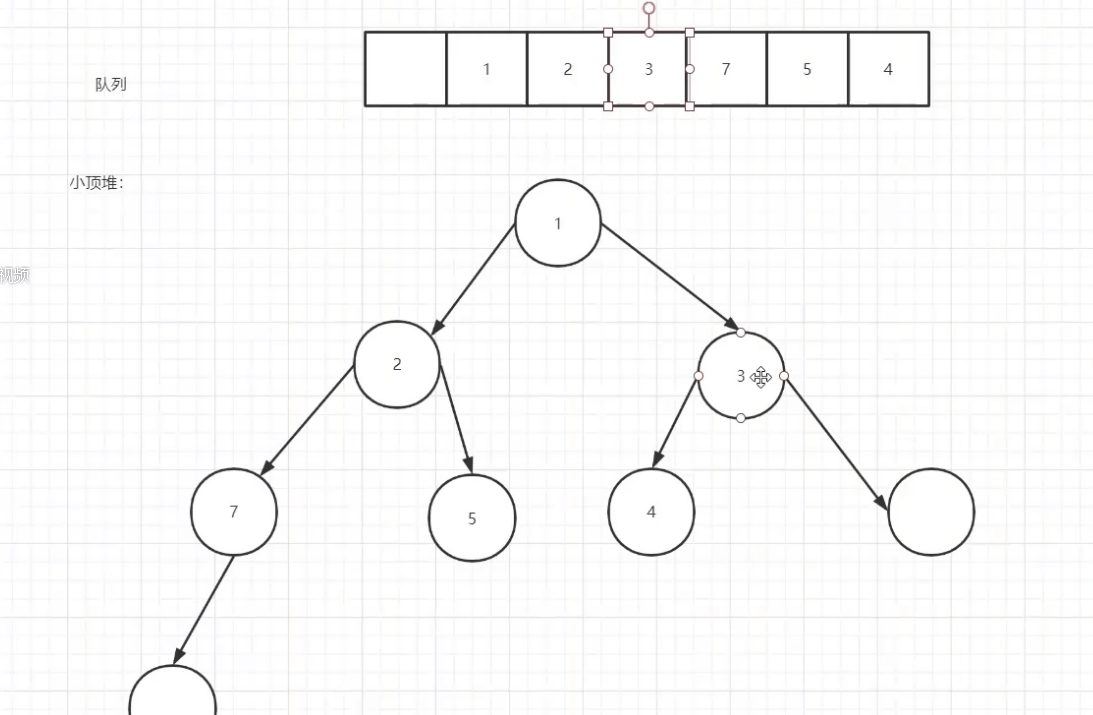
可以进行排序
@Testpublic void test5(){int[] arr = {3,2,5,8,1,9};PriorityQueue<Integer> priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue(arr.length);for(int i : arr){priorityQueue.add(i);}Iterator iterator = priorityQueue.iterator();while (iterator.hasNext()){System.out.print(iterator.next() + ",");}// 输出:1,2,5,8,3,9, 迭代器没有顺序int size = priorityQueue.size();for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {System.out.print(priorityQueue.poll() + ",");}// 输出:1,2,3,5,8,9, poll是有顺序的}
入队:
public boolean offer(E e) {if (e == null)throw new NullPointerException();final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;lock.lock();int n, cap;Object[] array;while ((n = size) >= (cap = (array = queue).length))// 这里执行扩容的方法,使用的cas,因为已进入方法就吧锁释放了tryGrow(array, cap);try {Comparator<? super E> cmp = comparator;if (cmp == null)siftUpComparable(n, e, array);elsesiftUpUsingComparator(n, e, array, cmp);size = n + 1;notEmpty.signal();} finally {lock.unlock();}return true;}private void tryGrow(Object[] array, int oldCap) {// 这里释放锁的原因是不阻塞读lock.unlock(); // must release and then re-acquire main lockObject[] newArray = null;// 只需要一个线程做扩容if (allocationSpinLock == 0 &&UNSAFE.compareAndSwapInt(this, allocationSpinLockOffset,0, 1)) {try {int newCap = oldCap + ((oldCap < 64) ?(oldCap + 2) : // grow faster if small(oldCap >> 1));if (newCap - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) { // possible overflowint minCap = oldCap + 1;if (minCap < 0 || minCap > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE)throw new OutOfMemoryError();newCap = MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;}if (newCap > oldCap && queue == array)newArray = new Object[newCap];} finally {allocationSpinLock = 0;}}// 让扩容后的线程优先拿到资源if (newArray == null) // back off if another thread is allocatingThread.yield();lock.lock();if (newArray != null && queue == array) {queue = newArray;System.arraycopy(array, 0, newArray, 0, oldCap);}}
DelayQueue 延迟队列
具有阻塞的功能,线程安全
// 创建一个延迟线程池里面是通过它的内部类DelayedWorkQueue来做的延迟功能,但是原理和DelayQueue差不多ScheduledExecutorService scheduledExecutorService = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(10);public ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize) {super(corePoolSize, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 0, NANOSECONDS,new DelayedWorkQueue());}
private final transient ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();// 内部调用的就是优先级队列的方法private final PriorityQueue<E> q = new PriorityQueue<E>();// 当前是否有线程再排队,用于取元素的时候,当取得时候发现有线程在排队那就不用取了,直接排 //队就好了private Thread leader = null;private final Condition available = lock.newCondition();
public boolean offer(E e) {final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;lock.lock();try {// 入队直接调用PriorityQueue的offer方法q.offer(e);if (q.peek() == e) {leader = null;available.signal();}return true;} finally {lock.unlock();}}

