Service
- 本地服务
- 该服务依附在主进程上而不是独立的进程
- 不需要IPC,不需要AIDL
- 应用被杀,service也会被杀
- 远程服务
- 独立进程·
- 对应进程名格式为所在包名加上你指定的android:process字符串。一般定义方式 android:process=”:service”
- Activity所在进程被Kill的时候,该服务依然在运行,不受其他进程影响
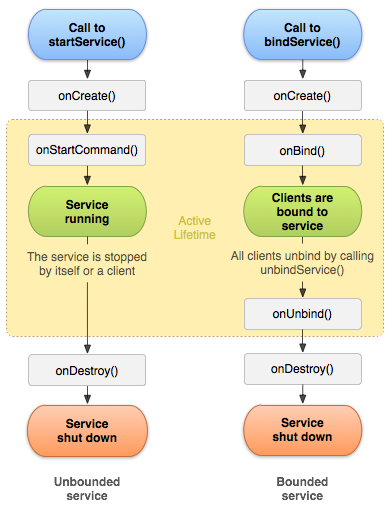
Service状态
- 启动状态
- 通过调用 startService() 启动服务时,服务即处于“启动”状态
- 一旦启动,服务即可在后台无限期运行,即使启动服务的组件已被销毁也不受影响,除非手动调用才能停止服务
- 如果想要启动一个后台服务长期进行某项任务,那么使用startService
- 多次startService不会重复执行onCreate回调,但每次都会执行onStartCommand回调。
- onCreate -> onStartCommand -> onDestory
- stopService
- 绑定状态
- 调用 bindService() 绑定到服务时,服务即处于“绑定”状态
- 绑定服务提供了一个客户端-服务器接口,允许组件与服务进行交互、发送请求、获取结果,甚至是利用进程间通信 (IPC) 跨进程执行这些操作
- 多个组件可以同时绑定到该服务,但全部取消绑定后,该服务即会被销毁
- 如果只是短暂的使用,那么使用bindService。
- onCreate -> onBind -> onUnbind -> onDestory
- unbindService
- 对于既使用startService,又使用bindService的情况,Service的终止,需要unbindService和stopService都调用才行
IntentService
- 内部compose了ServiceHandler,并且在onCreate的时候创建新线程
- 重写其中的onHandleIntent(Intent)方法接收一个Intent对象,在适当的时候会停止自己(一般在工作完成的时候).
onHandleIntent(Intent)执行在子线程
public abstract class IntentService extends Service {private volatile Looper mServiceLooper;private volatile ServiceHandler mServiceHandler;private String mName;private boolean mRedelivery;private final class ServiceHandler extends Handler {public ServiceHandler(Looper looper) {super(looper);}@Overridepublic void handleMessage(Message msg) {onHandleIntent((Intent)msg.obj);stopSelf(msg.arg1);}}@Overridepublic void onCreate() {// TODO: It would be nice to have an option to hold a partial wakelock// during processing, and to have a static startService(Context, Intent)// method that would launch the service & hand off a wakelock.super.onCreate();HandlerThread thread = new HandlerThread("IntentService[" + mName + "]");thread.start();mServiceLooper = thread.getLooper();mServiceHandler = new ServiceHandler(mServiceLooper);}

