苹果Swift语言官方文档(中文翻译版)
本文档由长沙戴维营教育组织翻译和校对,由于英语水平有限,请大家指正。
长沙戴维营教育还为本教程录制了配套的视频教程在乌班图学院上免费提供,欢迎大家一起学习。
下面的章节,如果为蓝色链接表示以及翻译完毕,可以查看,如果为黑色则表示正在紧张的翻译中。本文档中文版每天都会更新,大家可以随时查看。如由Bug欢迎改正。
Swift编程
流程控制
Swift提供C语言类似的流程控制结构。它使用for和while执行重复操作;if和switch实现分支判断;break和continue进行跳转。
除了C语言中的for-condition-increment循环形式,Swift还提供for-in快速循环,使得对数组、字典、范围、字符串或其它的序列结构进行遍历变得更加简单。
Swift的switch语句比C语言中更加强大。它不需要使用break来结束每个case。每个case能够匹配更多类型的模式,包括范围、元组等,对于复杂的条件还能使用where进行判断,而C语言中只能使用整数。
for循环
for循环可以让一组语句执行特定的次数。Swift提供了两种类型的for循环:
for-in遍历范围、序列、集合等数据结构。for-condition-increment执行循环体,直到不满足条件。
for-in
for-in类型的循环可以对集合中的元素进行遍历,如一组数值、一个数组或者字符串。下面是循环打印五次:
for index in 1...5 {println("\(index) times 5 is \(index * 5)")}// 1 times 5 is 5// 2 times 5 is 10// 3 times 5 is 15// 4 times 5 is 20// 5 times 5 is 25
提示
index常量的作用域只在循环体里面。如果需要在外面使用它的值,则应该在循环体外面定义一个遍历。
如果不需要从范围中获取值的话,可以使用下划线_代替常量index的名字,从而忽略这个常量的值:
let base = 3let power = 10var answer = 1for _ in 1...power {answer *= base}println("\(base) to the power of \(power) is \(answer)")//prints "3 to the power of 10 is 59049"
下面是使用for-in遍历数组里的元素:
let names = ["Anna", "Alex", "Brain", "Jack"]for name in names {println("Hello, \(name)!")}//Hello, Anna!//Hello, Alex!//Hello, Brain!//Hello, Jack!
还可以使用键值对遍历字典:
let numberOfLegs = ["spider": 8, "ant": 6, "cat": 4]for (animalName, legCount) in numberOfLegs {println("\(animalName)s have \(legCount) legs")}//spiders have 8 legs//ants have 6 legs//cats have 4 legs
由于字典是无序的,因此迭代的顺序不一定和插入顺序相同。
对于字符串String进行遍历的时候,得到的是里面的字符Character:
for character in "Hello" {println(character)}// H// e// l// l// o
for-condition-increment
第二种形式的for循环与C语言相同,需要一个循环条件和递增的变量:
for var index = 0; index < 3; ++index {println("index is \(index)")}//index is 0//index is 1//index is 2
下面是这种循环的通用格式,for循环中的分号不能省略:
for 初始化; 循环条件; 递增变量 {
循环体语句
}
这些语句的执行顺序如下:
- 第一次进入是先执行初始化表达式,给循环中用到的常量和变量赋值。
- 执行循环条件表达式,如果为
false,循环结束,否则执行花括号{}里的循环体语句。 - 循环体执行完后,递增遍历表达式执行,然后再回到上面的第2条。
这中形式的for循环可以用下面的while循环等价替换:
初始化while 循环条件 {循环体语句递增变量}
在初始化是声明的常量或变量的作用域为for循环里面,如果需要在循环结束后使用index的值,需要在for循环之前进行声明:
var index: Intfor index = 0; index < 3; ++index {println("index is \(index)")}//index is 0//index is 1//index is 2println("The loop statements were executed \(index) times")//prints "The loop statements were executed 3 times"
while循环
while循环也有两种形式:
while在执行循环体之前先判断循环条件。do-while先执行循环体,然后再判断循环条件。
while循环
while的通用格式:
while 循环条件 {循环体语句}
do-while循环
do-while循环的通用格式:
do {循环体语句}while(循环条件)
条件判断语句
条件判断语句包括if和switch。
if语句
最简单的形式就是一个if语句,当if的判断条件为true的时候,执行if里面的语句:
var temperatureInFahrenheit = 30if temperatureInFahrenheit <= 32 {println("It's very cold. Consider wearing a scarf.")}//prints "It's very cold. Consider wearing a scarf."
如果需要在if的判断条件为false的时候执行一些操作,可以加入else语句:
temperatureInFahrenheit = 40if temperatureInFahrenheit <= 32 {println("It's very cold. Consider wearing a scarf.")}else {println("It's not that cold. Wear a t-shirt.")}//prints "It's not that cold. Wear a t-shirt."
如果需要增加更多的判断条件,可以将多个if-else语句链接起来:
temperatureInFahrenheit = 90if temperatureInFahrenheit <= 32 {println("It's very cold. Consider wearing a scarf.")}else if temperatureInFahrenheit >= 86 {println("It's really warm. Don't forget to wear sunscreen.")}else {println("It's not that cold. Wear a t-shirt.")}//prints "It's really warm. Don't forget to wear sunscreen."
最后一个else是可选的,如果不需要执行任何操作,可以不写。
temperatureInFahrenheit = 72if temperatureInFahrenheit <= 32 {println("It's very cold. Consider wearing a scarf.")} else if temperatureInFahrenheit >= 86 {println("It's really warm. Don't forget to wear sunscreen.")}
switch语句
switch语句可以将同一个值与多个判断条件进行比较,找出合适的代码进行执行。最简单的形式是将一个值与多个同类型的值进行比较:
switch 需要进行判断的值 {case 值1:代码块case 值1, 值2:代码块default:代码块}
需要在switch中覆盖所有可能的值,对于没法不能在case中覆盖到的,应该在default中进行处理。
let someCharacter: Character = "e"switch someCharacter {case "a", "e", "i", "o", "u":println("\(someCharacter) is a vowel")case "b", "c", "d", "f", "g", "h", "j", "k", "l", "m","n", "p", "q", "r", "s", "t", "v", "w", "x", "y", "z":println("\(someCharacter) is a consonant")default:println("\(someCharacter) is not a vowel or a consonant")}// prints "e is a vowel"
在Swift里,switch的每个case都必须要有语句,它不像C语言一样遇到空的case就自动往下执行,下面的写法会出现编译错误:
let anotherCharacter: Character = "a"switch anotherCharacter {case "a":case "A":println("The letter A")default:println("Not the letter A")}// this will report a compile-time error
同一个case可以对应多个值,每个值之间用,隔开。
提示 如果在一个
case执行完后,继续执行下面的case,需要使用fallthrough关键字。
范围匹配
switch可以对一个范围进行判断,从而确定是否执行某个case下的语句:
let count = 3_000_000_000_000let countedThings = "stars in the Milky Way"var naturalCount: Stringswitch count {case 0:naturalCount = "no"case 1...3:naturalCount = "a few"case 4...9:naturalCount = "several"case 10...99:naturalCount = "tens of"case 100...999:naturalCount = "hundreds of"case 1000...999_999:naturalCount = "thousands of"default:naturalCount = "millions and millions of"}println("There are \(naturalCount) \(countedThings).")// prints "There are millions and millions of stars in the Milky Way."
提示 Swift中的整数,可以用下划线
_分隔,便于查看。
元组
Swift可以在switch中对元组进行判断。元组的每个元素都会与对应的值进行比较,可以使用下划线_表示匹配任意值。下面用switch来判断一个点是否在某个范围内:
let somePoint = (1, 1)switch somePoint {case (0, 0):println("(0, 0) is at the origin")case (_, 0):println("(\(somePoint.0), 0) is on the x-axis")case (0, _):println("(0, \(somePoint.1)) is on the y-axis")case (-2...2, -2...2):println("(\(somePoint.0), \(somePoint.1)) is inside the box")default:println("(\(somePoint.0), \(somePoint.1)) is outside of the box")}// prints "(1, 1) is inside the box"
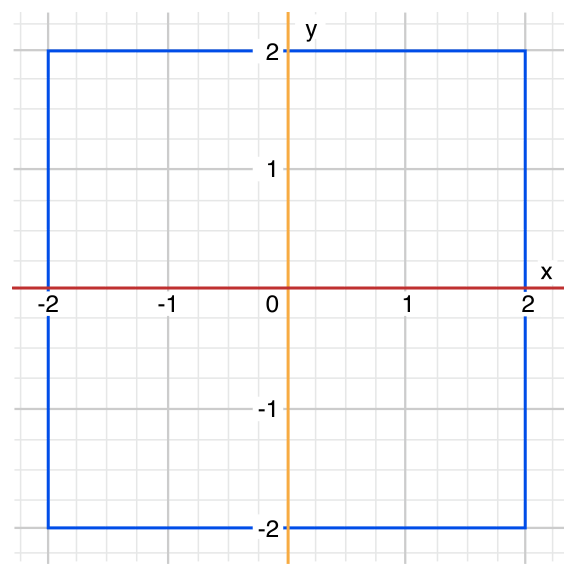
Swift中case表示的范围可以是重叠的,但是会匹配最先发现的值。
值的绑定
switch能够将值绑定到临时的常量或变量上,然后在case中使用,被称为value binding。
let anotherPoint = (2, 0)switch anotherPoint {case (let x, 0):println("on the x-axis with an x value of \(x)")case (0, let y):println("on the y-axis with a y value of \(y)")case let (x, y):println("somewhere else at (\(x), \(y))")}// prints "on the x-axis with an x value of 2"
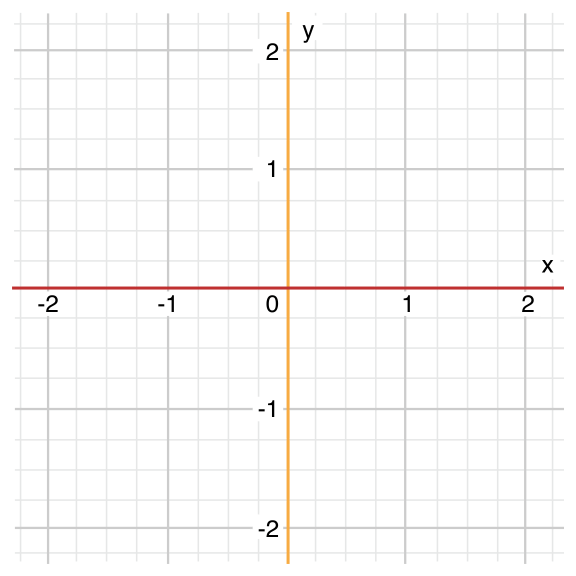
上面的代码匹配所有y等于0的元组,并将常量x初始化为2,x的作用域为它所在的case。你也可以将x用var关键字声明为变量。
where语句
switch中可以使用where增加额外的判断条件:
let yetAnotherPoint = (1, -1)switch yetAnotherPoint {case let (x, y) where x == y:println("(\(x), \(y)) is on the line x == y")case let (x, y) where x == -y:println("(\(x), \(y)) is on the line x == -y")case let (x, y):println("(\(x), \(y)) is just some arbitrary point")}// prints "(1, -1) is on the line x == -y"
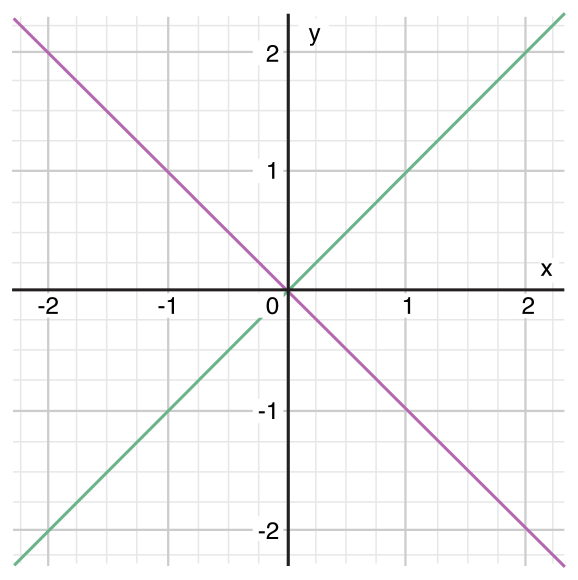
流程转换语句
流程转换语句(跳转语句)可以改变代码的执行流程。Swift包含下面四种跳转语句:
continuebreakfallthroughreturn
下面会对continue、break和fallthrough进行讲解,而return表达式将在函数中进行介绍。
continue表达式
continue语句可以提前结束一次循环,之间调到第二次循环开始,但是并不会终止循环。
提示 在
for-condition-increment类型的循环中,自增语句在continue后仍然会执行。
下面的例子会删除字符串中的元音字符和空格:
let puzzleInput = "great minds think alike"var puzzleOutput = ""for character in puzzleInput {switch character {case "a", "e", "i", "o", "u", " ":continuedefault:puzzleOutput += character}}println(puzzleOutput)// prints "grtmndsthnklk"
上面的代码在遇到元音或空格后,执行continue语句,不将它们添加到输出字符串中。
break语句
break语句之间结束整个循环,可以被用在switch和循环语句中。
循环语句中使用break
break直接结束循环,调到循环体后的语句进行执行。
switch语句中使用break
break会导致switch语句执行终止,只要用于忽略一个case的执行。因为switch中不能有空的case,所以可以用break来忽略一个case的执行。
let numberSymbol: Character = "三" // Simplified Chinese for the number 3var possibleIntegerValue: Int?switch numberSymbol {case "1", "١", "一", "๑":possibleIntegerValue = 1case "2", "٢", "二", "๒":possibleIntegerValue = 2case "3", "٣", "三", "๓":possibleIntegerValue = 3case "4", "٤", "四", "๔":possibleIntegerValue = 4default:break}if let integerValue = possibleIntegerValue {println("The integer value of \(numberSymbol) is \(integerValue).")} else {println("An integer value could not be found for \(numberSymbol).")}// prints "The integer value of 三 is 3."
fallthrough语句
Swift的switch语句中不能在一个case执行完后继续执行另外一个case,这遇C语言中的情况不一样。如果你需要实现类似于C语言中switch的行为,可以使用fallthrough关键字。
let integerToDescribe = 5var description = "The number \(integerToDescribe) is"switch integerToDescribe {case 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19:description += " a prime number, and also"fallthroughdefault:description += " an integer."}println(description)// prints "The number 5 is a prime number, and also an integer."
提示
fallthrough语句执行后,switch不会再去检查下面的case的值。
标号语句
在循环或者switch语句中使用break只能跳出最内层,如果有多个循环语句嵌套的话,需要使用标号语句才能一次性跳出这些循环。
标号语句的基本写法为:
标号名称: while 条件语句 {循环体}
下面是标号语句的一个例子:
let finalSquare = 25var board = Int[](count: finalSquare + 1, repeatedValue: 0)board[03] = +08; board[06] = +11; board[09] = +09; board[10] = +02board[14] = -10; board[19] = -11; board[22] = -02; board[24] = -08var square = 0var diceRoll = 0gameLoop: while square != finalSquare {if ++diceRoll == 7 { diceRoll = 1 }switch square + diceRoll {case finalSquare:// diceRoll will move us to the final square, so the game is overbreak gameLoopcase let newSquare where newSquare > finalSquare:// diceRoll will move us beyond the final square, so roll againcontinue gameLoopdefault:// this is a valid move, so find out its effectsquare += diceRollsquare += board[square]}}println("Game over!")
break或continue执行后,会跳转到标号语句处执行,其中break会终止循环,而continue则终止当前这次循环的执行。

