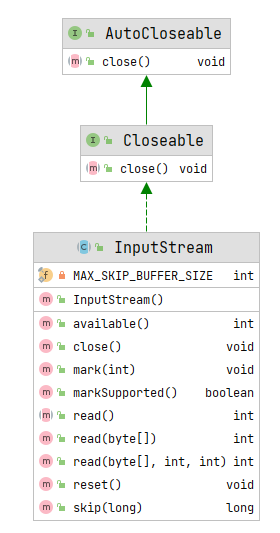
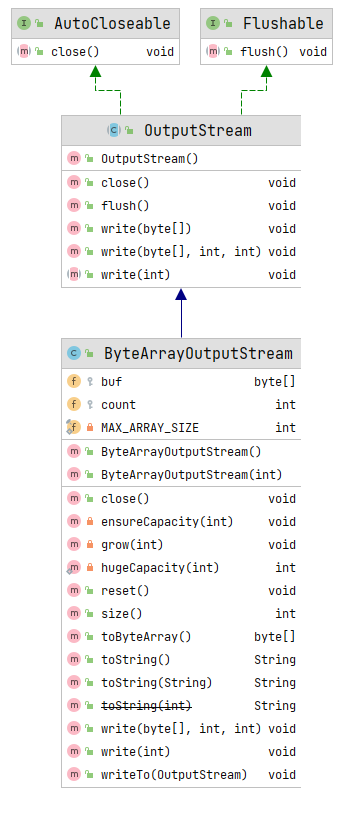
- 输出流需要关闭,因此需要Closeable接口
- 缓冲流需要刷新,因此需要Flushable接口
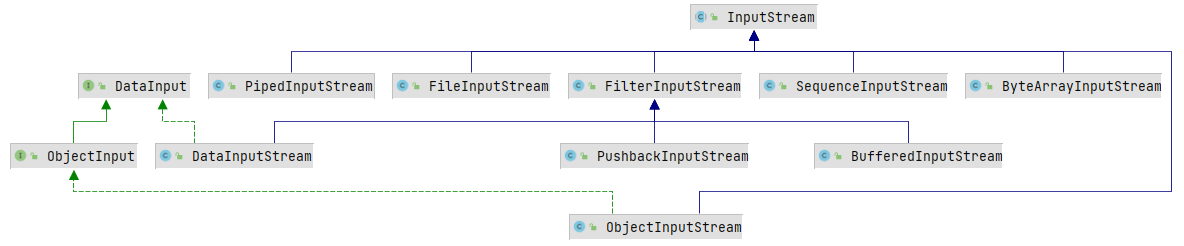
输入流的架构
输出流的基类
UML概述
重要方法
输入流将具体如何读,如何关闭留给了子类
read
从输入流中读取下一个字节的数据。值字节以 0 到 255 范围内的 int 形式返回(即int只有低八位有效,和写操作相对应)。如果由于已到达流的末尾而没有可用字节,则返回值 -1。此方法会阻塞,直到输入数据可用、检测到流结束或抛出异常为止。子类必须提供此方法的实现。
/*** Reads the next byte of data from the input stream. The value byte is* returned as an <code>int</code> in the range <code>0</code> to* <code>255</code>. If no byte is available because the end of the stream* has been reached, the value <code>-1</code> is returned. This method* blocks until input data is available, the end of the stream is detected,* or an exception is thrown.** <p> A subclass must provide an implementation of this method.** @return the next byte of data, or <code>-1</code> if the end of the* stream is reached.* @exception IOException if an I/O error occurs.*/public abstract int read() throws IOException;
将输入流中最多 len 个数据字节读入 byte 数组。尝试读取 len 个字节,但读取的字节也可能小于该值。以整数形式返回实际读取的字节数。在输入数据可用、检测到流末尾或者抛出异常前,此方法一直阻塞。如果 len 为 0,则不读取任何字节并返回 0;否则,尝试读取至少一个字节。如果因为流位于文件末尾而没有可用的字节,则返回值 -1;否则,至少读取一个字节并将其存储在 b 中。
将读取的第一个字节存储在元素 b[off] 中,下一个存储在 b[off+1] 中,依次类推。读取的字节数最多等于 len。设 k 为实际读取的字节数;这些字节将存储在 b[off] 到 b[off+k-1] 的元素中,不影响 b[off+k] 到 b[off+len-1] 的元素。在任何情况下,b[0] 到 b[off] 的元素以及 b[off+len] 到 b[b.length-1] 的元素都不会受到影响。
类 InputStream 的 read(b, off, len) 方法重复调用方法 read()。如果第一次这样的调用导致 IOException,则从对 read(b, off, len) 方法的调用中返回该异常。如果对 read() 的任何后续调用导致 IOException,则捕获该异常并将其视为到达文件末尾;到达该点时读取的字节存储在 b 中,并返回发生异常之前读取的字节数。千言万语一句话,就是中途抛异常不影响已经读到的数据。
在已读取输入数据 len 的请求数量、检测到文件结束标记、抛出异常前,此方法的默认实现将一直阻塞。建议子类提供此方法更为有效的实现。
/*** Reads up to <code>len</code> bytes of data from the input stream into* an array of bytes. An attempt is made to read as many as* <code>len</code> bytes, but a smaller number may be read.* The number of bytes actually read is returned as an integer.** <p> This method blocks until input data is available, end of file is* detected, or an exception is thrown.** <p> If <code>len</code> is zero, then no bytes are read and* <code>0</code> is returned; otherwise, there is an attempt to read at* least one byte. If no byte is available because the stream is at end of* file, the value <code>-1</code> is returned; otherwise, at least one* byte is read and stored into <code>b</code>.** <p> The first byte read is stored into element <code>b[off]</code>, the* next one into <code>b[off+1]</code>, and so on. The number of bytes read* is, at most, equal to <code>len</code>. Let <i>k</i> be the number of* bytes actually read; these bytes will be stored in elements* <code>b[off]</code> through <code>b[off+</code><i>k</i><code>-1]</code>,* leaving elements <code>b[off+</code><i>k</i><code>]</code> through* <code>b[off+len-1]</code> unaffected.** <p> In every case, elements <code>b[0]</code> through* <code>b[off]</code> and elements <code>b[off+len]</code> through* <code>b[b.length-1]</code> are unaffected.** <p> The <code>read(b,</code> <code>off,</code> <code>len)</code> method* for class <code>InputStream</code> simply calls the method* <code>read()</code> repeatedly. If the first such call results in an* <code>IOException</code>, that exception is returned from the call to* the <code>read(b,</code> <code>off,</code> <code>len)</code> method. If* any subsequent call to <code>read()</code> results in a* <code>IOException</code>, the exception is caught and treated as if it* were end of file; the bytes read up to that point are stored into* <code>b</code> and the number of bytes read before the exception* occurred is returned. The default implementation of this method blocks* until the requested amount of input data <code>len</code> has been read,* end of file is detected, or an exception is thrown. Subclasses are encouraged* to provide a more efficient implementation of this method.** @param b the buffer into which the data is read.* @param off the start offset in array <code>b</code>* at which the data is written.* @param len the maximum number of bytes to read.* @return the total number of bytes read into the buffer, or* <code>-1</code> if there is no more data because the end of* the stream has been reached.* @exception IOException If the first byte cannot be read for any reason* other than end of file, or if the input stream has been closed, or if* some other I/O error occurs.* @exception NullPointerException If <code>b</code> is <code>null</code>.* @exception IndexOutOfBoundsException If <code>off</code> is negative,* <code>len</code> is negative, or <code>len</code> is greater than* <code>b.length - off</code>* @see java.io.InputStream#read()*/public int read(byte b[], int off, int len) throws IOException {if (b == null) {throw new NullPointerException();} else if (off < 0 || len < 0 || len > b.length - off) {throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();} else if (len == 0) {return 0;}int c = read();if (c == -1) {return -1;}b[off] = (byte)c;int i = 1;try {for (; i < len ; i++) {c = read();if (c == -1) {break;}b[off + i] = (byte)c;}} catch (IOException ee) {}return i;}
skip
MAX_SKIP_BUFFER_SIZE 用于确定跳过时要使用的最大缓冲区大小。skip本身也是读操作,只不过不返回读到的数据,读到的数据也是通过读缓冲区来保存,只不过这里叫skipBuffer
跳过和丢弃此输入流中数据的 n 个字节。出于各种原因, skip 方法结束时跳过的字节数可能小于该数,也可能为 0。导致这种情况的原因很多,跳过 n 个字节之前已到达文件末尾只是其中一种可能。返回跳过的实际字节数。如果 n 为负,则不跳过任何字节。此类的 skip 方法创建一个 byte 数组,然后重复将字节读入其中,直到读够 n 个字节或已到达流末尾为止。建议子类提供此方法更为有效的实现。例如,可依赖搜索能力的实现。
// MAX_SKIP_BUFFER_SIZE is used to determine the maximum buffer size to// use when skipping.private static final int MAX_SKIP_BUFFER_SIZE = 2048;/*** Skips over and discards <code>n</code> bytes of data from this input* stream. The <code>skip</code> method may, for a variety of reasons, end* up skipping over some smaller number of bytes, possibly <code>0</code>.* This may result from any of a number of conditions; reaching end of file* before <code>n</code> bytes have been skipped is only one possibility.* The actual number of bytes skipped is returned. If {@code n} is* negative, the {@code skip} method for class {@code InputStream} always* returns 0, and no bytes are skipped. Subclasses may handle the negative* value differently.** <p> The <code>skip</code> method of this class creates a* byte array and then repeatedly reads into it until <code>n</code> bytes* have been read or the end of the stream has been reached. Subclasses are* encouraged to provide a more efficient implementation of this method.* For instance, the implementation may depend on the ability to seek.** @param n the number of bytes to be skipped.* @return the actual number of bytes skipped.* @exception IOException if the stream does not support seek,* or if some other I/O error occurs.*/public long skip(long n) throws IOException {long remaining = n;int nr;if (n <= 0) {return 0;}int size = (int)Math.min(MAX_SKIP_BUFFER_SIZE, remaining);byte[] skipBuffer = new byte[size];while (remaining > 0) {nr = read(skipBuffer, 0, (int)Math.min(size, remaining));if (nr < 0) {break;}remaining -= nr;}return n - remaining;}
available
返回此输入流下一个方法调用可以不受阻塞地从此输入流读取(或跳过)的估计字节数。下一个调用可能是同一个线程,也可能是另一个线程。一次读取或跳过此估计数个字节不会受阻塞,但读取或跳过的字节数可能小于该数。注意,有些 InputStream 的实现将返回流中的字节总数,但也有很多实现不会这样做。试图使用此方法的返回值分配缓冲区,以保存此流所有数据的做法是不正确的。
如果已经调用 close() 方法关闭了此输入流,那么此方法的子类实现可以选择抛出 IOException。类 InputStream 的 available 方法总是返回 0。此方法应该由子类重写。
/*** Returns an estimate of the number of bytes that can be read (or* skipped over) from this input stream without blocking by the next* invocation of a method for this input stream. The next invocation* might be the same thread or another thread. A single read or skip of this* many bytes will not block, but may read or skip fewer bytes.** <p> Note that while some implementations of {@code InputStream} will return* the total number of bytes in the stream, many will not. It is* never correct to use the return value of this method to allocate* a buffer intended to hold all data in this stream.** <p> A subclass' implementation of this method may choose to throw an* {@link IOException} if this input stream has been closed by* invoking the {@link #close()} method.** <p> The {@code available} method for class {@code InputStream} always* returns {@code 0}.** <p> This method should be overridden by subclasses.** @return an estimate of the number of bytes that can be read (or skipped* over) from this input stream without blocking or {@code 0} when* it reaches the end of the input stream.* @exception IOException if an I/O error occurs.*/public int available() throws IOException {return 0;}
mark
很多读数据的操作都会提供类似mark的方法,用来作为游标,在数据或记录中游走。并且会匹配reset的设计。
在此输入流中标记当前的位置。对 reset 方法的后续调用会在最后标记的位置重新定位此流,**以便后续回到该位置重新读取相同的字节**。readlimit 参数告知此输入流在标记位置失效之前允许读取的字节数。mark 的常规协定是:如果方法 markSupported 返回 true,那么输入流总是在调用 mark 之后记录所有读取的字节,并时刻准备在调用方法 reset 时(无论何时),再次提供这些相同的字节。但是,如果在调用 reset 之前可以从流中读取多于 readlimit 的字节,则不需要该流记录任何数据。**标记已关闭的流对其无效。InputStream 的 mark 方法不执行任何操作。**
/*** Marks the current position in this input stream. A subsequent call to* the <code>reset</code> method repositions this stream at the last marked* position so that subsequent reads re-read the same bytes.** <p> The <code>readlimit</code> arguments tells this input stream to* allow that many bytes to be read before the mark position gets* invalidated.** <p> The general contract of <code>mark</code> is that, if the method* <code>markSupported</code> returns <code>true</code>, the stream somehow* remembers all the bytes read after the call to <code>mark</code> and* stands ready to supply those same bytes again if and whenever the method* <code>reset</code> is called. However, the stream is not required to* remember any data at all if more than <code>readlimit</code> bytes are* read from the stream before <code>reset</code> is called.** <p> Marking a closed stream should not have any effect on the stream.** <p> The <code>mark</code> method of <code>InputStream</code> does* nothing.** @param readlimit the maximum limit of bytes that can be read before* the mark position becomes invalid.* @see java.io.InputStream#reset()*/public synchronized void mark(int readlimit) {}
markSupported
并非所有流都支持设置标记。测试此输入流是否支持 mark 和 reset 方法。是否支持 mark 和 reset 是特定输入流实例的不变属性。 InputStream 的 markSupported 方法返回 false。
/*** Tests if this input stream supports the <code>mark</code> and* <code>reset</code> methods. Whether or not <code>mark</code> and* <code>reset</code> are supported is an invariant property of a* particular input stream instance. The <code>markSupported</code> method* of <code>InputStream</code> returns <code>false</code>.** @return <code>true</code> if this stream instance supports the mark* and reset methods; <code>false</code> otherwise.* @see java.io.InputStream#mark(int)* @see java.io.InputStream#reset()*/public boolean markSupported() {return false;}
reset
将此流重新定位到最后一次对此输入流调用 mark 方法时的位置。reset 的常规协定是:
- 如果方法 markSupported 返回 true,那么:
- 如果创建流以后未调用方法 mark,或最后调用 mark 以后从该流读取的字节数大于最后调用 mark 时的参数,则可能抛出 IOException。
- 如果未抛出这样的 IOException,则将该流重新设置为这种状态:最近一次调用 mark 以后(如果未调用过 mark,则从文件开头开始)读取的所有字节将重新提供给 read 方法的后续调用者,后跟任何从调用 reset 时起将作为下一输入数据的字节。
- 如果方法 markSupported 返回 false,那么:
- 对 reset 的调用可能抛出 IOException。
- 如果未抛出 IOException,则将该流重新设置为一种固定状态,该状态取决于输入流的特定类型及其创建方式。提供给 read 方法后续调用者的字节取决于特定类型的输入流。
除了抛出 IOException 之外,类 InputStream 的方法 reset 不执行任何操作。
/*** Repositions this stream to the position at the time the* <code>mark</code> method was last called on this input stream.** <p> The general contract of <code>reset</code> is:** <ul>* <li> If the method <code>markSupported</code> returns* <code>true</code>, then:** <ul><li> If the method <code>mark</code> has not been called since* the stream was created, or the number of bytes read from the stream* since <code>mark</code> was last called is larger than the argument* to <code>mark</code> at that last call, then an* <code>IOException</code> might be thrown.** <li> If such an <code>IOException</code> is not thrown, then the* stream is reset to a state such that all the bytes read since the* most recent call to <code>mark</code> (or since the start of the* file, if <code>mark</code> has not been called) will be resupplied* to subsequent callers of the <code>read</code> method, followed by* any bytes that otherwise would have been the next input data as of* the time of the call to <code>reset</code>. </ul>** <li> If the method <code>markSupported</code> returns* <code>false</code>, then:** <ul><li> The call to <code>reset</code> may throw an* <code>IOException</code>.** <li> If an <code>IOException</code> is not thrown, then the stream* is reset to a fixed state that depends on the particular type of the* input stream and how it was created. The bytes that will be supplied* to subsequent callers of the <code>read</code> method depend on the* particular type of the input stream. </ul></ul>** <p>The method <code>reset</code> for class <code>InputStream</code>* does nothing except throw an <code>IOException</code>.** @exception IOException if this stream has not been marked or if the* mark has been invalidated.* @see java.io.InputStream#mark(int)* @see java.io.IOException*/public synchronized void reset() throws IOException {throw new IOException("mark/reset not supported");}
close
关闭此输入流并释放与该流关联的所有系统资源。InputStream 的 close 方法不执行任何操作。
/*** Closes this input stream and releases any system resources associated* with the stream.** <p> The <code>close</code> method of <code>InputStream</code> does* nothing.** @exception IOException if an I/O error occurs.*/public void close() throws IOException {}
输入流的子类
ByteArrayInputStream
这个类是一个字节数组输入流,数据是被读入内存中的字节数组。ByteArrayInputStream 包含一个内部缓冲区,该缓冲区包含从流中读取的字节。内部计数器跟踪 read 方法要提供的下一个字节。关闭 ByteArrayInputStream 无效。此类中的方法在关闭此流后仍可被调用,而不会产生任何 IOException。
UML概述
重要方法
构造函数
- buf[] - 由流的创建者提供的字节数组。元素 buf[0] 到 buf[count-1] 是唯一可以从流中读取的字节;元素 buf[pos] 是要读取的下一个字节。
- pos - 要从输入流缓冲区读取的下一个字符的索引。该值应始终为非负且不大于计数值。要从输入流缓冲区读取的下一个字节将是 buf[pos]
- mark - 流中当前标记的位置。 ByteArrayInputStream 对象在构造时默认标记在位置零。它们可以通过 mark() 方法在缓冲区内的另一个位置进行标记。当前缓冲区位置由 reset() 方法设置到这一点。如果未设置标记,则标记的值是传递给构造函数的偏移量(如果未提供偏移量,则为 0 )
- count - 比输入流缓冲区中最后一个有效字符大一的索引。该值应始终为非负且不大于 buf 的长度。它比 buf 中可以从输入流缓冲区读取的最后一个字节的位置大 1。
publicclass ByteArrayInputStream extends InputStream {/*** An array of bytes that was provided* by the creator of the stream. Elements <code>buf[0]</code>* through <code>buf[count-1]</code> are the* only bytes that can ever be read from the* stream; element <code>buf[pos]</code> is* the next byte to be read.*/protected byte buf[];/*** The index of the next character to read from the input stream buffer.* This value should always be nonnegative* and not larger than the value of <code>count</code>.* The next byte to be read from the input stream buffer* will be <code>buf[pos]</code>.*/protected int pos;/*** The currently marked position in the stream.* ByteArrayInputStream objects are marked at position zero by* default when constructed. They may be marked at another* position within the buffer by the <code>mark()</code> method.* The current buffer position is set to this point by the* <code>reset()</code> method.* <p>* If no mark has been set, then the value of mark is the offset* passed to the constructor (or 0 if the offset was not supplied).** @since JDK1.1*/protected int mark = 0;/*** The index one greater than the last valid character in the input* stream buffer.* This value should always be nonnegative* and not larger than the length of <code>buf</code>.* It is one greater than the position of* the last byte within <code>buf</code> that* can ever be read from the input stream buffer.*/protected int count;/*** Creates <code>ByteArrayInputStream</code>* that uses <code>buf</code> as its* buffer array. The initial value of <code>pos</code>* is <code>offset</code> and the initial value* of <code>count</code> is the minimum of <code>offset+length</code>* and <code>buf.length</code>.* The buffer array is not copied. The buffer's mark is* set to the specified offset.** @param buf the input buffer.* @param offset the offset in the buffer of the first byte to read.* @param length the maximum number of bytes to read from the buffer.*/public ByteArrayInputStream(byte buf[], int offset, int length) {this.buf = buf;this.pos = offset;this.count = Math.min(offset + length, buf.length);this.mark = offset;}
read()
从此输入流中读取下一个数据字节。返回一个 0 到 255 范围内的 int 字节值。如果因为到达流末尾而没有可用的字节,则返回值 -1。此 read 方法不会阻塞。
/*** Reads the next byte of data from this input stream. The value* byte is returned as an <code>int</code> in the range* <code>0</code> to <code>255</code>. If no byte is available* because the end of the stream has been reached, the value* <code>-1</code> is returned.* <p>* This <code>read</code> method* cannot block.** @return the next byte of data, or <code>-1</code> if the end of the* stream has been reached.*/public synchronized int read() {return (pos < count) ? (buf[pos++] & 0xff) : -1;}
读取一个字节的时候有些特别,需要将字节转成一个int值返回,并且是一个 0 到 255 范围内的无符号的数值。因此通过位运算 buf[pos++] & 0xff 进行无符号int的转换。
在byte 到 int 的无符号转换中,int 的高 24 位必须为零,低 8 位继续等于 byte 参数的位。
public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {byte b1 = (byte) 1;int i1 = (int) b1;System.out.println(i1); // 1System.out.println(Integer.toBinaryString(b1)); // 1byte b2 = (byte) 127;int i2 = (int) b2;System.out.println(i2); // 127System.out.println(Integer.toBinaryString(b2)); // 1111111byte b3 = (byte) 128;int i3 = (int) b3;System.out.println(i3); // -128System.out.println(Integer.toBinaryString(i3)); // 11111111111111111111111110000000// Integer.MAX_VALUE = 2147483647 = 2^31byte b4 = (byte) 128;int i4 = (int) (b4 & 0xff);System.out.println(i4); // 128}}
read(byte b[], int off, int len)
将最多 len 个数据字节从此输入流读入 byte 数组。如果 pos 等于 count,则返回 -1 指示文件结束。否则,读取的字节数 k 等于 len 和 count-pos 中的较小者。如果 k 是正数,则以 System.arraycopy 执行的方式将 buf[pos] 到 buf[pos+k-1] 的字节复制到 b[off] 到 b[off+k-1] 中。将值 k 与 pos 相加并返回 k。此 read 方法不会阻塞。
/*** Reads up to <code>len</code> bytes of data into an array of bytes* from this input stream.* If <code>pos</code> equals <code>count</code>,* then <code>-1</code> is returned to indicate* end of file. Otherwise, the number <code>k</code>* of bytes read is equal to the smaller of* <code>len</code> and <code>count-pos</code>.* If <code>k</code> is positive, then bytes* <code>buf[pos]</code> through <code>buf[pos+k-1]</code>* are copied into <code>b[off]</code> through* <code>b[off+k-1]</code> in the manner performed* by <code>System.arraycopy</code>. The* value <code>k</code> is added into <code>pos</code>* and <code>k</code> is returned.* <p>* This <code>read</code> method cannot block.** @param b the buffer into which the data is read.* @param off the start offset in the destination array <code>b</code>* @param len the maximum number of bytes read.* @return the total number of bytes read into the buffer, or* <code>-1</code> if there is no more data because the end of* the stream has been reached.* @exception NullPointerException If <code>b</code> is <code>null</code>.* @exception IndexOutOfBoundsException If <code>off</code> is negative,* <code>len</code> is negative, or <code>len</code> is greater than* <code>b.length - off</code>*/public synchronized int read(byte b[], int off, int len) {if (b == null) {throw new NullPointerException();} else if (off < 0 || len < 0 || len > b.length - off) {throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();}if (pos >= count) {return -1;}int avail = count - pos;if (len > avail) {len = avail;}if (len <= 0) {return 0;}System.arraycopy(buf, pos, b, off, len);pos += len;return len;}
skip
从此输入流中跳过 n 个输入字节。如果已到达输入流末尾,则可能会跳过较少的字节。实际跳过的字节数 k 等于 n 和 count-pos 中的较小者。将值 k 与 pos 相加并返回 k。
千言万语一句话,向后跳过n个位置,但是不要越界,如果会越界就跳到末尾就可以了。
/*** Skips <code>n</code> bytes of input from this input stream. Fewer* bytes might be skipped if the end of the input stream is reached.* The actual number <code>k</code>* of bytes to be skipped is equal to the smaller* of <code>n</code> and <code>count-pos</code>.* The value <code>k</code> is added into <code>pos</code>* and <code>k</code> is returned.** @param n the number of bytes to be skipped.* @return the actual number of bytes skipped.*/public synchronized long skip(long n) {long k = count - pos;if (n < k) {k = n < 0 ? 0 : n;}pos += k;return k;}
available
返回可从此输入流读取(或跳过)的剩余字节数。返回值是 count - pos,它是要从输入缓冲区中读取的剩余字节数。
/*** Returns the number of remaining bytes that can be read (or skipped over)* from this input stream.* <p>* The value returned is <code>count - pos</code>,* which is the number of bytes remaining to be read from the input buffer.** @return the number of remaining bytes that can be read (or skipped* over) from this input stream without blocking.*/public synchronized int available() {return count - pos;}
markSupported
测试此 InputStream 是否支持 mark/reset。 ByteArrayInputStream 的 markSupported 方法始终返回 true。
/*** Tests if this <code>InputStream</code> supports mark/reset. The* <code>markSupported</code> method of <code>ByteArrayInputStream</code>* always returns <code>true</code>.** @since JDK1.1*/public boolean markSupported() {return true;}
mark
设置流中的当前标记位置。构造时默认将 ByteArrayInputStream 对象标记在位置零处。通过此方法可将其标记在缓冲区内的另一个位置处。如果尚未设置标记,则标记值是传递给构造方法的偏移量(如果未提供偏移量,则标记值为 0)。注:readAheadLimit 对于此类没有意义。
/*** Set the current marked position in the stream.* ByteArrayInputStream objects are marked at position zero by* default when constructed. They may be marked at another* position within the buffer by this method.* <p>* If no mark has been set, then the value of the mark is the* offset passed to the constructor (or 0 if the offset was not* supplied).** <p> Note: The <code>readAheadLimit</code> for this class* has no meaning.** @since JDK1.1*/public void mark(int readAheadLimit) {mark = pos;}
reset
将缓冲区的位置重置为标记位置。除非已标记了另一个位置,或者在构造方法中指定了一个偏移量,否则该标记位置是 0。
/*** Resets the buffer to the marked position. The marked position* is 0 unless another position was marked or an offset was specified* in the constructor.*/public synchronized void reset() {pos = mark;}
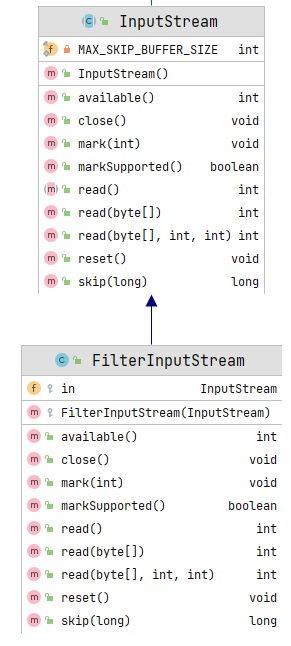
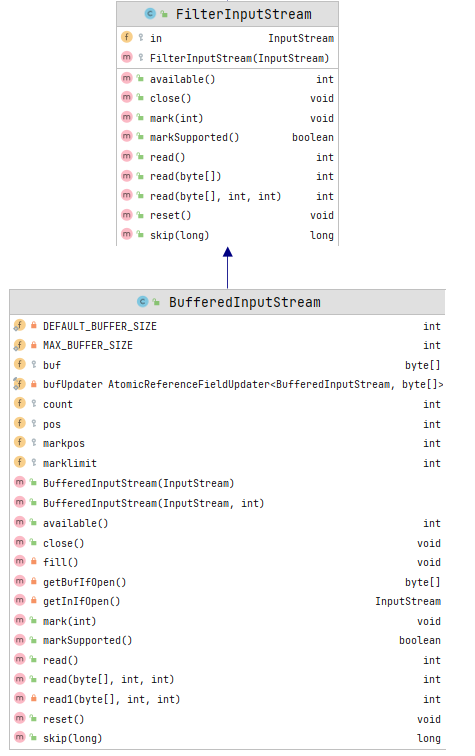
FilterInputStream
FilterInputStream 包含其他一些输入流,它将这些流用作其基本数据源,它可以直接传输数据或提供一些额外的功能。FilterInputStream 类本身只是简单地重写那些将所有请求传递给所包含输入流的 InputStream 的所有方法。FilterInputStream 的子类可进一步重写这些方法中的一些方法,并且还可以提供一些额外的方法和字段。
千言万语一句话就是用来对数据进行过滤拦截的用的,在数据的处理过程中对数据做一些额外的操作,数据经过一层一层的过滤器,被逐层处理,比如被缓冲,被压缩,被加密,或者什么都不做只是打印一下log,这是一种很常见的设计方式,比如MINA中的Filter等等。
UML概述
重要方法
构造函数
用一个外部的输入流来包装或者说是装饰一个内部输入流。大家可能知道IO是基于装饰器模式。而装饰器模式和代理模式看上去很相似,一般来说代理模式中代理类和被代理类之间的角色定义很明确。而装饰器模式中装饰器的装饰顺序并没有明确或固定的叠加顺序,非常灵活,甚至可以重复叠加,比如一个计算折扣的装饰器,被连续嵌套两次,就相当于折上折。当然也有一些装饰器需要遵循顺序,比如先缓冲区装饰器需要先写入缓冲区,再写入底层文件系统。
publicclass FilterInputStream extends InputStream {/*** The input stream to be filtered.*/protected volatile InputStream in;/*** Creates a <code>FilterInputStream</code>* by assigning the argument <code>in</code>* to the field <code>this.in</code> so as* to remember it for later use.** @param in the underlying input stream, or <code>null</code> if* this instance is to be created without an underlying stream.*/protected FilterInputStream(InputStream in) {this.in = in;}
read
从此输入流中读取下一个数据字节。返回一个 0 到 255 范围内的 int 字节值。如果因为已经到达流末尾而没有字节可用,则返回 -1。在输入数据可用、检测到流末尾或抛出异常之前,此方法将一直阻塞。此方法只执行 in.read() 并返回结果。
/*** Reads the next byte of data from this input stream. The value* byte is returned as an <code>int</code> in the range* <code>0</code> to <code>255</code>. If no byte is available* because the end of the stream has been reached, the value* <code>-1</code> is returned. This method blocks until input data* is available, the end of the stream is detected, or an exception* is thrown.* <p>* This method* simply performs <code>in.read()</code> and returns the result.** @return the next byte of data, or <code>-1</code> if the end of the* stream is reached.* @exception IOException if an I/O error occurs.* @see java.io.FilterInputStream#in*/public int read() throws IOException {return in.read();}
read(byte b[], int off, int len)
从此输入流中将 len 个字节的数据读入一个 byte 数组中。如果 len 不为 0,则在输入可用前,此方法将阻塞;否则,不读取任何字节并且返回 0。此方法只执行 in.read(b, off, len) 并返回结果。
/*** Reads up to <code>len</code> bytes of data from this input stream* into an array of bytes. If <code>len</code> is not zero, the method* blocks until some input is available; otherwise, no* bytes are read and <code>0</code> is returned.* <p>* This method simply performs <code>in.read(b, off, len)</code>* and returns the result.** @param b the buffer into which the data is read.* @param off the start offset in the destination array <code>b</code>* @param len the maximum number of bytes read.* @return the total number of bytes read into the buffer, or* <code>-1</code> if there is no more data because the end of* the stream has been reached.* @exception NullPointerException If <code>b</code> is <code>null</code>.* @exception IndexOutOfBoundsException If <code>off</code> is negative,* <code>len</code> is negative, or <code>len</code> is greater than* <code>b.length - off</code>* @exception IOException if an I/O error occurs.* @see java.io.FilterInputStream#in*/public int read(byte b[], int off, int len) throws IOException {return in.read(b, off, len);}
skip
跳过和丢弃此输入流中数据的 n 个字节。出于各种原因, skip 方法结束时跳过的字节数可能小于该数,也可能为 0。导致这种情况的原因很多,跳过 n 个字节之前已到达文件末尾只是其中一种可能。返回跳过的实际字节数。如果 n 为负,则不跳过任何字节。
此类的 skip 方法创建一个 byte 数组,然后重复将字节读入其中,直到读够 n 个字节或已到达流末尾为止。建议子类提供此方法更为有效的实现。例如,可依赖搜索能力的实现。
此方法只执行 in.skip(n)。
/*** Skips over and discards <code>n</code> bytes of data from the* input stream. The <code>skip</code> method may, for a variety of* reasons, end up skipping over some smaller number of bytes,* possibly <code>0</code>. The actual number of bytes skipped is* returned.* <p>* This method simply performs <code>in.skip(n)</code>.** @param n the number of bytes to be skipped.* @return the actual number of bytes skipped.* @exception IOException if the stream does not support seek,* or if some other I/O error occurs.*/public long skip(long n) throws IOException {return in.skip(n);}
available
返回下一次对此输入流调用的方法可以不受阻塞地从此输入流读取(或跳过)的估计剩余字节数。下一个调用者可能是同一个线程,也可能是另一个线程。一次读取或跳过此数量个字节不会发生阻塞,但读取或跳过的字节可能小于该数。此方法返回 [in](https://tool.oschina.net/uploads/apidocs/jdk-zh/java/io/FilterInputStream.html#in).available() 的结果。
/*** Returns an estimate of the number of bytes that can be read (or* skipped over) from this input stream without blocking by the next* caller of a method for this input stream. The next caller might be* the same thread or another thread. A single read or skip of this* many bytes will not block, but may read or skip fewer bytes.* <p>* This method returns the result of {@link #in in}.available().** @return an estimate of the number of bytes that can be read (or skipped* over) from this input stream without blocking.* @exception IOException if an I/O error occurs.*/public int available() throws IOException {return in.available();}
close
关闭此输入流并释放与此流关联的所有系统资源。此方法只执行 in.close()。
/*** Closes this input stream and releases any system resources* associated with the stream.* This* method simply performs <code>in.close()</code>.** @exception IOException if an I/O error occurs.* @see java.io.FilterInputStream#in*/public void close() throws IOException {in.close();}
mark
在输入流中的当前位置上作标记。 reset 方法的后续调用将此流重新定位在最后标记的位置上,以便后续读取操作重新读取相同的字节。readlimit 参数告知此输入流在标记位置无效之前允许读取的字节数。此方法只执行 in.mark(readlimit)。
/*** Marks the current position in this input stream. A subsequent* call to the <code>reset</code> method repositions this stream at* the last marked position so that subsequent reads re-read the same bytes.* <p>* The <code>readlimit</code> argument tells this input stream to* allow that many bytes to be read before the mark position gets* invalidated.* <p>* This method simply performs <code>in.mark(readlimit)</code>.** @param readlimit the maximum limit of bytes that can be read before* the mark position becomes invalid.* @see java.io.FilterInputStream#in* @see java.io.FilterInputStream#reset()*/public synchronized void mark(int readlimit) {in.mark(readlimit);}
reset
将此流重新定位到对此输入流最后调用 mark 方法时的位置。此方法只执行 in.reset()。在需要提前读取一小部分数据以查看流中有什么的情况下,可以使用流的标记。通过调用通用解析器常常最容易做到这一点。如果流属于通过解析处理的类型,那么解析起来就很容易。如果流不属于那种类型,那么解析器应该在解析失败时抛出一个异常。如果这发生在 readlimit 个字节内,那么它允许外部代码重置流,并尝试另一种解析器。
/*** Repositions this stream to the position at the time the* <code>mark</code> method was last called on this input stream.* <p>* This method* simply performs <code>in.reset()</code>.* <p>* Stream marks are intended to be used in* situations where you need to read ahead a little to see what's in* the stream. Often this is most easily done by invoking some* general parser. If the stream is of the type handled by the* parse, it just chugs along happily. If the stream is not of* that type, the parser should toss an exception when it fails.* If this happens within readlimit bytes, it allows the outer* code to reset the stream and try another parser.** @exception IOException if the stream has not been marked or if the* mark has been invalidated.* @see java.io.FilterInputStream#in* @see java.io.FilterInputStream#mark(int)*/public synchronized void reset() throws IOException {in.reset();}
markSupported
测试此输入流是否支持 mark 和 reset 方法。此方法只执行 in.markSupported()。
/*** Tests if this input stream supports the <code>mark</code>* and <code>reset</code> methods.* This method* simply performs <code>in.markSupported()</code>.** @return <code>true</code> if this stream type supports the* <code>mark</code> and <code>reset</code> method;* <code>false</code> otherwise.* @see java.io.FilterInputStream#in* @see java.io.InputStream#mark(int)* @see java.io.InputStream#reset()*/public boolean markSupported() {return in.markSupported();}
BufferedInputStream
BufferedInputStream 为另一个输入流添加一些功能,即缓冲输入以及支持 mark 和 reset 方法的能力。在创建 BufferedInputStream 时,会创建一个内部缓冲区数组。在读取或跳过流中的字节时,可根据需要从包含的输入流再次填充该内部缓冲区,一次填充多个字节。mark 操作记录输入流中的某个点,reset 操作使得在从包含的输入流中获取新字节之前,再次读取自最后一次 mark 操作后读取的所有字节。
UML概述
重要方法
构造函数
创建具有指定缓冲区大小的 BufferedInputStream 并保存其参数,即输入流 in,以便将来使用。创建一个长度为 size 的内部缓冲区数组并将其存储在 buf 中。
publicclass BufferedInputStream extends FilterInputStream {private static int DEFAULT_BUFFER_SIZE = 8192;/*** The maximum size of array to allocate.* Some VMs reserve some header words in an array.* Attempts to allocate larger arrays may result in* OutOfMemoryError: Requested array size exceeds VM limit*/private static int MAX_BUFFER_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;/*** Creates a <code>BufferedInputStream</code>* with the specified buffer size,* and saves its argument, the input stream* <code>in</code>, for later use. An internal* buffer array of length <code>size</code>* is created and stored in <code>buf</code>.** @param in the underlying input stream.* @param size the buffer size.* @exception IllegalArgumentException if {@code size <= 0}.*/public BufferedInputStream(InputStream in, int size) {super(in);if (size <= 0) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("Buffer size <= 0");}buf = new byte[size];}
read
返回缓冲区中的下一个数据字节,如果到达流末尾,则返回 -1。
/*** See* the general contract of the <code>read</code>* method of <code>InputStream</code>.** @return the next byte of data, or <code>-1</code> if the end of the* stream is reached.* @exception IOException if this input stream has been closed by* invoking its {@link #close()} method,* or an I/O error occurs.* @see java.io.FilterInputStream#in*/public synchronized int read() throws IOException {if (pos >= count) {fill();if (pos >= count)return -1;}return getBufIfOpen()[pos++] & 0xff;}
read1(byte[] b, int off, int len)
从此字节输入流中给定偏移量处开始将各字节读取到指定的 byte 数组中。
此方法实现了 [InputStream](https://tool.oschina.net/uploads/apidocs/jdk-zh/java/io/InputStream.html) 类相应 [read](https://tool.oschina.net/uploads/apidocs/jdk-zh/java/io/InputStream.html#read(byte[],%20int,%20int)) 方法的常规协定。另一个便捷之处在于,它将通过重复地调用底层流的 read 方法,尝试读取尽可能多的字节。这种迭代的 read 会一直继续下去,直到满足以下条件之一:
- 已经读取了指定的字节数,
- 底层流的
read方法返回-1,指示文件末尾(end-of-file),或者 - 底层流的
available方法返回 0,指示将阻塞后续的输入请求。
如果第一次对底层流调用 read 返回 -1(指示文件末尾),则此方法返回 -1。否则此方法返回实际读取的字节数。鼓励(但不是必须)此类的各个子类以相同的方式尝试读取尽可能多的字节。
/*** Reads bytes from this byte-input stream into the specified byte array,* starting at the given offset.** <p> This method implements the general contract of the corresponding* <code>{@link InputStream#read(byte[], int, int) read}</code> method of* the <code>{@link InputStream}</code> class. As an additional* convenience, it attempts to read as many bytes as possible by repeatedly* invoking the <code>read</code> method of the underlying stream. This* iterated <code>read</code> continues until one of the following* conditions becomes true: <ul>** <li> The specified number of bytes have been read,** <li> The <code>read</code> method of the underlying stream returns* <code>-1</code>, indicating end-of-file, or** <li> The <code>available</code> method of the underlying stream* returns zero, indicating that further input requests would block.** </ul> If the first <code>read</code> on the underlying stream returns* <code>-1</code> to indicate end-of-file then this method returns* <code>-1</code>. Otherwise this method returns the number of bytes* actually read.** <p> Subclasses of this class are encouraged, but not required, to* attempt to read as many bytes as possible in the same fashion.** @param b destination buffer.* @param off offset at which to start storing bytes.* @param len maximum number of bytes to read.* @return the number of bytes read, or <code>-1</code> if the end of* the stream has been reached.* @exception IOException if this input stream has been closed by* invoking its {@link #close()} method,* or an I/O error occurs.*/public synchronized int read(byte b[], int off, int len)throws IOException{getBufIfOpen(); // Check for closed streamif ((off | len | (off + len) | (b.length - (off + len))) < 0) {throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();} else if (len == 0) {return 0;}int n = 0;for (;;) {int nread = read1(b, off + n, len - n);if (nread <= 0)return (n == 0) ? nread : n;n += nread;if (n >= len)return n;// if not closed but no bytes available, returnInputStream input = in;if (input != null && input.available() <= 0)return n;}}
available
返回可以从此输入流读取(或跳过)、且不受此输入流接下来的方法调用阻塞的估计字节数。接下来的调用可能是同一个线程,也可能是不同的线程。一次读取或跳过这么多字节将不会受阻塞,但可以读取或跳过数量更少的字节。此方法返回缓冲区中剩余的待读取字节数 (count - pos) 与调用 in.available() 的结果之和。
千言万语一句话就是 available 等于 当前输入流自身缓冲区的available(count - pos) + 底层输入流的available 就是整体的available。包装类和被包装类各管各的available,重量就是它们之和。
/*** Returns an estimate of the number of bytes that can be read (or* skipped over) from this input stream without blocking by the next* invocation of a method for this input stream. The next invocation might be* the same thread or another thread. A single read or skip of this* many bytes will not block, but may read or skip fewer bytes.* <p>* This method returns the sum of the number of bytes remaining to be read in* the buffer (<code>count - pos</code>) and the result of calling the* {@link java.io.FilterInputStream#in in}.available().** @return an estimate of the number of bytes that can be read (or skipped* over) from this input stream without blocking.* @exception IOException if this input stream has been closed by* invoking its {@link #close()} method,* or an I/O error occurs.*/public synchronized int available() throws IOException {int n = count - pos;int avail = getInIfOpen().available();return n > (Integer.MAX_VALUE - avail)? Integer.MAX_VALUE: n + avail;}
mark
设置一个mark,rest的时候可以回到这里。readlimit - 在mark位置变为无效之前可以读取字节的最大限制。
/*** See the general contract of the <code>mark</code>* method of <code>InputStream</code>.** @param readlimit the maximum limit of bytes that can be read before* the mark position becomes invalid.* @see java.io.BufferedInputStream#reset()*/public synchronized void mark(int readlimit) {marklimit = readlimit;markpos = pos;}
reset
如果 markpos 为 -1(尚未设置标记,或者标记已失效),则抛出 IOException。否则将 pos 设置为与 markpos 相等。
/*** See the general contract of the <code>reset</code>* method of <code>InputStream</code>.* <p>* If <code>markpos</code> is <code>-1</code>* (no mark has been set or the mark has been* invalidated), an <code>IOException</code>* is thrown. Otherwise, <code>pos</code> is* set equal to <code>markpos</code>.** @exception IOException if this stream has not been marked or,* if the mark has been invalidated, or the stream* has been closed by invoking its {@link #close()}* method, or an I/O error occurs.* @see java.io.BufferedInputStream#mark(int)*/public synchronized void reset() throws IOException {getBufIfOpen(); // Cause exception if closedif (markpos < 0)throw new IOException("Resetting to invalid mark");pos = markpos;}
markSupported
测试此输入流是否支持 mark 和 reset 方法。 BufferedInputStream 的 markSupported 方法返回 true。
/*** Tests if this input stream supports the <code>mark</code>* and <code>reset</code> methods. The <code>markSupported</code>* method of <code>BufferedInputStream</code> returns* <code>true</code>.** @return a <code>boolean</code> indicating if this stream type supports* the <code>mark</code> and <code>reset</code> methods.* @see java.io.InputStream#mark(int)* @see java.io.InputStream#reset()*/public boolean markSupported() {return true;}
close
关闭此输入流并释放与该流关联的所有系统资源。关闭了该流之后,后续的 read()、available()、reset() 或 skip() 调用都将抛出 IOException。关闭之前已关闭的流不会产生任何效果。
/*** Closes this input stream and releases any system resources* associated with the stream.* Once the stream has been closed, further read(), available(), reset(),* or skip() invocations will throw an IOException.* Closing a previously closed stream has no effect.** @exception IOException if an I/O error occurs.*/public void close() throws IOException {byte[] buffer;while ( (buffer = buf) != null) {if (bufUpdater.compareAndSet(this, buffer, null)) {InputStream input = in;in = null;if (input != null)input.close();return;}// Else retry in case a new buf was CASed in fill()}}