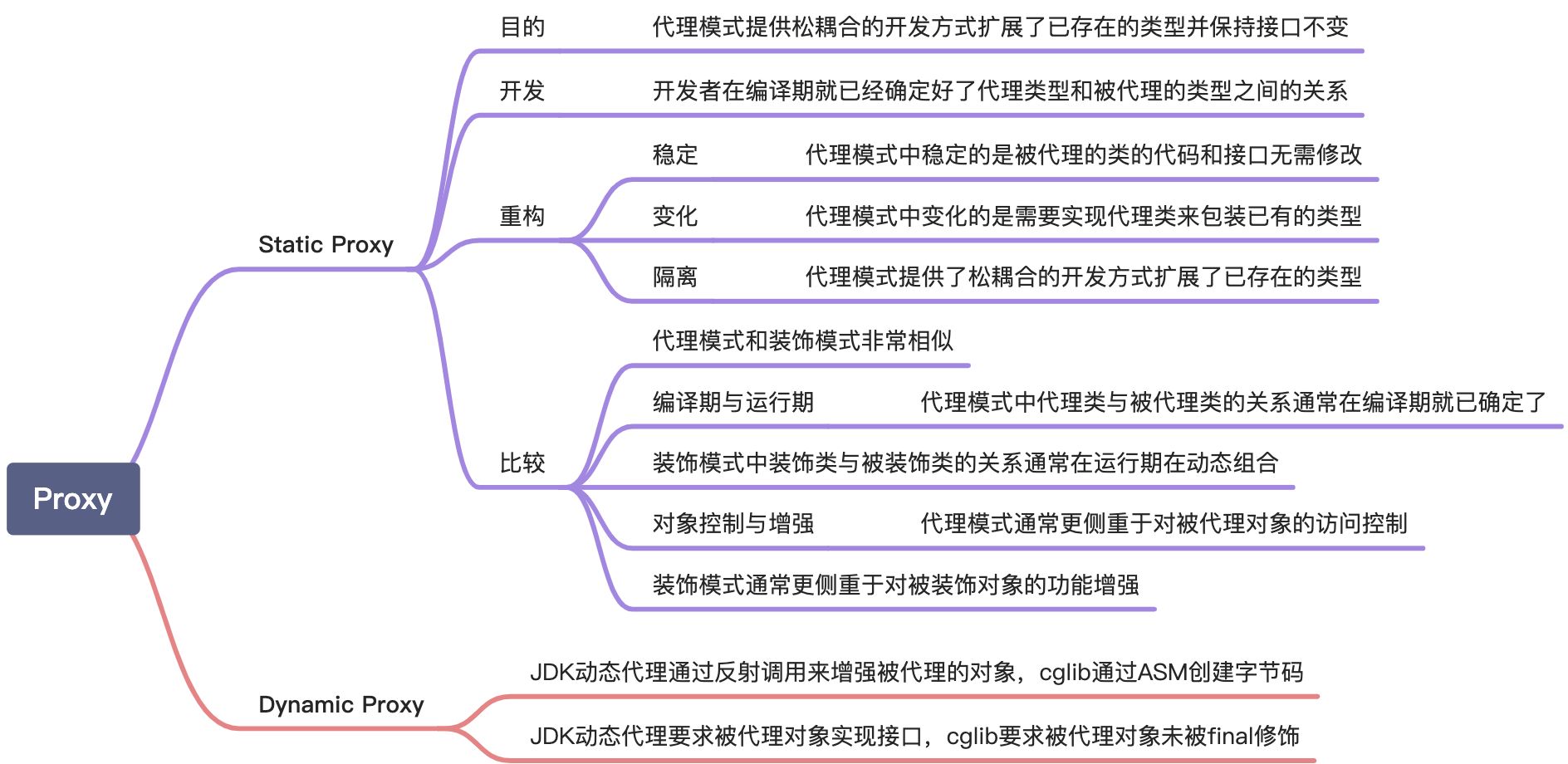
Proxy概述
玩具代码案例 - 日志代理
被代理类型
IBusinessService
package online.javabook.gof.structural.patterns7.proxy.logger;public interface IBusinessService {void doSomething1();void doSomething2();}
BusinessService
package online.javabook.gof.structural.patterns7.proxy.logger;public class BusinessService implements IBusinessService {@Overridepublic void doSomething1() {System.out.println("Do something1");}@Overridepublic void doSomething2() {System.out.println("Do something2");}}
代理类
代理类在不破坏被代理类现有的逻辑的前提下扩展了被代理类的功能
BusinessServiceLoggerProxy
package online.javabook.gof.structural.patterns7.proxy.logger;public class BusinessServiceLoggerProxy implements IBusinessService {public IBusinessService businessService;public BusinessServiceLoggerProxy(IBusinessService businessService) {this.businessService = businessService;}@Overridepublic void doSomething1() {System.out.println("Log begin.........");businessService.doSomething1();System.out.println("Log finish........");}@Overridepublic void doSomething2() {System.out.println("Log begin.........");businessService.doSomething2();System.out.println("Log finish........");}}
不基于静态代理模式的实现
BadBusinessService
package online.javabook.gof.structural.patterns7.proxy.app.bad;import online.javabook.gof.structural.patterns7.proxy.logger.IBusinessService;public class BadBusinessService implements IBusinessService {@Overridepublic void doSomething1() {System.out.println("Log begin.........");System.out.println("Do something1");System.out.println("Log finish........");}@Overridepublic void doSomething2() {System.out.println("Log begin.........");System.out.println("Do something2");System.out.println("Log finish........");}}
Main
package online.javabook.gof.structural.patterns7.proxy.app.bad;import online.javabook.gof.structural.patterns7.proxy.logger.IBusinessService;public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {IBusinessService businessService = new BadBusinessService();businessService.doSomething1();businessService.doSomething2();}}
Console
Log begin.........Do something1Log finish........Log begin.........Do something2Log finish........
基于静态代理模式的实现
Main
package online.javabook.gof.structural.patterns7.proxy.app.good;import online.javabook.gof.structural.patterns7.proxy.logger.BusinessService;import online.javabook.gof.structural.patterns7.proxy.logger.BusinessServiceLoggerProxy;import online.javabook.gof.structural.patterns7.proxy.logger.IBusinessService;public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {IBusinessService businessService = new BusinessService();IBusinessService loggerProxy = new BusinessServiceLoggerProxy(businessService);loggerProxy.doSomething1();loggerProxy.doSomething2();}}
Console
Log begin.........Do something1Log finish........Log begin.........Do something2Log finish........
基于JDK动态代理模式的实现
基于JDK的InvocationHandler实行的动态代理,静态代理容易造成需要为每一个被代理的类都创建类似的代理类,导致开发的类数量迅速膨胀。需要注意的是,使用JDK的动态代理技术要求被代理的类型一定要实现了一个接口。
BusinessServiceLoggerJDKProxy
package online.javabook.jvm.aop.proxy.jdk;import org.apache.log4j.Logger;import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;import java.lang.reflect.Method;import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;/*** @author Summer Lu* @email gmluyang@gmail.com* @date 2014-8-22**/public class BusinessServiceLoggerJDKProxy implements InvocationHandler {private Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(BusinessServiceLoggerJDKProxy.class.getName());/*** delegate*/private Object delegate;public <T> T proxy(Class<T> delegateClass) throws IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException {this.delegate = delegateClass.newInstance();return (T)Proxy.newProxyInstance(delegate.getClass().getClassLoader(), delegate.getClass().getInterfaces(), this);}@Overridepublic Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {try {logger.info("Begin invoke........." + method.getName());Object result = method.invoke(delegate, args);logger.info("Finish invoke........." + method.getName());return result;}catch (Exception exception){logger.error("Exception invoke........." + method.getName(), exception);throw exception;}}}
Main
package online.javabook.jvm.aop.proxy.jdk;import online.javabook.jvm.aop.service.BusinessService;import online.javabook.jvm.aop.service.IBusinessService;public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) throws InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {BusinessServiceLoggerJDKProxy businessServiceLoggerProxy = new BusinessServiceLoggerJDKProxy();IBusinessService businessServiceProxy = businessServiceLoggerProxy.proxy(BusinessService.class);businessServiceProxy.doSomething1();System.out.println();businessServiceProxy.doSomething2();System.out.println();System.out.println("businessServiceProxy.getClass().getName() -> " + businessServiceProxy.getClass().getName());System.out.println("businessServiceProxy.getClass().getSuperclass() -> " + businessServiceProxy.getClass().getSuperclass());System.out.println("businessServiceProxy.getClass().getInterfaces()[0] -> " + businessServiceProxy.getClass().getInterfaces()[0]);}}
Console
0 [main] INFO online.javabook.jvm.aop.proxy.jdk.BusinessServiceLoggerJDKProxy - Begin invoke.........doSomething1Do something11 [main] INFO online.javabook.jvm.aop.proxy.jdk.BusinessServiceLoggerJDKProxy - Finish invoke.........doSomething11 [main] INFO online.javabook.jvm.aop.proxy.jdk.BusinessServiceLoggerJDKProxy - Begin invoke.........doSomething2Do something21 [main] INFO online.javabook.jvm.aop.proxy.jdk.BusinessServiceLoggerJDKProxy - Finish invoke.........doSomething2businessServiceProxy.getClass().getName() -> com.sun.proxy.$Proxy0businessServiceProxy.getClass().getSuperclass() -> class java.lang.reflect.ProxybusinessServiceProxy.getClass().getInterfaces()[0] -> interface online.javabook.jvm.aop.service.IBusinessService
基于CGLIB动态代理模式的实现
基于CGLIB的Enhancer实行的动态代理,CGLIB不要求被代理的类型有接口,通过字节码增强的方式动态创建类型实现功能的植入
BusinessServiceLoggerCglibProxy
package online.javabook.jvm.aop.proxy.cglib;import net.sf.cglib.proxy.Enhancer;import net.sf.cglib.proxy.MethodInterceptor;import org.apache.log4j.Logger;public class BusinessServiceLoggerCglibProxy {private static Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(BusinessServiceLoggerCglibProxy.class.getName());public static <T> T proxy(Class<T> delegateClass) {Enhancer enhancer = new Enhancer();enhancer.setSuperclass(delegateClass);enhancer.setCallback((MethodInterceptor) (obj, method, objects, proxy) -> {try {logger.info("Begin invoke........." + method.getName());Object result = proxy.invokeSuper(obj, objects);logger.info("Finish invoke........." + method.getName());return result;}catch (Exception exception){logger.error("Exception invoke........." + method.getName(), exception);throw exception;}});return (T) enhancer.create();}}
Main
package online.javabook.jvm.aop.proxy.cglib;
import online.javabook.jvm.aop.service.BusinessService;
import online.javabook.jvm.aop.service.IBusinessService;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BusinessServiceLoggerCglibProxy businessServiceLoggerCglibProxy = new BusinessServiceLoggerCglibProxy();
IBusinessService businessServiceProxy = businessServiceLoggerCglibProxy.proxy(BusinessService.class);
businessServiceProxy.doSomething1();
System.out.println();
businessServiceProxy.doSomething2();
System.out.println();
System.out.println("businessServiceProxy.getClass().getName() -> " + businessServiceProxy.getClass().getName());
System.out.println("businessServiceProxy.getClass().getSuperclass() -> " + businessServiceProxy.getClass().getSuperclass());
System.out.println("businessServiceProxy.getClass().getInterfaces()[0] -> " + businessServiceProxy.getClass().getInterfaces()[0]);
}
}
Console
0 [main] INFO online.javabook.jvm.aop.proxy.cglib.BusinessServiceLoggerCglibProxy - Begin invoke.........doSomething1
Do something1
12 [main] INFO online.javabook.jvm.aop.proxy.cglib.BusinessServiceLoggerCglibProxy - Finish invoke.........doSomething1
12 [main] INFO online.javabook.jvm.aop.proxy.cglib.BusinessServiceLoggerCglibProxy - Begin invoke.........doSomething2
Do something2
12 [main] INFO online.javabook.jvm.aop.proxy.cglib.BusinessServiceLoggerCglibProxy - Finish invoke.........doSomething2
businessServiceProxy.getClass().getName() -> online.javabook.jvm.aop.service.BusinessService$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$8b3ecd6d
businessServiceProxy.getClass().getSuperclass() -> class online.javabook.jvm.aop.service.BusinessService
businessServiceProxy.getClass().getInterfaces()[0] -> interface net.sf.cglib.proxy.Factory
基于AspectJ动态代理模式的实现
基于AspectJ的ProceedingJoinPoint实行的动态代理,AspectJ提供编译期和运行时的字节码增强,提供跟精细的切入点,切面,切入范围的定义
BusinessServiceLoggerAspectJProxy
package online.javabook.jvm.aop.proxy.aspectj;
import org.apache.log4j.Logger;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Arrays;
@Aspect
@Component
public class BusinessServiceLoggerAspectJProxy {
private static Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(BusinessServiceLoggerAspectJProxy.class.getName());
@Pointcut("execution(* online.javabook.jvm.aop.service.BusinessService.*(..))")
public void log() {}
@Around("log()")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) throws Throwable {
log(proceedingJoinPoint, "around before calling proceed()");
Object result = proceedingJoinPoint.proceed();
log(proceedingJoinPoint, "around after calling proceed()");
return result;
}
@Before("log()")
public void before(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
log(joinPoint, "before");
}
@After("log()")
public void after(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
log(joinPoint, "after");
}
@AfterReturning(pointcut = "log()", returning = "result")
public void afterReturning(JoinPoint joinPoint, Object result) {
log(joinPoint, String.format("afterReturning %s", result));
}
@AfterThrowing(pointcut="log()", throwing="throwable")
public void afterThrowing(JoinPoint joinPoint, Throwable throwable) {
log(joinPoint, String.format("afterThrowing %s", throwable));
}
private void log(JoinPoint joinPoint, String adviceType) {
Object target = joinPoint.getTarget();
String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
String msg = String.format("%s %s.%s(%s)", adviceType, target.getClass().getName(), methodName, Arrays.toString(args));
logger.info(msg);
}
}
Main
package online.javabook.jvm.aop.proxy.aspectj;
import online.javabook.jvm.aop.service.IBusinessService;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] ags) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
IBusinessService businessService = context.getBean(IBusinessService.class);
businessService.doSomething1();
System.out.println();
businessService.doSomething2();
System.out.println();
System.out.println("businessServiceProxy.getClass().getName() -> " + businessService.getClass().getName());
System.out.println("businessServiceProxy.getClass().getSuperclass() -> " + businessService.getClass().getSuperclass());
System.out.println("businessServiceProxy.getClass().getInterfaces()[0] -> " + businessService.getClass().getInterfaces()[0]);
}
}
Console
0 [main] INFO online.javabook.jvm.aop.proxy.aspectj.BusinessServiceLoggerAspectJProxy - around before calling proceed() online.javabook.jvm.aop.service.BusinessService.doSomething1([])
1 [main] INFO online.javabook.jvm.aop.proxy.aspectj.BusinessServiceLoggerAspectJProxy - before online.javabook.jvm.aop.service.BusinessService.doSomething1([])
Do something1
1 [main] INFO online.javabook.jvm.aop.proxy.aspectj.BusinessServiceLoggerAspectJProxy - afterReturning null online.javabook.jvm.aop.service.BusinessService.doSomething1([])
1 [main] INFO online.javabook.jvm.aop.proxy.aspectj.BusinessServiceLoggerAspectJProxy - after online.javabook.jvm.aop.service.BusinessService.doSomething1([])
1 [main] INFO online.javabook.jvm.aop.proxy.aspectj.BusinessServiceLoggerAspectJProxy - around after calling proceed() online.javabook.jvm.aop.service.BusinessService.doSomething1([])
2 [main] INFO online.javabook.jvm.aop.proxy.aspectj.BusinessServiceLoggerAspectJProxy - around before calling proceed() online.javabook.jvm.aop.service.BusinessService.doSomething2([])
2 [main] INFO online.javabook.jvm.aop.proxy.aspectj.BusinessServiceLoggerAspectJProxy - before online.javabook.jvm.aop.service.BusinessService.doSomething2([])
Do something2
2 [main] INFO online.javabook.jvm.aop.proxy.aspectj.BusinessServiceLoggerAspectJProxy - afterReturning null online.javabook.jvm.aop.service.BusinessService.doSomething2([])
2 [main] INFO online.javabook.jvm.aop.proxy.aspectj.BusinessServiceLoggerAspectJProxy - after online.javabook.jvm.aop.service.BusinessService.doSomething2([])
3 [main] INFO online.javabook.jvm.aop.proxy.aspectj.BusinessServiceLoggerAspectJProxy - around after calling proceed() online.javabook.jvm.aop.service.BusinessService.doSomething2([])
businessServiceProxy.getClass().getName() -> com.sun.proxy.$Proxy22
businessServiceProxy.getClass().getSuperclass() -> class java.lang.reflect.Proxy
businessServiceProxy.getClass().getInterfaces()[0] -> interface online.javabook.jvm.aop.service.IBusinessService
现实世界中的代理模式
JDK collections中的同步容器类型实现了Collection接口,但它本身并没有具体的算法实现,它就是一个代理类,被代理的Collection对象被它一包装,在即保留原有功能和接口的基础上,瞬间变成了一个线程安全的同步Collection。并且不需要改变现有的接口,比如增加:synchronizedSize(),synchronizedSizeIsEmpty()这样的新接口。
static class SynchronizedCollection<E> implements Collection<E>, Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 3053995032091335093L;
final Collection<E> c; // Backing Collection
final Object mutex; // Object on which to synchronize
SynchronizedCollection(Collection<E> c) {
this.c = Objects.requireNonNull(c);
mutex = this;
}
SynchronizedCollection(Collection<E> c, Object mutex) {
this.c = Objects.requireNonNull(c);
this.mutex = Objects.requireNonNull(mutex);
}
public int size() {
synchronized (mutex) {return c.size();}
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
synchronized (mutex) {return c.isEmpty();}
}
public boolean contains(Object o) {
synchronized (mutex) {return c.contains(o);}
}
public Object[] toArray() {
synchronized (mutex) {return c.toArray();}
}
public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) {
synchronized (mutex) {return c.toArray(a);}
}
public Iterator<E> iterator() {
return c.iterator(); // Must be manually synched by user!
}
public boolean add(E e) {
synchronized (mutex) {return c.add(e);}
}
public boolean remove(Object o) {
synchronized (mutex) {return c.remove(o);}
}
public boolean containsAll(Collection<?> coll) {
synchronized (mutex) {return c.containsAll(coll);}
}
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> coll) {
synchronized (mutex) {return c.addAll(coll);}
}
public boolean removeAll(Collection<?> coll) {
synchronized (mutex) {return c.removeAll(coll);}
}
public boolean retainAll(Collection<?> coll) {
synchronized (mutex) {return c.retainAll(coll);}
}
public void clear() {
synchronized (mutex) {c.clear();}
}
public String toString() {
synchronized (mutex) {return c.toString();}
}
// Override default methods in Collection
@Override
public void forEach(Consumer<? super E> consumer) {
synchronized (mutex) {c.forEach(consumer);}
}
@Override
public boolean removeIf(Predicate<? super E> filter) {
synchronized (mutex) {return c.removeIf(filter);}
}
@Override
public Spliterator<E> spliterator() {
return c.spliterator(); // Must be manually synched by user!
}
@Override
public Stream<E> stream() {
return c.stream(); // Must be manually synched by user!
}
@Override
public Stream<E> parallelStream() {
return c.parallelStream(); // Must be manually synched by user!
}
private void writeObject(ObjectOutputStream s) throws IOException {
synchronized (mutex) {s.defaultWriteObject();}
}
}