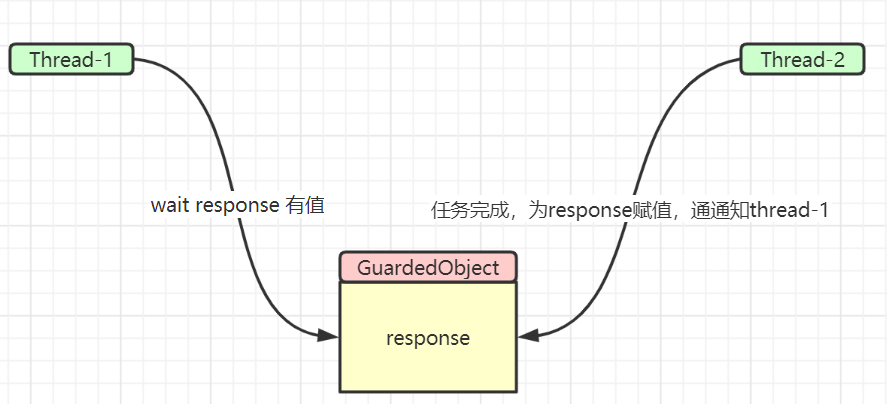
同步模式之保护性暂停
一个线程等待另一个线程的执行结果
要点:
- 有一个结果需要从一个线程传递到另一个线程,让他们关联同一个 Guarded Suspension
- 如果有结果不断从一个线程到另一个线程那么可以使用消息队列
- JDK 中,join 实现、Future 的实现,采用的就是此模式
- 因为要等待另一方的结果,因此归类到同步模式
死锁
定位死锁
- 检测死锁可以使用 jconsole 工具,线程tab中有个检测死锁的功能;
- 使用 jps 定位进程 id,再用 jstack 定位死锁;
模拟死锁
```java package top.simba1949;
/**
- @author Anthony
@date 2020/10/26 16:48 */ public class Application { public static void main(String[] args) {
Object a = new Object();Object b = new Object();Thread t1 = new Thread(() ->{synchronized (a){System.out.println("lock a");try {Thread.sleep(10);synchronized (b){System.out.println("lock b");}} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}, "t1");Thread t2 = new Thread(() ->{synchronized (b){System.out.println("lock b");try {Thread.sleep(5);synchronized (a){System.out.println("lock a");}} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}} ,"t2");t1.start();t2.start();
同步控制
顺序控制
wait¬ify实现
```java package top.simba1949;
/**
- @author Anthony
@date 2020/10/24 10:01 */ public class Application {
static final Object lock = new Object(); /**
t2 是否运行过 */ static boolean t2RunBl = false;
public static void main(String[] args) { Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
synchronized (lock){while (!t2RunBl){try {// 如果线程2未执行,进入等待状态lock.wait();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}System.out.println("t1线程");}
}, “t1”);
Thread t2 = new Thread(() -> {
try {// 使用 sleep 可以放大控制顺序的效果Thread.sleep(10000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}synchronized (lock){System.out.println("t2线程");t2RunBl = true;lock.notify();}
}, “t2”);
t1.start(); t2.start(); } } ```
ReentrantLock和条件变量实现
```java package top.simba1949;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition; import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
/**
- @author Anthony
@date 2020/10/24 10:01 */ public class Application {
static final ReentrantLock reentrantLock = new ReentrantLock(); static Condition condition = reentrantLock.newCondition(); /**
t2 是否运行过 */ static boolean t2RunBl = false;
public static void main(String[] args) { Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
reentrantLock.lock();try{while (!t2RunBl){try {// 没有获取到锁的线程,进入线程休息室休息,等待唤醒,// 唤醒后从这条语句后面开始执行condition.await();System.out.println("t1");} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}finally {reentrantLock.unlock();}
}, “t1”);
Thread t2 = new Thread(() -> {
try {// 使用 sleep 可以放大控制顺序的效果Thread.sleep(10000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}reentrantLock.lock();try{System.out.println("t2");t2RunBl = true;condition.signal();}finally {reentrantLock.unlock();}
}, “t2”);
t1.start(); t2.start(); } } ```
park&unpark实现
```java package top.simba1949;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.LockSupport;
/**
- @author Anthony
@date 2020/10/24 10:01 */ public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {LockSupport.park();System.out.println("t1");}, "t1");t1.start();Thread t2 = new Thread(() -> {System.out.println("t2");LockSupport.unpark(t1);}, "t2");t2.start();
}
}
<a name="aCFuT"></a>## 交替输出<a name="QoNlu"></a>### wait¬ify实现```javapackage top.simba1949;/*** 输出结果为 a——>b——>c——>a——>b——>c——>...* 输出内容 等待标记 下一个标记* a 1 2* b 2 3* c 3 1* @author Anthony* @date 2020/10/24 10:01*/public class Application4 {public static void main(String[] args) {WaitNotify waitNotify = new WaitNotify(1, 5);new Thread(() -> waitNotify.print("a", 1, 2), "t1").start();new Thread(() -> waitNotify.print("b", 2, 3), "t2").start();new Thread(() -> waitNotify.print("c", 3, 1), "t3").start();}}class WaitNotify{// 等待标记private int flag;// 循环次数private int loopNumber;public WaitNotify(int flag, int loopNumber) {this.flag = flag;this.loopNumber = loopNumber;}/*** 打印* 设计思路:* 如果当前的标记与当前线程等待的标记一致,执行打印内容,并设置当前线程的下一个标记为当前标记,并唤醒其他线程* 如果当前的标记与当前线程等待的标记不一致,当前线程进入wait状态* @param str* @param waitFlag* @param nextFlag*/public void print(String str, int waitFlag, int nextFlag){for (int i = 0; i < loopNumber; i++) {synchronized (this){while (flag != waitFlag){try {this.wait();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}// 打印内容,设置等待标记flagSystem.out.print(str + "->");flag = nextFlag;this.notifyAll();}}}}
ReentrantLock和条件变量实现
通过 ReentrantLock 对象实现
package top.simba1949;import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;/*** 输出结果为 a——>b——>c——>a——>b——>c——>...* 输出内容 等待标记 下一个标记* a 1 2* b 2 3* c 3 1* @author Anthony* @date 2020/10/24 10:01*/public class Application6 {public static void main(String[] args) {WaitNotify6 waitNotify = new WaitNotify6(1, 10);new Thread(() -> waitNotify.print("a", 1, 2), "t1").start();new Thread(() -> waitNotify.print("b", 2, 3), "t2").start();new Thread(() -> waitNotify.print("c", 3, 1), "t3").start();}}class WaitNotify6 {private final ReentrantLock reentrantLock = new ReentrantLock();// 线程休息室private Condition condition = reentrantLock.newCondition();// 等待标记private int flag;// 循环次数private int loopNumber;public WaitNotify6(int flag, int loopNumber) {this.flag = flag;this.loopNumber = loopNumber;}/*** 打印* 设计思路:* 如果当前的标记与当前线程等待的标记一致,执行打印内容,并设置当前线程的下一个标记为当前标记,并唤醒其他线程* 如果当前的标记与当前线程等待的标记不一致,当前线程进入wait状态* @param str* @param waitFlag* @param nextFlag*/public void print(String str, int waitFlag, int nextFlag){for (int i = 0; i < loopNumber; i++) {reentrantLock.lock();while (flag != waitFlag){try {// 当前线程进入休息室休息condition.await();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}try {// 打印内容,设置等待标记flagSystem.out.print(str + "->");flag = nextFlag;condition.signalAll();}finally {reentrantLock.unlock();}}}}
通过继承 ReentrantLock 实现——比较唤醒
package top.simba1949;import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;/*** 输出结果为 a——>b——>c——>a——>b——>c——>...* 输出内容 等待标记 下一个标记* a 1 2* b 2 3* c 3 1* @author Anthony* @date 2020/10/24 10:01*/public class Application5 {public static void main(String[] args) {WaitNotify5 waitNotify = new WaitNotify5(1, 10);new Thread(() -> waitNotify.print("a", 1, 2), "t1").start();new Thread(() -> waitNotify.print("b", 2, 3), "t2").start();new Thread(() -> waitNotify.print("c", 3, 1), "t3").start();}}class WaitNotify5 extends ReentrantLock {private static final long serialVersionUID = -5778347071247661102L;// 等待队列private final Condition condition = this.newCondition();// 等待标记private int flag;// 循环次数private int loopNumber;public WaitNotify5(int flag, int loopNumber) {this.flag = flag;this.loopNumber = loopNumber;}/*** 打印* 设计思路:* 如果当前的标记与当前线程等待的标记一致,执行打印内容,并设置当前线程的下一个标记为当前标记,并唤醒其他线程* 如果当前的标记与当前线程等待的标记不一致,当前线程进入wait状态* @param str* @param waitFlag* @param nextFlag*/public void print(String str, int waitFlag, int nextFlag){for (int i = 0; i < loopNumber; i++) {this.lock();while (flag != waitFlag){try {// 当前线程进入休息室休息condition.await();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}try {// 打印内容,设置等待标记flagSystem.out.print(str + "->");flag = nextFlag;condition.signalAll();}finally {this.unlock();}}}}
通过继承 ReentrantLock 实现——控制唤醒顺序
package top.simba1949;import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;/*** 输出结果为 a——>b——>c——>a——>b——>c——>...* 输出内容 等待标记 下一个标记* a 1 2* b 2 3* c 3 1* @author Anthony* @date 2020/10/24 10:01*/public class Application9 {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {WaitNotify9 waitNotify = new WaitNotify9(10);Condition conditionA = waitNotify.newCondition();Condition conditionB = waitNotify.newCondition();Condition conditionC = waitNotify.newCondition();new Thread(() -> waitNotify.print("a", conditionA, conditionB), "a").start();new Thread(() -> waitNotify.print("b", conditionB, conditionC), "b").start();new Thread(() -> waitNotify.print("c", conditionC, conditionA), "c").start();// 主要 await 和 signal 方法必须在lock和unlock之间使用waitNotify.lock();try{// 主线程等待数秒之后,保证线程a已经启动,并且进入休息室Thread.sleep(1000);// 主线程程唤醒线程 aconditionA.signal();}finally {waitNotify.unlock();}}}class WaitNotify9 extends ReentrantLock {private static final long serialVersionUID = 6794432110745744142L;// 循环次数private int loopNumber;public WaitNotify9(int loopNumber) {this.loopNumber = loopNumber;}/*** 打印* 设计思路:* 首先所有线程运行时首先进入休息室condition中,控制线程唤醒顺序,通过主线程唤醒第一个线程开始即可* @param str* @param current* @param next*/public void print(String str, Condition current, Condition next){for (int i = 0; i < loopNumber; i++) {this.lock();try {// 线程执行的时候先进入各自的休息室休息current.await();// 打印内容,设置等待标记flagSystem.out.print(str + "->");next.signal();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {this.unlock();}}}}
park&unpark实现——控制唤醒顺序
package top.simba1949;import java.util.concurrent.locks.LockSupport;/*** 输出结果为 a——>b——>c——>a——>b——>c——>...* 输出内容 等待标记 下一个标记* a 1 2* b 2 3* c 3 1* @author Anthony* @date 2020/10/24 10:01*/public class Application8 {static Thread ta;static Thread tb;static Thread tc;public static void main(String[] args) {WaitNotify8 waitNotify8 = new WaitNotify8(10);ta = new Thread(() -> waitNotify8.print("a", tb), "ta");tb = new Thread(() -> waitNotify8.print("b", tc), "tb");tc = new Thread(() -> waitNotify8.print("c", ta), "tc");ta.start();tb.start();tc.start();// 主线程唤醒第一个线程LockSupport.unpark(ta);}}class WaitNotify8 {// 循环次数private int loopNumber;public WaitNotify8(int loopNumber) {this.loopNumber = loopNumber;}/*** 打印* 设计思路:**/public void print(String str, Thread next){for (int i = 0; i < loopNumber; i++) {// 针对当前线程LockSupport.park();System.out.print(str + "->");LockSupport.unpark(next);}}}