本篇文章基于go1.18版本。 参考了halffrost的博客。https://halfrost.com/
简介
不要通过共享内存进行通信。建议,通过通信来共享内存。(Do not communicate by sharing memory; instead, share memory by communicating)这是 Go 语言并发的哲学座右铭。相比与其他语言,go实现了channel来进行通信,下面我们来看一下channel是如何实现的。
基本结构
channel的底层文件是 src/runtime/chan.go 。
type hchan struct {qcount uint // 队列中所有数据总数dataqsiz uint // 环形队列的 sizebuf unsafe.Pointer // 指向 dataqsiz 长度的数组(环形队列)elemsize uint16 // 元素大小closed uint32elemtype *_type // 元素类型sendx uint // 已发送的元素在环形队列中的位置recvx uint // 已接收的元素在环形队列中的位置recvq waitq // 接收者的等待队列(双向链表)sendq waitq // 发送者的等待队列(双向链表)lock mutex //保护资源}
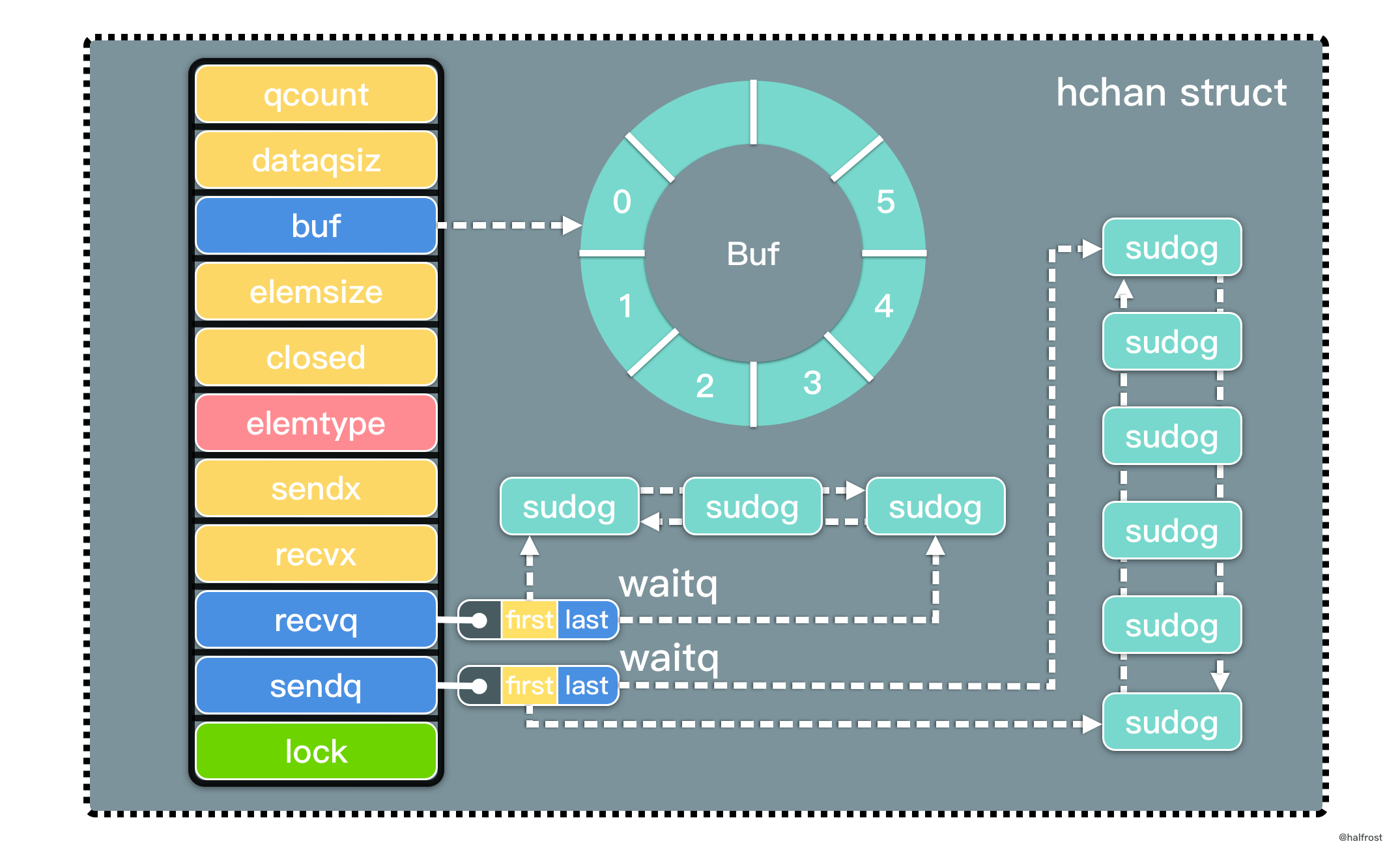
图1 channel基本结构
channel 最核心的数据结构是 sudog。sudog 代表了一个在等待队列中的 g。sudog 是 Go 中非常重要的数据结构,因为 g 与同步对象关系是多对多的。一个 g 可以出现在许多等待队列上,因此一个 g 可能有很多sudog。并且多个 g 可能正在等待同一个同步对象,因此一个对象可能有许多 sudog。sudog 是从特殊池中分配出来的。使用 acquireSudog 和 releaseSudog 分配和释放它们。
type sudog struct {g *gnext *sudogprev *sudogelem unsafe.Pointer // 指向数据 (可能指向栈)acquiretime int64releasetime int64ticket uint32isSelect boolsuccess boolparent *sudog // semaRoot 二叉树waitlink *sudog // g.waiting 列表或者 semaRootwaittail *sudog // semaRootc *hchan // channel}
创建channel
创建 channel 的主要实现在 makechan() 函数中:
func makechan(t *chantype, size int) *hchan {elem := t.elem// 编译器检查数据项大小不能超过 64KBif elem.size >= 1<<16 {throw("makechan: invalid channel element type")}// 检查对齐是否正确if hchanSize%maxAlign != 0 || elem.align > maxAlign {throw("makechan: bad alignment")}// 缓冲区大小检查,判断是否溢出mem, overflow := math.MulUintptr(elem.size, uintptr(size))if overflow || mem > maxAlloc-hchanSize || size < 0 {panic(plainError("makechan: size out of range"))}var c *hchanswitch {case mem == 0:// 队列或者元素大小为 zero 时c = (*hchan)(mallocgc(hchanSize, nil, true))// Race 竞争检查利用这个地址来进行同步操作c.buf = c.raceaddr()case elem.ptrdata == 0:// 元素不包含指针时。一次分配 hchan 和 buf 的内存。c = (*hchan)(mallocgc(hchanSize+mem, nil, true))c.buf = add(unsafe.Pointer(c), hchanSize)default:// 元素包含指针时c = new(hchan)c.buf = mallocgc(mem, elem, true)}// 设置属性c.elemsize = uint16(elem.size)c.elemtype = elemc.dataqsiz = uint(size)lockInit(&c.lock, lockRankHchan)if debugChan {print("makechan: chan=", c, "; elemsize=", elem.size, "; dataqsiz=", size, "\n")}return c}
发送数据
walkSend() 函数中主要逻辑调用了 chansend1(),而 chansend1() 只是 chansend() 的“外壳”。所以 channel 发送数据的核心实现在 chansend() 中。根据阻塞与否,chansend可以分为四个部分:异常检查、同步发送、异步发送、阻塞发送。
异常检查
func chansend(c *hchan, ep unsafe.Pointer, block bool, callerpc uintptr) bool {// 判断 channel 是否为 nilif c == nil {if !block {return false}gopark(nil, nil, waitReasonChanSendNilChan, traceEvGoStop, 2)throw("unreachable")}if debugChan {print("chansend: chan=", c, "\n")}if raceenabled {racereadpc(c.raceaddr(), callerpc, funcPC(chansend))}// 简易快速的检查if !block && c.closed == 0 && full(c) {return false}......}

