13.2.1面向字节的输入流
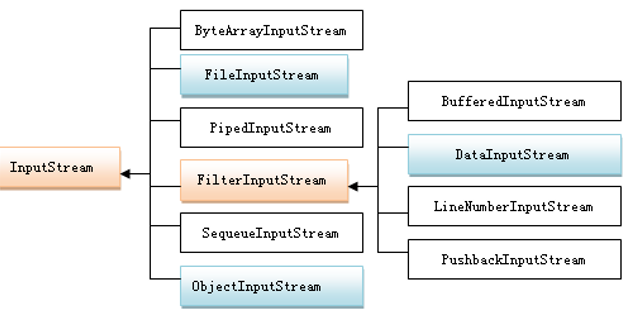
1. 类InputStream介绍
public int read() :读一个字节 public int read(byte b[]):读多个字节到字节数组 ,方法返回结果为实际读到的字节数public int read(byte[] b, int off, int len) : 从输入流读指定长度的数据到数组,数据从数组的off处开始存放。 public long skip(long n) :指针跳过n个字节,定位输入位置指针的方法 public void mark():在当前位置指针处做一标记 public void reset() :将位置指针返回标记处 public void close() :关闭流
将键盘输入的十六进制数转化为十进制---直接转化----> Integer.parseInt(s,16);import java.io.*;public class Convert{public static void main(String args[ ]) {try {char ch=' '; //存放输入的字符int x=0; //存放转换后的数字long d=0; //存放转换的十进制数System.out.print("输入一个十六进数:");ch=(char)System.in.read( ); //读一个字符 (char)强制转换,read读入的整形while (ch!='\r') {switch (ch) {case '0':case '1':case '2':case '3':case '4':case '5':case '6':case '7':case '8':case '9':x=(ch-'0');break;case 'A':case 'B':case 'C':case 'D':case 'E':case 'F':x=(ch-'A')+10;break;case 'a':case 'b':case 'c':case 'd':case 'e':case 'f':x=(ch-'a')+10;break;default:System.out.println("非法符号");System.exit(0);}d = d*16 + x; //转换结果拼接ch=(char)System.in.read();} // while 结尾System.out.println("十进制="+d);} catch (IOException e) { }}}运行示例:输入一个十六进数:2a十进制=42
2.类InputStream的子类的使用
| 类名 | 构造方法的主要参数 | 功能描述 |
|---|---|---|
| ByteArrayInputStream | 字节数组 | 以字节数组作为输入源。 |
| FileInputStream | 类File的对象或字符串表示的文件名 | 以文件作为数据源。 |
| PipedInputStream | PipedOutputStream的对象 | 与另一输出管道相连,读取写入到输出管道中的数据,用于程序中线程间通信 |
| FilterInputStream | InputStream的对象 | 用于装饰另一输入流以提供对输入数据的附加处理功能,子类见表13-2 |
| SequeueInputStream | 系列InputStream的对象 | 将两个其他流首尾相接,合并为一个完整的输入流。 |
| ObjectInputStream | InputStream的对象 | 用于从输入流读取串行化对象。可实现轻量级对象持久性。 |
类FilterInputStream的常见子类
| 类名 | 功能描述 |
|---|---|
| BufferedInputStream | 为所装饰的输入流提供缓冲区的功能,以提高输入数据的效率 |
| DataInputStream | 为所装饰的输入流提供数据转换的功能,可从数据源读取各种基本类型的数据。 |
| LineNumberInputStream | 为文本文件输入流附加行号 |
| PushbackInputStream | 提供回压数据的功能,可以多次读同样数据 |
import java.io.*;public class DisplayFile{public static void main(String args[]){try{FileInputStream infile = new FileInputStream(args[0]);int byteRead = infile.read(); 以字节为单位访问while (byteRead!=-1) {System.out.print((char)byteRead);byteRead = infile.read();}}catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e){System.out.println("需要提供一个文件名作为命令行参数 ");}catch(FileNotFoundException e) {System.out.println("file not find! ");}catch(IOException e) { }}}
FileInputStream infile = new FileInputStream(args[0]);
BufferedInputStream buin=new BufferedInputStream(infile); 创建输入流包装
相当于:BufferedInputStream buin=new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(args[0]));
String str=new String(buffer,0,byteRead); 读取的字节转换为字符
System.out.print(str);
相当于:System.out.print((char)byteRead);将字节转化成字符输出
import java.io.*;public class DisplayFile{public static void main(String args[]){try{FileInputStream infile = new FileInputStream(args[0]); 从命令行获取要显示的文件名BufferedInputStream buin=new BufferedInputStream(infile); 创建输入流byte[] buffer=new byte[64];int byteRead = buin.read(buffer);while (byteRead!=-1){ //判断是否读到文件的末尾String str=new String(buffer,0,byteRead); 读取的字节转换为字符System.out.print(str);//System.out.print((char)byteRead);byteRead = buin.read(buffer); read()方法读到文件结尾返回-1,读取文件时一个一个字节读入}buin.close();}catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {System.out.println("需要提供一个文件名作为命令行参数 ");}catch(FileNotFoundException e) {System.out.println("file not find! ");}catch(IOException e) { }}}
数据输入流DataInputStream
- 实现各种基本类型数据的输入处理
- 实现DataInput接口
- byte readByte()
- boolean readBoolean()
- short readShort()
- char readChar()
- int readInt()—-读整数
- long readLong()
- float readFloat()
- double readDouble()
//以上为:以数据类型为单位访问数据
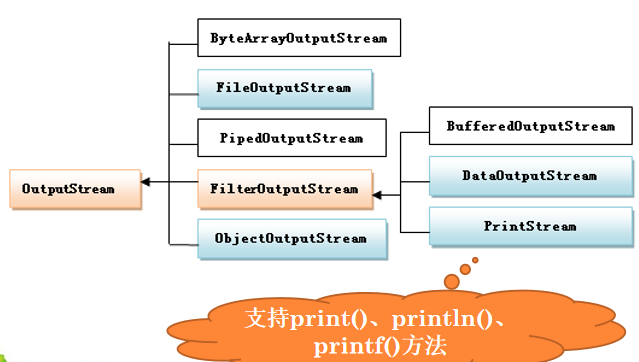
void write(int b):将参数b的低字节写入输出流void write(byte b[]):将字节数组全部写入输出流void write(byte b[],int off, int len): 将字节数组从off位置开始的len个字节写入输出流void flush():强制将缓冲区数据写入输出流对应的外设-
以字节为单位写入数据——-文件输入/输出流的使用
import java.io.*;public class BigToSmall {public static void main(String args[]){int number=0;final int size=Integer.parseInt(args[1]); 小文件大小byte[] b = new byte[size];try{FileInputStream infile = new FileInputStream(args[0]); 大文件名称while (true){FileOutputStream outfile = new FileOutputStream("file"+number); 小文件的名称number++;int byteRead = infile.read(b); 以字节为单位读数据if (byteRead==-1)break;outfile.write(b,0,byteRead); 以字节为单位写入数据outfile.close(); 写完之后必须关闭文件}}catch(IOException e) { }}}运行程序输入两个参数:1、需拆分的大文件名 2、小文件的大小。分拆的小文件名为file0、file1、file2.....注意:将数据写入文件用write(b,0,byteRead)方法保证将当前读到的数据写入文件;不使用write(b)因为最后一个文件会更小
基本数据类型数据的读写问题
类DataOutputStream实现各种类型数据的输出处理,它实现了DataOutput接口,在该接口中定义了基本数据类型数据的输出方法
- void writeByte(int x) //参数x的8个低位
- void writeBytes(String x) //按字节顺序写入
- void writeChar(int x) //一个char值(2字节)写入
- void writeBoolean(boolean x)
- void writeChars(String x) //按字符顺序写入
- void writeInt(int x)
- void writeLong(long x)
- void writeFloat(float x)
- void writeDouble(double x)
- void writeUTF(String x)//使用UTF-8编码
找出10~100之间的所有姐妹素数,写入到文件中。所谓姐妹素数是指相邻两个奇数均为素数
import java.io.*;public class FindSisterPrime{public static boolean isPrime(int n){for (int k=2;k<=Math.sqrt(n);k++){if (n%k==0)return false;}return true;}public static void main(String[] args){try{FileOutputStream file = new FileOutputStream("x.dat"); 创建一个文件输出流,文件不存在则自动生成DataOutputStream out=new DataOutputStream(file); 对FileOutputStream包装,创建一个DataOutputStream流,利用该流向文件写入各种类型的数据for (int n=11;n<100;n+=2){if (isPrime(n)&&isPrime(n+2)){out.writeInt(n); DataOutputStream的writeInt方法,写入整数out.writeInt(n+2);}}out.close();}catch (IOException e) { };}}结果输出将显示乱码,原因在于该文件中的数据不是文本格式数据,想要获取数据,需要以输入流的方式访问文件//获取数据import java.io.*;public class OutSisterPrime{public static void main(String[] arguments){try{FileInputStream file = new FileInputStream("x.dat");DataInputStream in=new DataInputStream(file);while(true){int n1=in.readInt(); 以整数为单位读int n2=in.readInt();System.out.println(n1+","+n2);}}catch (EOFException e) { }catch (IOException e) { }}}while(true)遇到文件结束抛出EOFException异常。可改为:while(in.available()!=0),返回要读取的字节长度。思考:将20个随机整数写入文件x.dat中public class test1{public static void main(String args[]){try{DataOutputStream out = new DataOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("x.dat"));for(int j=1; j<=20; j++){int x=(int)(Math.random()*100);out.writeInt(x); 输出是乱码}out.close();}catch(IOException e);}}