203 移除链表元素
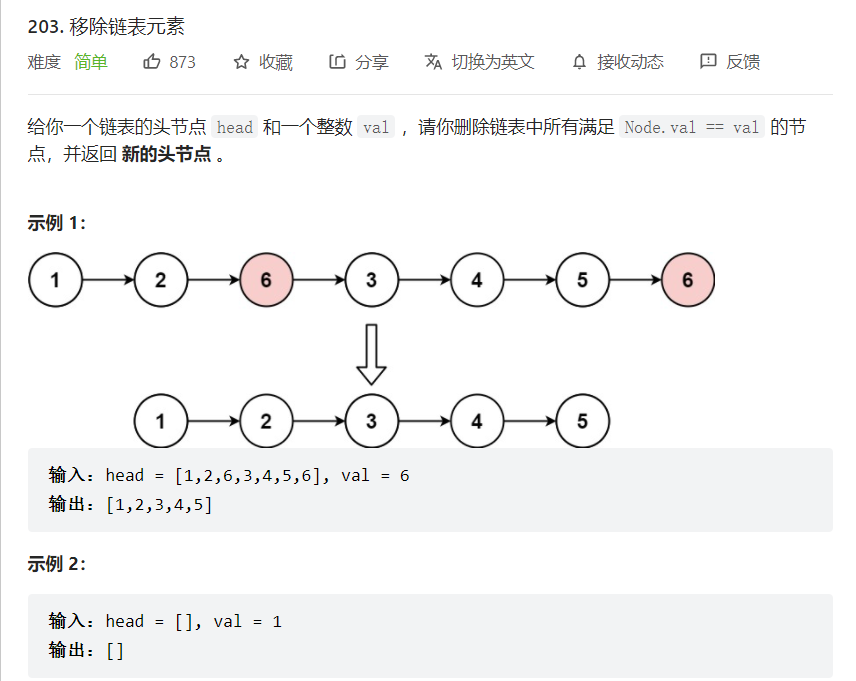

思路:
删除结点的步骤
找到该结点的前一个结点
进行删除操作
代码
#虚拟头节点class Solution:def removeElements(self, head: ListNode, val: int) -> ListNode:dummyHead = ListNode(-1, head)cur = dummyHeadwhile cur.next:if cur.next.val == val:cur.next = cur.next.nextelse:cur = cur.nextreturn dummyHead.next#递归struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val){if (head == NULL) {return NULL;}head->next = removeElements(head->next, val);return head->val == val ? head->next : head;}#栈class Solution {public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {Stack<ListNode> stack = new Stack<ListNode>();while (head != null) {if (head.val != val) {stack.push(head);}head = head.next;}while (!stack.isEmpty()) {stack.peek().next = head;head = stack.pop();}return head;}}#迭代class Solution:def removeElements(self, head: ListNode, val: int) -> ListNode:while head and head.val == val:head = head.nextif not head: returnpre = headwhile pre.next:if pre.next.val == val:pre.next = pre.next.nextelse:pre = pre.nextreturn head
//删除头结点时另做考虑(由于头结点没有前一个结点)class Solution {public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {//删除值相同的头结点后,可能新的头结点也值相等,用循环解决while(head!=null&&head.val==val){head=head.next;}if(head==null)return head;ListNode prev=head;//确保当前结点后还有结点while(prev.next!=null){if(prev.next.val==val){prev.next=prev.next.next;}else{prev=prev.next;}}return head;}}//添加一个虚拟头结点,删除头结点就不用另做考虑class Solution {public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {//创建一个虚拟头结点ListNode dummyNode=new ListNode(val-1);dummyNode.next=head;ListNode prev=dummyNode;//确保当前结点后还有结点while(prev.next!=null){if(prev.next.val==val){prev.next=prev.next.next;}else{prev=prev.next;}}return dummyNode.next;}}//递归class Solution {public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {if(head==null)return null;head.next=removeElements(head.next,val);if(head.val==val){return head.next;}else{return head;}}}
206反转链表
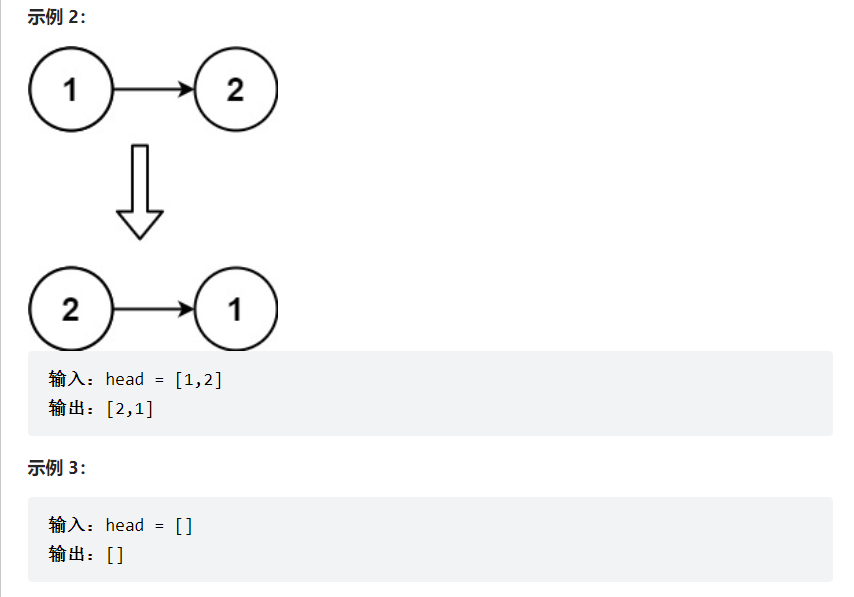
思路:
双指针迭代:
申请两个指针,第一个指针叫 pre,最初是指向 null 的。第二个指针 cur 指向 head,然后不断遍历 cur。
每次迭代到 cur,都将 cur 的 next 指向 pre,然后 pre 和 cur 前进一位。都迭代完了(cur 变成 null 了),pre 就是最后一个节点了。
递归:
递归的两个条件:
终止条件是当前节点或者下一个节点==null
在函数内部,改变节点的指向,也就是 head 的下一个节点指向 head 递归函数那句
head.next.next = head( head 的下一个节点指向head。
递归函数中每次返回的 cur 其实只最后一个节点,在递归函数内部,改变的是当前节点的指向。
代码
#迭代class Solution(object):def reverseList(self, head):""":type head: ListNode:rtype: ListNode"""# 申请两个节点,pre和 cur,pre指向Nonepre = Nonecur = head# 遍历链表,while循环里面的内容其实可以写成一行# 这里只做演示,就不搞那么骚气的写法了while cur:# 记录当前节点的下一个节点tmp = cur.next# 然后将当前节点指向precur.next = pre# pre和cur节点都前进一位pre = curcur = tmpreturn pre#递归class Solution(object):def reverseList(self, head):""":type head: ListNode:rtype: ListNode"""# 递归终止条件是当前为空,或者下一个节点为空if(head==None or head.next==None):return head# 这里的cur就是最后一个节点cur = self.reverseList(head.next)# 这里请配合动画演示理解# 如果链表是 1->2->3->4->5,那么此时的cur就是5# 而head是4,head的下一个是5,下下一个是空# 所以head.next.next 就是5->4head.next.next = head# 防止链表循环,需要将head.next设置为空head.next = None# 每层递归函数都返回cur,也就是最后一个节点return cur
//迭代class Solution {public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {//申请节点,pre和 cur,pre指向nullListNode pre = null;ListNode cur = head;ListNode tmp = null;while(cur!=null) {//记录当前节点的下一个节点tmp = cur.next;//然后将当前节点指向precur.next = pre;//pre和cur节点都前进一位pre = cur;cur = tmp;}return pre;}}//递归class Solution {public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {//递归终止条件是当前为空,或者下一个节点为空if(head==null || head.next==null) {return head;}//这里的cur就是最后一个节点ListNode cur = reverseList(head.next);//这里请配合动画演示理解//如果链表是 1->2->3->4->5,那么此时的cur就是5//而head是4,head的下一个是5,下下一个是空//所以head.next.next 就是5->4head.next.next = head;//防止链表循环,需要将head.next设置为空head.next = null;//每层递归函数都返回cur,也就是最后一个节点return cur;}}
![17)XXKE3AB6H)OVLZU]UYPT.png](/uploads/projects/rui17@eisp2e/36d547b5696d3262b9e092ceb6885a3e.png)
![N{45`XBN3$]GKL{E0O8}I7F.png](/uploads/projects/rui17@eisp2e/964ff83369e404fb569f26a796456b3f.png)

