3.1 微服务中的雪崩效应
什么是微服务中的雪崩效应呢?
微服务中,⼀个请求可能需要多个微服务接⼝才能实现,会形成复杂的调⽤链路。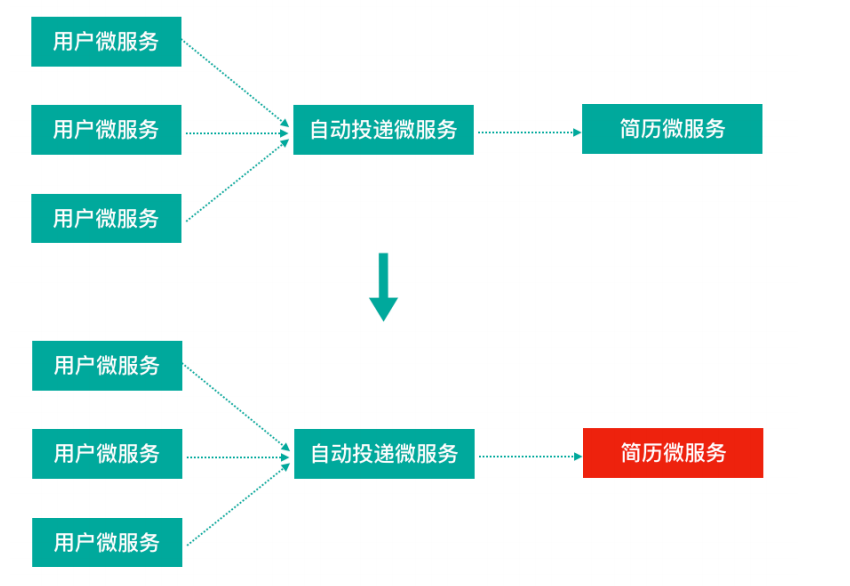
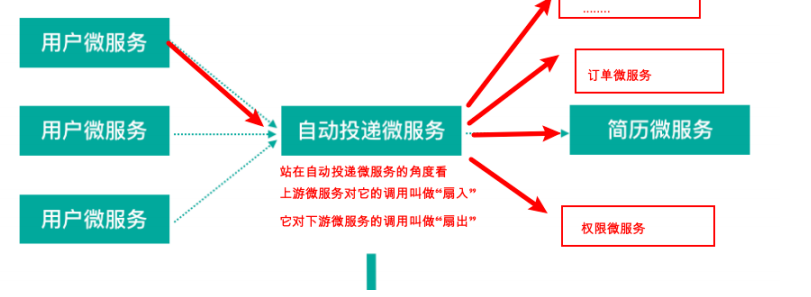
扇⼊:代表着该微服务被调⽤的次数,扇⼊⼤,说明该模块复⽤性好
扇出:该微服务调⽤其他微服务的个数,扇出⼤,说明业务逻辑复杂
扇⼊⼤是⼀个好事,扇出⼤不⼀定是好事
在微服务架构中,⼀个应⽤可能会有多个微服务组成,微服务之间的数据交互通过远程过程调⽤完成。
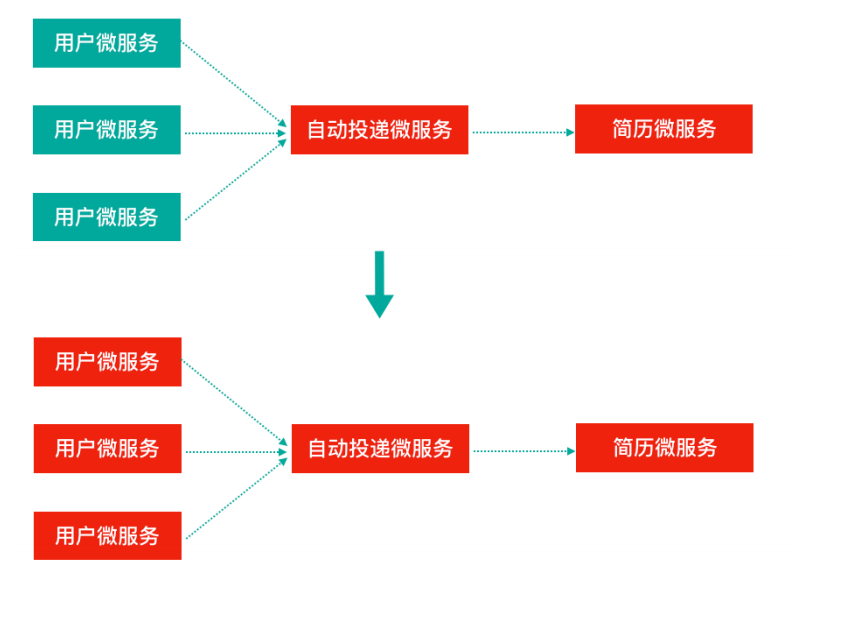
这就带来⼀个问题,假设微服务A调⽤微服务B和微服务C,微服务B和微服务C⼜调⽤其它的微服务,这就是所谓的“扇出”。如果扇出的链路上某个微服务的调⽤响应时间过⻓或者不可⽤,对微服务A的调⽤就会占⽤越来越多的系统资源,进⽽引起系统崩溃,所谓的“雪崩效应”。如图中所示,最下游简历微服务响应时间过⻓,⼤量请求阻塞,⼤量线程不会释放,会导致服务器资源耗尽,最终导致上游服务甚⾄整个系统瘫痪。
3.2 雪崩效应解决⽅案
从可⽤性可靠性着想,为防⽌系统的整体缓慢甚⾄崩溃,采⽤的技术⼿段;
下⾯,我们介绍三种技术⼿段应对微服务中的雪崩效应,这三种⼿段都是从系统可⽤性、可靠性⻆度出发,尽量防⽌系统整体缓慢甚⾄瘫痪。
服务熔断
熔断机制是应对雪崩效应的⼀种微服务链路保护机制。我们在各种场景下都会接触到熔断这两个字。⾼压电路中,如果某个地⽅的电压过⾼,熔断器就会熔断,对电路进⾏保护。股票交易中,如果股票指数过⾼,也会采⽤熔断机制,暂停股票的交易。同样,在微服务架构中,熔断机制也是起着类似的作⽤。当扇出链路的某个微服务不可⽤或者响应时间太⻓时,熔断该节点微服务的调⽤,进⾏服务的降级,快速返回错误的响应信息。当检测到该节点微服务调⽤响应正常后,恢复调⽤链路。
注意:
1)服务熔断重点在“断”,切断对下游服务的调⽤
2)服务熔断和服务降级往往是⼀起使⽤的,Hystrix就是这样。
服务降级
通俗讲就是整体资源不够⽤了,先将⼀些不关紧的服务停掉(调⽤我的时候,给你返回⼀个预留的值,也叫做兜底数据),待渡过难关⾼峰过去,再把那些服务打开。
服务降级⼀般是从整体考虑,就是当某个服务熔断之后,服务器将不再被调⽤,此刻客户端可以⾃⼰准备⼀个本地的fallback回调,返回⼀个缺省值,这样做,虽然服务⽔平下降,但好⽍可⽤,⽐直接挂掉要强。
服务限流
服务降级是当服务出问题或者影响到核⼼流程的性能时,暂时将服务屏蔽掉,待⾼峰或者问题解决后再打开;但是有些场景并不能⽤服务降级来解决,⽐如秒杀业务这样的核⼼功能,这个时候可以结合服务限流来限制这些场景的并发/请求量
限流措施也很多,⽐如
- 限制总并发数(⽐如数据库连接池、线程池)
- 限制瞬时并发数(如nginx限制瞬时并发连接数)
- 限制时间窗⼝内的平均速率(如Guava的RateLimiter、nginx的limit_req模块,限制每秒的平均速率)
-
3.3 Hystrix简介
[来⾃官⽹]Hystrix(豪猪——->刺),宣⾔“defend your app”是由Netflflix开源的⼀个延迟和容错库,⽤于隔离访问远程系统、服务或者第三⽅库,防⽌级联失败,从⽽提升系统的可⽤性与容错性。Hystrix主要通过以下⼏点实现延迟和容错。
包裹请求:使⽤HystrixCommand包裹对依赖的调⽤逻辑。 ⾃动投递微服务⽅法(@HystrixCommand 添加Hystrix控制) ——调⽤简历微服务
- 跳闸机制:当某服务的错误率超过⼀定的阈值时,Hystrix可以跳闸,停⽌请求该服务⼀段时间。
- 资源隔离:Hystrix为每个依赖都维护了⼀个⼩型的线程池(舱壁模式)(或者信号量)。如果该线程池已满, 发往该依赖的请求就被⽴即拒绝,⽽不是排队等待,从⽽加速失败判定。
- 监控:Hystrix可以近乎实时地监控运⾏指标和配置的变化,例如成功、失败、超时、以及被拒绝的请求等。
- 回退机制:当请求失败、超时、被拒绝,或当断路器打开时,执⾏回退逻辑。回退逻辑由开发⼈员⾃⾏提供,例如返回⼀个缺省值。
- ⾃我修复:断路器打开⼀段时间后,会⾃动进⼊“半开”状态。
3.4 Hystrix熔断应⽤
⽬的:简历微服务⻓时间没有响应,服务消费者—>⾃动投递微服务快速失败给⽤户提示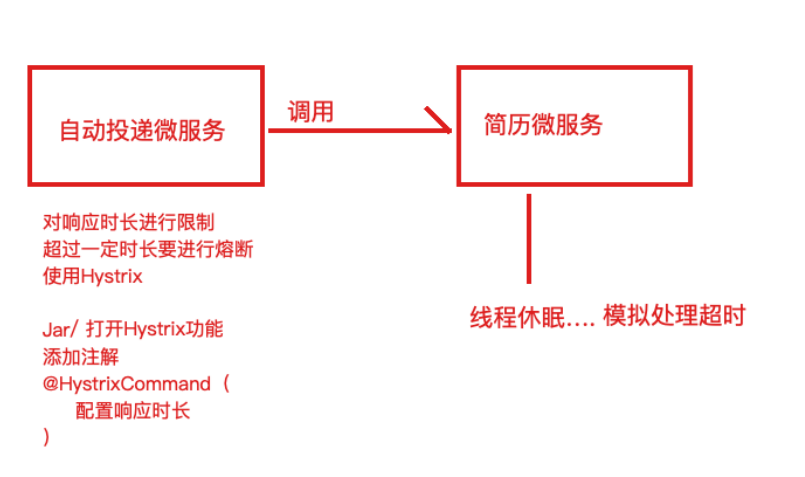
服务消费者⼯程(⾃动投递微服务)中引⼊Hystrix依赖坐标(也可以添加在⽗⼯程中)
服务消费者⼯程(⾃动投递微服务)的启动类中添加熔断器开启注解@EnableCircuitBreaker ```java package com.lagou.edu; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.domain.EntityScan; import org.springframework.cloud.client.circuitbreaker.EnableCircuitBreaker; import org.springframework.cloud.client.discovery.EnableDiscoveryClient; import org.springframework.cloud.client.loadbalancer.LoadBalanced; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate; /**<!--熔断器Hystrix--><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId><artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-hystrix</artifactId></dependency>
- 注解简化写法
- @SpringCloudApplication =
@SpringBootApplication+@EnableDiscoveryClient+@EnableCircuitBreaker
/
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableDiscoveryClient // 开启服务发现
@EnableCircuitBreaker // 开启熔断
public class AutodeliverApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(AutodeliverApplication.class, args);
}
/*
- 注⼊RestTemplate
- @return
*/
@Bean
// Ribbon负载均衡
@LoadBalanced
public RestTemplate getRestTemplate() {
return new RestTemplate();
}
}
定义服务降级处理⽅法,并在业务⽅法上使⽤@HystrixCommand的fallbackMethod属性关联到<br />服务降级处理⽅法java package com.lagou.edu.controller;
import com.netflix.hystrix.contrib.javanica.annotation.HystrixCommand; import com.netflix.hystrix.contrib.javanica.annotation.HystrixProperty; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.cloud.client.ServiceInstance; import org.springframework.cloud.client.discovery.DiscoveryClient; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
import java.util.List;
@RestController @RequestMapping(“/autodeliver”) public class AutodeliverController {
@Autowired
private RestTemplate restTemplate;
// /autodeliver/checkState/1545132
/*@GetMapping("/checkState/{userId}")
public Integer findResumeOpenState(@PathVariable Long userId) {
// 调用远程服务—> 简历微服务接口 RestTemplate -> JdbcTempate
// httpclient封装好多内容进行远程调用
Integer forObject = restTemplate.getForObject("http://localhost:8080/resume/openstate/" + userId, Integer.class);
return forObject;
}*/
@Autowired
private DiscoveryClient discoveryClient;
/**
* 服务注册到Eureka之后的改造
* @param userId
* @return
*/
/*@GetMapping("/checkState/{userId}")
public Integer findResumeOpenState(@PathVariable Long userId) {
// TODO 从Eureka Server中获取我们关注的那个服务的实例信息以及接口信息
// 1、从 Eureka Server中获取lagou-service-resume服务的实例信息(使用客户端对象做这件事)
List<ServiceInstance> instances = discoveryClient.getInstances("lagou-service-resume");
// 2、如果有多个实例,选择一个使用(负载均衡的过程)
ServiceInstance serviceInstance = instances.get(0);
// 3、从元数据信息获取host port
String host = serviceInstance.getHost();
int port = serviceInstance.getPort();
String url = "http://" + host + ":" + port + "/resume/openstate/" + userId;
System.out.println("===============>>>从EurekaServer集群获取服务实例拼接的url:" + url);
// 调用远程服务—> 简历微服务接口 RestTemplate -> JdbcTempate
// httpclient封装好多内容进行远程调用
Integer forObject = restTemplate.getForObject(url, Integer.class);
return forObject;
}*/
/**
* 使用Ribbon负载均衡
* @param userId
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("/checkState/{userId}")
public Integer findResumeOpenState(@PathVariable Long userId) {
// 使用ribbon不需要我们自己获取服务实例然后选择一个那么去访问了(自己的负载均衡)
String url = "http://lagou-service-resume/resume/openstate/" + userId; // 指定服务名
Integer forObject = restTemplate.getForObject(url, Integer.class);
return forObject;
}
/**
* 提供者模拟处理超时,调用方法添加Hystrix控制
* @param userId
* @return
*/
// 使用@HystrixCommand注解进行熔断控制
@HystrixCommand(
// 线程池标识,要保持唯一,不唯一的话就共用了
threadPoolKey = "findResumeOpenStateTimeout",
// 线程池细节属性配置
threadPoolProperties = {
@HystrixProperty(name="coreSize",value = "1"), // 线程数
@HystrixProperty(name="maxQueueSize",value="20") // 等待队列长度
},
// commandProperties熔断的一些细节属性配置
commandProperties = {
// 每一个属性都是一个HystrixProperty
@HystrixProperty(name="execution.isolation.thread.timeoutInMilliseconds",value="2000")
}
)
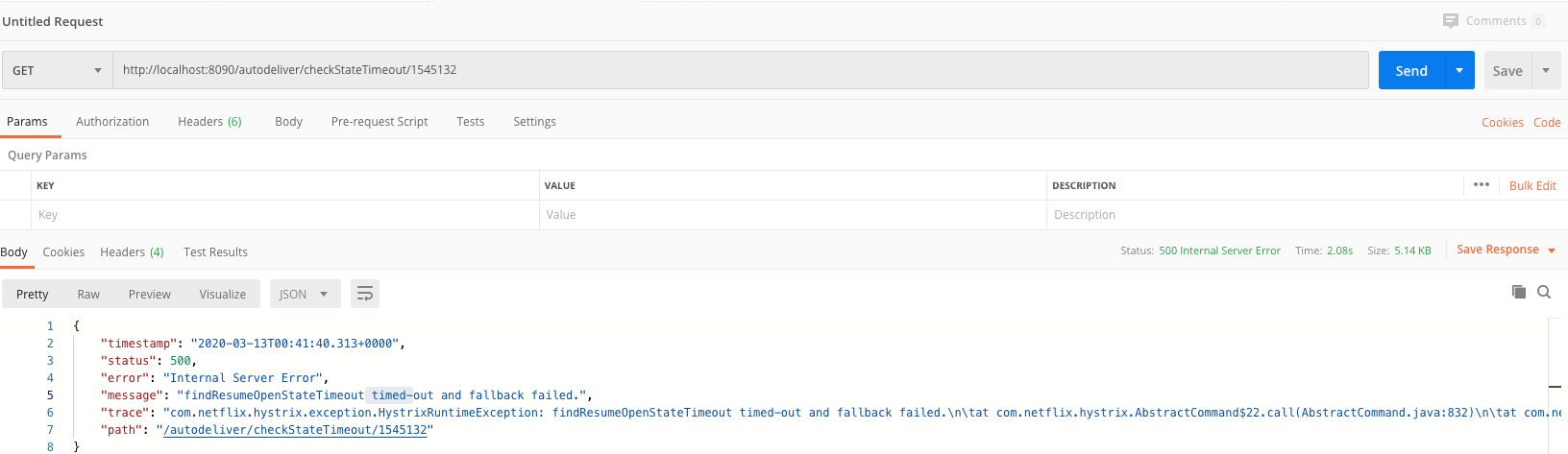
@GetMapping("/checkStateTimeout/{userId}")
public Integer findResumeOpenStateTimeout(@PathVariable Long userId) {
// 使用ribbon不需要我们自己获取服务实例然后选择一个那么去访问了(自己的负载均衡)
String url = "http://lagou-service-resume/resume/openstate/" + userId; // 指定服务名
Integer forObject = restTemplate.getForObject(url, Integer.class);
return forObject;
}
@GetMapping("/checkStateTimeoutFallback/{userId}")
@HystrixCommand(
// 线程池标识,要保持唯一,不唯一的话就共用了
threadPoolKey = "findResumeOpenStateTimeoutFallback",
// 线程池细节属性配置
threadPoolProperties = {
@HystrixProperty(name="coreSize",value = "2"), // 线程数
@HystrixProperty(name="maxQueueSize",value="20") // 等待队列长度
},
// commandProperties熔断的一些细节属性配置
commandProperties = {
// 每一个属性都是一个HystrixProperty
@HystrixProperty(name="execution.isolation.thread.timeoutInMilliseconds",value="2000")
// hystrix高级配置,定制工作过程细节
,
// 统计时间窗口定义
@HystrixProperty(name = "metrics.rollingStats.timeInMilliseconds",value = "8000"),
// 统计时间窗口内的最小请求数
@HystrixProperty(name = "circuitBreaker.requestVolumeThreshold",value = "2"),
// 统计时间窗口内的错误数量百分比阈值
@HystrixProperty(name = "circuitBreaker.errorThresholdPercentage",value = "50"),
// 自我修复时的活动窗口长度
@HystrixProperty(name = "circuitBreaker.sleepWindowInMilliseconds",value = "3000")
},
fallbackMethod = "myFallBack" // 回退方法
)
public Integer findResumeOpenStateTimeoutFallback(@PathVariable Long userId) {
// 使用ribbon不需要我们自己获取服务实例然后选择一个那么去访问了(自己的负载均衡)
String url = "http://lagou-service-resume/resume/openstate/" + userId; // 指定服务名
Integer forObject = restTemplate.getForObject(url, Integer.class);
return forObject;
}
/*
定义回退方法,返回预设默认值
注意:该方法形参和返回值与原始方法保持一致
*/
public Integer myFallBack(Long userId) {
return -123333; // 兜底数据
}
/**
* 1)服务提供者处理超时,熔断,返回错误信息
* 2)有可能服务提供者出现异常直接抛出异常信息
*
* 以上信息,都会返回到消费者这里,很多时候消费者服务不希望把收到异常/错误信息再抛到它的上游去
* 用户微服务 — 注册微服务 — 优惠券微服务
* 1 登记注册
* 2 分发优惠券(并不是核心步骤),这里如果调用优惠券微服务返回了异常信息或者是熔断后的错误信息,这些信息如果抛给用户很不友好
* 此时,我们可以返回一个兜底数据,预设的默认值(服务降级)
*
*
*/
}
<br />注意**<br />降级(兜底)⽅法必须和被降级⽅法相同的⽅法签名(相同参数列表、相同返回值)
- 可以在类上使⽤@DefaultProperties注解统⼀指定整个类中共⽤的降级(兜底)⽅法
- 服务提供者端(简历微服务)模拟请求超时(线程休眠3s),只修改8080实例,8081不修改,对⽐观察
```java
package com.lagou.edu.controller;
import com.lagou.edu.service.ResumeService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/resume")
public class ResumeController {
@Autowired
private ResumeService resumeService;
@Value("${server.port}")
private Integer port;
//"/resume/openstate/1545132"
@GetMapping("/openstate/{userId}")
public Integer findDefaultResumeState(@PathVariable Long userId) {
// 模拟处理超时
/*try {
Thread.sleep(10000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}*/
//return resumeService.findDefaultResumeByUserId(userId).getIsOpenResume();
System.out.println("====>>>>>>>>>>>>>>我是8080,访问到我这里了......");
return port;
}
}
因为我们已经使⽤了Ribbon负载(轮询),所以我们在请求的时候,⼀次熔断降级,⼀次正常返回
熔断降级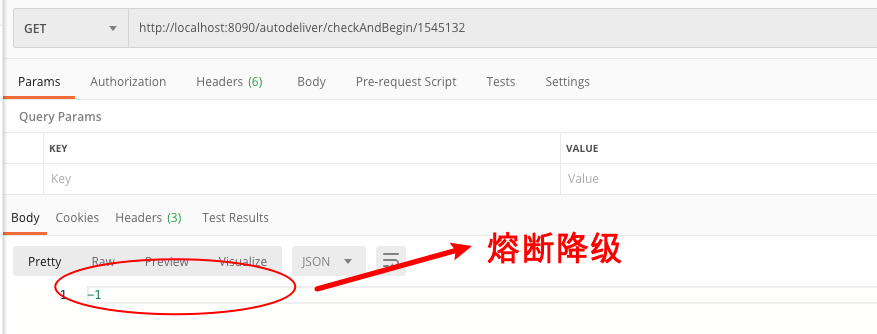
正常返回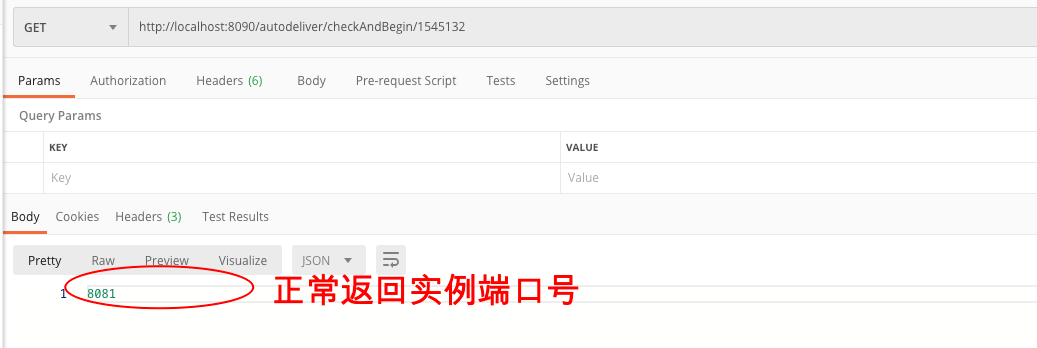
3.5 Hystrix舱壁模式(线程池隔离策略)
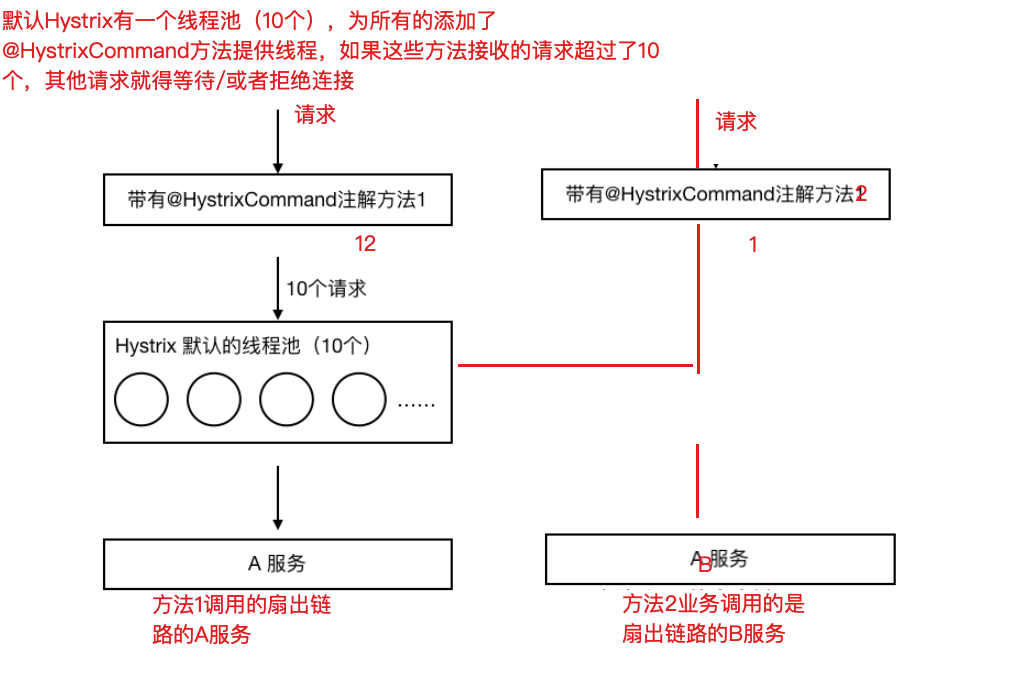
如果不进⾏任何设置,所有熔断⽅法使⽤⼀个Hystrix线程池(10个线程),那么这样的话会导致问题,这个问题并不是扇出链路微服务不可⽤导致的,⽽是我们的线程机制导致的,如果⽅法A的请求把10个线程都⽤了,⽅法2请求处理的时候压根都没法去访问B,因为没有线程可⽤,并不是B服务不可⽤。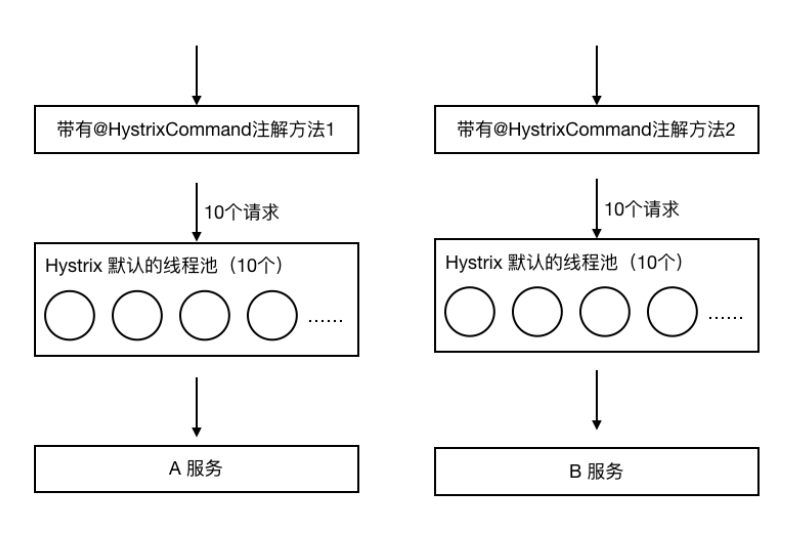
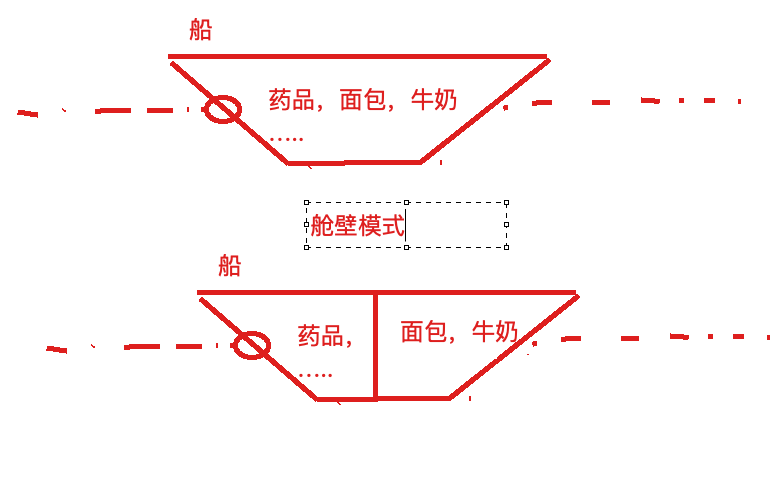
为了避免问题服务请求过多导致正常服务⽆法访问,Hystrix 不是采⽤增加线程数,⽽是单独的为每⼀个控制⽅法创建⼀个线程池的⽅式,这种模式叫做“舱壁模式”,也是线程隔离的⼿段。
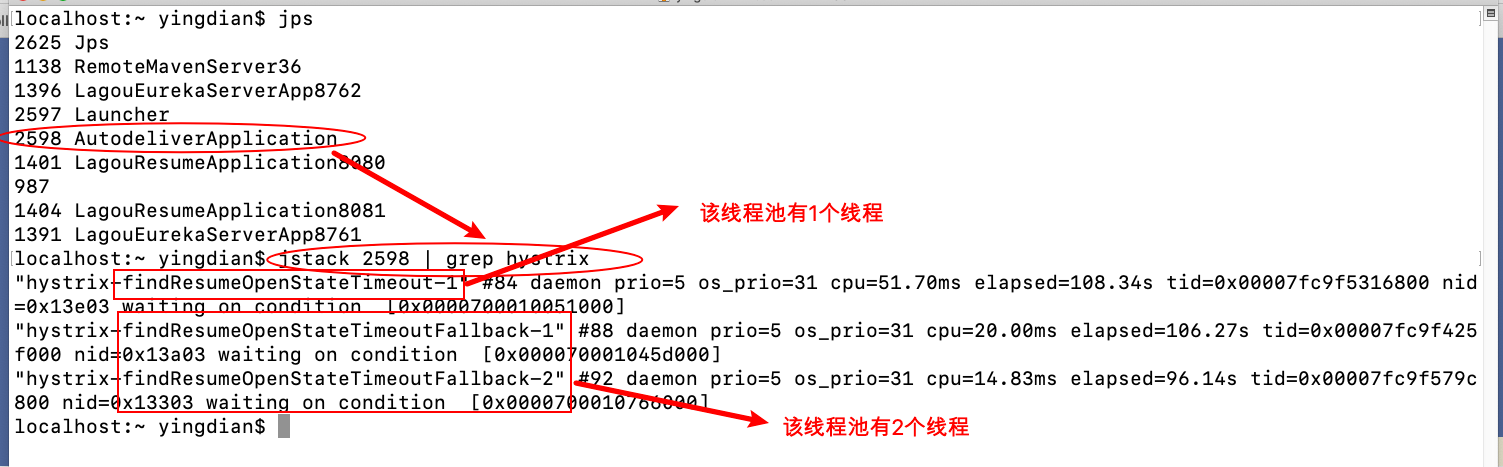
我们可以使⽤⼀些⼿段查看线程情况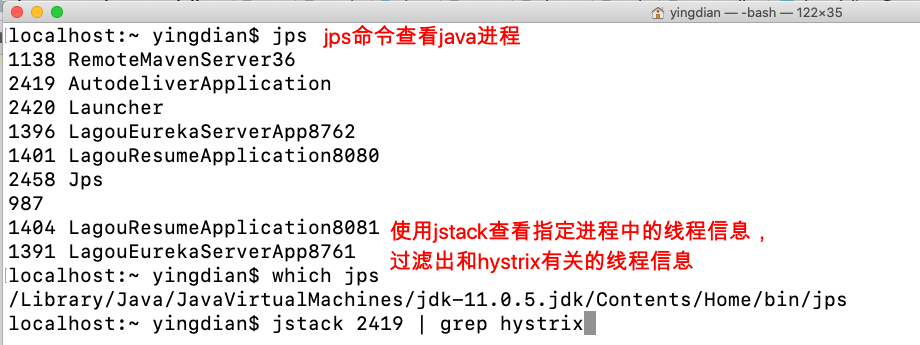
发起请求,可以使⽤PostMan模拟批量请求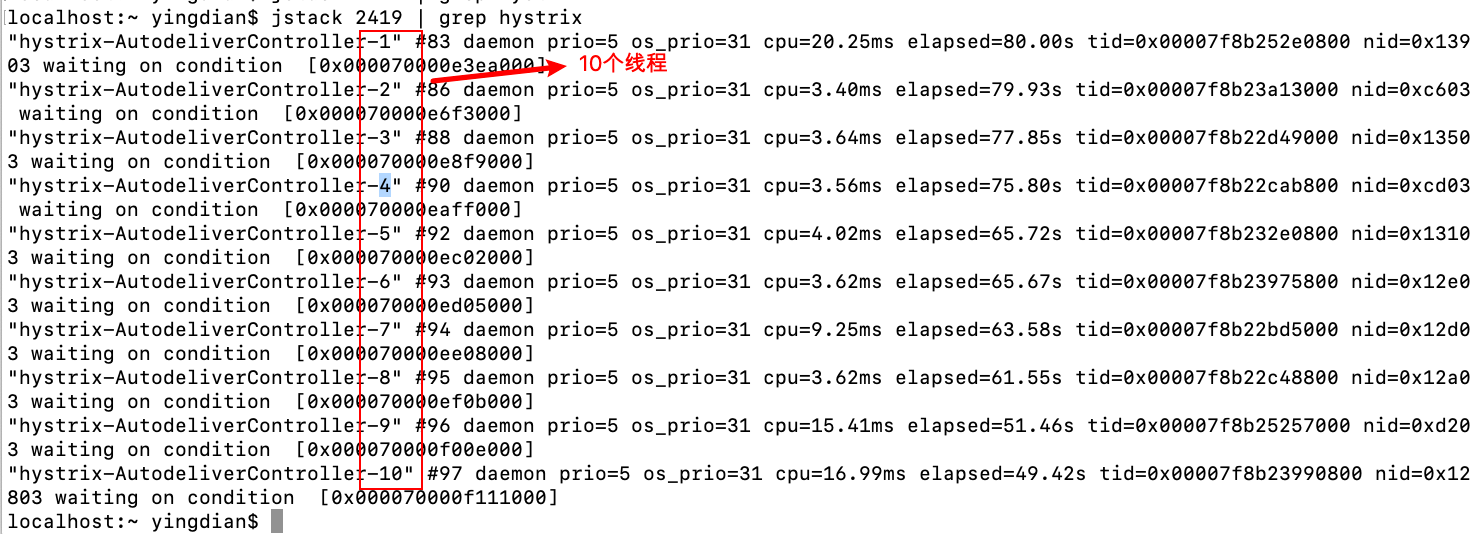
Hystrix舱壁模式程序修改
/**
* 提供者模拟处理超时,调用方法添加Hystrix控制
* @param userId
* @return
*/
// 使用@HystrixCommand注解进行熔断控制
@HystrixCommand(
// 线程池标识,要保持唯一,不唯一的话就共用了
threadPoolKey = "findResumeOpenStateTimeout",
// 线程池细节属性配置
threadPoolProperties = {
@HystrixProperty(name="coreSize",value = "1"), // 线程数
@HystrixProperty(name="maxQueueSize",value="20") // 等待队列长度
},
// commandProperties熔断的一些细节属性配置
commandProperties = {
// 每一个属性都是一个HystrixProperty
@HystrixProperty(name="execution.isolation.thread.timeoutInMilliseconds",value="2000")
}
)
@GetMapping("/checkStateTimeout/{userId}")
public Integer findResumeOpenStateTimeout(@PathVariable Long userId) {
// 使用ribbon不需要我们自己获取服务实例然后选择一个那么去访问了(自己的负载均衡)
String url = "http://lagou-service-resume/resume/openstate/" + userId; // 指定服务名
Integer forObject = restTemplate.getForObject(url, Integer.class);
return forObject;
}
@GetMapping("/checkStateTimeoutFallback/{userId}")
@HystrixCommand(
// 线程池标识,要保持唯一,不唯一的话就共用了
threadPoolKey = "findResumeOpenStateTimeoutFallback",
// 线程池细节属性配置
threadPoolProperties = {
@HystrixProperty(name="coreSize",value = "2"), // 线程数
@HystrixProperty(name="maxQueueSize",value="20") // 等待队列长度
},
// commandProperties熔断的一些细节属性配置
commandProperties = {
// 每一个属性都是一个HystrixProperty
@HystrixProperty(name="execution.isolation.thread.timeoutInMilliseconds",value="2000")
// hystrix高级配置,定制工作过程细节
,
// 统计时间窗口定义
@HystrixProperty(name = "metrics.rollingStats.timeInMilliseconds",value = "8000"),
// 统计时间窗口内的最小请求数
@HystrixProperty(name = "circuitBreaker.requestVolumeThreshold",value = "2"),
// 统计时间窗口内的错误数量百分比阈值
@HystrixProperty(name = "circuitBreaker.errorThresholdPercentage",value = "50"),
// 自我修复时的活动窗口长度
@HystrixProperty(name = "circuitBreaker.sleepWindowInMilliseconds",value = "3000")
},
fallbackMethod = "myFallBack" // 回退方法
)
public Integer findResumeOpenStateTimeoutFallback(@PathVariable Long userId) {
// 使用ribbon不需要我们自己获取服务实例然后选择一个那么去访问了(自己的负载均衡)
String url = "http://lagou-service-resume/resume/openstate/" + userId; // 指定服务名
Integer forObject = restTemplate.getForObject(url, Integer.class);
return forObject;
}
3.6 Hystrix⼯作流程与⾼级应⽤
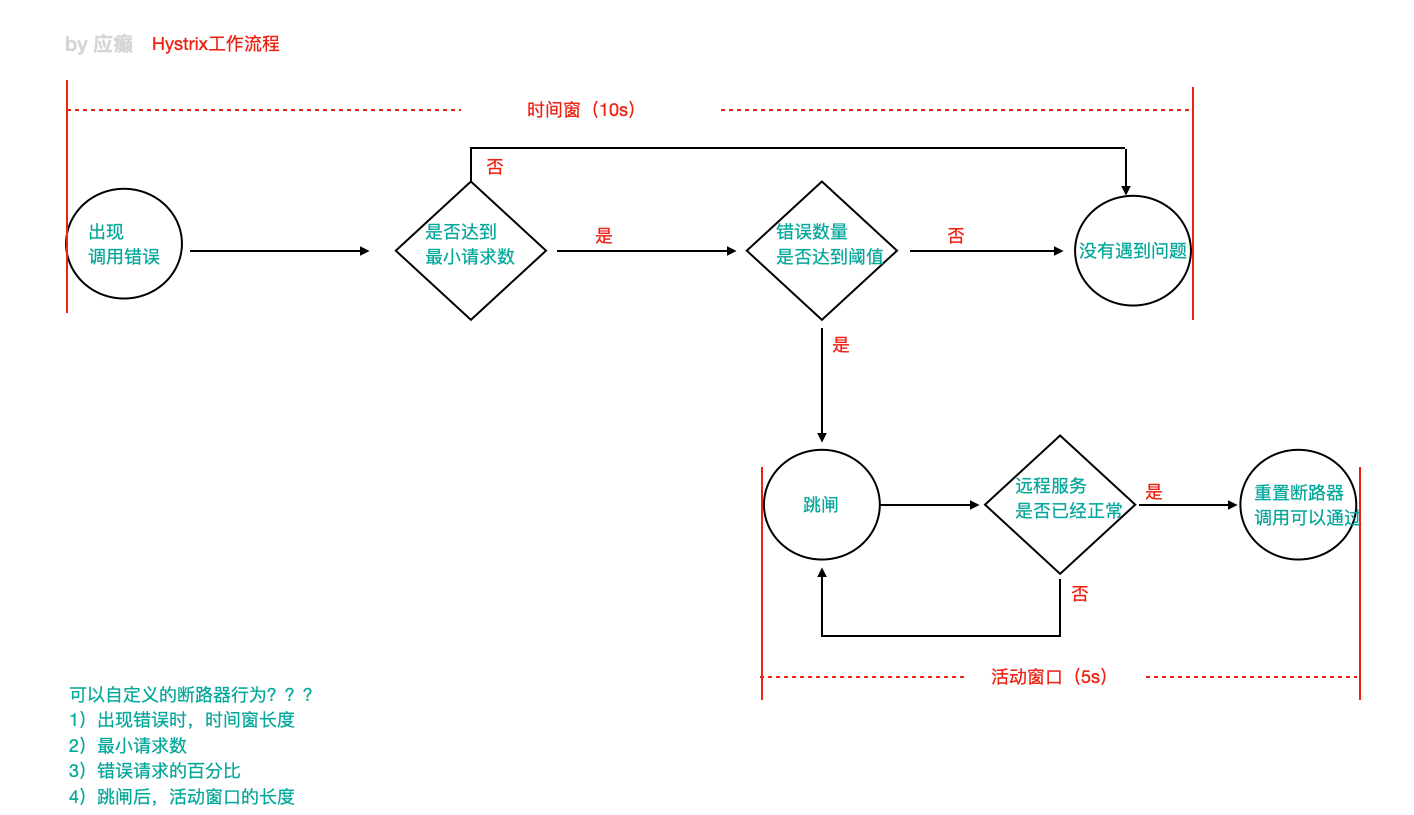
1)当调⽤出现问题时,开启⼀个时间窗(10s)
2)在这个时间窗内,统计调⽤次数是否达到最⼩请求数?
如果没有达到,则重置统计信息,回到第1步
如果达到了,则统计失败的请求数占所有请求数的百分⽐,是否达到阈值?
如果达到,则跳闸(不再请求对应服务)
如果没有达到,则重置统计信息,回到第1步
3)如果跳闸,则会开启⼀个活动窗⼝(默认5s),每隔5s,Hystrix会让⼀个请求通过,到达那个问题服务,看 是否调⽤成功,如果成功,重置断路器回到第1步,如果失败,回到第3步
/**
* 8秒钟内,请求次数达到2个,并且失败率在50%以上,就跳闸
* 跳闸后活动窗⼝设置为3s
*/
@HystrixCommand(
commandProperties = {
@HystrixProperty(name =
"metrics.rollingStats.timeInMilliseconds",value = "8000"),
@HystrixProperty(name =
"circuitBreaker.requestVolumeThreshold",value = "2"),
@HystrixProperty(name =
"circuitBreaker.errorThresholdPercentage",value = "50"),
@HystrixProperty(name =
"circuitBreaker.sleepWindowInMilliseconds",value = "3000")
}
)
我们上述通过注解进⾏的配置也可以配置在配置⽂件中
# 配置熔断策略:
hystrix:
command:
default:
circuitBreaker:
# 强制打开熔断器,如果该属性设置为true,强制断路器进⼊打开状态,将会拒绝所有的请
求。 默认false关闭的
forceOpen: false
# 触发熔断错误⽐例阈值,默认值50%
errorThresholdPercentage: 50
# 熔断后休眠时⻓,默认值5秒
sleepWindowInMilliseconds: 3000
# 熔断触发最⼩请求次数,默认值是20
requestVolumeThreshold: 2
execution:
isolation:
thread:
# 熔断超时设置,默认为1秒
timeoutInMilliseconds: 2000
基于springboot的健康检查观察跳闸状态(⾃动投递微服务暴露健康检查细节)
# springboot中暴露健康检查等断点接⼝
management:
endpoints:
web:
exposure:
include: "*"
# 暴露健康接⼝的细节
endpoint:
health:
show-details: always
访问健康检查接⼝:http://localhost:8090/actuator/health
hystrix正常⼯作状态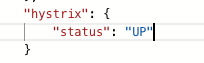
跳闸状态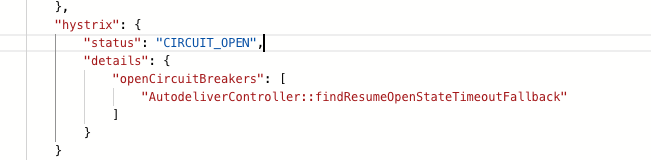
活动窗⼝内⾃我修复
3.7 Hystrix Dashboard断路监控仪表盘
正常状态是UP,跳闸是⼀种状态CIRCUIT_OPEN,可以通过/health查看,前提是⼯程中需要引⼊SpringBoot的actuator(健康监控),它提供了很多监控所需的接⼝,可以对应⽤系统进⾏配置查看、相关功能统计等。
已经统⼀添加在⽗⼯程中
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
如果我们想看到Hystrix相关数据,⽐如有多少请求、多少成功、多少失败、多少降级等,那么引⼊SpringBoot健康监控之后,访问/actuator/hystrix.stream接⼝可以获取到监控的⽂字信息,但是不直观,所以Hystrix官⽅还提供了基于图形化的DashBoard(仪表板)监控平 台。Hystrix仪表板可以显示每个断路器(被@HystrixCommand注解的⽅法)的状态。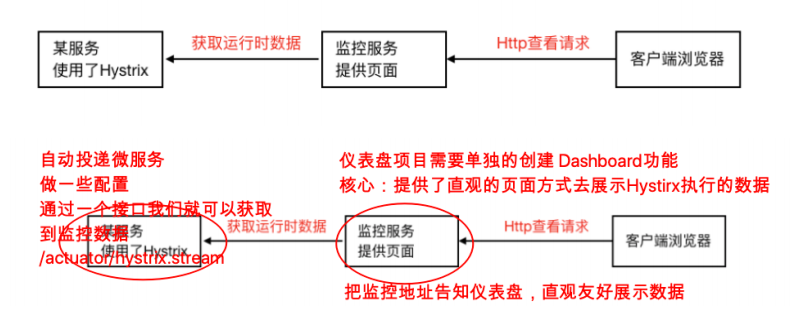
1)新建⼀个监控服务⼯程,导⼊依赖
<!--hystrix-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-hystrix</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--hystrix 仪表盘-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-hystrix-dashboard</artifactId>
</dependency> <dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId>
</dependency>
2)启动类添加@EnableHystrixDashboard激活仪表盘
package com.lagou.edu;
import com.netflix.hystrix.contrib.metrics.eventstream.HystrixMetricsStreamServlet;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.ServletRegistrationBean;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.discovery.EnableDiscoveryClient;
import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.hystrix.dashboard.EnableHystrixDashboard;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableDiscoveryClient
@EnableHystrixDashboard // 开启hystrix dashboard
public class HystrixDashboard9000 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(HystrixDashboard9000.class,args);
}
}
3) application.yml
server:
port: 9000
Spring:
application:
name: lagou-cloud-hystrix-dashboard
eureka:
client:
serviceUrl: # eureka server的路径
defaultZone: http://lagoucloudeurekaservera:8761/eureka/,http://lagoucloudeurekaserverb:8762/eureka/ #把 eureka 集群中的所有 url 都填写了进来,也可以只写一台,因为各个 eureka server 可以同步注册表
instance:
#使用ip注册,否则会使用主机名注册了(此处考虑到对老版本的兼容,新版本经过实验都是ip)
prefer-ip-address: true
#自定义实例显示格式,加上版本号,便于多版本管理,注意是ip-address,早期版本是ipAddress
instance-id: ${spring.cloud.client.ip-address}:${spring.application.name}:${server.port}:@project.version@
4)在被监测的微服务中注册监控servlet(⾃动投递微服务,监控数据就是来⾃于这个微服务)
@Bean
public ServletRegistrationBean getServlet(){
HystrixMetricsStreamServlet streamServlet = new
HystrixMetricsStreamServlet();
ServletRegistrationBean registrationBean = new
ServletRegistrationBean(streamServlet);
registrationBean.setLoadOnStartup(1);
registrationBean.addUrlMappings("/actuator/hystrix.stream");
registrationBean.setName("HystrixMetricsStreamServlet");
return registrationBean;
}
被监控微服务发布之后,可以直接访问监控servlet,但是得到的数据并不直观,后期可以结合仪表盘更友好的展示
5)访问测试http://localhost:9000/hystrix
输⼊监控的微服务端点地址,展示监控的详细数据,⽐如监控服务消费者http://localhost:8090/actuator/hystrix.stream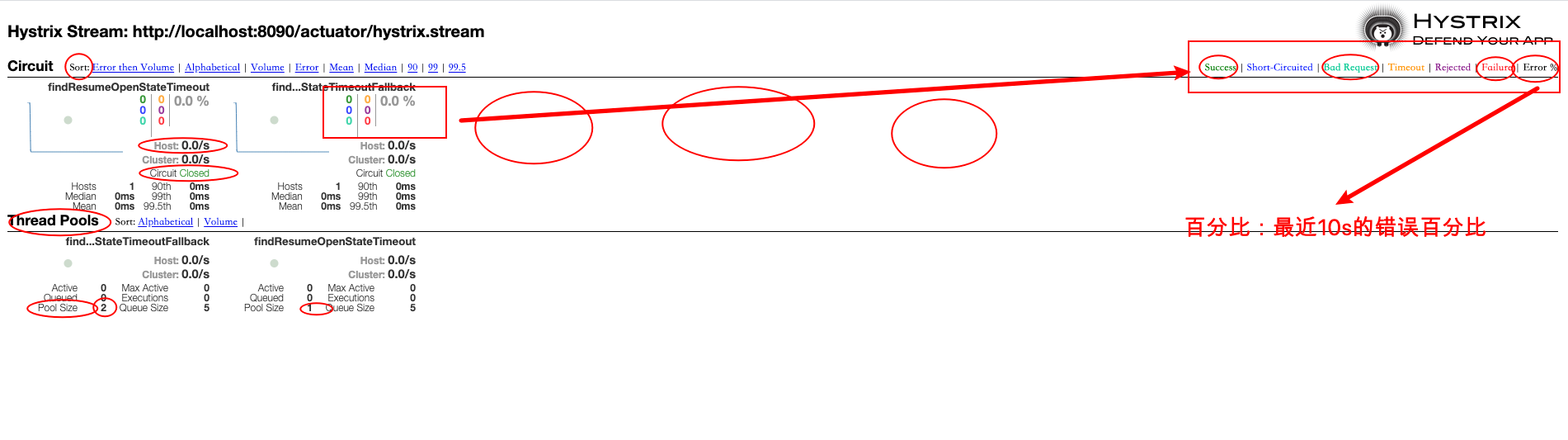
百分⽐,10s内错误请求百分⽐
实⼼圆:
- ⼤⼩:代表请求流量的⼤⼩,流量越⼤球越⼤
- 颜⾊:代表请求处理的健康状态,从绿⾊到红⾊递减,绿⾊代表健康,红⾊就代表很不健康
曲线波动图:
记录了2分钟内该⽅法上流量的变化波动图,判断流量上升或者下降的趋势
3.8 Hystrix Turbine聚合监控
之前,我们针对的是⼀个微服务实例的Hystrix数据查询分析,在微服务架构下,⼀个微服务的实例往往
是多个(集群化)
⽐如⾃动投递微服务
实例1(hystrix) ip1:port1/actuator/hystrix.stream
实例2(hystrix) ip2:port2/actuator/hystrix.stream
实例3(hystrix) ip3:port3/actuator/hystrix.stream
按照已有的⽅法,我们就可以结合dashboard仪表盘每次输⼊⼀个监控数据流url,进去查看⼿⼯操作能否被⾃动功能替代?Hystrix Turbine聚合(聚合各个实例上的hystrix监控数据)监控
Turbine(涡轮)
思考:微服务架构下,⼀个微服务往往部署多个实例,如果每次只能查看单个实例的监控,就需要经常切换很不⽅便,在这样的景下,我们可以使⽤ Hystrix Turbine 进⾏聚合监控,它可以把相关微服务的监控数据聚合在⼀起,便于查看
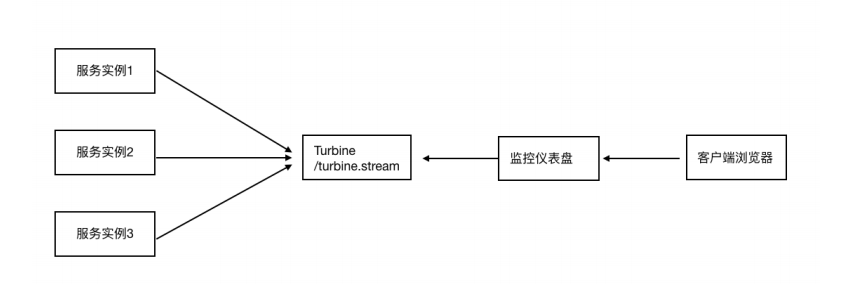
Turbine服务搭建
1)新建项⽬lagou-cloud-hystrix-turbine-9001,引⼊依赖坐标
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<parent>
<artifactId>lagou-parent</artifactId>
<groupId>com.lagou.edu</groupId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</parent>
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<artifactId>lagou-cloud-hystrix-turbine-9001</artifactId>
<dependencies>
<!--hystrix turbine聚合监控-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-turbine</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--
引入eureka客户端的两个原因
1、老师说过,微服务架构下的服务都尽量注册到服务中心去,便于统一管理
2、后续在当前turbine项目中我们需要配置turbine聚合的服务,比如,我们希望聚合
lagou-service-autodeliver这个服务的各个实例的hystrix数据流,那随后
我们就需要在application.yml文件中配置这个服务名,那么turbine获取服务下具体实例的数据流的
时候需要ip和端口等实例信息,那么怎么根据服务名称获取到这些信息呢?
当然可以从eureka服务注册中心获取
-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
2)将需要进⾏Hystrix监控的多个微服务配置起来,在⼯程application.yml中开启Turbine及进⾏相关配置
server:
port: 9001
Spring:
application:
name: lagou-cloud-hystrix-turbine
eureka:
client:
serviceUrl: # eureka server的路径
defaultZone: http://lagoucloudeurekaservera:8761/eureka/,http://lagoucloudeurekaserverb:8762/eureka/ #把 eureka 集群中的所有 url 都填写了进来,也可以只写一台,因为各个 eureka server 可以同步注册表
instance:
#使用ip注册,否则会使用主机名注册了(此处考虑到对老版本的兼容,新版本经过实验都是ip)
prefer-ip-address: true
#自定义实例显示格式,加上版本号,便于多版本管理,注意是ip-address,早期版本是ipAddress
instance-id: ${spring.cloud.client.ip-address}:${spring.application.name}:${server.port}:@project.version@
#turbine配置
turbine:
# appCofing配置需要聚合的服务名称,比如这里聚合自动投递微服务的hystrix监控数据
# 如果要聚合多个微服务的监控数据,那么可以使用英文逗号拼接,比如 a,b,c
appConfig: lagou-service-autodeliver
clusterNameExpression: "'default'" # 集群默认名称
3)在当前项⽬启动类上添加注解@EnableTurbine,开启仪表盘以及Turbine聚合
package com.lagou.edu;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.discovery.EnableDiscoveryClient;
import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.turbine.EnableTurbine;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableDiscoveryClient
@EnableTurbine // 开启Turbine聚合功能
public class HystrixTurbineApplication9001 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(HystrixTurbineApplication9001.class,args);
}
}
4)浏览器访问Turbine项⽬,http://localhost:9001/turbine.stream,就可以看到监控数据了
我们通过dashboard的⻚⾯查看数据更直观,把刚才的地址输⼊dashboard地址栏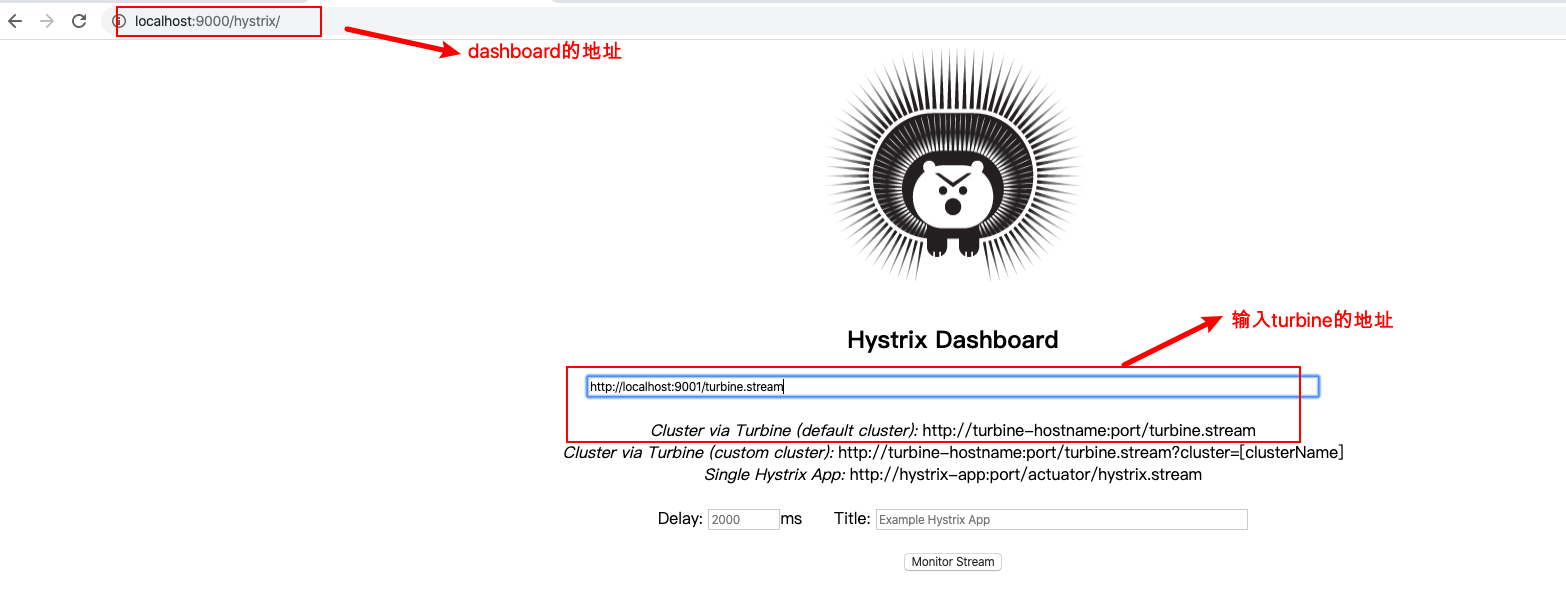
监控⻚⾯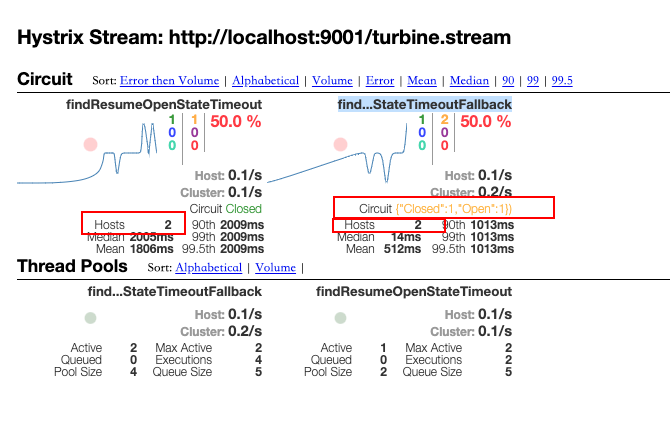
3.9 Hystrix核⼼源码剖析
springboot装配、⾯向切⾯编程、RxJava响应式编程的知识等等,我们剖析下主体脉络。分析⼊⼝:@EnableCircuitBreaker注解激活了熔断功能,那么该注解就是Hystrix源码追踪的⼊⼝.@EnableCircuitBreaker注解激活熔断器
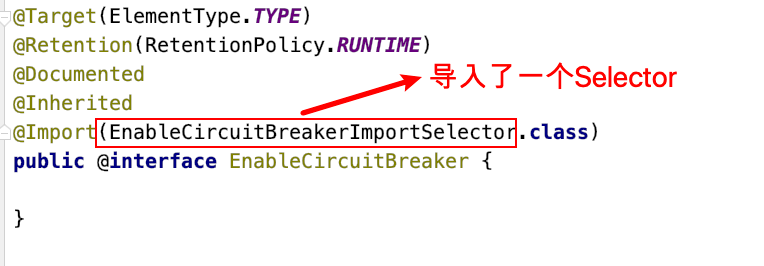
查看EnableCircuitBreakerImportSelector类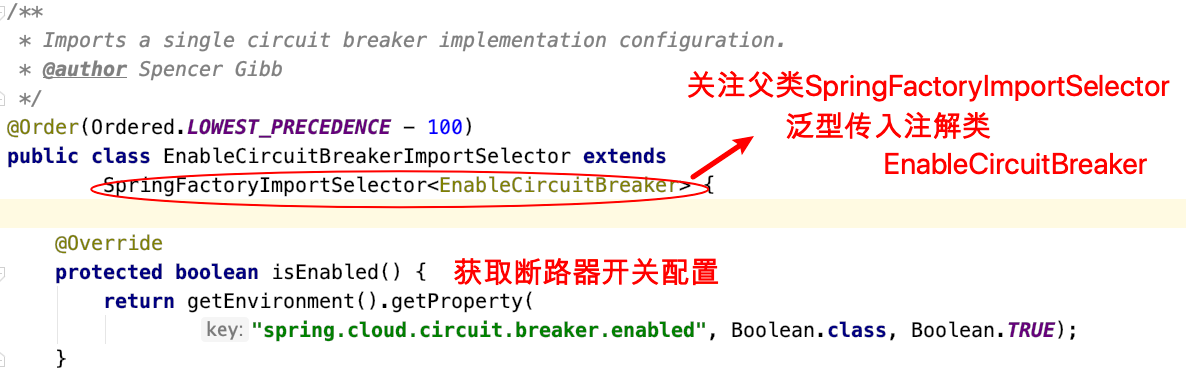
继续关注⽗类 SpringFactoryImportSelector

spring.factories⽂件内容如下
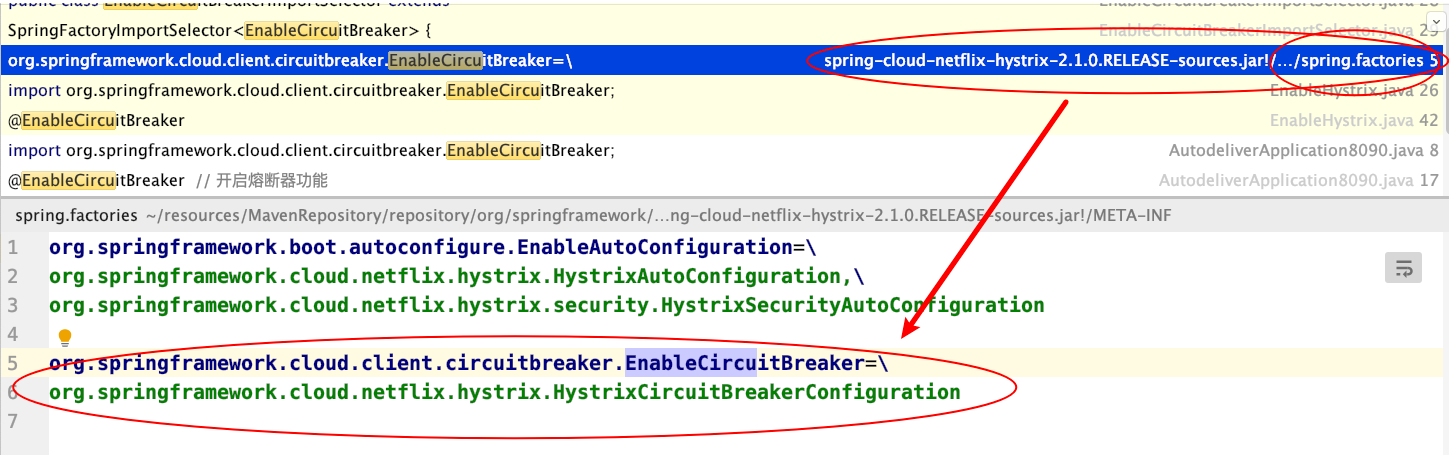
会注⼊org.springframework.cloud.netflflix.hystrix.HystrixCircuitBreakerConfifiguration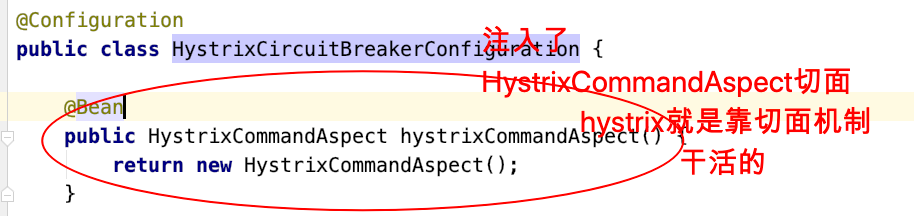
关注切⾯:com.netflflix.hystrix.contrib.javanica.aop.aspectj.HystrixCommandAspect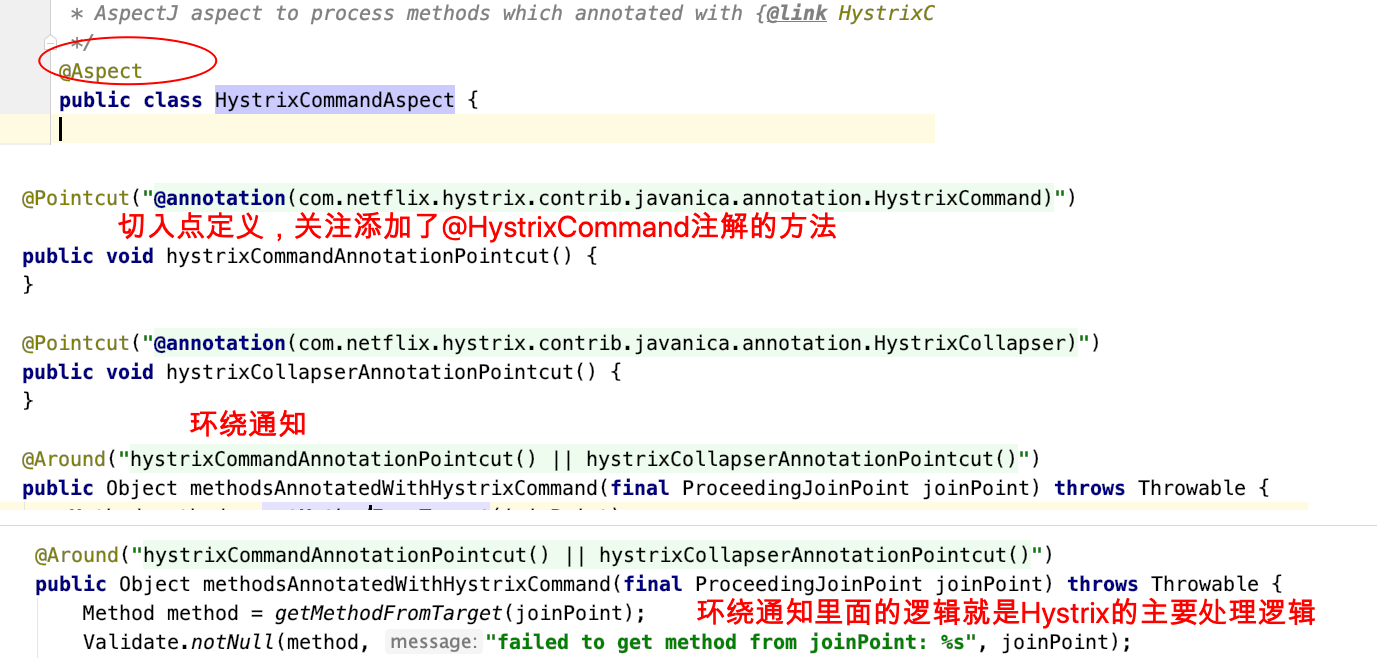
重点分析环绕通知⽅法

GenericCommand中根据元数据信息重写了两个很核⼼的⽅法,⼀个是run⽅法封装了对原始⽬标⽅法的调⽤,另外⼀个是getFallBack⽅法
它封装了对回退⽅法的调⽤
另外,在GenericCommand的上层类构造函数中会完成资源的初始化,⽐如线程池
GenericCommand —>AbstractHystrixCommand—>HystrixCommand—>AbstractCommand


接下来回到环绕通知⽅法那张截图
进⼊execute执⾏这⾥
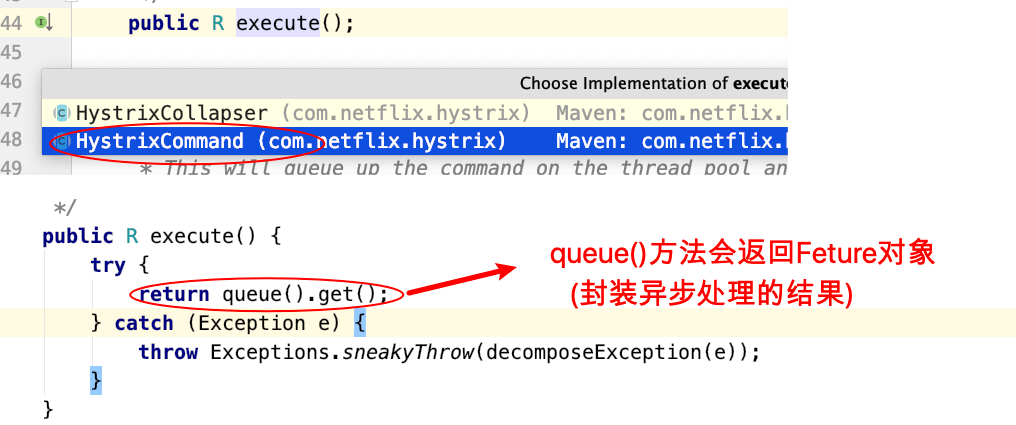

另外,我们观察,GenericCommand⽅法中根据元数据信息等重写了run⽅法(对⽬标⽅法的调⽤),
getFallback⽅法(对回退⽅法的调⽤),在RxJava处理过程中会完成对这两个⽅法的调⽤。