并发下的ArrayList
package com.demo.base;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.List;public class ThreadDemo {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {MyRunnable myRunnable = new MyRunnable();Thread t1 = new Thread(myRunnable);Thread t2 = new Thread(myRunnable);t1.start();t2.start();t1.join();t2.join();System.out.println("list 的大小为: " + myRunnable.list.size());}}class MyRunnable implements Runnable {List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();@Overridepublic void run() {for (int i=0; i<10000; i++){list.add(i);}}}
注意:
ArrayList 是一个线程不安全的容器,在多线程下,ArrayList 可能会有以下结果:
- 程序正常结束,ArrayList 的大小为 20000,这说明并发程序即使有问题,也不是每次都会表现出来。
- 程序正常结束,ArrayList 的大小小于 20000,这是由于多线程访问冲突,多个线程同时对 ArrayList 的同一位置进行赋值导致的。
- 程序抛出数组下标越界的异常
Exception in thread “Thread-0” java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: 244
这是因为 ArrayList 在扩容过程中,内部一致性被破坏,但由于没有锁的保护,另一个线程访问到了不一致的内部状态,导致出现越界问题。
解决方法
- 使用线程安全的 Vector 代替 ArrayList
- 在向 ArrayList 中添加元素时,加锁
- 使用 JUC 包下的安全容器 CopyOnWriteArrayList 代替 ArrayList
并发下的HashMap
```java package com.demo.base;
import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map;
public class ThreadDemo {
static Map
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {Thread t1 = new Thread(new MyRunnable());Thread t2 = new Thread(new MyRunnable());t1.start();t2.start();t1.join();t2.join();System.out.println(map.size());}static class MyRunnable implements Runnable{@Overridepublic void run() {for(int i=0; i<10000; i++){map.put(Thread.currentThread().getName() + i, i + "");}}}
注意:
运行这段代码,也可能得到3个结果:
- 程序正常结束,HashMap的最终大小为20000。
- 程序正常结束,但HashMap的大小小于20000。这两点跟ArrayList问题类似。
- 程序抛出异常
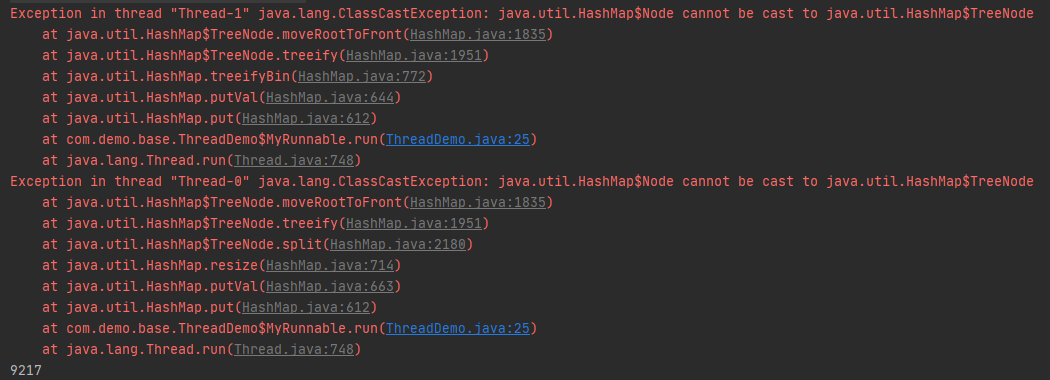
这个异常是在jdk8中会出现的,原因是HashMap的数据结构是数组和链表组成的,当链表在达到阈值时,链表结构(Node类型节点)会转换成红黑树结构(TreeNode类型节点)。于是当一个线程将Node类型节点转换成TreeNode类型节点并平衡红黑树时,另一个线程执行put方法并正好将数据放到同一个数组格子中时,先会插入Node类型的数据,这将导致前一个线程平衡红黑树时在转换数据类型时发生异常。

